Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIL L1 Presentation
MIL L1 Presentation
Uploaded by
malifi ciado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views63 pagesThe document defines key terms related to media, information, literacy, and communication. It discusses different types of communication including interpersonal, mediated interpersonal, organizational, and public communication. It also outlines the eight elements that constitute the creation of a message: the source, encoding, transmitting, channels, decoding, receiver, feedback, and noise/interference. Finally, it describes the evolution of media from the prehistoric age to the current digital age.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to media, information, literacy, and communication. It discusses different types of communication including interpersonal, mediated interpersonal, organizational, and public communication. It also outlines the eight elements that constitute the creation of a message: the source, encoding, transmitting, channels, decoding, receiver, feedback, and noise/interference. Finally, it describes the evolution of media from the prehistoric age to the current digital age.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views63 pagesMIL L1 Presentation
MIL L1 Presentation
Uploaded by
malifi ciadoThe document defines key terms related to media, information, literacy, and communication. It discusses different types of communication including interpersonal, mediated interpersonal, organizational, and public communication. It also outlines the eight elements that constitute the creation of a message: the source, encoding, transmitting, channels, decoding, receiver, feedback, and noise/interference. Finally, it describes the evolution of media from the prehistoric age to the current digital age.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 63
Media refers to all electronic or
digital means and print or artistic
visuals used to transmit
messages, a means of
communication.
Information is an abstract
concept that refers to
that which has the power
to inform.
Literacy
- is the ability to encode and
decode symbols and to
synthesize and analyze
messages.
- ability to read and write.
Media literacy is the ability to
access, analyze, evaluate, and
create media.
Information literacy is the
ability to find, evaluate,
organize, use, and communicate
information in all its various
formats
Technology literacy is a term
used to describe an individual’s
ability to assess, acquire and
communicate information in a
fully digital environment.
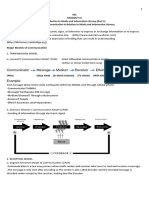
Communication
- people or group of people
imparting or exchanging messages
through speaking, writing, gesture,
or even using other symbolic forms
by utilizing variety of channels for
sending and receiving.
Message
– collection of symbols that
appear purposefully organized
(meaningful) to those sending
or receiving them.
Turow(2009,7)
INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION
- the process by which people exchange
information, feelings, and meaning
through verbal and non-verbal messages:
it is face-to-face communication.
MEDIATED INTERPERSONAL COMMUNIATION
- refers to communication carried out by
the use of information communication
technology, and can be contrasted to
face-to-face communication.
ORGANIZATIONAL COMMUNICATION
- The process by which activities of a society are
collected and coordinated to reach the goals of
both individuals and the collective group. It is a
subfield of general communications studies and
is often a component to effective management
in a workplace environment.
PUBLIC COMMUNICATION
- Involves one person
communicating to a
large number of people.
Turow (2009, 9-11) outline eight elements that constitute the creation of a
message
1. Source: The source is
where the message came
from. It can be a person or
an organization.
2. Encoding – the process by
which a message is translated so
it can be transmitted and
communicated to another party.
3. Transmitting- the actual act of
sending the message. It can either
be through the person’s vocal
cords and facial muscles
complemented with hand gesture,
if we mean the act of speaking.
4. Channels- technologies
are the lines that enable
the act of sending or
transmitting.
5. Decoding – the transmitted
impulses are converted to signs as
the brain perceives and processes it.
The reverse of encoding, decoding is
the process by which the receiver
translates the source’s thoughts and
ideas so they can have meaning.
6. Receiver- receiver is the one who
gets the message that was transmitted
through the channels. Like the source
or sender, the receiver can be an
individual or an organization.
However, it is possible that the
intended receiver may not receive
7. Feedback- is the
response generated by the
message that was sent to
the receiver. It can either
be immediate or delayed.
8. Noise Interference – “interference”
is known as noise. Oise may be treated
both literally and figuratively. Literally, it
is mechanical sound that is perhaps
more resonant than the message
drowning it. It can also mean other
message with conflicting tones
drowning the original message .
The Evolution of Traditional to New Media
PREHISTORIC AGE (before 1700s)
People discovered fire, developed paper
from plants and forged equipment or
weapon through stone, bronze, copper
and iron.
INDUSTRIAL AGE (1700s -1930s)
People used the power of steam,
developed machine tools, established iron
production and manufacturing of various
products (including books through the
printing press).
ELECTRONIC AGE (1930s – 1980s)
People harnessed the power of electricity
that led to electrical telegraphy, electrical
circuits and the early large scale computers
(through vacuum tubes, transistors and
integrated circuits). In this age, long distance
communication became possible.
NEW (DIGITAL) AGE (mid 1900s – 2000s)
INFORMATION AGE
People advanced the use of microelectronics in the
invention of personal
computers, mobile devices and wearable technology.
In this age, the Internet paved the way for faster
communication and the creation of the social
network. Moreover, voice, image, sound and data are
digitalized.
WEB BROWSER
SEARCH ENGINE
BLOGGING SITES
SOCIAL NETWORKS
MICROBLOGGING
PHOTO AND VIDEO SHARING
WEBSITE
INSTANT MESSAGING & VIDEO CONFERENCING
PORTABLE COMPUTERS
MOBILE PHONES
WEARABLE TECHNOLOGY
CLOUD AND BIG DATA
You might also like
- Introduction To ComputingDocument10 pagesIntroduction To ComputingRashid Mumtaz67% (3)
- Technology For Teaching and Learning Part 3Document6 pagesTechnology For Teaching and Learning Part 3japhethNo ratings yet
- Calculating Mortar DataDocument259 pagesCalculating Mortar DataGasMaskBob100% (3)
- Digital Devices Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDigital Devices Lesson Planandrdav100% (1)
- Review Summary Chapter 5: It Infrastructure and Emerging TechnologiesDocument1 pageReview Summary Chapter 5: It Infrastructure and Emerging Technologiesghina adhha hauraNo ratings yet
- Module Media and Information LiteracyDocument70 pagesModule Media and Information LiteracyRianne Mhay Balbuena100% (1)
- Lesson1 MediaDocument7 pagesLesson1 MediaMs. Aira YanesNo ratings yet
- The World of Media and Information LITERACYDocument6 pagesThe World of Media and Information LITERACYCorazon ReymarNo ratings yet
- Study Guide in MilDocument3 pagesStudy Guide in MilCj RomoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - MilDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - MilBARNUEVO HONEY MARIENo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document7 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1Arjay Cloud de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Intrapersonal Communication: TH STDocument2 pagesIntrapersonal Communication: TH STFrancis100% (1)
- MIl ReviewerDocument4 pagesMIl Reviewerallen alabaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: From Interpersonal To Mass CommunicationDocument8 pagesLesson 1: From Interpersonal To Mass CommunicationjannyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson 1Document25 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson 1AnalouNo ratings yet
- MIL 1st Quarter Lesson SummaryDocument5 pagesMIL 1st Quarter Lesson SummaryRalph Francis GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information Literacykyleandreaison12.schoolNo ratings yet
- Media Information and LiteracyDocument16 pagesMedia Information and LiteracyMary Grace T. BitasNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument5 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerSamantha Nicole GibaNo ratings yet
- Q1 SummaryDocument9 pagesQ1 Summaryjedidiahkian77No ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer 3Document13 pagesMIL Reviewer 3Jewel Anne A. DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information LiteracyBhea D. CruzNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument11 pagesMedia and Information Literacydarkmontero8285No ratings yet
- ENTREPQ1M1Document36 pagesENTREPQ1M1Syvelle DayonotNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Media and Information LiteracyRuby CanjaNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument3 pagesMIL Reviewerkkaoritabataa16No ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument5 pagesMIL ReviewerLaurence Andrew B. LugtuNo ratings yet
- Mil Handout 1Document10 pagesMil Handout 1cklc5650No ratings yet
- 2019 2020.qa Lecture Reviewer - Media and Information LiteracyDocument8 pages2019 2020.qa Lecture Reviewer - Media and Information LiteracyJesusaNo ratings yet
- Mil!!!!Document8 pagesMil!!!!Bea Loreen CordovaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument50 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyDianne PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Mil - Reviewer - Week 1 8 1Document8 pagesMil - Reviewer - Week 1 8 1ZannieNo ratings yet
- MIL Lesson 1Document24 pagesMIL Lesson 125princeperezNo ratings yet
- Communicator Message Medium Receiver EffectDocument3 pagesCommunicator Message Medium Receiver EffectJohn Aaron OlarteNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentnashvilleNo ratings yet
- Project On ICTDocument59 pagesProject On ICTVinayPawarNo ratings yet
- Year 8. Week 4. Data & InformationDocument2 pagesYear 8. Week 4. Data & InformationvioletamachreeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document5 pagesLecture 1mohamedabdesselembecharef879No ratings yet
- World of MIL-EDITEDDocument39 pagesWorld of MIL-EDITEDJulius King A. QuezonNo ratings yet
- HandoutDocument2 pagesHandoutHange SanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-MilDocument31 pagesLesson 1-MilCgc Juliet NicolNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy NotesDocument26 pagesMedia and Information Literacy NotesKesha Adelyn Gawidan100% (1)
- MIL ReviewerDocument6 pagesMIL Reviewersaimond linNo ratings yet
- Module No 1 What-Is-MediaDocument37 pagesModule No 1 What-Is-MediaAllanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CommunicationDocument3 pagesLesson 1 CommunicationAngel MaguinsawanNo ratings yet
- Mil Lesson 1Document11 pagesMil Lesson 1Ivan TanNo ratings yet
- Communication PracticesDocument8 pagesCommunication Practicesimene IBNo ratings yet
- Mil MidtrmsDocument9 pagesMil Midtrmsronanmorales93No ratings yet
- Mil Week1 3Document10 pagesMil Week1 3Alexandra MariNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument6 pagesMil ReviewerKristine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument15 pagesMedia and Information Literacyنجشو گحوشNo ratings yet
- Inbound 2426763356328743931Document2 pagesInbound 2426763356328743931Harry Serrano AlvaeraNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument10 pagesMil ReviewerjohnlloydrocasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Communication: From Interpersonal To Mass CommunicationDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Communication: From Interpersonal To Mass CommunicationReigna GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Media PowerpointDocument21 pagesMedia PowerpointBRYAN MILANONo ratings yet
- 1 - The - World - of Media - and - Information - LiteracyDocument65 pages1 - The - World - of Media - and - Information - LiteracyEdward AlmazanNo ratings yet
- IX-Final Resource BookDocument24 pagesIX-Final Resource BookShalu AgarwalNo ratings yet
- MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY ReviewerDocument4 pagesMEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY ReviewerConie Teña Macaraig AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer, MILDocument5 pagesReviewer, MILIsla Rae RanaraNo ratings yet
- Mil Prelim ReviewerDocument3 pagesMil Prelim Reviewerdesteen klaire montefalcoNo ratings yet
- Mid ReviewerDocument4 pagesMid ReviewerGerard Manimtim gerardmanimtimNo ratings yet
- Summary For ComDocument96 pagesSummary For ComEnock MaunyaNo ratings yet
- Communication: Bsba FM 1-1Document11 pagesCommunication: Bsba FM 1-1Ivory Mae Montecillo100% (1)
- Cor 016Document7 pagesCor 016Rhea Ann Ramirez VenturaNo ratings yet
- Innovations in RoboticsDocument2 pagesInnovations in Roboticsmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9-Charity ApDocument45 pagesGrade 9-Charity Apmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Activity Sheet - Polynomial FunctionDocument2 pagesMath 10 Activity Sheet - Polynomial Functionmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- q2 Scince 7 Parallel TestDocument2 pagesq2 Scince 7 Parallel Testmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Parallel Test 2021-2022Document6 pagesScience 7 Parallel Test 2021-2022malifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- 21st CenturyDocument10 pages21st Centurymalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument26 pagesPresentationmalifi ciadoNo ratings yet
- Acc 118 Week 5 ModuleDocument7 pagesAcc 118 Week 5 ModuleChristine Joy SonioNo ratings yet
- Tvl-Ict-Css: Quarter 3 - Module 7-8: Installing and Configuring Computer System (Iccs)Document26 pagesTvl-Ict-Css: Quarter 3 - Module 7-8: Installing and Configuring Computer System (Iccs)juanito zamora100% (3)
- Computer Science #3Document356 pagesComputer Science #3Sean s Chipanga100% (1)
- L6M7 Test 2Document18 pagesL6M7 Test 2Tlotlo RamotlhabiNo ratings yet
- IX Guess 2011Document5 pagesIX Guess 2011SunnycandoeverythingNo ratings yet
- Technical Support What Are The Main Responsibilities?Document6 pagesTechnical Support What Are The Main Responsibilities?Orlando NajeraNo ratings yet
- CVDocument36 pagesCVTalha AsadNo ratings yet
- OS Questions and AnswerDocument185 pagesOS Questions and AnswerG/herNo ratings yet
- Fts 2007Document7 pagesFts 2007andhracollegesNo ratings yet
- ECDL Module 1 Basic Concepts of IT Training Manual: C C T G L O B A L - C O MDocument42 pagesECDL Module 1 Basic Concepts of IT Training Manual: C C T G L O B A L - C O MJusri JuseNo ratings yet
- BSIT New 2019 PDFDocument92 pagesBSIT New 2019 PDFFaisal ShahNo ratings yet
- Revised Local Water District Manual MaCRODocument68 pagesRevised Local Water District Manual MaCROSheila Ricafrente- Milante67% (3)
- Basic Python NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Python NotesVamsi Krishna KazaNo ratings yet
- Content Weightage - Public Sector Organization PDFDocument4 pagesContent Weightage - Public Sector Organization PDFJunaid HassanNo ratings yet
- Types of IcDocument2 pagesTypes of IcEdbert CatapangNo ratings yet
- 5403-1 ADocument22 pages5403-1 Aadnan.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Re-Test Compter SC Xi-ADocument2 pagesRe-Test Compter SC Xi-AANIKET ROYNo ratings yet
- Back To School Sales Tax Holiday 2022Document7 pagesBack To School Sales Tax Holiday 2022ABC Action NewsNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in ICT 9Document10 pagesSummative Test in ICT 9kristineNo ratings yet
- Mad Project ReportDocument16 pagesMad Project ReportNaik SamNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Duration: 50 Min.: School: LYBIBOJ Academic Year: 2020-2021 Test: No. 5 Subject: Class: F2 20Document2 pagesComputer Science Duration: 50 Min.: School: LYBIBOJ Academic Year: 2020-2021 Test: No. 5 Subject: Class: F2 20NKETCHOGUE MPATCHIE HENSCHELNo ratings yet
- Cengage Learning Stock Report 28th October 2014Document48 pagesCengage Learning Stock Report 28th October 2014kkp0650No ratings yet
- OS ModuleDocument163 pagesOS ModuleHabtie TesfahunNo ratings yet
- IT Tools and Business System Book NIELIT DOEACCDocument525 pagesIT Tools and Business System Book NIELIT DOEACCJayadrata Middey50% (2)