Professional Documents
Culture Documents
My Mini Presentation On LASER
My Mini Presentation On LASER
Uploaded by
live life with Peggy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views12 pagesA laser is a device that emits light through stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 and was based on earlier theoretical work. Lasers produce coherent, monochromatic, directional light through a process called optical amplification that occurs when electrons in excited atoms emit photons that stimulate additional photon emissions. Helium-neon lasers are commonly used lasers that emit in the visible spectrum and operate continuously through electrical pumping of a gas mixture. Lasers have many applications including optical storage, medicine, manufacturing, communications, and entertainment.
Original Description:
Original Title
My mini presentation on LASER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA laser is a device that emits light through stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 and was based on earlier theoretical work. Lasers produce coherent, monochromatic, directional light through a process called optical amplification that occurs when electrons in excited atoms emit photons that stimulate additional photon emissions. Helium-neon lasers are commonly used lasers that emit in the visible spectrum and operate continuously through electrical pumping of a gas mixture. Lasers have many applications including optical storage, medicine, manufacturing, communications, and entertainment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views12 pagesMy Mini Presentation On LASER
My Mini Presentation On LASER
Uploaded by
live life with PeggyA laser is a device that emits light through stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 and was based on earlier theoretical work. Lasers produce coherent, monochromatic, directional light through a process called optical amplification that occurs when electrons in excited atoms emit photons that stimulate additional photon emissions. Helium-neon lasers are commonly used lasers that emit in the visible spectrum and operate continuously through electrical pumping of a gas mixture. Lasers have many applications including optical storage, medicine, manufacturing, communications, and entertainment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
LASER
Soni Behera(EC-4) En no:216150311011
Purva Pandey(EC-8) En no:216150311006
Prabha Sahani(EC-11) En no:216150311016
• A laser is a device that emits light through a
process of optical amplification based on the
simulated amission of electromagnetic radiation
• The word "laser" is an acronym for "light
What is amplification by stimulated emission of
LASER? radiation"
• The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H.
Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based
on theoretical work by Charles Hard
Townes andArthur Leeonard Schewlow.
Diffrence
between
Laser
and
ordinary
light:
Production of laser light
• Laser light is produced when stimulated emission occurs.
• This process occurs when an electron in the ground state
(the lowest energy state of an atom or other particle) is
supplied with energy, making it pump up to a higher energy
level.
• In this level, the electron is now in an excited state (when an
electron absorbs energy), and is also in the metastable state
(an excited state of an atom that has a longer lifetime than
other excited states).
• When this happens, a photon (particle representing a quantum of light
or other electromagnetic radiation) meets with an electron that is within
the same energy level as the initial electron which produced the first
photon.
• After this happens, a second photon is produced by the electron.
This photon has the same wavelength and direction as the first photon.
• As shown above, the lasting medium is paired with two mirrors.
• Mirror 1 is a full mirror, while mirror 2 is partially (half) a mirror,
allowing necessary light to exit.
• These mirrors make the photons reflect off both the mirrors
continuously in the lasting medium. While these photons bounce
back and forth, they meet other electrons and encourage them to
emit photons which possess the same wavelength and direction.
• This is kind of like a chain effect, similar to the fission of uranium in a
nuclear power plant.
• This process, as mentioned before, gives lasers its monochromatic,
coherent, and directional properties.
• mirror 2 is partially silver, meaning that it allows light to pass
through. While this entire process happens, the light that passes
through mirror 2 is the light we know as laser light.
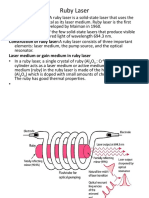
What is helium-neon laser?
• At room temperature, a ruby laser will only emit short bursts of a laser light,
each laser pulse occurring after a flash of pumping light.
• It would be better to have a laser that emits a light continuously. Such a laser
is called a continuous wave laser (cw).
• Helium-neon lasers are the most widely used gas lasers. These lasers have
many industrial and scientific uses and are often used in laboratory
demonstrations of optics.
• In He-Ne lasers, the optical pumping method is not used instead an electrical
pumping method is used. The excitation of electrons in the He-Ne gas active
medium is achieved by passing an electric current through the gas.
• The helium-neon laser operates at a wavelength of 632.8 nanometers (nm),
in the red portion of the visible spectrum.
Working of helium-neon laser
• In helium-neon lasers, we use high voltage DC as the pump source. A
high voltage DC produces energetic electrons that travel through the
gas mixture.
• The gas mixture in helium-neon laser is mostly comprised of helium
atoms. Therefore, helium atoms observe most of the energy supplied
by the high voltage DC.
Advantages of helium-neon laser
• Helium-neon laser emits laser light in the visible portion
of the spectrum.
• High stability
• Low cost
• Operates without damage at higher temperatures
Disadvantages of helium-neon laser
• Low efficiency
• Low gain
• Helium-neon lasers are limited to low power tasks
Applications of helium-neon lasers
• Helium-neon lasers are used in industries.
• Helium-neon lasers are used in scientific instruments.
• Helium-neon lasers are used in the college laboratories.
Applications of LASER:
• Laser Photogrammetry • Disc Drive
• Astronomy • Military
• Level Tool • Optical Tweezers
• Medical • Gun Sight
• Fiber Optical Cable • Barcode Scanner
• Laser Tag • Laser Printer
• Material Processing • Entertainment
You might also like
- Aircraft Carrier Climate Control Investigation Team (ACCCIT) HVAC ManualDocument143 pagesAircraft Carrier Climate Control Investigation Team (ACCCIT) HVAC Manualezmerelda50% (2)
- AS380 Integrated Drive Instruction Manual.Document271 pagesAS380 Integrated Drive Instruction Manual.Rebecca Dang100% (1)
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Determining The Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide ExperimentDocument2 pagesDetermining The Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide ExperimentJennifer Moore50% (2)
- Smart and Multifunctional Concrete Toward Sustainable Infrastructures PDFDocument409 pagesSmart and Multifunctional Concrete Toward Sustainable Infrastructures PDFhijerNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document8 pagesCH 1Mariam ragabNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - 10th Sept20222Document32 pagesClass 8 - 10th Sept20222Muttu PattarNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument22 pagesLasersAtul KhattarNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics and Electronics: TopicDocument31 pagesModern Physics and Electronics: TopicAmandeep Singh KheraNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Laser, Action, Einstein Theory of Laser, Types, Applications in Industry & Medical FieldDocument15 pagesTerm Paper Laser, Action, Einstein Theory of Laser, Types, Applications in Industry & Medical FieldGarima SoniNo ratings yet
- Helium PDFDocument2 pagesHelium PDFKONAL PURINo ratings yet
- State Principle of Laser and How It Can Be Utilized in Computer Aided InspectionDocument6 pagesState Principle of Laser and How It Can Be Utilized in Computer Aided InspectionAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 LaserDocument19 pagesChapter 7 LaserYohannesNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument11 pagesLasersKristiyan GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Lasers PDFDocument24 pagesLasers PDFReghunaath A ANo ratings yet
- Helium-Neon Lasers: A.A.REGHUNAATH: 18BCE0227 A.V.Abhishek Arjun: 18bce0232 ARJUN.S: 18BCE0236Document24 pagesHelium-Neon Lasers: A.A.REGHUNAATH: 18BCE0227 A.V.Abhishek Arjun: 18bce0232 ARJUN.S: 18BCE0236Reghunaath A ANo ratings yet
- 18bce0227 VL2018191000937 Adl PDFDocument24 pages18bce0227 VL2018191000937 Adl PDFReghunaath A ANo ratings yet
- Lasers 140314053209 Phpapp01Document84 pagesLasers 140314053209 Phpapp01apurvzNo ratings yet
- Laser Lecture 1Document29 pagesLaser Lecture 1yo391174No ratings yet
- Applied Physics Presentation: Topic:-Laser and Its ApplicationsDocument14 pagesApplied Physics Presentation: Topic:-Laser and Its ApplicationsVishal ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Laser10 11 11Document49 pagesLaser10 11 11Gaurav LakshkarNo ratings yet
- L Light A Amplification S Stimulated E Emission R RadiationDocument8 pagesL Light A Amplification S Stimulated E Emission R RadiationArjun Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Laser in OperativeDocument99 pagesLaser in OperativeAnisha AnilNo ratings yet
- Laser, Action, Einstein Theory of Laser, Types, Applications in IndustryDocument27 pagesLaser, Action, Einstein Theory of Laser, Types, Applications in IndustryChad Smith100% (5)
- Phy AnsDocument28 pagesPhy Ansstanygregor87No ratings yet
- Ight Mplification by Timulated Mission of Adiation: L A S E RDocument40 pagesIght Mplification by Timulated Mission of Adiation: L A S E RSparsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument49 pagesLaserMahmoud AlsaidNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety Training - December 2017Document33 pagesLaser Safety Training - December 2017Luqman KhanNo ratings yet
- Fiber LaserDocument23 pagesFiber LaserGourav ThakurNo ratings yet
- Laser: Department of Applied SciencesDocument64 pagesLaser: Department of Applied SciencesAnimesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- # 6 Laser Beam MachiningDocument81 pages# 6 Laser Beam MachiningRohan RautNo ratings yet
- Laser System EngineringDocument213 pagesLaser System EngineringwooDefyNo ratings yet
- Psychedelic PDFDocument155 pagesPsychedelic PDFNishanth VigneshNo ratings yet
- 057 PDFDocument15 pages057 PDFVương BanNo ratings yet
- LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)Document44 pagesLASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)Mehroz FatimaNo ratings yet
- Laser Group 2 PresentationDocument24 pagesLaser Group 2 PresentationANIRUDH SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Ruby Laser and CO2 Laser - PowerPointToPdfDocument15 pagesRuby Laser and CO2 Laser - PowerPointToPdfchirag pandeyNo ratings yet
- Lasers: Condition For Laser ActionDocument18 pagesLasers: Condition For Laser ActiongrinneNo ratings yet
- Lasers in DentistryDocument53 pagesLasers in DentistryDr. Nikhil saranNo ratings yet
- Laser - 2nd BPT - 1st ClassDocument20 pagesLaser - 2nd BPT - 1st Classamitesh_mpthNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument20 pagesLasertsrockon28No ratings yet
- 2nd Semester Laser NotesDocument48 pages2nd Semester Laser NotesAbhay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LASERDocument4 pagesLASERAbhishek NaikNo ratings yet
- Some Basics of LasersDocument102 pagesSome Basics of LasersVinisha Vipin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Laser - WikipediaDocument148 pagesLaser - WikipediaAnkur SinghNo ratings yet
- Lasers: Basic Principle and Uses in Dermatology: DR Rohit Kr. Singh Res. (Dermatology) Base Hospital LKODocument68 pagesLasers: Basic Principle and Uses in Dermatology: DR Rohit Kr. Singh Res. (Dermatology) Base Hospital LKODiah Ayu Kusuma DewiNo ratings yet
- LaserDocument22 pagesLaserRaghuveer ReddyNo ratings yet
- 15) Lasers in OrthodonticsDocument220 pages15) Lasers in OrthodonticsPatel JainilNo ratings yet
- He - Ne LASERDocument19 pagesHe - Ne LASERAnshika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Advanced DWDM TrainingDocument144 pagesAdvanced DWDM TrainingShaytaanNo ratings yet
- Laser: "Laser Light" Redirects Here. For The Song, See - For Laser Light Show, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument25 pagesLaser: "Laser Light" Redirects Here. For The Song, See - For Laser Light Show, See - For Other Uses, SeepagalNo ratings yet
- CAI Assgnmnt 1Document8 pagesCAI Assgnmnt 1Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Laser in The Biomedical FieldDocument26 pagesApplications of Laser in The Biomedical FieldAnikaNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety Manual: University of Victoria, Chemistry DepartmentDocument27 pagesLaser Safety Manual: University of Victoria, Chemistry DepartmentKOMATSU SHOVELNo ratings yet
- LASERDocument5 pagesLASERHARSHA PNo ratings yet
- 1.laser TherapyDocument12 pages1.laser TherapyFaisal Mehboob67% (3)
- Lasers in Pediatric Dentistry - 2Document82 pagesLasers in Pediatric Dentistry - 2Shameena KnNo ratings yet
- Principle of Laser: P A LaDocument5 pagesPrinciple of Laser: P A LaAineekamranNo ratings yet
- Lasers in ProsthodonticsDocument27 pagesLasers in ProsthodonticsPremshith CpNo ratings yet
- JS Laser TypesDocument20 pagesJS Laser TypesLM_SNo ratings yet
- Components of Optical InstrumentsDocument45 pagesComponents of Optical InstrumentsMasudRanaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Fluorescent Gems and Minerals - An Exposition and Catalog of the Fluorescent and Phosphorescent Gems and Minerals, Including the Use of Ultraviolet Light in the Earth SciencesFrom EverandHandbook of Fluorescent Gems and Minerals - An Exposition and Catalog of the Fluorescent and Phosphorescent Gems and Minerals, Including the Use of Ultraviolet Light in the Earth SciencesNo ratings yet
- Types of BatteryDocument5 pagesTypes of Batterylive life with PeggyNo ratings yet
- Exp PINCDocument5 pagesExp PINClive life with PeggyNo ratings yet
- Suspicious PartnerDocument1 pageSuspicious Partnerlive life with PeggyNo ratings yet
- Suspicious PartnerDocument1 pageSuspicious Partnerlive life with PeggyNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ReportDocument14 pagesSummer Internship Reportlive life with PeggyNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Isoprene ProductionDocument4 pagesFeasibility Study of Isoprene ProductionIntratec SolutionsNo ratings yet
- 2021 - 02 - 16 App. FGD in Power PlantsDocument24 pages2021 - 02 - 16 App. FGD in Power PlantsApply SofttechNo ratings yet
- The Global Desalination Market: Christopher Gasson Global Water IntelligenceDocument24 pagesThe Global Desalination Market: Christopher Gasson Global Water Intelligencesaket-mehtaNo ratings yet
- York YMAE Series Air-Cooled Full DC Inverter Modular Chiller and Heat PumpDocument20 pagesYork YMAE Series Air-Cooled Full DC Inverter Modular Chiller and Heat PumpMajd KyNo ratings yet
- Machine-Room-Less Electrical Gearless Solutions (MRLG) : Orona 3GDocument2 pagesMachine-Room-Less Electrical Gearless Solutions (MRLG) : Orona 3GSomea NoneaNo ratings yet
- PP Aaa PP1 150Document17 pagesPP Aaa PP1 150Rabah AmidiNo ratings yet
- ABB Motors, Drives and Services For The Metals Industry: Improving Efficiency and Performance, Boosting SustainabilityDocument26 pagesABB Motors, Drives and Services For The Metals Industry: Improving Efficiency and Performance, Boosting SustainabilitySubbuNo ratings yet
- M9-B Plate Type Cooler Manual For M3, M6, M10, TS6, T2, T5, T8, T10, TL3, TL6 PDFDocument30 pagesM9-B Plate Type Cooler Manual For M3, M6, M10, TS6, T2, T5, T8, T10, TL3, TL6 PDFAnonymous uTO1WINo ratings yet
- 2010 0291Document87 pages2010 0291Rk ZhokuNo ratings yet
- Article 22Document6 pagesArticle 22Khensley ColegaNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report-Final Sakthi SugarsDocument12 pagesSummer Internship Report-Final Sakthi SugarsSangeetha Prabha83% (6)
- STATCOM IEEE14-BusDocument5 pagesSTATCOM IEEE14-BusPhùng Tiến ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Solar Heated Air Rice Dehydrator (S.H.A.R.D) For Cost Effective Means of Drying PalayDocument34 pagesSolar Heated Air Rice Dehydrator (S.H.A.R.D) For Cost Effective Means of Drying PalayVince LagumbayNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics NotesDocument15 pagesModern Physics NotesSigwa Timo100% (1)
- John Deere 6081 GeneradorDocument2 pagesJohn Deere 6081 GeneradoremmanuelNo ratings yet
- ZEOCHEM General BrochureDocument8 pagesZEOCHEM General BrochureFabricio100% (1)
- Management Controls Systems by Stockland Corporation Limited Introduction To StocklandDocument4 pagesManagement Controls Systems by Stockland Corporation Limited Introduction To StocklandShahrukh NaqviNo ratings yet
- Self Evaluation Test PDFDocument4 pagesSelf Evaluation Test PDFUddhav SharmaNo ratings yet
- EPC B XungDocument4 pagesEPC B XungNguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Food Extrusion FoodkidaDocument38 pagesFood Extrusion Foodkidamonicaad shankarNo ratings yet
- Test PDFDocument373 pagesTest PDFheissenriyadhovicNo ratings yet
- L36 - Combustion ReactionsDocument25 pagesL36 - Combustion ReactionsĐặng Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- FSK-628D Gobernador Electronico de MotorDocument35 pagesFSK-628D Gobernador Electronico de Motorsoldadores motoresNo ratings yet
- Siklus Thermal PembangkitDocument15 pagesSiklus Thermal PembangkitIwan RuhiyanaNo ratings yet
- Afl PowerpointDocument43 pagesAfl Powerpointapi-273819184No ratings yet
- 442Document11 pages442Najam SiddiquiNo ratings yet