Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic GD&T Training 1
Basic GD&T Training 1
Uploaded by
trandangbkOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic GD&T Training 1
Basic GD&T Training 1
Uploaded by
trandangbkCopyright:
Available Formats
GD&T BASICS
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
01. WHAT IS GD&T
Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) is a system for defining and
communicating engineering tolerances.
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
02. Features Overview Review
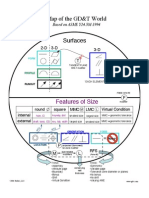
1. GD&T can apply to two types of features:
o Surface Features – Surface with no dimension
o Features of Size – Any feature or section that has dimensional size to it
2. Features of size
o Internal Features are defined by the lack of material like a hole or slot
o External Features are defined by the presence of material like a pin or 3D object
3. The material condition
o MMC: Max Material Condition is the dimension where the most amount of
material exists.
o LML: Least Material Condition is the dimension where the least amount of material
exists
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
03. RULE NUMBER 1 : ENVELOPE PRINCIPLE
Definition: where only a tolerance of size is specified, the limits of size
of an individual feature of size prescribe the extent to which variations in
its geometric form, as well as its size, are allowed.
If the paper is small (LMC), it doesn’t have to be straight or flat edges to
insert into envelope
If the paper is large (MMC), you need to insert the it perfectly straight,
and have no variation
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
03. RULE NUMBER 1 : ENVELOPE PRINCIPLE_EXAMPLE
Exp.1: If the dimension measured to have diameter of 20.4 .
How much form tolerance ( bend ) can you have ?
NONE: part is at MMC so it cannot deviate from it
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
03. RULE NUMBER 1 : ENVELOPE PRINCIPLE_EXAMPLE
Exp.2: If the dimension measured to have diameter of
20.37 . How much form tolerance are you allowed if
straightness 0.1 is called out
0.03: 20.4(MMC)-20.37
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
03. RULE NUMBER 1 : ENVELOPE PRINCIPLE_EXAMPLE
Exp.3: If the dimension measured to have diameter of
15.55 . How much form tolerance are you allowed in
the hole ?
0.15: 15.55-15.4(MMC)
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
04. MATERIAL CONDITIONAL MODIFIER
Bonus Tol (external feature) : MMC-Actual.
Bonus Tol (internal feature) : Actual-MMC
Example :
Bonus = 10.2-9.8= 0.4 mm
Perpendicularity = Bonus + called = 0.4+0.2 = 0.6
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. DATUMS
1. What is datum : is theoretical reference plane, axis, or point. Orientation, profile,
location, or runout of geometric features are controlled in reference to these datum
Which letter would represent the actual Which of the above datum callouts are
datum feature A? A,B,C,D ? surface datums?
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. DOF-DEGREES OF FREEDOM
How many degrees of freedom are Which combination of datum controls below would fully
being controlled by the datum reference constrain the part in all 6 degrees of freedom when used in
frame |L|N|? the Feature Control Frame for the 5±0.25 hole?
1. L|N|M ? 2. N|P ? 3. P|M ?
4. P|L|M ? 5 P|M|N
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. DOF-DATUM SELECTION
HOW: reasons to choose a datum in order of importance :
1. Part Functionality : how does the part mate at the next assembly ?
2. Constraining the Part : what features are going to provide the best stability within the part’s
datum reference frame ? Is SLOF met ?
3. Inspection/Manufacturability : what is a good datum reference frame will be practical
regarding the production and inspection of the parts ?
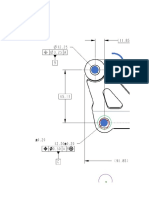
Lets add some GD&T to this drawing :
Primary datum ? Secondary datum, tertiary
datum ? Which refer to which one ?
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. DATUM TARGET
Definition: datum target is datum point, plane, or axis allow you to specify exact locations to
secure your parts for measurement
1. Symbols:
o Upper portion : contains the target size
o Lower portion : datum target letter and number
2. Datum Target Point : single point of contact btw the
datum simulator and the part by using spherical-tipped gauge pin
3. Datum target line: A phantom line designating a line contact
btw the datum simulator and the part by using the edge of a
cylindrical gauge pin
4. Datum target area : A designated area location specified on
a part where the datum simulator and the part should make contact
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. DATUM TARGET
The part illustrated is frequently used to cover electrical cables
Example and Quiz running along the exterior length of a rocket motor. It is made of bent
sheet metal and will not rest flat on the inspection table. As the
designer, you elect to use datum targets and want to control all 6
degrees of freedom when you set this up for measurement.
Select the 2 Answers that describe errors with this drawing.
A. There are not enough points to secure
Datum A in 3 DOF
B. Datum B uses both lines and points
which is not allowed
C. The part is not controlled in all 6 DOF
D. The locations of Datum Targets A & B
are not fully defined in the X ( left and
right ) axis
E. You can not use datum targets on a
curved part ( datum target A )
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. MAXIMUM/LEAST MATERIAL BOUNDARIES ( MMB/LMB )
1. Definition: MMB is the condition of a datum surface or feature of size, where the part has the
maximum amount of material
2. Compare to MMC:
MMC : specify a material condition for the feature being MMB : specify a ‘ boundary for a particular datum
controlled by Feature Control Frame referenced by the feature called out in the Feature Control
Frame
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. MAXIMUM/LEAST MATERIAL BOUNDARIES ( MMB/LMB )
Example : at RMB which is diameter of the center pin gauge to be designed ?
The gauge must be expandable ( contracting pins, mandrels, chucks, etc.. )
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. MAXIMUM/LEAST MATERIAL BOUNDARIES ( MMB/LMB )
Example : at MMB which is diameter of the center pin gauge to be designed ?
The center gauge’s diameter is fixed at any value as long as it is within feature’s tolerance
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. SLOF : SIZE-LOCATION-ORIENTATION-FORM
The four components to a complete drawing
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. STRAIGHTNESS
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. FLATNESS
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. CIRCULARITY & CYLINDRICITY
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. PARALLELISM
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. PERPENDICULARITY
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. ANGULARITY
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. PROFILE OF A LINE & SURFACE
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. POSITION
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. CONCENTRICITY
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. SYMMETRY
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
05. RUNOUT & TOTAL RUNOUT
NORTHSTAR PRECISION VIET
NAM
You might also like
- Oxford Science 9 Second Edition Victorian CurriculumDocument244 pagesOxford Science 9 Second Edition Victorian CurriculumOjasvi GULATI100% (2)
- BKM-Z24B (III) Maintenance ManualDocument36 pagesBKM-Z24B (III) Maintenance ManualJosselyn Stephanie Ayala Solís100% (1)
- GD&T NotesDocument24 pagesGD&T NotesDarshan Sn100% (1)
- Gd&t-Multi MetricsDocument356 pagesGd&t-Multi MetricsdramiltNo ratings yet
- (Gene Cogorno) Geometric Dimensioning and Toleranc (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFDocument105 pages(Gene Cogorno) Geometric Dimensioning and Toleranc (B-Ok - Xyz) PDFamasiddayNo ratings yet
- ASME Y14.5-2009, Geometric Boundaries 2Document9 pagesASME Y14.5-2009, Geometric Boundaries 2Keith Admin60% (5)
- GD&T For Mpii 26-4-22Document134 pagesGD&T For Mpii 26-4-22sai tejaNo ratings yet
- F 5 Geo TolerancesDocument23 pagesF 5 Geo TolerancesRodrigo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Rules &conceptsDocument55 pagesRules &conceptsLokesh RajaNo ratings yet
- Rules and Concepts of GD&T PDFDocument31 pagesRules and Concepts of GD&T PDFMahender KumarNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Quality Engineering PowerpointDocument15 pagesDimensional Quality Engineering PowerpointSalman JavedNo ratings yet
- What Is The Tolerance Analysis - QRDocument15 pagesWhat Is The Tolerance Analysis - QRAnonymous tQhtrPbNo ratings yet
- GDT Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing Training ASME Y14.5-2009Document8 pagesGDT Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing Training ASME Y14.5-2009Giv MeeNo ratings yet
- GD&T Pre Post TestDocument3 pagesGD&T Pre Post TestVaibhav GadhaweNo ratings yet
- BookGD T PDFDocument14 pagesBookGD T PDFAbsolute ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument5 pagesGD&Travindra_2011No ratings yet
- 08 ParallelismMeasurement80Document31 pages08 ParallelismMeasurement80maddy_scribdNo ratings yet
- Rule #1 Explained: 2.7.1 Variations of Form (Rule #1: Envelope Principle)Document6 pagesRule #1 Explained: 2.7.1 Variations of Form (Rule #1: Envelope Principle)Anonymous 7ZTcBnNo ratings yet
- Metrology: ME3190 Machine Tools and MetrologyDocument64 pagesMetrology: ME3190 Machine Tools and MetrologySujit MuleNo ratings yet
- OrientationDocument39 pagesOrientationKumar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- IIGDT - Tolerancing Optimization Examples With $ SignsDocument9 pagesIIGDT - Tolerancing Optimization Examples With $ Signsநளின் கான்No ratings yet
- GD&TDocument10 pagesGD&TShahed FacebookNo ratings yet
- Krulikowski Chapter 03Document17 pagesKrulikowski Chapter 03Preet BadwalNo ratings yet
- GD&T ReferenceDocument2 pagesGD&T ReferenceJosh ByronNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - G D & T 17.11Document96 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - G D & T 17.11vijaykkhal100% (1)
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument7 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) : College of Engineering and TechnologyDienies TorresNo ratings yet
- Metrology 1CDocument44 pagesMetrology 1CRadhaMadhavNo ratings yet
- Workshop On GD & T: Faculty: Abhijeet ChinchorkarDocument75 pagesWorkshop On GD & T: Faculty: Abhijeet ChinchorkarRajdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- GD&T Training BrochureDocument5 pagesGD&T Training BrochurePritam PolekarNo ratings yet
- List of Abbreviations: Rev. No /date Issue No /date Ybf/Qsm/IDocument2 pagesList of Abbreviations: Rev. No /date Issue No /date Ybf/Qsm/IPradip Gangarde100% (1)
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDocument8 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- Composite Positional TolerancingDocument5 pagesComposite Positional TolerancingCarlos García Hernández100% (1)
- Notes On Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument68 pagesNotes On Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Form and PositionDocument54 pagesForm and PositionThangadurai Senthil Ram PrabhuNo ratings yet
- GD&T 1Document69 pagesGD&T 1JayanthiANo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument1 pageGD&TvrushalmaniyarNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Part3Document10 pagesDimensional Engineering Part3Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols Reference GuideDocument2 pagesGD&T Symbols Reference Guidecreating_24No ratings yet
- Composite Tolerance GDTDocument67 pagesComposite Tolerance GDTGanesanGovindarjNo ratings yet
- AE - Gage Standards - 2012 PDFDocument74 pagesAE - Gage Standards - 2012 PDFeazaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument6 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingPedro LeosNo ratings yet
- GD&T QuestionsDocument1 pageGD&T QuestionsjcetmechanicalNo ratings yet
- GD&T Training PresentationDocument20 pagesGD&T Training Presentationmariappan128No ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardDocument49 pagesDimensional Engineering: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardBhaskar KrishnacharNo ratings yet
- GD&T CylindricityDocument15 pagesGD&T CylindricityjaithilagarajNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Stack Up Analysis What Is Stack Up Analysis?Document25 pagesTolerance Stack Up Analysis What Is Stack Up Analysis?Venkadakrishnan ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Datum ShiftDocument11 pagesDatum ShiftHarshottam DhakadNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Requirements: Defines in The Following WayDocument7 pagesSimultaneous Requirements: Defines in The Following WayNishant PatilNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Document89 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Vijay PawarNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument19 pagesGD&Tpavan_joshi_5No ratings yet
- Composte TolDocument5 pagesComposte TolJuan Posada G100% (1)
- GD&T Glossary and Resource - GD&T Symbols and TermsDocument4 pagesGD&T Glossary and Resource - GD&T Symbols and TermsMohammed Adil100% (1)
- Tolerance Stack-Up Analysis: Consulting Training SoftwareDocument3 pagesTolerance Stack-Up Analysis: Consulting Training SoftwarenmjboseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancinganandparasuNo ratings yet
- Roundness and CircularityDocument16 pagesRoundness and CircularityKiran MadhavanNo ratings yet
- GD&T Self Evaluation Test - Difficulty Level - 9 (Of 10)Document27 pagesGD&T Self Evaluation Test - Difficulty Level - 9 (Of 10)dilipbangaruNo ratings yet
- GD&T: Theory To Reality: Mission StatementDocument67 pagesGD&T: Theory To Reality: Mission StatementCharlie Tej100% (1)
- ElementsDocument75 pagesElementsAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Me3072e L4Document61 pagesMe3072e L4hieuphamtrung21No ratings yet
- GD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedDocument77 pagesGD&T - All Slides - Chapters 1-11 - Q&A - AnimatedOmar RiosNo ratings yet
- GD&T Basics (Level-1)Document85 pagesGD&T Basics (Level-1)Thiyagu rajNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Wideband Antennas and Propagation: For Communications, Radar and ImagingFrom EverandUltra-Wideband Antennas and Propagation: For Communications, Radar and ImagingNo ratings yet
- 1028862asm 014Document4 pages1028862asm 014trandangbkNo ratings yet
- 1028828asm 013Document4 pages1028828asm 013trandangbkNo ratings yet
- Shot Peening Media ReviewDocument4 pagesShot Peening Media ReviewtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- 1028765asm 016Document4 pages1028765asm 016trandangbkNo ratings yet
- 1028577asm 010Document4 pages1028577asm 010trandangbkNo ratings yet
- 1028529asm 011Document4 pages1028529asm 011trandangbkNo ratings yet
- Oval Head Semi Tubular RivetsDocument1 pageOval Head Semi Tubular RivetstrandangbkNo ratings yet
- MMC, LMC, RFSDocument7 pagesMMC, LMC, RFStrandangbkNo ratings yet
- Datum Shift IllustratorDocument21 pagesDatum Shift IllustratortrandangbkNo ratings yet
- Position With Only One DatumDocument15 pagesPosition With Only One DatumtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- Position ToleranceDocument81 pagesPosition TolerancetrandangbkNo ratings yet
- Surface Tolerance CalculationDocument7 pagesSurface Tolerance CalculationtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- AbrreviationDocument33 pagesAbrreviationtrandangbkNo ratings yet
- DJ12 100Document2 pagesDJ12 100ParvezNo ratings yet
- Ngara Girls High School ReportDocument14 pagesNgara Girls High School ReportSimon GikonyoNo ratings yet
- Huba Control 604 - Pressure - SwitchDocument4 pagesHuba Control 604 - Pressure - SwitchNORODDINENo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument32 pagesLevels of OrganizationZayra GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Covalent BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Covalent BondingKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Unit 2 Electricity Student Progress SheetDocument6 pagesAQA Physics Unit 2 Electricity Student Progress SheetGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Analysis: Problems: I R R IDocument13 pagesAC Circuit Analysis: Problems: I R R IWenzy BorromeoNo ratings yet
- AN296285 BLDC Driver For Automotive Fuel PumpsDocument28 pagesAN296285 BLDC Driver For Automotive Fuel PumpslcisnydeksdtaujutlNo ratings yet
- GBT 8175-2008Document24 pagesGBT 8175-2008BUĞRANo ratings yet
- Cavitation of A Water Jet in WaterDocument82 pagesCavitation of A Water Jet in WaterAung KyiNo ratings yet
- IEEE - C37.04i - 1991 AC HV Circuit BreakersDocument3 pagesIEEE - C37.04i - 1991 AC HV Circuit BreakersSamir MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Semester AssignmentDocument7 pagesSemester AssignmentSulman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Grade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2018 English Medium Western ProvinceDocument8 pagesGrade 07 Science 2nd Term Test Paper 2018 English Medium Western ProvinceFawzar Sabir100% (1)
- BS 6500 Flexible CablesDocument60 pagesBS 6500 Flexible CablesPrafulla SupekarNo ratings yet
- Fire Test (EN13501-1)Document8 pagesFire Test (EN13501-1)Vinka PrintNo ratings yet
- PI&DمختصراتDocument2 pagesPI&DمختصراتMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Game Instructions CardsDocument26 pagesSchrodinger Game Instructions CardsAnonymous xmWYLiGvzNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument24 pagesProperties of FluidYash PatelNo ratings yet
- Sheet 7Document3 pagesSheet 7Mo EidNo ratings yet
- Automatic Load Sharing of Power Transformer Using MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesAutomatic Load Sharing of Power Transformer Using MicrocontrollerNEHA SOMANINo ratings yet
- Year 11 IGCSE Question PaperDocument17 pagesYear 11 IGCSE Question PaperMaitrey TelangNo ratings yet
- D3238Document3 pagesD3238HilmanHasrunNiamNo ratings yet
- DS/CFT Duality in Cosmology: Ramtin AmintaheriDocument81 pagesDS/CFT Duality in Cosmology: Ramtin AmintaherialiakouNo ratings yet
- Elec TechnDocument6 pagesElec TechnIsraelNo ratings yet
- AGES - Method Statement For PDADocument8 pagesAGES - Method Statement For PDAResearcherNo ratings yet
- Road Studs - Types, Requirement, and PlacementDocument7 pagesRoad Studs - Types, Requirement, and PlacementNoor Kamarul Baharin100% (2)
- PC Girder Class 10 - MistDocument264 pagesPC Girder Class 10 - MistnibirNo ratings yet
- Munck CraneDocument268 pagesMunck CraneEduardo OvalleNo ratings yet