Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 viewsData Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Data Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Uploaded by
Santhosh kumar KDijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path between nodes in a graph. It works by picking the unvisited vertex with the lowest distance and updating neighbor distances if shorter. Kruskal's algorithm finds a minimum spanning tree by selecting the lowest weight edge that connects trees without cycles. Prim's algorithm also finds a minimum spanning tree by growing a tree with the minimum weight edge connecting vertices not yet in the tree.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Prim's Algorithm: Rafael Nobleza Masallo CS501M Assignment - Desalgo 9-12-17Document3 pagesPrim's Algorithm: Rafael Nobleza Masallo CS501M Assignment - Desalgo 9-12-17Paeng kokoyNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Tree (Prim's and Kruskal's Algorithms)Document17 pagesMinimum Spanning Tree (Prim's and Kruskal's Algorithms)HANISH THARWANI 21BCE11631No ratings yet
- Prim 33Document1 pagePrim 33lonesarirNo ratings yet
- DS Module5Document28 pagesDS Module5Sreekesh GiriNo ratings yet
- Ads-Unit V PDFDocument11 pagesAds-Unit V PDFrajasekharv86No ratings yet
- Kruskal AlgoDocument8 pagesKruskal Algothakornikita001.nt10No ratings yet
- Graphs - DAADocument68 pagesGraphs - DAAD07Vaishnavi ShindeCENo ratings yet
- PATH FINDING - Dijkstra's Algorithm: Ravikiran Jaliparthi VenkatDocument6 pagesPATH FINDING - Dijkstra's Algorithm: Ravikiran Jaliparthi VenkatMimansha SharmaNo ratings yet
- DijkstraDocument4 pagesDijkstraLiana AndronescuNo ratings yet
- 20IS42 Module 3Document60 pages20IS42 Module 3madhuryat105No ratings yet
- ShowclassmstDocument17 pagesShowclassmstVijaya AzimuddinNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning TreesDocument24 pagesMinimum Spanning TreesTestNo ratings yet
- IanGravesMinimum Spanning TreesDocument25 pagesIanGravesMinimum Spanning TreesaadityakrjainNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path AlgorithmsDocument26 pagesShortest Path AlgorithmsZryan MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Algorithm U4 Answer KeyDocument27 pagesAlgorithm U4 Answer KeyVikram NairyNo ratings yet
- Lecture# 11 Shortest Path ProblemDocument19 pagesLecture# 11 Shortest Path ProblemShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path AlgorithmsDocument25 pagesShortest Path AlgorithmsZryan Muhammed100% (1)
- Greedy Technique Definition:: On Each Step, The Choice Made Must BeDocument14 pagesGreedy Technique Definition:: On Each Step, The Choice Made Must BePrateekMandiNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning TreeDocument11 pagesMinimum Spanning TreeAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- What Is Greedy Algorithm?Document4 pagesWhat Is Greedy Algorithm?Yuyun JoeNo ratings yet
- Ada MTE PresentationDocument20 pagesAda MTE Presentationanuraagkumar 24No ratings yet
- Kruskal's Algorithm: Graph Tree Search AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesKruskal's Algorithm: Graph Tree Search AlgorithmsMohanah JayakumaranNo ratings yet
- Kruskal PrintDocument18 pagesKruskal PrintAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument9 pagesShortest Path Dijkstra AlgorithmJC CarpioNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's Algorithm - WikipediaDocument10 pagesDijkstra's Algorithm - WikipediagjNo ratings yet
- Dijkstras AlgorithmDocument10 pagesDijkstras Algorithmpriyanshushawarn8183No ratings yet
- Lecture 26 (Minimum Spanning Tree)Document24 pagesLecture 26 (Minimum Spanning Tree)avinashNo ratings yet
- D1, L4 Graphs and NetworksDocument52 pagesD1, L4 Graphs and NetworksmokhtarppgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document43 pagesLecture 11varunsingh214761No ratings yet
- Greedy AlgorithmDocument28 pagesGreedy AlgorithmSyed Aoun AbbasNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Prep History of ScienceDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Prep History of ScienceMuntean Filip MihaiNo ratings yet
- Question # 1: What Are The Differences Between Bellman Ford's and Dijkstra's Algorithms?Document12 pagesQuestion # 1: What Are The Differences Between Bellman Ford's and Dijkstra's Algorithms?Devil PrinceNo ratings yet
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm - DP-23: Recommended: Please Solve It On "PRACTICE " First, Before Moving On To The SolutionDocument3 pagesBellman-Ford Algorithm - DP-23: Recommended: Please Solve It On "PRACTICE " First, Before Moving On To The SolutionPrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Tree ArticleDocument5 pagesMinimum Spanning Tree ArticleUnsaJawaidNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path Problem Is A Problem of Finding TheDocument15 pagesShortest Path Problem Is A Problem of Finding TheHemalatha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- DijkstraDocument5 pagesDijkstraLegesse SamuelNo ratings yet
- The Maximum Network Flow ProblemDocument10 pagesThe Maximum Network Flow ProblemRomar PanopioNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory AlgorithmsDocument19 pagesGraph Theory AlgorithmsLn Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Solution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmDocument5 pagesSolution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmRejithaVijayachandranNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument19 pagesDijkstra's AlgorithmAlexander Obi DavidsNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument13 pagesDijkstra's Algorithmjoseph676No ratings yet
- Exposed of Algorithmes in TGDocument2 pagesExposed of Algorithmes in TGMoh AmmedNo ratings yet
- DjkarDocument15 pagesDjkarDavid TemaelNo ratings yet
- Prims AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesPrims AlgorithmsnofeelingrahulNo ratings yet
- Graphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegeDocument61 pagesGraphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegesangeethaNo ratings yet
- Lec-15 Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument18 pagesLec-15 Dijkstra AlgorithmAlishba GondalNo ratings yet
- MCA Spanning Tree CODE 212Document8 pagesMCA Spanning Tree CODE 212souvik CNo ratings yet
- Graph Algorithms: Minimum - Cost Spanning TreeDocument10 pagesGraph Algorithms: Minimum - Cost Spanning TreeYesudasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AADocument13 pagesChapter 3 AAselemon GamoNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument13 pagesDijkstra AlgorithmLucasNo ratings yet
- Chinese Postman ProblemDocument15 pagesChinese Postman ProblemMithelesh KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?Document5 pagesWhat Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?akurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- Greedy Algorithm LectueNoteDocument33 pagesGreedy Algorithm LectueNotedagiNo ratings yet
- A Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph GDocument8 pagesA Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph GsaumyaNo ratings yet
- Spanning Trees: Introduction To AlgorithmsDocument69 pagesSpanning Trees: Introduction To AlgorithmsAsad-Ullah SheikhNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloDocument14 pages6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloJaxon RiegoNo ratings yet
- Shortest Routing Algorithm Analysis With Dijkstra's Algorithm and Bellman - FordDocument3 pagesShortest Routing Algorithm Analysis With Dijkstra's Algorithm and Bellman - FordSukarma PutraNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search: BFS PseudocodeDocument9 pagesBreadth First Search: BFS PseudocodeAchmad Hadzami SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Prim and Krushkal AlgorithmDocument4 pagesPrim and Krushkal AlgorithmakurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- Minimum Bounding Box: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Optimization in Computer VisionFrom EverandMinimum Bounding Box: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Optimization in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Linked List: Unit 1 - Part 4 Bca, NGMCDocument13 pagesData Structure Linked List: Unit 1 - Part 4 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 3 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument9 pagesData Structures: Unit 3 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 1 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument18 pagesData Structures: Unit 1 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Trees: Unit 2 - Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument10 pagesData Structures Trees: Unit 2 - Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Trees: Unit 2 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument9 pagesData Structures Trees: Unit 2 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument7 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Queue: Unit 1-Part 3 BCADocument10 pagesData Structure Queue: Unit 1-Part 3 BCASanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument7 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument8 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 4 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 4 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Hotel Booking DescriptionDocument3 pagesHotel Booking DescriptionSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- IT8711 CLOUD COMPUTING RecordDocument93 pagesIT8711 CLOUD COMPUTING RecordSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Discrete Topic in MathsDocument2 pagesDiscrete Topic in MathsShatabbdi SsinhaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Trees: Text Prim's AlgorithmDocument41 pagesMinimum Spanning Trees: Text Prim's AlgorithmsdawdwsqNo ratings yet
- COMP2521 Week 6 - Minimum Spanning TreesDocument24 pagesCOMP2521 Week 6 - Minimum Spanning TreesHysan DaxNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document14 pagesLec 1Coada CatalinNo ratings yet
- What Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?Document5 pagesWhat Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?akurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1 Kruskal's AlgorithmDocument5 pages3.4.1 Kruskal's Algorithmkollavivek_534195858No ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAbhinav TayadeNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Analizi 21-SlidesDocument13 pagesAlgoritma Analizi 21-Slidesslgnc2534No ratings yet
- Homework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2Document1 pageHomework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2AceNo ratings yet
- Kruskals AlgorithmDocument15 pagesKruskals AlgorithmJ SIRISHA DEVINo ratings yet
- Tut 4Document1 pageTut 4monu jangidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Kruskal's MST Algorithm: CLRS Chapter 23Document15 pagesLecture 11: Kruskal's MST Algorithm: CLRS Chapter 23Seaton HarnsNo ratings yet
- TD SpanningtreeDocument4 pagesTD SpanningtreeKarine DeschinkelNo ratings yet
- FdbdfgreDocument8 pagesFdbdfgreAnonymous 8oNe6jzNo ratings yet
- D1, L5 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsDocument18 pagesD1, L5 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsmokhtarppgNo ratings yet
- Tree-Width and Circumference of Graphs: Etienne BirmeleDocument2 pagesTree-Width and Circumference of Graphs: Etienne BirmeleDaniel GregorioNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document6 pagesNull 1Srajan SolankiNo ratings yet
- Prims and Kruskals AlgorithmDocument15 pagesPrims and Kruskals AlgorithmBharadwajaGllNo ratings yet
- Topics: Minimum Spanning TreesDocument33 pagesTopics: Minimum Spanning TreesAnonymous s8OrImv8No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1MONA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Reverse Delete Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeDocument3 pagesReverse Delete Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeHasibul IslamNo ratings yet
- DMS MSE Question Bank - 21-22Document3 pagesDMS MSE Question Bank - 21-22Rohan YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document43 pagesModule 7Kshitiz GoyalNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Trees: (Some Material Adapted From Slides by Peter Lee)Document23 pagesMinimum Spanning Trees: (Some Material Adapted From Slides by Peter Lee)mdhuq1No ratings yet
- Math 38. Graph Theory. Spring 2014 Solutions To Homework 4Document2 pagesMath 38. Graph Theory. Spring 2014 Solutions To Homework 4sivaNo ratings yet
- K-Tuple Domination in GraphsDocument6 pagesK-Tuple Domination in GraphsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Bipartite GraphsDocument2 pagesBipartite Graphskumbhakararjun92No ratings yet
- The L21-Labeling Problem On GraphsDocument16 pagesThe L21-Labeling Problem On GraphsMair A-WNo ratings yet
- Bahria University, Islamabad Campus Department of Computer Sciences Discrete Math Assignment 1Document2 pagesBahria University, Islamabad Campus Department of Computer Sciences Discrete Math Assignment 1BurhanNo ratings yet
- MST Kruskals PrimsDocument18 pagesMST Kruskals PrimsRanil FernandoNo ratings yet
Data Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Data Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Uploaded by
Santhosh kumar K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views10 pagesDijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path between nodes in a graph. It works by picking the unvisited vertex with the lowest distance and updating neighbor distances if shorter. Kruskal's algorithm finds a minimum spanning tree by selecting the lowest weight edge that connects trees without cycles. Prim's algorithm also finds a minimum spanning tree by growing a tree with the minimum weight edge connecting vertices not yet in the tree.
Original Description:
Original Title
DS 3.4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path between nodes in a graph. It works by picking the unvisited vertex with the lowest distance and updating neighbor distances if shorter. Kruskal's algorithm finds a minimum spanning tree by selecting the lowest weight edge that connects trees without cycles. Prim's algorithm also finds a minimum spanning tree by growing a tree with the minimum weight edge connecting vertices not yet in the tree.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views10 pagesData Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Data Structures: Unit III - Part 4 Bca, NGMC
Uploaded by
Santhosh kumar KDijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path between nodes in a graph. It works by picking the unvisited vertex with the lowest distance and updating neighbor distances if shorter. Kruskal's algorithm finds a minimum spanning tree by selecting the lowest weight edge that connects trees without cycles. Prim's algorithm also finds a minimum spanning tree by growing a tree with the minimum weight edge connecting vertices not yet in the tree.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Data Structures
Unit III – Part 4
BCA, NGMC
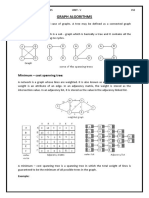
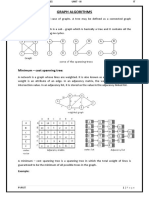
Dijkstra's algorithm
• Dijkstra's algorithm (or Dijkstra's Shortest
Path First algorithm, SPF algorithm) is an
algorithm for finding the shortest paths
between nodes in a graph, which may
represent, for example, road networks. It was
conceived by computer scientist Edsger W.
Dijkstra in 1956.
• This algorithm is used to find the shortest path
between two given nodes.
•Dijkstra's algorithm to
find the shortest path
between a and b.
•It picks the unvisited
vertex with the low
distance, calculates the
distance through it to
each unvisited neighbor,
and updates the
neighbor's distance if
smaller.
•Mark visited (set to red)
when done with
neighbors.
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
• A minimum spanning tree (MST) or minimum
weight spanning tree is a subset of the edges
of a connected, edge-weighted undirected
graph that connects all the vertices together,
without any cycles and with the minimum
possible total edge weight.
• That is, it is a spanning tree whose sum of
edge weights is as small as possible.
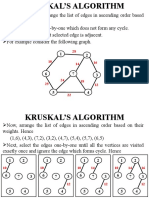
Kruskal's algorithm
• Kruskal's algorithm is a
minimum-spanning-tree algorithm which finds
an edge of the least possible weight that
connects any two trees in the forest.
• It is a greedy algorithm in graph theory as it
finds a minimum spanning tree for a
connected weighted graph adding increasing
cost arcs at each step.
Method
AD and CE are the shortest edges,
with length 5, and AD has been
arbitrarily chosen, so it is highlighted.
CE is now the shortest edge that
does not form a cycle, with length
5, so it is highlighted as the second
edge.
The next edge, DF with length 6, is
highlighted using much the same
method.
The next-shortest edges are AB and BE,
both with length 7. AB is chosen
arbitrarily, and is highlighted. The
edge BD has been highlighted in red,
because there already exists a path (in
green) between B and D, so it would form
a cycle (ABD) if it were chosen.
The process continues to highlight
the next-smallest edge, BE with
length 7. Many more edges are
highlighted in red at this
stage: BC because it would form the
loop BCE, DE because it would form
the loop DEBA, and FE because it
would form FEBAD.
Finally, the process finishes with the
edge EG of length 9, and the
minimum spanning tree is found.
Prime’s Algorithm
• Prim's algorithm is a minimum spanning tree algorithm that
takes a graph as input and finds the subset of the edges of
that graph which
– form a tree that includes every vertex
– has the minimum sum of weights among all the trees that can be
formed from the graph
• Like Kruskal’s algorithm, Prim’s algorithm is also a
Greedy algorithm.
• The algorithm was developed in 1930
by Czech mathematician Vojtech Jarnik and later
rediscovered and republished by computer scientists
Robert C. Prim in 1957.
Algorithm
1. Initialize a tree with a single vertex, chosen
arbitrarily from the graph.
2. Grow the tree by one edge: of the edges that
connect the tree to vertices not yet in the
tree, find the minimum-weight edge, and
transfer it to the tree.
3. Repeat step 2 (until all vertices are in the
tree).
You might also like
- Prim's Algorithm: Rafael Nobleza Masallo CS501M Assignment - Desalgo 9-12-17Document3 pagesPrim's Algorithm: Rafael Nobleza Masallo CS501M Assignment - Desalgo 9-12-17Paeng kokoyNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Tree (Prim's and Kruskal's Algorithms)Document17 pagesMinimum Spanning Tree (Prim's and Kruskal's Algorithms)HANISH THARWANI 21BCE11631No ratings yet
- Prim 33Document1 pagePrim 33lonesarirNo ratings yet
- DS Module5Document28 pagesDS Module5Sreekesh GiriNo ratings yet
- Ads-Unit V PDFDocument11 pagesAds-Unit V PDFrajasekharv86No ratings yet
- Kruskal AlgoDocument8 pagesKruskal Algothakornikita001.nt10No ratings yet
- Graphs - DAADocument68 pagesGraphs - DAAD07Vaishnavi ShindeCENo ratings yet
- PATH FINDING - Dijkstra's Algorithm: Ravikiran Jaliparthi VenkatDocument6 pagesPATH FINDING - Dijkstra's Algorithm: Ravikiran Jaliparthi VenkatMimansha SharmaNo ratings yet
- DijkstraDocument4 pagesDijkstraLiana AndronescuNo ratings yet
- 20IS42 Module 3Document60 pages20IS42 Module 3madhuryat105No ratings yet
- ShowclassmstDocument17 pagesShowclassmstVijaya AzimuddinNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning TreesDocument24 pagesMinimum Spanning TreesTestNo ratings yet
- IanGravesMinimum Spanning TreesDocument25 pagesIanGravesMinimum Spanning TreesaadityakrjainNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path AlgorithmsDocument26 pagesShortest Path AlgorithmsZryan MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Algorithm U4 Answer KeyDocument27 pagesAlgorithm U4 Answer KeyVikram NairyNo ratings yet
- Lecture# 11 Shortest Path ProblemDocument19 pagesLecture# 11 Shortest Path ProblemShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path AlgorithmsDocument25 pagesShortest Path AlgorithmsZryan Muhammed100% (1)
- Greedy Technique Definition:: On Each Step, The Choice Made Must BeDocument14 pagesGreedy Technique Definition:: On Each Step, The Choice Made Must BePrateekMandiNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning TreeDocument11 pagesMinimum Spanning TreeAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- What Is Greedy Algorithm?Document4 pagesWhat Is Greedy Algorithm?Yuyun JoeNo ratings yet
- Ada MTE PresentationDocument20 pagesAda MTE Presentationanuraagkumar 24No ratings yet
- Kruskal's Algorithm: Graph Tree Search AlgorithmsDocument16 pagesKruskal's Algorithm: Graph Tree Search AlgorithmsMohanah JayakumaranNo ratings yet
- Kruskal PrintDocument18 pagesKruskal PrintAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument9 pagesShortest Path Dijkstra AlgorithmJC CarpioNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's Algorithm - WikipediaDocument10 pagesDijkstra's Algorithm - WikipediagjNo ratings yet
- Dijkstras AlgorithmDocument10 pagesDijkstras Algorithmpriyanshushawarn8183No ratings yet
- Lecture 26 (Minimum Spanning Tree)Document24 pagesLecture 26 (Minimum Spanning Tree)avinashNo ratings yet
- D1, L4 Graphs and NetworksDocument52 pagesD1, L4 Graphs and NetworksmokhtarppgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document43 pagesLecture 11varunsingh214761No ratings yet
- Greedy AlgorithmDocument28 pagesGreedy AlgorithmSyed Aoun AbbasNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Prep History of ScienceDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Prep History of ScienceMuntean Filip MihaiNo ratings yet
- Question # 1: What Are The Differences Between Bellman Ford's and Dijkstra's Algorithms?Document12 pagesQuestion # 1: What Are The Differences Between Bellman Ford's and Dijkstra's Algorithms?Devil PrinceNo ratings yet
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm - DP-23: Recommended: Please Solve It On "PRACTICE " First, Before Moving On To The SolutionDocument3 pagesBellman-Ford Algorithm - DP-23: Recommended: Please Solve It On "PRACTICE " First, Before Moving On To The SolutionPrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Tree ArticleDocument5 pagesMinimum Spanning Tree ArticleUnsaJawaidNo ratings yet
- Shortest Path Problem Is A Problem of Finding TheDocument15 pagesShortest Path Problem Is A Problem of Finding TheHemalatha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- DijkstraDocument5 pagesDijkstraLegesse SamuelNo ratings yet
- The Maximum Network Flow ProblemDocument10 pagesThe Maximum Network Flow ProblemRomar PanopioNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory AlgorithmsDocument19 pagesGraph Theory AlgorithmsLn Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Solution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmDocument5 pagesSolution-: Prim's Algorithm Kruskal's AlgorithmRejithaVijayachandranNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument19 pagesDijkstra's AlgorithmAlexander Obi DavidsNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDocument13 pagesDijkstra's Algorithmjoseph676No ratings yet
- Exposed of Algorithmes in TGDocument2 pagesExposed of Algorithmes in TGMoh AmmedNo ratings yet
- DjkarDocument15 pagesDjkarDavid TemaelNo ratings yet
- Prims AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesPrims AlgorithmsnofeelingrahulNo ratings yet
- Graphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegeDocument61 pagesGraphs: Presented By, M.Sangeetha, Ap/Cse, Kongu Engineering CollegesangeethaNo ratings yet
- Lec-15 Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument18 pagesLec-15 Dijkstra AlgorithmAlishba GondalNo ratings yet
- MCA Spanning Tree CODE 212Document8 pagesMCA Spanning Tree CODE 212souvik CNo ratings yet
- Graph Algorithms: Minimum - Cost Spanning TreeDocument10 pagesGraph Algorithms: Minimum - Cost Spanning TreeYesudasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AADocument13 pagesChapter 3 AAselemon GamoNo ratings yet
- Dijkstra AlgorithmDocument13 pagesDijkstra AlgorithmLucasNo ratings yet
- Chinese Postman ProblemDocument15 pagesChinese Postman ProblemMithelesh KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?Document5 pagesWhat Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?akurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- Greedy Algorithm LectueNoteDocument33 pagesGreedy Algorithm LectueNotedagiNo ratings yet
- A Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph GDocument8 pagesA Spanning Tree Is A Subset of Graph GsaumyaNo ratings yet
- Spanning Trees: Introduction To AlgorithmsDocument69 pagesSpanning Trees: Introduction To AlgorithmsAsad-Ullah SheikhNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloDocument14 pages6.1 Spanning Trees - AlfredBarbosa - MarkEmanDigdigan - ManaloJaxon RiegoNo ratings yet
- Shortest Routing Algorithm Analysis With Dijkstra's Algorithm and Bellman - FordDocument3 pagesShortest Routing Algorithm Analysis With Dijkstra's Algorithm and Bellman - FordSukarma PutraNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search: BFS PseudocodeDocument9 pagesBreadth First Search: BFS PseudocodeAchmad Hadzami SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Prim and Krushkal AlgorithmDocument4 pagesPrim and Krushkal AlgorithmakurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- Minimum Bounding Box: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Optimization in Computer VisionFrom EverandMinimum Bounding Box: Unveiling the Power of Spatial Optimization in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Linked List: Unit 1 - Part 4 Bca, NGMCDocument13 pagesData Structure Linked List: Unit 1 - Part 4 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 3 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument9 pagesData Structures: Unit 3 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 1 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument18 pagesData Structures: Unit 1 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Trees: Unit 2 - Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument10 pagesData Structures Trees: Unit 2 - Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Trees: Unit 2 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument9 pagesData Structures Trees: Unit 2 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument7 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Queue: Unit 1-Part 3 BCADocument10 pagesData Structure Queue: Unit 1-Part 3 BCASanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument7 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 4 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument8 pagesData Structures: Unit 4 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 2 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 2 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 1 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 1 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 3 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 3 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: Unit 5 Part 4 Bca, NGMCDocument6 pagesData Structures: Unit 5 Part 4 Bca, NGMCSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Hotel Booking DescriptionDocument3 pagesHotel Booking DescriptionSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- IT8711 CLOUD COMPUTING RecordDocument93 pagesIT8711 CLOUD COMPUTING RecordSanthosh kumar KNo ratings yet
- Discrete Topic in MathsDocument2 pagesDiscrete Topic in MathsShatabbdi SsinhaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Trees: Text Prim's AlgorithmDocument41 pagesMinimum Spanning Trees: Text Prim's AlgorithmsdawdwsqNo ratings yet
- COMP2521 Week 6 - Minimum Spanning TreesDocument24 pagesCOMP2521 Week 6 - Minimum Spanning TreesHysan DaxNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document14 pagesLec 1Coada CatalinNo ratings yet
- What Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?Document5 pagesWhat Is Spanning Tree? What Are The Properties and Applications of Spanning Tree?akurathikotaiahNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1 Kruskal's AlgorithmDocument5 pages3.4.1 Kruskal's Algorithmkollavivek_534195858No ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument6 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAbhinav TayadeNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Analizi 21-SlidesDocument13 pagesAlgoritma Analizi 21-Slidesslgnc2534No ratings yet
- Homework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2Document1 pageHomework Solutions - Unit 4: Chapter 23: Exercise 23.1-2AceNo ratings yet
- Kruskals AlgorithmDocument15 pagesKruskals AlgorithmJ SIRISHA DEVINo ratings yet
- Tut 4Document1 pageTut 4monu jangidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11: Kruskal's MST Algorithm: CLRS Chapter 23Document15 pagesLecture 11: Kruskal's MST Algorithm: CLRS Chapter 23Seaton HarnsNo ratings yet
- TD SpanningtreeDocument4 pagesTD SpanningtreeKarine DeschinkelNo ratings yet
- FdbdfgreDocument8 pagesFdbdfgreAnonymous 8oNe6jzNo ratings yet
- D1, L5 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsDocument18 pagesD1, L5 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsmokhtarppgNo ratings yet
- Tree-Width and Circumference of Graphs: Etienne BirmeleDocument2 pagesTree-Width and Circumference of Graphs: Etienne BirmeleDaniel GregorioNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document6 pagesNull 1Srajan SolankiNo ratings yet
- Prims and Kruskals AlgorithmDocument15 pagesPrims and Kruskals AlgorithmBharadwajaGllNo ratings yet
- Topics: Minimum Spanning TreesDocument33 pagesTopics: Minimum Spanning TreesAnonymous s8OrImv8No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document3 pagesProblem Set 1MONA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Reverse Delete Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeDocument3 pagesReverse Delete Algorithm For Minimum Spanning TreeHasibul IslamNo ratings yet
- DMS MSE Question Bank - 21-22Document3 pagesDMS MSE Question Bank - 21-22Rohan YadavNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document43 pagesModule 7Kshitiz GoyalNo ratings yet
- Minimum Spanning Trees: (Some Material Adapted From Slides by Peter Lee)Document23 pagesMinimum Spanning Trees: (Some Material Adapted From Slides by Peter Lee)mdhuq1No ratings yet
- Math 38. Graph Theory. Spring 2014 Solutions To Homework 4Document2 pagesMath 38. Graph Theory. Spring 2014 Solutions To Homework 4sivaNo ratings yet
- K-Tuple Domination in GraphsDocument6 pagesK-Tuple Domination in GraphsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Bipartite GraphsDocument2 pagesBipartite Graphskumbhakararjun92No ratings yet
- The L21-Labeling Problem On GraphsDocument16 pagesThe L21-Labeling Problem On GraphsMair A-WNo ratings yet
- Bahria University, Islamabad Campus Department of Computer Sciences Discrete Math Assignment 1Document2 pagesBahria University, Islamabad Campus Department of Computer Sciences Discrete Math Assignment 1BurhanNo ratings yet
- MST Kruskals PrimsDocument18 pagesMST Kruskals PrimsRanil FernandoNo ratings yet