Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Globalization Mittal
Globalization Mittal
Uploaded by
Mahendra Kotakonda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views18 pagesThe document discusses various aspects of globalization strategies for companies. It covers 4 levels of global operations from minimal exports/imports to substantial foreign investment. Reasons for going global can be proactive like accessing new markets or reactive like responding to international competition. The 4 strategic orientations of global firms range from ethnocentric focusing on the home country to geocentric taking a global systems approach. Developing an effective global strategy requires understanding the complex global environment and whether the industry is better suited to a multidomestic or global approach. Key factors that drive truly global companies include having a global management team, strategy, operations, technology, financing and marketing.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various aspects of globalization strategies for companies. It covers 4 levels of global operations from minimal exports/imports to substantial foreign investment. Reasons for going global can be proactive like accessing new markets or reactive like responding to international competition. The 4 strategic orientations of global firms range from ethnocentric focusing on the home country to geocentric taking a global systems approach. Developing an effective global strategy requires understanding the complex global environment and whether the industry is better suited to a multidomestic or global approach. Key factors that drive truly global companies include having a global management team, strategy, operations, technology, financing and marketing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views18 pagesGlobalization Mittal
Globalization Mittal
Uploaded by
Mahendra KotakondaThe document discusses various aspects of globalization strategies for companies. It covers 4 levels of global operations from minimal exports/imports to substantial foreign investment. Reasons for going global can be proactive like accessing new markets or reactive like responding to international competition. The 4 strategic orientations of global firms range from ethnocentric focusing on the home country to geocentric taking a global systems approach. Developing an effective global strategy requires understanding the complex global environment and whether the industry is better suited to a multidomestic or global approach. Key factors that drive truly global companies include having a global management team, strategy, operations, technology, financing and marketing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
Globalization
Globalization refers to the strategy of approaching
worldwide markets with standardized products
Threats & Opp …----Managers should know
Understanding the nuances of competing in
global markets—VV IMP
Development of a Global Corporation
Four Levels
1. Export/import--Minimal effect on the existing
management orientation or on existing product lines
2. Foreign licencing & technology tranfer-Requires
little change in management or operation
3. Overseas operations--Direct investment in
manufacturing plants (requires global mgmt skill-
MNC)
4. The most involved level is characterized by a
substantial increase in foreign investment, with
foreign assets comprising a significant portion of
total assets (also global approach to sales, finance)
Reasons for Going Global
PROACTIVE REACTIVE
Additional resources Trade barriers
Lowered costs International customers
Incentives
New, expanded markets
International
competition
Exploitation of firm-specific
advantages Regulations
Taxes Chance
Economies of scale
Synergy
Power and prestige
Protect home market
4 Strategic Orientations of Global Firms
1. An ethnocentric orientation believes that the values and
priorities of the parent organization should guide the strategic
decision making of all its operations.
2. A polycentric orientation means the culture of the country in
which a strategy is to be implemented is allowed to dominate the
decision-making process.
3. A regiocentric orientation exists when the parent attempts to
blend its own predispositions with those of the region under
consideration, thereby arriving at a region-sensitive compromise.
4. A corporation with a geocentric orientation adopts a global
systems approach to strategic decision making, thereby
emphasizing global integration.
4 Strategic Orientations of Global Firms
Ethnocentric Polycentric Regiocentric Geocentric
Mission Profitability Public Both Both
acceptance
Governance Top down Bottom up Mutually Mutually
negotiated negotiated at all
between region levels of
and subsidiaries corporation
Strategy Global National Regional Integ Global
integration responsivenes & National Resp integration and
n.r.
Marketing Home country Local Regional needs Global product
needs(country)
Finance Taking back to Retention in Redist. In region Redistribute
home host country globally
Culture Home country Host country Regional Global
At the Start of Globalization
External and internal assessments are
conducted before a firm enters global
markets
External assessment involves careful
examination of critical features of the
global environment
Internal assessment involves identification
of the basic strengths of a firm’s operations
Complexity of the Global
Environment
Five factors affecting the increasing complexity of global
strategic planning: ( Coke in india)
Multiple political, economic, legal, social, and cultural
environments as well as various rates of change-
interactions are complex
Geographic separation, cultural and national differences,
and variations in business practices---(HQ vs branch)
Global face extreme competition(diff in indu strucutre)
Global trade restriction (EEC,FTA etc)
Control Problems of the Global Firm
Financial policies typically are designed to further
the goals of the parent company and pay minimal
attention to the goals of the host countries
DIFFERENT FINANCIAL ENVIRONMENTS
DIFFERENCE IN MEASUREMENT &
CONTROL
How to avoid all the above (Ans– by Strategic
Planning)
Global Strategic Planning
1ST STEP---
PLEASE SEE WHAT ENVIRONMENT WILL
YOUR FOREIGN BRANCH OPERATE IN ?
MULTIDOMESTI (insurance) OR GLOBAL(TV)
Multidomestic Industry facets
( insurance)…
The need for customized products to meet the tastes or
preferences of local customers
Fragmentation of the industry, with many competitors
in each national market
A lack of economies of scale in the functional
activities of firms in the industry
Distribution channels unique to each country
A low technological dependence of subsidiaries on
R&D provided by the global firm
GLOBAL INDUSTRY IS CREATED BY
FACTORS BELOW
Economies of scale in the functional activities of
firms in the industry
A high level of R&D expenditures on products that
require more than one market to recover
development costs
The presence in the industry of predominantly
global firms that expect consistency of products and
services across markets
The presence of homogeneous product needs across
markets,
The presence of a small group of global competitors
WHY SHOULD THE STRATEGY
BE GLOBAL FOR GLOBAL
INDUSTRY?
The increased scope of the global management task
(impossible without who does what)
The increased globalization of firms
The information explosion (formal plan is needed)
The increase in global competition
The rapid development of technology
Strategic management planning breeds managerial
confidence
Global Strategic PlanningWHAT TO
DO NOW AFTER KNOWING
For MULTIDOMESTIC INDUSTRY, make
each subsiditary autonomous, having authority
to make independent decisions in the response
to local mkt.
For GLOBAL INDUSTRY, make global
straegy ( not local)
Factors That Drive Global Companies
Global Management Team-
Global vision/cross-cultural training
Global Strategy—cross country alliances(no
home-country thing)
Global Operations and Products-Common
operating process qty and uniformity.
Product will have best cost & market
advantage.
Global Technology and R&D
Global Financing
Global Marketing
Factors That Drive Global
Companies
Global Technology and R&D
Global Financing—global financing
lowest cost, hedge, local currency, listing
Global Marketing—global brands,
GLOBAL CHALLENGE--Market
Requirements and Product Characteristics
Firms must assess two key dimensions of
customer demand:
customers’ acceptance of standardized products
The rate of product innovation desired
Products can be arrayed along a continuum from
products that are not subject to frequent product
innovations to products that are often upgraded
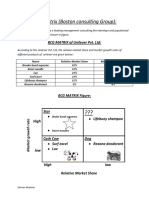
Quadrant Wise— Marketing &
Products (for globalization)
1-Computer Chips, Automotive Electronics—
MAINTAIN DIFFERENTIATION
2-Steel,Cola—MINIMIZE DELIVERY COST
3-Consumer Electronics, Toothpaste,
Shampoo—MAINTAIN EVER-
CHANGING GLOBAL WAREHOUSE
4- —PRACTICE NICHE
International Markets—Mode of Operations
You might also like
- The Art Business of Ghostwriting How To Make 10,000 Per Month Writing For Other People OnlineDocument281 pagesThe Art Business of Ghostwriting How To Make 10,000 Per Month Writing For Other People Onlinemexagi7221100% (1)
- Sustainable Growth in Global Markets: Strategic Choices and Managerial ImplicationsFrom EverandSustainable Growth in Global Markets: Strategic Choices and Managerial ImplicationsNo ratings yet
- Personal Selling PDFDocument16 pagesPersonal Selling PDFSuraj Luthra100% (3)
- Globalization - International Processing StrategyDocument23 pagesGlobalization - International Processing StrategyAnand MauryaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 International StrategiesDocument28 pagesWEEK 9 International StrategiesNella RodriguezNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Lecture 8Document40 pagesPowerPoint Lecture 8hrleenNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Lecture 8Document40 pagesPowerPoint Lecture 8hrleenNo ratings yet
- International StrategyDocument33 pagesInternational StrategyGohar SaeedNo ratings yet
- International StrategyDocument23 pagesInternational StrategyKendrew SujideNo ratings yet
- MGT4001 International Strategy For StudentsDocument26 pagesMGT4001 International Strategy For Studentss225830No ratings yet
- Strategic Management 1Document28 pagesStrategic Management 1dharmveer555No ratings yet
- Strategies For Going GlobalDocument31 pagesStrategies For Going GlobalMuskaan ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 Pcs Bm3303Document39 pagesChap 4 Pcs Bm3303Kayula Carla ShulaNo ratings yet
- MBS 3rd Semester International BusinessDocument135 pagesMBS 3rd Semester International BusinessfierceaadarshaNo ratings yet
- 4 International Strategic Management ADocument111 pages4 International Strategic Management AKiran RimalNo ratings yet
- International StrategyDocument34 pagesInternational Strategyarvindgupta_2005100% (2)
- Global Organization Design: Chapter-5Document36 pagesGlobal Organization Design: Chapter-5Gaurav jainNo ratings yet
- CH 005Document12 pagesCH 005zeyad mostafaNo ratings yet
- Intl Econ Rel - 2Document55 pagesIntl Econ Rel - 2donatello499No ratings yet
- Global - Environment Week 5Document37 pagesGlobal - Environment Week 5Melanie Cruz ConventoNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 IBM NewDocument13 pagesUNIT - 1 IBM NewAnusha kanmaniNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 IBM NewDocument13 pagesUNIT - 1 IBM NewAnusha kanmaniNo ratings yet
- SM 6 NotesDocument23 pagesSM 6 NotespradeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SumaryDocument3 pagesChapter 8 SumarydskjbfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SVDocument51 pagesChapter 6 SVMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Formulating International Business StrategyDocument29 pagesLecture 5 - Formulating International Business StrategyMeenakshi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3Document144 pagesUnit - 3Manikandan SuriyanarayananNo ratings yet
- Tema 5 International Business PDFDocument33 pagesTema 5 International Business PDFBlah BlamNo ratings yet
- Strategy in Global EnvironmentDocument15 pagesStrategy in Global EnvironmentAmit YadavNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing Chapter 1-2Document36 pagesGlobal Marketing Chapter 1-2Iyus Darmawan PYNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Theory and Cases An Integrated Approach 11th Edition Hill Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesStrategic Management Theory and Cases An Integrated Approach 11th Edition Hill Solutions Manualabnormalhumble35j4i100% (31)
- International Marketing EnvironmentDocument29 pagesInternational Marketing EnvironmentsujeetleopardNo ratings yet
- P3 Business Analysis LECTURER: Stanford Allen Class Notes 4: Richmond Academy Page 1 of 13 December 2015Document13 pagesP3 Business Analysis LECTURER: Stanford Allen Class Notes 4: Richmond Academy Page 1 of 13 December 2015S. AllenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 10 SummaryAnnabel SeahNo ratings yet
- Global MarketingDocument30 pagesGlobal Marketingchandni kundelNo ratings yet
- According To Kedia & Mukherji (1999) (Wortzel, 1991)Document21 pagesAccording To Kedia & Mukherji (1999) (Wortzel, 1991)Maliha ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- International Strategy: Lecture - SPUP - Marjorie L. BambalanDocument28 pagesInternational Strategy: Lecture - SPUP - Marjorie L. BambalanzesrtyryytshrtNo ratings yet
- UCV Session 1 Introduction IMDocument29 pagesUCV Session 1 Introduction IMLuis GarciaNo ratings yet
- Critical Discussion QuestionDocument4 pagesCritical Discussion QuestionYun LINo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument32 pagesChapter IVSudhir BogatiNo ratings yet
- 6.international StrategyDocument10 pages6.international Strategyphuongnhung122103No ratings yet
- ELEN03B Module 7.0Document14 pagesELEN03B Module 7.0Sayy CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - International Strategy: Mgnt428 Business Policy & Strategy Dr. Gar Wiggs, InstructorDocument37 pagesChapter 8 - International Strategy: Mgnt428 Business Policy & Strategy Dr. Gar Wiggs, InstructorDa-lex WattNo ratings yet
- IBM Unit III 2018 05.09.2018Document94 pagesIBM Unit III 2018 05.09.2018Arunkumar PoMNo ratings yet
- I.Strategic Planning II. Organizational Structure III. Controlling Global Marketing EffortsDocument12 pagesI.Strategic Planning II. Organizational Structure III. Controlling Global Marketing Effortssudeep_rsNo ratings yet
- 8 International+StrategyDocument28 pages8 International+StrategyRizeNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 International MarketingDocument87 pagesTopic 11 International MarketingSAKHAWAT HOSSAIN KHAN MDNo ratings yet
- International Business Managment Unit 4Document38 pagesInternational Business Managment Unit 4Praveena RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Opportunities and Outcomes of International StrategyDocument22 pagesChapter 8: Opportunities and Outcomes of International StrategyCiise Cali HaybeNo ratings yet
- Environment Perspective BusinessDocument36 pagesEnvironment Perspective BusinessPriyanka KansalNo ratings yet
- The Global Environme NT: Labrador, EloisaDocument15 pagesThe Global Environme NT: Labrador, EloisaRonaldo ConventoNo ratings yet
- After Studying Chapter 6, You Will KnowDocument32 pagesAfter Studying Chapter 6, You Will Knowahr slmNo ratings yet
- Tema 2. Multinational CorporationsDocument8 pagesTema 2. Multinational Corporationsot2023juantinNo ratings yet
- IBS Notes-2Document166 pagesIBS Notes-2Kristian ListNo ratings yet
- International Business: Opening Case: Wal-MartDocument6 pagesInternational Business: Opening Case: Wal-MartSunail HussainNo ratings yet
- SM2 PGP22-24 M2 Samar21Jul23Document75 pagesSM2 PGP22-24 M2 Samar21Jul23Himanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 80Document32 pagesChapter 80Kashif Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Global Business Management: Session - I: Dr. R K JainDocument72 pagesGlobal Business Management: Session - I: Dr. R K Jainmaheshkumar553No ratings yet
- International StrategyDocument34 pagesInternational StrategymanicatewatiaNo ratings yet
- Model Answer: E-Commerce store launch by Unilever in Sri LankaFrom EverandModel Answer: E-Commerce store launch by Unilever in Sri LankaNo ratings yet
- Trade and Competitiveness Global PracticeFrom EverandTrade and Competitiveness Global PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ABC Business Plan 2021Document7 pagesABC Business Plan 2021akdmech9621No ratings yet
- Franchise Dossier enDocument58 pagesFranchise Dossier enKIRE CENTERNo ratings yet
- Case of AppleDocument49 pagesCase of AppleNidhi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Customer ServiceDocument2 pagesCustomer ServiceJuninho OrtizNo ratings yet
- Volkswagen Master ThesisDocument5 pagesVolkswagen Master Thesisstaceycruzwashington100% (2)
- E-Business In: OrganizationDocument23 pagesE-Business In: OrganizationRomi SikderNo ratings yet
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning of Asian PaintsDocument5 pagesSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning of Asian PaintsAbhijeet kohatNo ratings yet
- The Early Stage Opportunity in IndiaDocument29 pagesThe Early Stage Opportunity in IndiaAbhishek BaliNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Last Year Paper PDF by Aashish AroraDocument51 pagesSBI Clerk Last Year Paper PDF by Aashish Arorarajnish sharmaNo ratings yet
- Entrep Q2 Module 3 9Document67 pagesEntrep Q2 Module 3 9Eunice TellesNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group)Document2 pagesBCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group)Mohammed SahalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Seminar (FINAL)Document25 pagesConsumer Behaviour Seminar (FINAL)Vaibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Continental AirlinesDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Continental Airlinesafedsdlmz100% (1)
- Walmart SWOT Analysis & Recommendations: Walmart's Strengths (Internal Forces)Document3 pagesWalmart SWOT Analysis & Recommendations: Walmart's Strengths (Internal Forces)Ayesha SohailNo ratings yet
- Murali Krishna - Brand ManagerDocument2 pagesMurali Krishna - Brand Managermurali krishnaNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Content Inc Second Edition Start A Content First Business Build A Massive Audience and Become Radically Successful With Little To No Money Joe Pulizzi All Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesTextbook Ebook Content Inc Second Edition Start A Content First Business Build A Massive Audience and Become Radically Successful With Little To No Money Joe Pulizzi All Chapter PDFmarie.baez134100% (8)
- Financial Statement of Merchandising BusinessDocument3 pagesFinancial Statement of Merchandising BusinessDina Rose SardumaNo ratings yet
- Automotive Supply Chain Management in India: Kpis, Current & Future Challenges, Risks, and SolutionsDocument18 pagesAutomotive Supply Chain Management in India: Kpis, Current & Future Challenges, Risks, and Solutionspradnya_nagotkarNo ratings yet
- Cross-Cultural Variations IN Consumer BehaviorDocument28 pagesCross-Cultural Variations IN Consumer BehaviorĐặng Văn ThoạiNo ratings yet
- E-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessDocument45 pagesE-Business: Oxford University Press 2012. All Rights Reserved. E-BusinessShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument40 pagesProject ReportPragyaNo ratings yet
- Fernández Sergio ConditionalsDocument4 pagesFernández Sergio ConditionalsSergio LunaNo ratings yet
- Course-Structure-Syllabi-BCom 1-51-75Document25 pagesCourse-Structure-Syllabi-BCom 1-51-75Ram YadavNo ratings yet
- Tertiary ActivitiesDocument5 pagesTertiary Activitieshimanshu singhNo ratings yet
- MBA-513-Educational ToyDocument18 pagesMBA-513-Educational ToyRajuNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Executive September 2022Document44 pagesPharmaceutical Executive September 2022Papei GumihoNo ratings yet
- CRM Strategy of PantaloonsDocument5 pagesCRM Strategy of PantaloonsSrimon10No ratings yet
- Market Opportunities and Challenges: A Case Study of TescoDocument10 pagesMarket Opportunities and Challenges: A Case Study of TescoGohan SayanNo ratings yet