Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsBasic Needs of A Client
Basic Needs of A Client
Uploaded by
abigail melekiBasic hygiene needs for clients include bathing, skin care, oral care, hair care, and nail care. Bathing cleans and refreshes patients while allowing nurses to assess skin and observe any issues. Skin needs to be kept clean, dry, and protected from pressure to prevent conditions like pressure sores. Oral care promotes oral health and prevents infections. Hair care removes dirt and stimulates scalp circulation. Maintaining good hygiene is important for client health and well-being.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- End - Life of Care PPT 1 MainDocument48 pagesEnd - Life of Care PPT 1 MainNancy Singh63% (16)
- Pressure UlcerDocument35 pagesPressure Ulcerenam professor100% (1)
- WK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsDocument24 pagesWK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesUrinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Delivering Better Oral HealthDocument102 pagesDelivering Better Oral Healthsavrasx100% (1)
- Meeting The Hygienic Needs of The Client (Autosaved)Document115 pagesMeeting The Hygienic Needs of The Client (Autosaved)samitha madurangaNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and ComfortDocument63 pagesHygiene and Comfortrhearamirezucv2023No ratings yet
- Care of Dying PatientDocument17 pagesCare of Dying PatientPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Promoting Personal Hygiene & Promoting Rest & SleepDocument26 pagesPromoting Personal Hygiene & Promoting Rest & SleepYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sore or Decubitus Ulcer or Bed SoreDocument20 pagesPressure Sore or Decubitus Ulcer or Bed SorePrecious BlessingNo ratings yet
- Hygiene RevisedDocument70 pagesHygiene RevisedranariokenroeirvinNo ratings yet
- Bed Shampooing: Tray ContainingDocument7 pagesBed Shampooing: Tray ContainingAubrey GarateNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Health q1Document24 pagesMAPEH Health q1Jerne DeveraNo ratings yet
- Bed BathingDocument83 pagesBed BathingErika Agramon100% (1)
- Care of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniDocument25 pagesCare of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniAnn Merlin Jobin100% (1)
- Pressure SoresDocument15 pagesPressure SoresCedric MusakalaNo ratings yet
- Bedsore PDFDocument5 pagesBedsore PDFIam BabuNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedDocument18 pagesWeek 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Perilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathDocument23 pagesPerilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Perilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathDocument23 pagesPerilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (B)Document19 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (B)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument81 pagesThe Respiratory Systemapi-227612210No ratings yet
- SJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument10 pagesSJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityJoy CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Nursing: Dr. Rohit, MBBS, DNB Physical Medicine and RehabilitationDocument21 pagesRehabilitation Nursing: Dr. Rohit, MBBS, DNB Physical Medicine and RehabilitationRupali RautNo ratings yet
- NSE 111 Presentation-Student Version (1) .Hygiene - RevisedDocument10 pagesNSE 111 Presentation-Student Version (1) .Hygiene - Revisedphuongphuonganhanh171203No ratings yet
- Personal HygieneDocument2 pagesPersonal Hygieneanisarahma718No ratings yet
- Cupping TherapyDocument20 pagesCupping TherapyMohamed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation A3.Document27 pagesPresentation A3.Ali HusseinNo ratings yet
- Ralph Rigor M. Canlapan, RN: Faculty, College of Nursing and Midwifery College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel - PampangaDocument26 pagesRalph Rigor M. Canlapan, RN: Faculty, College of Nursing and Midwifery College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel - PampangaKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument7 pagesBed BathJaya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Decubitus UlcersDocument4 pagesDecubitus UlcersNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Bed SoresDocument16 pagesBed SoresSrinivas Polikepati50% (2)
- Decubetic Ulcer (Bed Sores)Document22 pagesDecubetic Ulcer (Bed Sores)Jerry ZahidNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers: by Mr. M. Shivanandha ReddyDocument35 pagesPressure Ulcers: by Mr. M. Shivanandha ReddyDr Ali100% (2)
- NU 18 Moisture Damage Pressure Ulcer Prevention v5 WebDocument4 pagesNU 18 Moisture Damage Pressure Ulcer Prevention v5 WebFaisal BayuNo ratings yet
- Perineal TearsDocument21 pagesPerineal TearsWhirmey ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Burns: College of NursingDocument12 pagesBurns: College of NursingAyr Masenas100% (1)
- Additional Nursing ProceduresDocument28 pagesAdditional Nursing ProceduresRona LynNo ratings yet
- Hygiene NotesDocument60 pagesHygiene NotesDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy BasicsDocument42 pagesPhysiotherapy Basicsakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Personal Care Skills: HygieneDocument24 pagesChapter 6: Personal Care Skills: Hygieneapi-236529076No ratings yet
- Cleansing Bed BathDocument19 pagesCleansing Bed BathCherie BanzonNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment Using NATDocument42 pagesHead To Toe Assessment Using NATTHEA KERSTI ECOTNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareDocument6 pagesNursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- 3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument53 pages3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- ORALDocument7 pagesORALHelda FyNo ratings yet
- Save Our SkinDocument14 pagesSave Our Skinapi-445612194No ratings yet
- HYGIENEDocument69 pagesHYGIENERhea Jane Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument49 pages3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- Mufulira Schools of Nursing and MidwiferyDocument53 pagesMufulira Schools of Nursing and MidwiferyHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Hygiene 2Document41 pagesHygiene 2Nermine ElcokanyNo ratings yet
- Care of BedriddenDocument18 pagesCare of BedriddenprashantNo ratings yet
- Neck DissectionDocument24 pagesNeck Dissectionhayat al akoumNo ratings yet
- SOURCEDocument10 pagesSOURCEKaren solibaNo ratings yet
- NutritionfocusedphysicalexamDocument19 pagesNutritionfocusedphysicalexamapi-239305061No ratings yet
- 3 Bed Bath Shampoo Oral FootDocument55 pages3 Bed Bath Shampoo Oral FootjajaNo ratings yet
- Colostomy CareDocument35 pagesColostomy CareRashmita DahalNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument22 pagesPressure UlcerMakanjuola Osuolale John100% (2)
- Endometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersFrom EverandEndometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Declaration FormBest JiratipNo ratings yet
- CMS Survey ProcessDocument16 pagesCMS Survey Processyanuar estho100% (1)
- Cvek Pulpotomy - RevisitedDocument5 pagesCvek Pulpotomy - RevisitedJose ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Syndrome Case PresentationDocument53 pagesSpinal Cord Syndrome Case PresentationPermata GBKP Runggun SurabayaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report: Polio Outbreak Response Immunization Bopv Round 2Document4 pagesNarrative Report: Polio Outbreak Response Immunization Bopv Round 2Cristina MelloriaNo ratings yet
- Green Ocean - Print PortalDocument3 pagesGreen Ocean - Print PortalKishore Kumar MsvNo ratings yet
- Letterstream 2024 2Document76 pagesLetterstream 2024 2swagswogNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument2 pagesThe BrainAlejandroGonzagaNo ratings yet
- Sampoorna Arogya - Onepager - 22042022Document2 pagesSampoorna Arogya - Onepager - 22042022adigupta100% (2)
- Brain Tumors: Primary BTDocument5 pagesBrain Tumors: Primary BTMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Dosages and SolutionDocument68 pagesDosages and SolutionRuan MarchessaNo ratings yet
- 53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesDocument5 pages53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesVictor PazNo ratings yet
- Letter For MSW Wayne State (Rosas Feliciano)Document2 pagesLetter For MSW Wayne State (Rosas Feliciano)api-283974130No ratings yet
- Lo 040 Human Performance & LimitationsDocument30 pagesLo 040 Human Performance & LimitationsflightdocNo ratings yet
- The Role of Perception in Personality DevelopmentDocument3 pagesThe Role of Perception in Personality DevelopmentOpen Access JournalNo ratings yet
- The Use of General Anesthesia For Pediatric Dentistry in Saskatchewan: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesThe Use of General Anesthesia For Pediatric Dentistry in Saskatchewan: A Retrospective StudyAbi de la PeñaNo ratings yet
- ACOG Fetal Maturity Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesACOG Fetal Maturity Guidelines PDFinayahsyNo ratings yet
- Johnston Et Al. - 2008 - A Preliminary Evaluation of The Safety and ToleranDocument5 pagesJohnston Et Al. - 2008 - A Preliminary Evaluation of The Safety and ToleranMiin ChanNo ratings yet
- Cryopreservation and Ivf: What Can Be Stored?Document2 pagesCryopreservation and Ivf: What Can Be Stored?Deepanshu ShakargayeNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Male Genital Examination CSG Healthy Male 2019Document2 pagesStep-By-Step Male Genital Examination CSG Healthy Male 2019Indo RhythmsNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Management of Pregnant With HELLP Syndrome With Fetal Intrauterine Exitus (#1123666) - 2457074Document3 pagesAnesthesia Management of Pregnant With HELLP Syndrome With Fetal Intrauterine Exitus (#1123666) - 2457074SALMA HANINANo ratings yet
- Model Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi BantenDocument8 pagesModel Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi Bantenyanuar anazdiNo ratings yet
- FNCP and HTPDocument11 pagesFNCP and HTPJesse SaygoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Assignment NCP Part 2Document3 pagesNCMB 316 Assignment NCP Part 2I'm a PepegaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Work Plan For Students 2022-2023Document34 pagesOncology Work Plan For Students 2022-2023Ahmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- MS GCS Cornual Ectopic PregnancyDocument57 pagesMS GCS Cornual Ectopic PregnancyCarelle Faith Serrano AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Anand Dhoka - AB - Numerology ReportDocument82 pagesAnand Dhoka - AB - Numerology ReportTaththasttuNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 Name: - Date: - Teacher: - SectionDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 Name: - Date: - Teacher: - SectionJoecel Mar Bautista Ambid100% (1)
- Social Skills Teaching For Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder - A Systematic Review (2020)Document12 pagesSocial Skills Teaching For Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder - A Systematic Review (2020)SarahNo ratings yet
Basic Needs of A Client
Basic Needs of A Client
Uploaded by
abigail meleki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesBasic hygiene needs for clients include bathing, skin care, oral care, hair care, and nail care. Bathing cleans and refreshes patients while allowing nurses to assess skin and observe any issues. Skin needs to be kept clean, dry, and protected from pressure to prevent conditions like pressure sores. Oral care promotes oral health and prevents infections. Hair care removes dirt and stimulates scalp circulation. Maintaining good hygiene is important for client health and well-being.
Original Description:
Original Title
basic needs of a client
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBasic hygiene needs for clients include bathing, skin care, oral care, hair care, and nail care. Bathing cleans and refreshes patients while allowing nurses to assess skin and observe any issues. Skin needs to be kept clean, dry, and protected from pressure to prevent conditions like pressure sores. Oral care promotes oral health and prevents infections. Hair care removes dirt and stimulates scalp circulation. Maintaining good hygiene is important for client health and well-being.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views21 pagesBasic Needs of A Client
Basic Needs of A Client
Uploaded by
abigail melekiBasic hygiene needs for clients include bathing, skin care, oral care, hair care, and nail care. Bathing cleans and refreshes patients while allowing nurses to assess skin and observe any issues. Skin needs to be kept clean, dry, and protected from pressure to prevent conditions like pressure sores. Oral care promotes oral health and prevents infections. Hair care removes dirt and stimulates scalp circulation. Maintaining good hygiene is important for client health and well-being.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
Basic Client Needs
Hygiene
• It is the science of health and its preservation.
• It is a condition of practice such as cleanliness that is
conducive to preservation of health.
1. Bathing
• This is one of the hygienic measures you need to take
as an individual as well as ensuring that the patients
under your care bath frequently
Importance of Bathing
• It cleans, refreshes the patient and makes him/her feel
comfortable.
• Provides chance for the nurse to make observations on
the patient, if remember under physical examination
we mentioned this. You can be able to observe the
patient when they undress to bath.
cont
• It stimulates the blood circulation because there is
dilatation of blood vessels leading increased blood
flow.
• Increases patient’s sense of wellbeing and self-
esteem
Types of Baths
• Shower bath
• Tab/plunge bath
• Bed bath.
During bed bath you must observe for the following:
• Posture and mental status- observe whether
changing or not, is the patient confused.
• Signs of discomfort if you are bathing the patient are
the patient comfortable, observe facial expressions.
• Breathing pattern-is it normal breathing or patient is
having difficulties in breathing.
• Odour from the body or clothes- is there an
offensive smell especially where the patient messes
himself
Care of the Skin
• When pressure is not relieved on any part of
the body regularly, blood supply to the area
will be interfered. This will result in affecting
the nutritional status and oxygen supply to the
area. The end result will be reddening of the
area with possible tissue break down. Good
skin care is helpful in preventing such
problems.
Pressure areas
• are areas of the body where tissues may be
compressed between the underlying bone and
bed leading to formation of pressure sores.
These are areas where the bones are
prominent and liable to formation of pressure
sores
pressure sore (Decubitus)
• A pressure sore or decubitus is an ulcer formed on
an area where the skin tissue has been destroyed
and there is progressive destruction of the
underlying tissues. The terms decubitus ulcer,
pressure sore and bed sore are used
interchangeably.
• A pressure sore is an ulcer or sore which forms
at a point of bone prominence due to pressure,
friction or moisture when the patient is confined
to bed or wheel chair
Predisposing Factors to Pressure Sore Formation
Moisture: It reduces skin’s resistance to other physical
factors such as force
Poor nutrition: clients with poor nutrition experience
serious muscle wasting and decrease in subcutaneous
tissue which serves as a pad between the skin and the
underlying bone.
Anaemia: decreased haemoglobin reduces oxygen carrying
capacity of blood and amount of oxygen available to the
tissues. Anaemia also alters cellular metabolism.
.
• Shearing force: force exerted when client is
being moved or pulled in bed. The skin
adheres to the surface of the bed while the
skin slides in the direction of the body
movement.
• Infection: It increases metabolic and
nutritional demand thereby depriving the
tissues of oxygen and nutrients
Signs of Pressure Sore Formation
• Bleaching of the skin
• Redness of the skin
• Heat
• Tenderness
• Skin irritation
• Pain on pressure area
Prevention of Pressure Sores
• Do routine check-ups of pressure areas during
baths for presence of pressure sore formation
• Keep the pressure area clean and free from
irritation to prevent pressure sore formation.
• Promote measures to improve nutritional
status of the patient because malnutrition
predisposes to pressure sore formation as the
skin can easily break
cont
• Change patient’s position 2 hourly and keep a
chart for turnings to relieve pressure from
bony prominence areas.
• Ensure the bed is free from wrinkles, bed
crumbs or other irritating materials that can
cause friction of the skin.
• Pressure area care should be done 4 hourly in
helpless patients e.g. unconscious patient
Care of the Mouth (Oral Toilet)
• This is the care given to the patient’s mouth
with the aim of cleansing the mouth, and
promotes the flow of saliva.
Indications for Oral Care
• unconscious and weak patients because there
are not able to clean their mouths.
• Patients with difficulties in breathing
• Those on milk or fluid diet to cleanse the
debris from milk.
• Patients with diseases of the mouth e.g.
stomatitis inflammation of the mouth,
gingivitis inflammation of the gums etc. to
prevent bad breath.
• Patients on artificial feeding
Advantages of Oral Care
• Increase salivary flow.
• Prevent mouth infections.
• Prevent dental carries.
• Prevents drying of the mucous membrane of
the mouth.
• Prevent sordes (dirty particles found in
between the teeth).
Complications of a Dirty Mouth
• Stomatitis– It is inflammation of the mouth.
• Gingivitis – It is inflammation of the gums.
• Tonsillitis– It is inflammation of the tonsils.
• Parotitis –It is the inflammation of the parotid glands.
• Otitis Media –This is inflammation of the middle ear.
• Glossitis– This is inflammation of the tongue.
• Halitosis–This is bad smell of the mouth.
• Anorexia– This is loss of appetite.
Care of the Hair and Nails.
Hair Care Purpose
• Remove dirt and old cells and avoid the skin irritation.
• Remove dead cells from the scalp.
• Stimulate scalp circulation just as you can promote blood
circulation when you give a patient a bath in the same way there is
blood vessel dilation hence increased blood circulation.
• Remove the chemicals especially when insecticide has been used
to clean the hair.
• It improves the patient’s body image as the patient will look nice
when the hair is washed especially with unkempt hair as a result of
self-care deficit
Indications
• Chronically ill patients
• Patient undergoing special operation on the
head.
• Patients with dirty hair.
• Patients infested with lice.
• Patients who have been in bed for too long.
• Mentally ill patients
Common Problems of the Scalp and Hair
1. Dandruff
2. Pediculosis
• types of pediculosis. These are:
I. Pediculosis capitis its found on the head
II. Pediculosis corporis its found on the body
III. Pediculosis pubis it’s found in the pubic area
3. Hair loss (alopecia) or Boldness
You might also like
- End - Life of Care PPT 1 MainDocument48 pagesEnd - Life of Care PPT 1 MainNancy Singh63% (16)
- Pressure UlcerDocument35 pagesPressure Ulcerenam professor100% (1)
- WK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsDocument24 pagesWK 4 Exam 2 Key ConceptsKrystel LahomNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesUrinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Delivering Better Oral HealthDocument102 pagesDelivering Better Oral Healthsavrasx100% (1)
- Meeting The Hygienic Needs of The Client (Autosaved)Document115 pagesMeeting The Hygienic Needs of The Client (Autosaved)samitha madurangaNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and ComfortDocument63 pagesHygiene and Comfortrhearamirezucv2023No ratings yet
- Care of Dying PatientDocument17 pagesCare of Dying PatientPoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Promoting Personal Hygiene & Promoting Rest & SleepDocument26 pagesPromoting Personal Hygiene & Promoting Rest & SleepYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- Pressure Sore or Decubitus Ulcer or Bed SoreDocument20 pagesPressure Sore or Decubitus Ulcer or Bed SorePrecious BlessingNo ratings yet
- Hygiene RevisedDocument70 pagesHygiene RevisedranariokenroeirvinNo ratings yet
- Bed Shampooing: Tray ContainingDocument7 pagesBed Shampooing: Tray ContainingAubrey GarateNo ratings yet
- MAPEH Health q1Document24 pagesMAPEH Health q1Jerne DeveraNo ratings yet
- Bed BathingDocument83 pagesBed BathingErika Agramon100% (1)
- Care of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniDocument25 pagesCare of A Bedridden Patient: Prepared by Jannet Reena PuraniAnn Merlin Jobin100% (1)
- Pressure SoresDocument15 pagesPressure SoresCedric MusakalaNo ratings yet
- Bedsore PDFDocument5 pagesBedsore PDFIam BabuNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedDocument18 pagesWeek 2 Bed Bath Proper Positioning OutlinedNICOLE MAGLAQUINo ratings yet
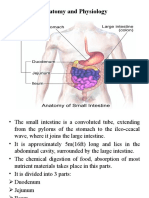
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Perilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathDocument23 pagesPerilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Perilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathDocument23 pagesPerilite Exposure and Hot Sitz BathJohn Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (B)Document19 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (B)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument81 pagesThe Respiratory Systemapi-227612210No ratings yet
- SJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument10 pagesSJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityJoy CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation Nursing: Dr. Rohit, MBBS, DNB Physical Medicine and RehabilitationDocument21 pagesRehabilitation Nursing: Dr. Rohit, MBBS, DNB Physical Medicine and RehabilitationRupali RautNo ratings yet
- NSE 111 Presentation-Student Version (1) .Hygiene - RevisedDocument10 pagesNSE 111 Presentation-Student Version (1) .Hygiene - Revisedphuongphuonganhanh171203No ratings yet
- Personal HygieneDocument2 pagesPersonal Hygieneanisarahma718No ratings yet
- Cupping TherapyDocument20 pagesCupping TherapyMohamed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation A3.Document27 pagesPresentation A3.Ali HusseinNo ratings yet
- Ralph Rigor M. Canlapan, RN: Faculty, College of Nursing and Midwifery College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel - PampangaDocument26 pagesRalph Rigor M. Canlapan, RN: Faculty, College of Nursing and Midwifery College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel - PampangaKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Bed BathDocument7 pagesBed BathJaya PriyaNo ratings yet
- Decubitus UlcersDocument4 pagesDecubitus UlcersNkk Aqnd MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Bed SoresDocument16 pagesBed SoresSrinivas Polikepati50% (2)
- Decubetic Ulcer (Bed Sores)Document22 pagesDecubetic Ulcer (Bed Sores)Jerry ZahidNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers: by Mr. M. Shivanandha ReddyDocument35 pagesPressure Ulcers: by Mr. M. Shivanandha ReddyDr Ali100% (2)
- NU 18 Moisture Damage Pressure Ulcer Prevention v5 WebDocument4 pagesNU 18 Moisture Damage Pressure Ulcer Prevention v5 WebFaisal BayuNo ratings yet
- Perineal TearsDocument21 pagesPerineal TearsWhirmey ChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Burns: College of NursingDocument12 pagesBurns: College of NursingAyr Masenas100% (1)
- Additional Nursing ProceduresDocument28 pagesAdditional Nursing ProceduresRona LynNo ratings yet
- Hygiene NotesDocument60 pagesHygiene NotesDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy BasicsDocument42 pagesPhysiotherapy Basicsakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Personal Care Skills: HygieneDocument24 pagesChapter 6: Personal Care Skills: Hygieneapi-236529076No ratings yet
- Cleansing Bed BathDocument19 pagesCleansing Bed BathCherie BanzonNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment Using NATDocument42 pagesHead To Toe Assessment Using NATTHEA KERSTI ECOTNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareDocument6 pagesNursing Assistant Educator: For Long Term CareMarnelie Guerrero AbuanNo ratings yet
- 3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument53 pages3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- ORALDocument7 pagesORALHelda FyNo ratings yet
- Save Our SkinDocument14 pagesSave Our Skinapi-445612194No ratings yet
- HYGIENEDocument69 pagesHYGIENERhea Jane Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeingDocument49 pages3.CH-3.Nursing Implication For Physical Aspects of AgeinglujainNo ratings yet
- Mufulira Schools of Nursing and MidwiferyDocument53 pagesMufulira Schools of Nursing and MidwiferyHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Hygiene 2Document41 pagesHygiene 2Nermine ElcokanyNo ratings yet
- Care of BedriddenDocument18 pagesCare of BedriddenprashantNo ratings yet
- Neck DissectionDocument24 pagesNeck Dissectionhayat al akoumNo ratings yet
- SOURCEDocument10 pagesSOURCEKaren solibaNo ratings yet
- NutritionfocusedphysicalexamDocument19 pagesNutritionfocusedphysicalexamapi-239305061No ratings yet
- 3 Bed Bath Shampoo Oral FootDocument55 pages3 Bed Bath Shampoo Oral FootjajaNo ratings yet
- Colostomy CareDocument35 pagesColostomy CareRashmita DahalNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument22 pagesPressure UlcerMakanjuola Osuolale John100% (2)
- Endometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersFrom EverandEndometriosis, A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DisordersNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Declaration FormBest JiratipNo ratings yet
- CMS Survey ProcessDocument16 pagesCMS Survey Processyanuar estho100% (1)
- Cvek Pulpotomy - RevisitedDocument5 pagesCvek Pulpotomy - RevisitedJose ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Syndrome Case PresentationDocument53 pagesSpinal Cord Syndrome Case PresentationPermata GBKP Runggun SurabayaNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report: Polio Outbreak Response Immunization Bopv Round 2Document4 pagesNarrative Report: Polio Outbreak Response Immunization Bopv Round 2Cristina MelloriaNo ratings yet
- Green Ocean - Print PortalDocument3 pagesGreen Ocean - Print PortalKishore Kumar MsvNo ratings yet
- Letterstream 2024 2Document76 pagesLetterstream 2024 2swagswogNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument2 pagesThe BrainAlejandroGonzagaNo ratings yet
- Sampoorna Arogya - Onepager - 22042022Document2 pagesSampoorna Arogya - Onepager - 22042022adigupta100% (2)
- Brain Tumors: Primary BTDocument5 pagesBrain Tumors: Primary BTMohamed Al-zichrawyNo ratings yet
- Dosages and SolutionDocument68 pagesDosages and SolutionRuan MarchessaNo ratings yet
- 53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesDocument5 pages53 Coronary Artery AnomaliesVictor PazNo ratings yet
- Letter For MSW Wayne State (Rosas Feliciano)Document2 pagesLetter For MSW Wayne State (Rosas Feliciano)api-283974130No ratings yet
- Lo 040 Human Performance & LimitationsDocument30 pagesLo 040 Human Performance & LimitationsflightdocNo ratings yet
- The Role of Perception in Personality DevelopmentDocument3 pagesThe Role of Perception in Personality DevelopmentOpen Access JournalNo ratings yet
- The Use of General Anesthesia For Pediatric Dentistry in Saskatchewan: A Retrospective StudyDocument9 pagesThe Use of General Anesthesia For Pediatric Dentistry in Saskatchewan: A Retrospective StudyAbi de la PeñaNo ratings yet
- ACOG Fetal Maturity Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesACOG Fetal Maturity Guidelines PDFinayahsyNo ratings yet
- Johnston Et Al. - 2008 - A Preliminary Evaluation of The Safety and ToleranDocument5 pagesJohnston Et Al. - 2008 - A Preliminary Evaluation of The Safety and ToleranMiin ChanNo ratings yet
- Cryopreservation and Ivf: What Can Be Stored?Document2 pagesCryopreservation and Ivf: What Can Be Stored?Deepanshu ShakargayeNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Male Genital Examination CSG Healthy Male 2019Document2 pagesStep-By-Step Male Genital Examination CSG Healthy Male 2019Indo RhythmsNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Management of Pregnant With HELLP Syndrome With Fetal Intrauterine Exitus (#1123666) - 2457074Document3 pagesAnesthesia Management of Pregnant With HELLP Syndrome With Fetal Intrauterine Exitus (#1123666) - 2457074SALMA HANINANo ratings yet
- Model Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi BantenDocument8 pagesModel Intervensi Hipertensi Di Kabupaten Lebak Provinsi Bantenyanuar anazdiNo ratings yet
- FNCP and HTPDocument11 pagesFNCP and HTPJesse SaygoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Assignment NCP Part 2Document3 pagesNCMB 316 Assignment NCP Part 2I'm a PepegaNo ratings yet
- Oncology Work Plan For Students 2022-2023Document34 pagesOncology Work Plan For Students 2022-2023Ahmed SaeedNo ratings yet
- MS GCS Cornual Ectopic PregnancyDocument57 pagesMS GCS Cornual Ectopic PregnancyCarelle Faith Serrano AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Anand Dhoka - AB - Numerology ReportDocument82 pagesAnand Dhoka - AB - Numerology ReportTaththasttuNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 Name: - Date: - Teacher: - SectionDocument4 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Mapeh 6 Name: - Date: - Teacher: - SectionJoecel Mar Bautista Ambid100% (1)
- Social Skills Teaching For Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder - A Systematic Review (2020)Document12 pagesSocial Skills Teaching For Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder - A Systematic Review (2020)SarahNo ratings yet