Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Market Structures
The Market Structures
Uploaded by
Xyron D. Huang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pagesOriginal Title
The+market+structures
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pagesThe Market Structures
The Market Structures
Uploaded by
Xyron D. HuangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
THE MARKET STRUCTURES
THE MARKET IS MORE THAN JUST A STATE OF EXCHANGING
GOODS…
…the market possesses the power
yielded by buyers and sellers in
negotiating with the market
MARKET POWER DEFINED
The ability of any actor or group of
actors in the market to significantly
influence the price in the market and the
quantity to be produced or sold.
THE ABILITY FOR MARKET PLAYERS TO POSSESS MARKET
POWER…
… will depend on the market
structure.
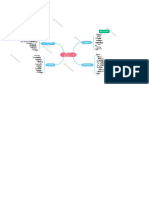
CLASSIFICATIONS OF MARKET STRUCTURE
PERFECT COMPETITION
Is a market structure where no single seller or buyer has power
to determine the price and the level of output in the market.
Has numerous firms and buyers supplying and buying the
product at any one time.
Because of the number of buyers and sellers, not a single one of
them has significant influence on the price and quantity of the
goods due to its undifferentiated nature.
MONOPOLY
A market structure characterized by one seller in the market.
A market structure where there is only one buyer is a monopsony.
Because only one seller or buyer exists, this single seller or buyer
have huge market power and influence.
Monopolists/monopsonists also create highly differentiated
products that discourages other players from joining them.
Examples are utility companies
OLIGOPOLY
A market structure characterized by a few sellers
producing similar and differentiated products
Examples are large scale cement and steel companies, and
the oil sector
Due to its setup, it is prone to collusion, as players come
together with the goal of manipulating prices of its goods
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
Has elements of both the competitive and monopolistic markets
Competitive because of numerous sellers and buyers in the
market that freely enters and leaves it
Monopolistic because products sold in the market are
differentiated by the seller through various means of advertising
and numerous ways of packaging
THE IMPLICATIONS OF MARKET STRUCTURES
FOR ENTREPRENEURS
ENTREPRENEURS WITH LIMITED RESOURCES CAN ONLY ENTER
A PERFECTLY COMPETITIVE MARKET
Because entry and exit is easy
But with many players,
earnings can be limited as well
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITIVE MARKETS MAY GIVE SMALL
SCALE BUSINESSES SOME ADVANTAGE
A small business who can differentiate
their goods well stands a chance of earning
big in a monopolistic competitive market
Example: Kangkong Chips
THE COST OF DOING BUSINESS REQUIRES ENTREPRENEURS TO
CONSIDER INTEREST AND INVESTMENT RATES
Because internal funds from businesses
may not be sufficient, borrowing funds
from banks and other lenders may be
necessary and this requires cost
BUSINESS OPERATIONS ON THE GROUND SHOULD CONSIDER
RENTAL AND OTHER LOGISTICS COSTS
It may not be feasible for start up businesses to
place their offices right away in high end business
districts due to high rental costs
This explains partly why online businesses are
rising fast
PLANNING FOR MANPOWER TO MANAGE COSTS OF PAYING
MINIMUM WAGES SHOULD BE CONSIDERED
Companies must only hire the
right amount of people to manage
the costs of paying wages to them
TAX CONSIDERATIONS
By rapidly depreciating their assets, companies can avail
of lower tax liabilities and bring more cash to them
Certain tax exemptions granted by the government can
also be given to encourage businesses to set up their shop
in the country
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Agricultural and Agribusiness SectorsDocument12 pagesThe Agricultural and Agribusiness SectorsXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of Profit MaximizationDocument15 pagesEconomic Analysis of Profit MaximizationXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Demand CurveDocument9 pagesChanges in The Demand CurveXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- 7603 On The Relationship Between KnowledgeDocument6 pages7603 On The Relationship Between KnowledgeXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- ParadigmDocument1 pageParadigmXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Supply CurveDocument19 pagesChanges in The Supply CurveXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Standard Company Bylaws ExampleDocument20 pagesStandard Company Bylaws ExampleXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Aquatics Introduction - SHSDocument2 pagesAquatics Introduction - SHSXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Comp BKKPNGDocument4 pagesComp BKKPNGXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Dimension of National Culture and Effective Leadership Patterns: Hofstede RevisitedDocument25 pagesDimension of National Culture and Effective Leadership Patterns: Hofstede RevisitedXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Afraid - Jefferey Deaver Freytag - S PyramidDocument1 pageAfraid - Jefferey Deaver Freytag - S PyramidXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- How Animals SurviveDocument31 pagesHow Animals SurviveXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- MRD Journal D 10 00111.1Document7 pagesMRD Journal D 10 00111.1Xyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- PEST AnalysisDocument1 pagePEST AnalysisXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- 7603 On The Relationship Between KnowledgeDocument6 pages7603 On The Relationship Between KnowledgeXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Comp 1Document1 pageComp 1Xyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- Tracing The Impacts Through The Distribution of OutputsDocument9 pagesTracing The Impacts Through The Distribution of OutputsXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet
- A Competency Analysis of ABM Students On Starting A BusinessDocument3 pagesA Competency Analysis of ABM Students On Starting A BusinessXyron D. HuangNo ratings yet