Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Narrative
The Narrative
Uploaded by
IndiraFthiaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Learning About Language Assessment - Dilemmas, Decisions, and Directions, Second Edition PDFDocument388 pagesLearning About Language Assessment - Dilemmas, Decisions, and Directions, Second Edition PDFSoklin Thy100% (4)
- Danois - GrammaireDocument47 pagesDanois - GrammaireAnonymous 6N5Ew3100% (1)
- Approaches To Arabic Dialects - VersteeghDocument417 pagesApproaches To Arabic Dialects - VersteeghTaromad100% (2)
- Types of Spoken Language L&SDocument13 pagesTypes of Spoken Language L&SAdrian Edry75% (4)
- Bahan Ajar Narrative Legenda Lilis SuryaniDocument3 pagesBahan Ajar Narrative Legenda Lilis Suryaniaida dan sakilaNo ratings yet
- LK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 3Document5 pagesLK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 3adiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1. 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul Profesional 3 - BahasaInggris - Novi AnggrainiDocument5 pagesLK 0.1. 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul Profesional 3 - BahasaInggris - Novi AnggrainiAan SumbersukoNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Profesional Bahasa Inggris Modul 3Document4 pagesLK 1 Profesional Bahasa Inggris Modul 3Farra PramitaNo ratings yet
- Story Board ICTDocument6 pagesStory Board ICTErna YulianiNo ratings yet
- Peta Konsep Kelas Vii Semester Ii Tahun Pelajaran 2020Document2 pagesPeta Konsep Kelas Vii Semester Ii Tahun Pelajaran 2020Chalwa AnjumitaNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 - Wa Ode Dinda Ayu P. UtamiDocument9 pagesLK Modul 3 - Wa Ode Dinda Ayu P. Utamiayu dindaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Narrative TextDocument2 pagesBahan Ajar Narrative Textria ristiNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 3Document5 pagesLK 1 Modul 3DindaCahyaKurniaPutriNo ratings yet
- Monolog TextDocument17 pagesMonolog TextDwi RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text - HermawanDocument13 pagesNarrative Text - HermawanonebusidahNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Module 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument3 pagesLK 0.1 Module 3 English For Social CommunicationarieNo ratings yet
- Nur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 3 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesNur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 3 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisNur Annisa Mei RizkiNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument6 pagesLK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationSari FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Isfa LiteraturaDocument6 pagesIsfa LiteraturaRomina Mart100% (1)
- Narrative Text HermawanDocument12 pagesNarrative Text HermawanJalaluddin Al Firdaus,s.pdNo ratings yet
- LK 01 Modul 03Document4 pagesLK 01 Modul 03reginaNo ratings yet
- Utin Nur'aini - LK 1.1 - Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument3 pagesUtin Nur'aini - LK 1.1 - Modul 3 English For Social Communicationutin nuraini100% (1)
- Narrative Text - XII AKL 2Document12 pagesNarrative Text - XII AKL 2Dwi JuliantiningsihNo ratings yet
- Descriptive TextDocument13 pagesDescriptive TextknajmahafNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 English For Sosial CommunicationsDocument5 pagesModul 3 English For Sosial CommunicationsNopita SariNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 3 BingDocument4 pagesLK 1 - Modul 3 BingCindra PdanNo ratings yet
- GenreDocument18 pagesGenresholahuddin aeNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1 - Modul 3 ProfesionalTaufik Ansyari100% (2)
- Narrative TextDocument10 pagesNarrative TextAlfi NNo ratings yet
- Announcement Text A. MeaningDocument5 pagesAnnouncement Text A. MeaningNofa AndrianaNo ratings yet
- AmrayfanDocument2 pagesAmrayfanErfira ShintaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9Document11 pagesTopic 9jeonnjjk44No ratings yet
- Description (Description)Document10 pagesDescription (Description)Apri AlskNo ratings yet
- Material About Recount Text, Narrative Text Dan Present TenseDocument7 pagesMaterial About Recount Text, Narrative Text Dan Present TenseRfkyyalfrziNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text - 1Document11 pagesDescriptive Text - 1surya dharmaNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument6 pagesLK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationtyaoktrianiNo ratings yet
- Descriptive TextDocument7 pagesDescriptive TextDewi Okta lisintiaNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument4 pagesLK 1.1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDwi WahyuniNo ratings yet
- N U Type Text Social Function Generic Structure Language FeaturesDocument4 pagesN U Type Text Social Function Generic Structure Language Featuresrusyda khoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- LK. 0.1 Modul 3Document4 pagesLK. 0.1 Modul 3Ana AthiyahNo ratings yet
- Sma Trensains X-Science 1: Understanding Descriptive TextDocument8 pagesSma Trensains X-Science 1: Understanding Descriptive Textriski satyaNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Example Descriptive Text. Descriptive Text Is ADocument1 pagePurpose and Example Descriptive Text. Descriptive Text Is AFajar AmiandaruNo ratings yet
- Coklat Krem Vintage Estetik Tugas Kelompok Presentasi - 20240211 - 211051 - 0000Document9 pagesCoklat Krem Vintage Estetik Tugas Kelompok Presentasi - 20240211 - 211051 - 0000iaditya99No ratings yet
- Narrative Text NewDocument8 pagesNarrative Text NewRatih HaryadiNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 9 English FAL Winter School Support MaterialDocument34 pagesGrade 8 9 English FAL Winter School Support MaterialYOLANDI BESTER100% (1)
- Narrative Text Kelompok8Document8 pagesNarrative Text Kelompok8Ayatullah NurjatiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2Document4 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2sanniahmadNo ratings yet
- Recount TextDocument15 pagesRecount Textagustinanesa98No ratings yet
- Descriptive Text - FASE EDocument12 pagesDescriptive Text - FASE E7777220012No ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: English For EntertainmentDocument3 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: English For EntertainmentDienha HabibieNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Modul 3Document3 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Modul 3Yundi NenohaiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document2 pagesModule 1tambusashleighmaureenNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - Kls 10 Narrative TextDocument13 pagesDocuments - Pub - Kls 10 Narrative Textroni wiliyanaNo ratings yet
- LK 1 PROFESIONAL MODUL 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument2 pagesLK 1 PROFESIONAL MODUL 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriMohammad Daifi Ibrahim100% (2)
- Different Types of StructuresDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of StructuresAleida JiménezNo ratings yet
- Narrative and Recount TextDocument18 pagesNarrative and Recount Textrahayu ramadaniNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesTable of ContentsYulyy FaziiraaNo ratings yet
- Learning NotesDocument6 pagesLearning NotesRatih RinandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Compare and ContrastDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Compare and Contrastapi-643975527No ratings yet
- Universidade Rovuma Extensão Do Niassa Curso de Licenciatura em Ensino de Biologia Plano Analítico Da Língua Inglesa IiDocument6 pagesUniversidade Rovuma Extensão Do Niassa Curso de Licenciatura em Ensino de Biologia Plano Analítico Da Língua Inglesa IiAgeu Lutero JaimeNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1 Modul 3 ProfesionalKaryantoNo ratings yet
- Happy Thanksgiving Infographics by SlidesgoDocument10 pagesHappy Thanksgiving Infographics by SlidesgoNguyễn Hà MyNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesLK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisAnnah SwanNo ratings yet
- Erzähltextanalyse [German-language Edition]: Modelle, Kategorien, ParameterFrom EverandErzähltextanalyse [German-language Edition]: Modelle, Kategorien, ParameterNo ratings yet
- NWABSD Lesson PlansDocument5 pagesNWABSD Lesson Plansapi-379699844No ratings yet
- A. Introduction: P R A G M A T I C SDocument6 pagesA. Introduction: P R A G M A T I C SQomaRiyahNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - EL 209Document27 pagesGroup 1 - EL 209araaachnidNo ratings yet
- Read The Questions 1-6. Then Match Them To The Correct Answers A-F. Circle The Correct Word in Each AnswerDocument1 pageRead The Questions 1-6. Then Match Them To The Correct Answers A-F. Circle The Correct Word in Each AnswerVasile ElenaNo ratings yet
- Text To Pakistan Sign Language For Urdu: Department of Computer ScienceDocument24 pagesText To Pakistan Sign Language For Urdu: Department of Computer ScienceLaiba SabirNo ratings yet
- Textbook The Phonetics and Phonology of Geminate Consonants First Edition Kubozono Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook The Phonetics and Phonology of Geminate Consonants First Edition Kubozono Ebook All Chapter PDFalma.brown118100% (3)
- Simple-Present-Final English WorkshopDocument5 pagesSimple-Present-Final English WorkshopSergio RoaNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocument22 pagesDirect Indirect SpeechLolita Setyaningrum91% (46)
- How To Speak Fluent English in 2023 - Speak EngliDocument6 pagesHow To Speak Fluent English in 2023 - Speak EngliPolina MininaNo ratings yet
- Conf. Univ. Dr. Luminiţa-Elena TURCUDocument1 pageConf. Univ. Dr. Luminiţa-Elena TURCUCatalin CiubotariuNo ratings yet
- Why Our Kids Cant ReadDocument10 pagesWhy Our Kids Cant Readapi-559290813No ratings yet
- Harold Conklin 1986 - Hanunoo Color CategoriesDocument7 pagesHarold Conklin 1986 - Hanunoo Color CategoriesJona Mae VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Romiette and Julio Final AssignmentDocument3 pagesRomiette and Julio Final Assignmentapi-260797837No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS Reading Test 149Document10 pagesAcademic IELTS Reading Test 149Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Year 9 English Unit PlanDocument5 pagesYear 9 English Unit Planapi-618196299No ratings yet
- Techniques-Ant and The DoveDocument6 pagesTechniques-Ant and The DoveazimahsallehNo ratings yet
- Ell DebateDocument4 pagesEll Debateapi-525214557No ratings yet
- Form (Structure) Meaning & Use Pronunciation: The Simple Past TenseDocument18 pagesForm (Structure) Meaning & Use Pronunciation: The Simple Past TenseArisma Handayani100% (1)
- B - A-I (English) Gen - Hons - Additional, Functional (80+20)Document18 pagesB - A-I (English) Gen - Hons - Additional, Functional (80+20)RadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hale Kissock Introduction EditedDocument190 pagesHale Kissock Introduction Editedmedjinejoachim.wbNo ratings yet
- Europass CV Mirko LaurilaDocument4 pagesEuropass CV Mirko LaurilaMikke90No ratings yet
- Module 9 (Human Factors) Sub Module 9.7 (Communication) - RevDocument13 pagesModule 9 (Human Factors) Sub Module 9.7 (Communication) - RevInterogator5No ratings yet
- Japanese: SyllabusDocument28 pagesJapanese: SyllabusW GangenathNo ratings yet
- PragmaticsDocument50 pagesPragmaticsMarianne ChristieNo ratings yet
- Concept of Information - Rafael CapurroDocument17 pagesConcept of Information - Rafael CapurroFau NesNo ratings yet
- Grammar Focus - Present Perfect and Past SimpleDocument1 pageGrammar Focus - Present Perfect and Past SimpleAjla IbrahimpasicNo ratings yet
The Narrative
The Narrative
Uploaded by
IndiraFthiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Narrative
The Narrative
Uploaded by
IndiraFthiaCopyright:
Available Formats
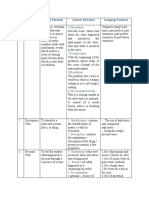
Significant
Social Function Generic
Lexicogrammatical
Genres (Tujuan / Structure
Features (Ciri – ciri
Fungsi Sosial) (Struktur)
yang menonjol)
a. Orientation:
Sets the scene
and introduces
the participants. a. Focus on specific
(Memperkenalkan usually
tokoh dan individualized
setting).b. participants. (Fokus
Complication : A pada tokoh – tokoh
crisis arises tertentu secara
(Munculnya individu).b. The use
masalah).c. of Simple Past
To amuse,
Resolution : the (Penggunaan
entertain, and to
crisis is resolved Tenses Masa
deal with actual
(Terselesainya Lampau)c. The use
or vicarious
masalah).e. of temporal
experiences in
Narrative Evaluation : A conjunction
different ways.
stepping back to (Penggunaan kata
(Untuk
evaluate the penghubung yang
menghibur
plight. menunjukkan waktu
pembaca
(Melangkah ke ex : After, before,
melalui cerita).
belakang untuk when dll).d. The use
memikirkan nilai / of noun phrases
makna sebuah (Penggunaan frasa
peristiwa, bisa kata benda yang
ada dan tidak)d. kaya dengan
Reorientation : adjective misalnya :
Optional (Bisa long black hair, two
ada / atau tidak red apples.
ada fungsinya
menyimpulkan isi
cerita )
a. Identification : a. The Use of
Identifies Simple Present
To describe a
phenomenon ( Tense (Penggunaan
particular
Mengidentifikasi / Simple Present
person, place or
pengenalan Tense).
thing (Untuk
fenomena / hal b. Focus on Specific
Descriptive menggambarkan
yang Participant (Fokus
orang, benda,
dideskripsikan). kepada Hal / orang /
atau tempat
b. Description : tempat secara
tertentu secara
Menggambarkan khusus)
khusus)
bagian, kualitas,
maupun ciri – ciri)
THE LANGUAGE
Language is a system of arbitary vocal system by which
human communicates
LANGUAGE AS A SYSTEM MEANING,
LANGUAGE CONSIST OF MANY SYSTEMS,
SYSTEM OF FORM, GRAMMAR, MEANING,
VOCABULARY, AND CULTURE.
And English is part of language
GRAMMAR
The rules that show how words are
combined, arranged, or changed to
show certain kinds of meaning
Michael Swan 2008
THE SENTENCE
We express our thoughts or ideas by
using words. We generally use those
words in group called sentences.
A sentence is a group of words which
makes complete sense/ meaning/ idea.
THE SENTENCE
Every sentence that we speak or write consists of two
parts.
1. We must talk about something if we talk at all.
2. We must say something about that thing.
Example :
Little boy John sat in the corner.
we must have a subject to
talk that is Little boy John
we must say or predicates
something about that
subject that is sat in the
corner.
THE SIMPLE PRESENT
We often use the simple present to
talk about permanent situation or
about things that happen regularly,
repeteadly or all the time
EXAMPLE
It always rains in december.
What do frogs eat? (not what are frogs eating? )
I play tennis every Wednesday.
Alice works for an insurance company.
Water boils at 100 degree celcius.
He has a sharp nose and black curly hair.
THE SIMPLE PAST
We use the simple past for many kinds
of past events: short, quickly finished
action and happenings, longer
situation, and repetead events.
EXAMPLE
Peter broke a window last night.
I spent all my childhood in Garut.
The simple past is common in stories and descriptions of past
events.
One day the princess decided that she didn’t like staying at home
all day, soshe told her father that she wanted to get a job.....
The simple past is often used with words refering to finished time.
I saw John yesterday morning. He told me..............
But in general, the simple past tense is the normal one for talking
about the past, we use itif we do not have a special reason for
using one of the other tenses.
You might also like
- Learning About Language Assessment - Dilemmas, Decisions, and Directions, Second Edition PDFDocument388 pagesLearning About Language Assessment - Dilemmas, Decisions, and Directions, Second Edition PDFSoklin Thy100% (4)
- Danois - GrammaireDocument47 pagesDanois - GrammaireAnonymous 6N5Ew3100% (1)
- Approaches To Arabic Dialects - VersteeghDocument417 pagesApproaches To Arabic Dialects - VersteeghTaromad100% (2)
- Types of Spoken Language L&SDocument13 pagesTypes of Spoken Language L&SAdrian Edry75% (4)
- Bahan Ajar Narrative Legenda Lilis SuryaniDocument3 pagesBahan Ajar Narrative Legenda Lilis Suryaniaida dan sakilaNo ratings yet
- LK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 3Document5 pagesLK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 3adiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1. 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul Profesional 3 - BahasaInggris - Novi AnggrainiDocument5 pagesLK 0.1. 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul Profesional 3 - BahasaInggris - Novi AnggrainiAan SumbersukoNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Profesional Bahasa Inggris Modul 3Document4 pagesLK 1 Profesional Bahasa Inggris Modul 3Farra PramitaNo ratings yet
- Story Board ICTDocument6 pagesStory Board ICTErna YulianiNo ratings yet
- Peta Konsep Kelas Vii Semester Ii Tahun Pelajaran 2020Document2 pagesPeta Konsep Kelas Vii Semester Ii Tahun Pelajaran 2020Chalwa AnjumitaNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 - Wa Ode Dinda Ayu P. UtamiDocument9 pagesLK Modul 3 - Wa Ode Dinda Ayu P. Utamiayu dindaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Narrative TextDocument2 pagesBahan Ajar Narrative Textria ristiNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 3Document5 pagesLK 1 Modul 3DindaCahyaKurniaPutriNo ratings yet
- Monolog TextDocument17 pagesMonolog TextDwi RahmadhaniNo ratings yet
- Narrative Text - HermawanDocument13 pagesNarrative Text - HermawanonebusidahNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Module 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument3 pagesLK 0.1 Module 3 English For Social CommunicationarieNo ratings yet
- Nur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 3 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesNur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 3 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisNur Annisa Mei RizkiNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument6 pagesLK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationSari FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Isfa LiteraturaDocument6 pagesIsfa LiteraturaRomina Mart100% (1)
- Narrative Text HermawanDocument12 pagesNarrative Text HermawanJalaluddin Al Firdaus,s.pdNo ratings yet
- LK 01 Modul 03Document4 pagesLK 01 Modul 03reginaNo ratings yet
- Utin Nur'aini - LK 1.1 - Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument3 pagesUtin Nur'aini - LK 1.1 - Modul 3 English For Social Communicationutin nuraini100% (1)
- Narrative Text - XII AKL 2Document12 pagesNarrative Text - XII AKL 2Dwi JuliantiningsihNo ratings yet
- Descriptive TextDocument13 pagesDescriptive TextknajmahafNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 English For Sosial CommunicationsDocument5 pagesModul 3 English For Sosial CommunicationsNopita SariNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 3 BingDocument4 pagesLK 1 - Modul 3 BingCindra PdanNo ratings yet
- GenreDocument18 pagesGenresholahuddin aeNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1 - Modul 3 ProfesionalTaufik Ansyari100% (2)
- Narrative TextDocument10 pagesNarrative TextAlfi NNo ratings yet
- Announcement Text A. MeaningDocument5 pagesAnnouncement Text A. MeaningNofa AndrianaNo ratings yet
- AmrayfanDocument2 pagesAmrayfanErfira ShintaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9Document11 pagesTopic 9jeonnjjk44No ratings yet
- Description (Description)Document10 pagesDescription (Description)Apri AlskNo ratings yet
- Material About Recount Text, Narrative Text Dan Present TenseDocument7 pagesMaterial About Recount Text, Narrative Text Dan Present TenseRfkyyalfrziNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text - 1Document11 pagesDescriptive Text - 1surya dharmaNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationDocument6 pagesLK Modul 3 English For Social CommunicationtyaoktrianiNo ratings yet
- Descriptive TextDocument7 pagesDescriptive TextDewi Okta lisintiaNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument4 pagesLK 1.1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDwi WahyuniNo ratings yet
- N U Type Text Social Function Generic Structure Language FeaturesDocument4 pagesN U Type Text Social Function Generic Structure Language Featuresrusyda khoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- LK. 0.1 Modul 3Document4 pagesLK. 0.1 Modul 3Ana AthiyahNo ratings yet
- Sma Trensains X-Science 1: Understanding Descriptive TextDocument8 pagesSma Trensains X-Science 1: Understanding Descriptive Textriski satyaNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Example Descriptive Text. Descriptive Text Is ADocument1 pagePurpose and Example Descriptive Text. Descriptive Text Is AFajar AmiandaruNo ratings yet
- Coklat Krem Vintage Estetik Tugas Kelompok Presentasi - 20240211 - 211051 - 0000Document9 pagesCoklat Krem Vintage Estetik Tugas Kelompok Presentasi - 20240211 - 211051 - 0000iaditya99No ratings yet
- Narrative Text NewDocument8 pagesNarrative Text NewRatih HaryadiNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 9 English FAL Winter School Support MaterialDocument34 pagesGrade 8 9 English FAL Winter School Support MaterialYOLANDI BESTER100% (1)
- Narrative Text Kelompok8Document8 pagesNarrative Text Kelompok8Ayatullah NurjatiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2Document4 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2sanniahmadNo ratings yet
- Recount TextDocument15 pagesRecount Textagustinanesa98No ratings yet
- Descriptive Text - FASE EDocument12 pagesDescriptive Text - FASE E7777220012No ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: English For EntertainmentDocument3 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: English For EntertainmentDienha HabibieNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Modul 3Document3 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Modul 3Yundi NenohaiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document2 pagesModule 1tambusashleighmaureenNo ratings yet
- Documents - Pub - Kls 10 Narrative TextDocument13 pagesDocuments - Pub - Kls 10 Narrative Textroni wiliyanaNo ratings yet
- LK 1 PROFESIONAL MODUL 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument2 pagesLK 1 PROFESIONAL MODUL 3 Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriMohammad Daifi Ibrahim100% (2)
- Different Types of StructuresDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of StructuresAleida JiménezNo ratings yet
- Narrative and Recount TextDocument18 pagesNarrative and Recount Textrahayu ramadaniNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument10 pagesTable of ContentsYulyy FaziiraaNo ratings yet
- Learning NotesDocument6 pagesLearning NotesRatih RinandaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Compare and ContrastDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Compare and Contrastapi-643975527No ratings yet
- Universidade Rovuma Extensão Do Niassa Curso de Licenciatura em Ensino de Biologia Plano Analítico Da Língua Inglesa IiDocument6 pagesUniversidade Rovuma Extensão Do Niassa Curso de Licenciatura em Ensino de Biologia Plano Analítico Da Língua Inglesa IiAgeu Lutero JaimeNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 3 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1 Modul 3 ProfesionalKaryantoNo ratings yet
- Happy Thanksgiving Infographics by SlidesgoDocument10 pagesHappy Thanksgiving Infographics by SlidesgoNguyễn Hà MyNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesLK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisAnnah SwanNo ratings yet
- Erzähltextanalyse [German-language Edition]: Modelle, Kategorien, ParameterFrom EverandErzähltextanalyse [German-language Edition]: Modelle, Kategorien, ParameterNo ratings yet
- NWABSD Lesson PlansDocument5 pagesNWABSD Lesson Plansapi-379699844No ratings yet
- A. Introduction: P R A G M A T I C SDocument6 pagesA. Introduction: P R A G M A T I C SQomaRiyahNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - EL 209Document27 pagesGroup 1 - EL 209araaachnidNo ratings yet
- Read The Questions 1-6. Then Match Them To The Correct Answers A-F. Circle The Correct Word in Each AnswerDocument1 pageRead The Questions 1-6. Then Match Them To The Correct Answers A-F. Circle The Correct Word in Each AnswerVasile ElenaNo ratings yet
- Text To Pakistan Sign Language For Urdu: Department of Computer ScienceDocument24 pagesText To Pakistan Sign Language For Urdu: Department of Computer ScienceLaiba SabirNo ratings yet
- Textbook The Phonetics and Phonology of Geminate Consonants First Edition Kubozono Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook The Phonetics and Phonology of Geminate Consonants First Edition Kubozono Ebook All Chapter PDFalma.brown118100% (3)
- Simple-Present-Final English WorkshopDocument5 pagesSimple-Present-Final English WorkshopSergio RoaNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect SpeechDocument22 pagesDirect Indirect SpeechLolita Setyaningrum91% (46)
- How To Speak Fluent English in 2023 - Speak EngliDocument6 pagesHow To Speak Fluent English in 2023 - Speak EngliPolina MininaNo ratings yet
- Conf. Univ. Dr. Luminiţa-Elena TURCUDocument1 pageConf. Univ. Dr. Luminiţa-Elena TURCUCatalin CiubotariuNo ratings yet
- Why Our Kids Cant ReadDocument10 pagesWhy Our Kids Cant Readapi-559290813No ratings yet
- Harold Conklin 1986 - Hanunoo Color CategoriesDocument7 pagesHarold Conklin 1986 - Hanunoo Color CategoriesJona Mae VictorianoNo ratings yet
- Romiette and Julio Final AssignmentDocument3 pagesRomiette and Julio Final Assignmentapi-260797837No ratings yet
- Academic IELTS Reading Test 149Document10 pagesAcademic IELTS Reading Test 149Lan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Year 9 English Unit PlanDocument5 pagesYear 9 English Unit Planapi-618196299No ratings yet
- Techniques-Ant and The DoveDocument6 pagesTechniques-Ant and The DoveazimahsallehNo ratings yet
- Ell DebateDocument4 pagesEll Debateapi-525214557No ratings yet
- Form (Structure) Meaning & Use Pronunciation: The Simple Past TenseDocument18 pagesForm (Structure) Meaning & Use Pronunciation: The Simple Past TenseArisma Handayani100% (1)
- B - A-I (English) Gen - Hons - Additional, Functional (80+20)Document18 pagesB - A-I (English) Gen - Hons - Additional, Functional (80+20)RadheShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hale Kissock Introduction EditedDocument190 pagesHale Kissock Introduction Editedmedjinejoachim.wbNo ratings yet
- Europass CV Mirko LaurilaDocument4 pagesEuropass CV Mirko LaurilaMikke90No ratings yet
- Module 9 (Human Factors) Sub Module 9.7 (Communication) - RevDocument13 pagesModule 9 (Human Factors) Sub Module 9.7 (Communication) - RevInterogator5No ratings yet
- Japanese: SyllabusDocument28 pagesJapanese: SyllabusW GangenathNo ratings yet
- PragmaticsDocument50 pagesPragmaticsMarianne ChristieNo ratings yet
- Concept of Information - Rafael CapurroDocument17 pagesConcept of Information - Rafael CapurroFau NesNo ratings yet
- Grammar Focus - Present Perfect and Past SimpleDocument1 pageGrammar Focus - Present Perfect and Past SimpleAjla IbrahimpasicNo ratings yet





























































![Erzähltextanalyse [German-language Edition]: Modelle, Kategorien, Parameter](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/338706338/149x198/821d80870e/1638576280?v=1)

























