Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 Introduction of CN 2
Unit 1 Introduction of CN 2
Uploaded by
Utkarsh Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesThis document discusses different types of computer network topologies and network types. It defines network topologies like point-to-point, bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, daisy chain, and hybrid. It also explains different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), and internetworks. The largest internetwork is the Internet, which connects networks globally and supports many functions in modern life.
Original Description:
c
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different types of computer network topologies and network types. It defines network topologies like point-to-point, bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, daisy chain, and hybrid. It also explains different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), and internetworks. The largest internetwork is the Internet, which connects networks globally and supports many functions in modern life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesUnit 1 Introduction of CN 2
Unit 1 Introduction of CN 2
Uploaded by
Utkarsh KumarThis document discusses different types of computer network topologies and network types. It defines network topologies like point-to-point, bus, star, ring, mesh, tree, daisy chain, and hybrid. It also explains different types of computer networks including personal area networks (PANs), local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), and internetworks. The largest internetwork is the Internet, which connects networks globally and supports many functions in modern life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
Introduction of Computer Network
Dr. Kamlesh Chandravanshi
VIT, Bhopal
School of Computer Science & Enginnering
UNIT-1 Content
Network Topology
Computer Network Types
Network Topologies
A Network Topology is the arrangement with which computer
systems or network devices are connected to each other.
Topologies may define both physical and logical aspect of the
network. Both logical and physical topologies could be same
or different in a same network.
◦ Point-to-Point
◦ Bus Topology
◦ Star Topology
◦ Ring Topology
◦ Mesh Topology
◦ Tree Topology
◦ Daisy Chain
◦ Hybrid Topology
Point-to-Point
Point-to-point networks contains exactly two
hosts such as computer, switches or routers,
servers connected back to back using a single
piece of cable.
Bus Topology
all devices share single communication line or cable. Bus
topology may have problem while multiple hosts sending data
at the same time.
Star Topology
All hosts in Star topology are connected to a central device,
known as hub device, using a point-to-point connection. That
is, there exists a point to point connection between hosts and
hub. The hub device can be any of the following:
◦ Layer-1 device such as hub or repeater
◦ Layer-2 device such as switch or bridge
◦ Layer-3 device such as router or gateway
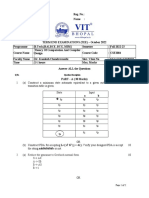
Switch 8 port 200rs
16 p-> 400rs
128 1000
256-> 1800
Use star topology and connect 130 pc
256 -> 1800
130 all of computer
256-130
Yes 128 + 8 port 136 (2port for two switch)=134
134 -130 => 4 unused
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each host machine connects to exactly two
other machines, creating a circular network structure. When
one host tries to communicate or send message to a host which
is not adjacent to it, the data travels through all intermediate
hosts.
Mesh Topology
A host is connected to one or multiple hosts. This topology has
hosts in point-to-point connection with every other host or
may also have hosts which are in point-to-point connection to
few hosts only.
Mesh technology comes into two types:
◦ Full Mesh
◦ Partially Mesh
Tree Topology
Also known as Hierarchical Topology, this is the most
common form of network topology in use presently. This
topology imitates as extended Star topology and inherits
properties of bus topology.
Daisy Chain
This topology connects all the hosts in a linear fashion.
Similar to Ring topology, all hosts are connected to two hosts
only, except the end hosts. Means, if the end hosts in daisy
chain are connected then it represents Ring topology.
Each link in daisy chain topology represents single point of
failure. Every link failure splits the network into two
segments. Every intermediate host works as relay for its
immediate hosts.
Hybrid Topology
A network structure whose design contains more than one
topology is said to be hybrid topology. Hybrid topology
inherits merits and demerits of all the incorporating
topologies.
Computer Network Types
Personal Area Network
Local Area Network
Metropolitan Area Network
Wide Area Network
Internetwork
Generally, networks are distinguished based on their
geographical span. A network can be as small as distance
between your mobile phone and its Bluetooth headphone and
as large as the internet itself, covering the whole geographical
world.
Personal Area Network
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is smallest network which is very
personal to a user. This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red
enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters. PAN may
include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled
headphones, wireless printers and TV remotes.
Local Area Network
A computer network spanned inside a building and operated
under single administrative system is generally termed as
Local Area Network (LAN). Usually, LAN covers an
organization’ offices, schools, colleges or universities.
Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from as least
as two to as much as 16 million.
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between
end users. The resources such as printers, file servers,
scanners, and internet are easily sharable among computers.
Metropolitan Area Network
The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) generally expands
throughout a city such as cable TV network. It can be in the
form of Ethernet, Token-ring, ATM, or Fiber Distributed Data
Interface (FDDI).
Wide Area Network
Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a wide area which may
span across provinces and even a whole country. Generally,
telecommunication networks are Wide Area Network. These
networks provide connectivity to MANs and LANs. Since
they are equipped with very high speed backbone, WANs use
very expensive network equipment.
Internetwork
A network of networks is called an internetwork, or simply the internet. It is
the largest network in existence on this planet. The internet hugely connects
all WANs and it can have connection to LANs and Home networks. Internet
uses TCP/IP protocol suite and uses IP as its addressing protocol.
Internet is serving many proposes and is involved in many aspects of life.
Some of them are:
◦ Web sites
◦ Instant Messaging
◦ Blogging
◦ Social Media
◦ Marketing
◦ Networking
◦ Resource Sharing
◦ Audio and Video Streaming
You might also like
- F5 DNS Guide PDFDocument102 pagesF5 DNS Guide PDFRohanNo ratings yet
- List of Cisco Exam Fee Changes:: CCNP 300-410 DumpsDocument7 pagesList of Cisco Exam Fee Changes:: CCNP 300-410 DumpsSiddheshSPatilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworkDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkUtpal KantNo ratings yet
- Quotation For New Internet Connection PDFDocument7 pagesQuotation For New Internet Connection PDFabcdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, NetworkingDocument15 pagesChapter 11, NetworkingRaj Srivastav RJNo ratings yet
- Personal Area NetworkDocument10 pagesPersonal Area Networkmwaurah ndunguNo ratings yet
- Types of NetworkDocument16 pagesTypes of NetworkPriyank RathoreNo ratings yet
- Network Types Network Topologies Transmission MediaDocument37 pagesNetwork Types Network Topologies Transmission MediatusharpalNo ratings yet
- Network IntroDocument48 pagesNetwork IntroJerlon ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- A Practical Assignment of 'Computer Networks and Internet - 16IMG22C5'' Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of The Award of MBA 2.2 Session (2020-2021)Document21 pagesA Practical Assignment of 'Computer Networks and Internet - 16IMG22C5'' Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of The Award of MBA 2.2 Session (2020-2021)SäKshï AhujaNo ratings yet
- TopologiesDocument8 pagesTopologiesvigneshNo ratings yet
- Topology and Its TypeDocument4 pagesTopology and Its TypeNEHA CHAHARNo ratings yet
- Sharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkDocument17 pagesSharing Files, Data, and Information. in A NetworkBharatNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab: Course Code: CSE 1006Document29 pagesComputer Networks Lab: Course Code: CSE 1006The Bong BoyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 2Document32 pagesModule 1 - Part 2Ver Laurence CuevasNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesTopic 8 Computer NetworksOsii JuliusNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking NotesDocument12 pagesData Communication and Networking NotesELIJAH AUGUSTIN TAMBA KOMBANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document57 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1casseyareolaNo ratings yet
- Computer Network FundamentalsDocument41 pagesComputer Network FundamentalsShadowCrew CruzNo ratings yet
- IoT Module1Document16 pagesIoT Module1skus0426No ratings yet
- Networking: Why Do We Need Computer Network?Document28 pagesNetworking: Why Do We Need Computer Network?Yogita UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Comp Networks - BarungiDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Comp Networks - BarungiMasaba Denis MadenNo ratings yet
- Data Communication & NetworkingDocument24 pagesData Communication & NetworkingZulqarnain JamilNo ratings yet
- Ca CH-3 Note 1Document17 pagesCa CH-3 Note 1Satya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Networking: Prepared By: Mr. Maverick Rovie S. LagmanDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networking: Prepared By: Mr. Maverick Rovie S. LagmanLenoverNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument20 pagesComputer Networkspmbrahvee115No ratings yet
- ICT Fundamentals ReportDocument49 pagesICT Fundamentals ReportJigs OlbesNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer NetworksDocument32 pagesTypes of Computer Networksfunny videos lastest songsNo ratings yet
- Networking in DMRCDocument16 pagesNetworking in DMRCaanchalbahl62100% (1)
- Computer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuDocument17 pagesComputer Application: Surbhi Goel 12455 Bcom Hons A Pgdav College DuManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Computer Networks and InternetDocument24 pagesIntroduction of Computer Networks and InternetChristy RagayNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer NetworkNirmanyu SoodNo ratings yet
- DCN NOTES For COURSE FILEDocument13 pagesDCN NOTES For COURSE FILEÃmît TíwârìNo ratings yet
- Network Types of Types Network Topologies: Presented by Faiz Muhammad Roll No: 21 Muhammad Ishaque Roll No: 22Document22 pagesNetwork Types of Types Network Topologies: Presented by Faiz Muhammad Roll No: 21 Muhammad Ishaque Roll No: 22FaizSheikhNo ratings yet
- Web Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesDocument14 pagesWeb Application Class XI Unit 1 NotesNaina Kanojia91% (11)
- Nure's PresentationDocument14 pagesNure's Presentationmdmintajur24No ratings yet
- Telecomms ConceptsDocument111 pagesTelecomms ConceptsKAFEEL AHMED KHANNo ratings yet
- Networking: Instructor: S.D.BanerjeeDocument70 pagesNetworking: Instructor: S.D.BanerjeeAnkur Chattopadhayay100% (1)
- A Computer NetworkDocument11 pagesA Computer NetworkBridget DindiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FirstDocument46 pagesUnit 1 FirstSimran LalchandaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Network and Data TransmissionDocument31 pagesTypes of Network and Data Transmissionkimberlyann alpuertoNo ratings yet
- Unit 13Document11 pagesUnit 13Luis Norbert SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Introduction CNDocument65 pagesIntroduction CNSaluNo ratings yet
- 4335 NetworkingemisDocument4 pages4335 NetworkingemisFavour JamesNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 - Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesSlide 1 - Computer NetworksAbdullahNo ratings yet
- CN Basics 2-3Document41 pagesCN Basics 2-3F. B. I.No ratings yet
- Computer Networks NetworkingDocument7 pagesComputer Networks Networkingzohebdhuka_libraNo ratings yet
- Comp Funda, NotesDocument14 pagesComp Funda, Notesandyrobin058No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Computer NetworksDocument37 pagesLecture 5 - Computer Networksamangeldinersultan200tNo ratings yet
- VYSHNAVI.M (18bcs) : Computer NetworksDocument6 pagesVYSHNAVI.M (18bcs) : Computer Networks18BCS120 VyshnaviNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Modem: LAN - Local Area NetworkDocument5 pagesBandwidth Modem: LAN - Local Area NetworkYvette IyadedeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document27 pagesLecture 2Mstafa MhamadNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument7 pagesNetworkingVikash JhunjhunwallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 P1Document6 pagesUnit 10 P1spookyleaf100% (2)
- 12th IP Networking 3-UnitDocument40 pages12th IP Networking 3-UnitHridyanshNo ratings yet
- W6 - IT102 - Unit2 - Lesson 6Document37 pagesW6 - IT102 - Unit2 - Lesson 6Aldrei BobierNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument33 pagesComputer NetworkingApeh Usman Isah100% (1)
- How Computer Network Works: Local Area Networks (Lans) Wide Area Networks (Wans) InternetDocument9 pagesHow Computer Network Works: Local Area Networks (Lans) Wide Area Networks (Wans) InternetASHFORD BORJANo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Presented byDocument34 pagesComputer Networks: Presented byJadedGoth100% (2)
- Chapter VDocument42 pagesChapter Vmigo267No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Computer Networking Class 12 (Aashi Nagiya)Document19 pagesUnit 3 Computer Networking Class 12 (Aashi Nagiya)Aashi NagiyaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking': Presentation OnDocument18 pagesComputer Networking': Presentation OnPrashant YadavNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Module 2Document122 pagesModule 2Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 SwitchingDocument36 pagesUnit 2 SwitchingUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- A11 - A12 - A13 - A14 - A15 - ECE3004 - Fall 2022-23 (Online) - MidtermDocument1 pageA11 - A12 - A13 - A14 - A15 - ECE3004 - Fall 2022-23 (Online) - MidtermUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- B11 - B12 - B13 - 0301 - CHY1001 - Engineering ChemistryDocument1 pageB11 - B12 - B13 - 0301 - CHY1001 - Engineering ChemistryUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Game TreesDocument11 pagesGame TreesUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Mat3003 Probability,-Statistics-And-Reliability LT 1.0 1 Mat3003Document2 pagesMat3003 Probability,-Statistics-And-Reliability LT 1.0 1 Mat3003Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- CSE2004-Theory of Computation and Compiler Design-TEEDocument2 pagesCSE2004-Theory of Computation and Compiler Design-TEEUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- D11 - D12 - 0662 - MGT2003 - Technology EntrepreneurshipDocument1 pageD11 - D12 - 0662 - MGT2003 - Technology EntrepreneurshipUtkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Aadhaar Masking API DocumentationDocument6 pagesAadhaar Masking API Documentationabhishek.kumarNo ratings yet
- (Update) Post Test Week 6 - Attempt ReviewwDocument5 pages(Update) Post Test Week 6 - Attempt ReviewwDita NoviyantiNo ratings yet
- Relays DNSDocument5 pagesRelays DNSaghil EchreshNo ratings yet
- 256267a1Document5,083 pages256267a1Елизавета ШепелеваNo ratings yet
- Lab # 1 Connectivity, NTP and SYSLOG INWK 6912: Master of Engineering in InternetworkingDocument27 pagesLab # 1 Connectivity, NTP and SYSLOG INWK 6912: Master of Engineering in InternetworkingVenkata KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Web Surfing: Anonymous Browsing OptionsDocument6 pagesWeb Surfing: Anonymous Browsing OptionsKB AganNo ratings yet
- Winner ListDocument926 pagesWinner ListW GeNo ratings yet
- 5G NR StandAlone NPI WorkshopDocument16 pages5G NR StandAlone NPI Workshop5gnew2025No ratings yet
- Discursive Writing - Term 3 - Computers Are A Blessing in Disguise What Are Your ViewsDocument2 pagesDiscursive Writing - Term 3 - Computers Are A Blessing in Disguise What Are Your Viewsapi-245384078No ratings yet
- Information AgeDocument33 pagesInformation AgeRheajen Mae RebamonteNo ratings yet
- Huge FilesDocument16 pagesHuge Filesaziz64pNo ratings yet
- Mpay VodafoneDocument6 pagesMpay VodafoneFlaviub23No ratings yet
- Ariva - HTTP Server: 1. Check Your Receiver IP Adress ?Document1 pageAriva - HTTP Server: 1. Check Your Receiver IP Adress ?jarmilaNo ratings yet
- Implementation Document - Pengadaan Perangkat HPE Aruba Dan Fortinet + ImplementasiDocument55 pagesImplementation Document - Pengadaan Perangkat HPE Aruba Dan Fortinet + ImplementasiROY LISTON PANAHATAN PANJAITANNo ratings yet
- TOSHIBA Satellite L600D TE3 DA0TE3MB6C0 PDFDocument43 pagesTOSHIBA Satellite L600D TE3 DA0TE3MB6C0 PDFHdac ChacónNo ratings yet
- MPLS Inter-AS Option ABDocument50 pagesMPLS Inter-AS Option ABJames OmaraNo ratings yet
- Full Chapter Beginning Machine Learning in The Browser 1St Edition Nagender Kumar Suryadevara PDFDocument53 pagesFull Chapter Beginning Machine Learning in The Browser 1St Edition Nagender Kumar Suryadevara PDFtimothy.long598100% (8)
- Coc Hack 2020】##New Updated CHEAT for android & iOS: 【Clash Of Clans Hack】【Document2 pagesCoc Hack 2020】##New Updated CHEAT for android & iOS: 【Clash Of Clans Hack】【daniel isholaNo ratings yet
- Mil Summative Quiz 1 CompleteDocument2 pagesMil Summative Quiz 1 CompleteEverdina GiltendezNo ratings yet
- VPC Best Practices BRKDCT-2378 PDFDocument91 pagesVPC Best Practices BRKDCT-2378 PDFHamza AbdelsalamNo ratings yet
- New Applications July 2021Document155 pagesNew Applications July 2021Varshith SureshNo ratings yet
- Web 2Document2 pagesWeb 2Titus ClementNo ratings yet
- EMTECH Handout 01 - Introduction To ICTDocument4 pagesEMTECH Handout 01 - Introduction To ICTericka junioNo ratings yet
- Web Browsing - G5 (Edited)Document25 pagesWeb Browsing - G5 (Edited)jonny lêNo ratings yet
- GAC005 Assessment Event 2Document11 pagesGAC005 Assessment Event 2PaulinaNo ratings yet
- 3com Switch 4500 Command Reference GuideDocument955 pages3com Switch 4500 Command Reference GuideandresreveloNo ratings yet
- DELL Studio - 1450 Foxconn - H830-LDocument50 pagesDELL Studio - 1450 Foxconn - H830-LPintu Kumar SinghNo ratings yet