Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mirrors and Lenses 5584a62befbcb
Mirrors and Lenses 5584a62befbcb
Uploaded by
Gerald0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views23 pagesThis document discusses mirrors and lenses. It defines plane mirrors, real and virtual images, and describes the characteristics of concave mirrors and convex lenses. Concave mirrors reflect light inward and produce real, inverted images. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and act like concave mirrors, producing real, inverted images. The mirror and lens equations relate the focal length, object distance, and image distance. Corrective lenses can address near-sightedness and far-sightedness.
Original Description:
Original Title
Fdocuments.net Mirrors and Lenses 5584a62befbcb
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses mirrors and lenses. It defines plane mirrors, real and virtual images, and describes the characteristics of concave mirrors and convex lenses. Concave mirrors reflect light inward and produce real, inverted images. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and act like concave mirrors, producing real, inverted images. The mirror and lens equations relate the focal length, object distance, and image distance. Corrective lenses can address near-sightedness and far-sightedness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views23 pagesMirrors and Lenses 5584a62befbcb
Mirrors and Lenses 5584a62befbcb
Uploaded by
GeraldThis document discusses mirrors and lenses. It defines plane mirrors, real and virtual images, and describes the characteristics of concave mirrors and convex lenses. Concave mirrors reflect light inward and produce real, inverted images. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and act like concave mirrors, producing real, inverted images. The mirror and lens equations relate the focal length, object distance, and image distance. Corrective lenses can address near-sightedness and far-sightedness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 23
Ch 18
Mirrors and Lenses
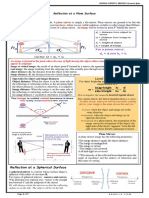
Plane Mirror
flat, smooth surface that
reflects light in a regular
way;
it produces an image
that is virtual, erect, and
the same size as the
object;
left and right appear to
be interchanged, but
front and back are
interchanged
Types of Images
Real image - source of converging light rays;
can be projected; are always inverted
Virtual image - source of diverging light rays;
cannot be projected; are always erect
Concave Mirror
reflects light off its inner surface
Focal point - (f) point on the principle axis where
reflecting light converges;
f equals one-half the radius of curvature (C)
Spherical Aberration
defect of all spherical mirrors when the parallel rays
don’t all reflect through the focal point;
correct this by using a parabolic mirror
Concave Mirror Characteristics
If the object is outside
C, the image is real,
inverted, and smaller
Concave Mirror Characteristics
If the object is at C, the
image is real, inverted,
and the same size
Concave Mirror Characteristics
If the object is between
C and f, the image is
real, inverted, and larger
Concave Mirror Characteristics
If the object is inside f,
the image is virtual,
erect, and larger
Mirror Equation
1 = 1 + 1 or di = f x do
f d o di do – f
f is the focal length
do is the object distance
di is the image distance
magnification - the ratio of the image size (hi) to the
object size (ho)
m = hi = - di
ho do
Mirror Equation Rules
di is positive for real images, negative for
virtual images
hi is positive for erect images, negative for
inverted images
f is positive for concave mirrors, negative for
convex mirrors
Convex mirror
reflects light off the
outer surface
images are always
virtual, erect, and
smaller
these are used as safety
mirrors because you get
a wider angle of vision
Lens
transparent material with a refractive index
larger than air
The focal length of the lens depends on the
shape and refractive index of the material
Convex Lens
Convex lens - (converging lens) thicker in the
middle than at the edges; acts like a concave
mirror.
Chromatic aberration - caused when light
passes thru the edge of a lens; the light is
dispersed; correct using an achromatic lens
Convex Lens Characteristics
Outside 2f, image is
real, inverted, and
smaller
Convex Lens Characteristics
At 2f, image is real,
inverted, and same size
Convex Lens Characteristics
Between 2f and f, image
is real, inverted, and
larger
Convex Lens Characteristics
Inside f, image is
virtual, erect, and larger
Concave lens
(diverging lens) thinner
in the middle than at the
edges
acts like a convex
mirror.
Always produces
virtual, erect, and
smaller image
Lens Equation Rules
The equation and rules stay the same except f
is positive for convex lens and negative for
concave lens
Corrective Lenses
Near-Sighted People
have too short a focal length
correct this using a concave (diverging) lens
Far-Sighted People
have too long a focal length,
correct this using a convex (converging) lens
You might also like
- ZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecDocument8 pagesZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecJaymarie ZabateNo ratings yet
- LIGHT Notes Class 7Document8 pagesLIGHT Notes Class 7anonymous2344444444444No ratings yet
- Light Class XDocument109 pagesLight Class XLekshmipriya PNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorDocument25 pagesPowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorPanuncialman, Johanna Mary B.No ratings yet
- 10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision MaterialDocument33 pages10 Cbse Physics CH - 1 & 2 Revision Material12-Criswin v geo-8ANo ratings yet
- B09 Ryan Delacruz - Q2 Cont - Module3Document7 pagesB09 Ryan Delacruz - Q2 Cont - Module3Mark SalvadorNo ratings yet
- LightDocument18 pagesLightAyush BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument18 pagesReflection and Refraction Notessundeepika2008No ratings yet
- LIGHT Chapter Notes - Grade10Document8 pagesLIGHT Chapter Notes - Grade10SriyaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalDocument27 pages1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalJohn Lester GenizeraNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument49 pagesMirrors and LensesjosephrandalldeiparineNo ratings yet
- Light Printed NotesDocument6 pagesLight Printed Notesphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument46 pagesMirrors and Lensesnvze999No ratings yet
- Physic - LensesDocument33 pagesPhysic - Lensesfelitrochristopher924No ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument72 pagesLight WavesJeffrey MaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument18 pagesMirrors and LensespamelaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Notes Grade 10Document9 pagesReflection Notes Grade 10Parv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection Spherical Mirror Part 1Document7 pagesLight-Reflection Spherical Mirror Part 1krishavsurya259No ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument10 pagesChapter Notes Light - Reflection & Refractionroseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument14 pages10 Lightnynaitikyadavu1No ratings yet
- Q2 Module 3Document34 pagesQ2 Module 3Ryza AcunaNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Mirror ImagesDocument18 pagesPlane and Spherical Mirror ImagesQueenie Faye TongolNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionMohammedNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors PDFDocument9 pagesSpherical Mirrors PDFAditya SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Plane MirrorJazelle PaciaNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument2 pagesHandoutsArque John Bertumen AbieraNo ratings yet
- Lens Ray DiagramsDocument24 pagesLens Ray DiagramsCarla Dane ManalangNo ratings yet
- Lenses and Mirrors Part1Document38 pagesLenses and Mirrors Part1Ian DibNo ratings yet
- Mirror and Lenses 10Document59 pagesMirror and Lenses 10Mesheil TaladroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15Document46 pagesLesson 15halifa5136No ratings yet
- Reflection of Light at Curved SurfacesDocument10 pagesReflection of Light at Curved SurfacesSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - W5Document13 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - W5rawisadaniNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument40 pagesOPTICSJanelle Ann BacoNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - NotesDocument17 pagesDelhi Public School Nadergul GRADE-10 Physical Science Light - Notesbaby doodlesNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFDocument7 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Light - ReflectionDocument6 pagesLight - ReflectionVenkataNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Charm Banlaoi100% (1)
- Concave and Convex MirrorDocument6 pagesConcave and Convex MirrorVijayalakshmi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightsDocument39 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightsHestia SimoneNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Concave & Convex Lens Notes, Ray Diagrams, & Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesConcave & Convex Lens Notes, Ray Diagrams, & Practice ProblemsT56KNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDocument14 pagesCLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Reflection of LightDocument44 pagesMirrors and Reflection of LightJennifer Bernas BerdulNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument16 pagesReflectiongiyu72623No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument19 pagesLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- S42 Class10ScienceNCERTSummaryPart IIDocument129 pagesS42 Class10ScienceNCERTSummaryPart IIsandeepkumarreddy2201No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reflection of LightDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Reflection of LightmbhksnvpNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3Document13 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Overview: - On Completion of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToDocument19 pagesOverview: - On Completion of This Lesson, Students Should Be Able Tothunder32xNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument89 pagesOpticsKarunya nidhi100% (1)
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- Week 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1Document90 pagesWeek 2 3 Mirror 21 22.pptx 1clairearabelle iloyNo ratings yet
- Science ReportingDocument26 pagesScience ReportingadreanneNo ratings yet
- Lens andDocument17 pagesLens andRandy AugustNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light in LensesDocument24 pagesRefraction of Light in LensesCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument13 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierXhenel Vincent LirioNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument57 pagesMirrors and Lensesohsangwoo215No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Optics NotesDocument5 pagesScience 10 - Optics NotesRina Marie Besin CartesianoNo ratings yet
- The Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesFrom EverandThe Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesNo ratings yet
- Photographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignFrom EverandPhotographic Composition: Principles of Image DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Fdocuments - in Biology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesDocument22 pagesFdocuments - in Biology Investigatory Project On Eye DiseasesSantosh SatputeNo ratings yet
- II Pu Physics VivaDocument2 pagesII Pu Physics VivashrishantkambarNo ratings yet
- Asahi TestDocument15 pagesAsahi TestdNo ratings yet
- Speed Detection of Moving Vehicle Using Speed Cameras Seminar Review 1 by Aniket Wadhe-1Document8 pagesSpeed Detection of Moving Vehicle Using Speed Cameras Seminar Review 1 by Aniket Wadhe-1aniket wadheNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Police Photography Latest Update 072314Document357 pagesReviewer in Police Photography Latest Update 072314Jay Masicampo100% (2)
- ES30C/ES31C Series Positioning System: Product SpecificationDocument4 pagesES30C/ES31C Series Positioning System: Product SpecificationdenfertNo ratings yet
- C Integra Solution Technology 2020Document10 pagesC Integra Solution Technology 2020Surhidayat Ibn MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Olympus OM-D E-M1 PT-EP11 Underwater System Chart EnglishDocument1 pageOlympus OM-D E-M1 PT-EP11 Underwater System Chart EnglishPatrick StivénNo ratings yet
- Drawing Aussie Flora: Australian National Botanic GardensDocument16 pagesDrawing Aussie Flora: Australian National Botanic GardensAna SantosNo ratings yet
- User's Guide: HDTV Multi-Standard, Multi-Format Camera SystemDocument110 pagesUser's Guide: HDTV Multi-Standard, Multi-Format Camera Systemcriss77No ratings yet
- The Biggest Little FarmDocument7 pagesThe Biggest Little FarmkatieNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmoscopy SlideDocument19 pagesOphthalmoscopy SlidemhixgoodieNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment AssignmentDocument7 pagesLab Equipment AssignmentWasi IslamNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 32Document6 pagesĐỀ 32hoangthanhngahuynh100% (1)
- Photography TipsDocument180 pagesPhotography Tipsgelb100% (1)
- How To Photograph Architectural ModelsDocument3 pagesHow To Photograph Architectural ModelswaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument7 pagesLensesStephanieNo ratings yet
- Q2, WEEK 8 S10FE IIh 52Document8 pagesQ2, WEEK 8 S10FE IIh 52CRISTINE MAE AREVALO100% (1)
- History of Photography Timeline-2020Document2 pagesHistory of Photography Timeline-2020api-530472333No ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Distribution of Calliptamus Barbarus Barbarus (Costa, 1836) (Orthoptera: Calliptaminae)Document7 pagesTaxonomy and Distribution of Calliptamus Barbarus Barbarus (Costa, 1836) (Orthoptera: Calliptaminae)Abasyn Journal of Life SciencesNo ratings yet
- CS H1CDocument6 pagesCS H1CWilbertNo ratings yet
- Dahua IP Camera & NVR Price List - January - 2020Document5 pagesDahua IP Camera & NVR Price List - January - 2020Parvez AlamNo ratings yet
- LMT Forensic Science NPTDocument7 pagesLMT Forensic Science NPTMariettaNo ratings yet
- Comparacion Celulares Cursos de InglesDocument1 pageComparacion Celulares Cursos de Inglesdayanncamilo montoyaNo ratings yet
- Stereoscopic Zoom Microscope SMZ645/ SMZ660: InstructionsDocument29 pagesStereoscopic Zoom Microscope SMZ645/ SMZ660: InstructionsRoBy RObNo ratings yet
- Flir E6 + Wifi - (63907-0704)Document4 pagesFlir E6 + Wifi - (63907-0704)Walter Guardia FariasNo ratings yet
- Guideto Dental PhotographyDocument5 pagesGuideto Dental PhotographyBence KlusóczkiNo ratings yet
- Power of Lens & Combination of LensesDocument15 pagesPower of Lens & Combination of LensesManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of Symmetry in PhotographyDocument6 pagesTypes of Symmetry in PhotographyVKVCPlaysNo ratings yet
- Call Sheet Template - SetHeroDocument2 pagesCall Sheet Template - SetHeroDhimas YudantoNo ratings yet