Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human
The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human
Uploaded by
Kurt Ivan Gonzales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pagesThe endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones which regulate processes throughout the body. The major glands include the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain, thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck, pancreas behind the stomach, adrenal glands above the kidneys, ovaries in women and testes in men, and the pineal gland in the brain. These glands work together to control growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction and other crucial bodily functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
The Endocrine System and Glands of the Human
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones which regulate processes throughout the body. The major glands include the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain, thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck, pancreas behind the stomach, adrenal glands above the kidneys, ovaries in women and testes in men, and the pineal gland in the brain. These glands work together to control growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction and other crucial bodily functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views10 pagesThe Endocrine System and Glands of The Human
The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human
Uploaded by
Kurt Ivan GonzalesThe endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones which regulate processes throughout the body. The major glands include the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain, thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck, pancreas behind the stomach, adrenal glands above the kidneys, ovaries in women and testes in men, and the pineal gland in the brain. These glands work together to control growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction and other crucial bodily functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
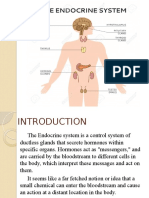
The Endocrine System and Glands of
the Human Body
What Is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a network of glands in your body
that make the hormones that help cells talk to each other.
They’re responsible for almost every cell, organ, and
function in your body.
If your endocrine system isn't healthy, you might have
problems developing during puberty, getting pregnant, or
managing stress.
You also might gain weight easily, have weak bones, or lack
energy because too much sugar stays in your blood instead
of moving into your cells where it's needed for energy.
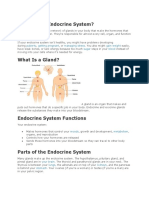
What Is a Gland?
A gland is an organ that
makes and puts out hormones
that do a specific job in your
body.
Endocrine and exocrine glands
release the substances they
make into your bloodstream.
Endocrine System Functions
Your endocrine system:
-Makes hormones that control your moods, growth and
development, metabolism, organs, and reproduction
-Controls how your hormones are released
-Sends those hormones into your bloodstream so they can
travel to other body parts.
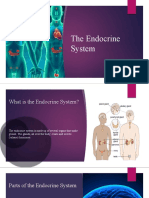
Parts of the Endocrine System thymus is between your lungs
Many glands make up the endocrine
system. adrenal are on top of your
kidneys
hypothalamus,
pituitary gland pancreas is behind your
FOUND IN BRAIN stomach.
pineal gland
ovaries (if you're a woman) or
thyroid testes (if you're a man) are in
parathyroid glands NECK your pelvic region.
•Hypothalamus. This organ connects your
endocrine system with your
nervous system.
•Its main job is to tell your pituitary gland
to start or stop making hormones.
•Pituitary gland.
•This is your endocrine system’s master gland.
•It uses information it gets from your brain to tell other glands in your
body what to do.
• It makes many important hormones,
prolactin •which helps including growth
breastfeeding moms hormone
make milk; antidiuretic which controls blood
thyroid-stimulating which stimulates the hormone(ADH) pressure helps control
hormone (TSH), production and secretion (vasopressin), body water balance
of thyroid hormones through its effect on
oxytocin which helps in milk the kidney
ejection during breast corticotropin /ACTH: which stimulates the
feeding Adrenocorticotrophic adrenal gland to make
luteinizing hormone which manages estrogen hormone certain hormones
in women and
testosterone in men
•Pineal gland. It makes a chemical called melatonin that helps your
body get ready to go to sleep.
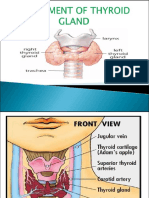
•Thyroid gland. This gland makes thyroid hormone, which controls
your growth and metabolism. If this gland doesn't make enough (a
condition called hypothyroidism), everything happens more slowly.
Your heart rate might slow down. You could get constipated. And you
might gain weight. If it makes too much (hyperthyroidism),
everything speeds up. Your heart might race. You could have diarrhea
. And you might lose weight without trying. The thyroid gland also
produces the hormone calcitonin, which may contribute to bone
strength by helping calcium to be incorporated into bone.
•Parathyroid. This is a set of four small glands behind your thyroid. They play
a role in bone health. The glands control your levels of calcium and
phosphorus.
•Thymus. This gland makes white blood cells called T-lymphocytes that fight
infection and are crucial as a child's immune system develops. The thymus
starts to shrink after puberty.
•Adrenals. Best known for making the "fight or flight" hormone adrenaline
(also called epinephrine), these two glands also make hormones called
corticosteroids. They affect your metabolism heart rate, oxygen intake, blood
flow, and sexual function, among other things.
•Pancreas. This organ is part of both your digestive and endocrine
systems. It makes digestive enzymes that break down food. It also
makes the hormones insulin and glucagon. These ensure you have the
right amount of sugar in your bloodstream and your cells.
•If you don't make insulin, which is the case for people with
type 1 diabetes, your blood sugar levels can get dangerously high. In
type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually makes some insulin but not
enough.
•Ovaries. In women, these organs make estrogen and progesterone.
These hormones help develop breasts at puberty, regulate the
menstrual cycle, and support a pregnancy.
•Testes. In men, the testes make testosterone. It helps them grow facial
and body hair at puberty. It also tells the penis to grow larger and plays
a role in making sperm.
You might also like
- Kulkarni Shilpa A.Document148 pagesKulkarni Shilpa A.MSKCNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesEndocrine SystemPunong Grande NHS Banga NHS Annex (R XII - South Cotabato)No ratings yet
- Endocrine!!!!!!!Document33 pagesEndocrine!!!!!!!Ungays ungaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine System and Glands of The Human BodyFungo JasmineNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine SystemAishwarya WilliamsNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine SystemanastaciasibikinaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemKryztoff AlambatinNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemkwatsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemThatsIan100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine Systemotienoomondi89No ratings yet
- Adama KanuDocument41 pagesAdama KanuAlie TholleyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PDFDocument113 pagesEndocrine System PDFfayeleechaiyapornkulNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument51 pagesHomeostasisKarla HyltonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 4-The Endocrine SystemkreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Anfis EndokrinDocument14 pagesAnfis Endokrinyolanda merinskyNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument24 pagesEndocrineCJ 1517No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument78 pagesEndocrine Systemrealwaseelarh123No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKirsten GomezNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Document13 pagesDiabetes 2nd Check Edited 5Catiereign VerdeNo ratings yet
- Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils PresentationDocument30 pagesHormones and Young Living Essential Oils Presentationapi-150039816100% (9)
- Quarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Document34 pagesQuarter 3 Week 1 Module 1Juliana Sophia BungalsoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Group #9Document12 pagesEndocrine System: Group #9Kier AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching First Law of Motion G8Document34 pagesDemo Teaching First Law of Motion G8Neil VelascoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesGhezyl LascoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 PPT 1Document58 pagesScience 10 PPT 1Sionny GandicelaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument48 pagesEndocrine SystemSeptember Neckohle AlunanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine SystemBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Glands: Subject AboutDocument17 pagesAdrenal Glands: Subject AboutHareth mohammad mahmod NawajaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemAliaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesScience 6 Endocrine Systemcharmaine_olivia_1100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine Systemsalmeohenzgabry100% (1)
- Lesson 10 Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesLesson 10 Endocrine SystemBai Donna S. AlimanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument5 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine SystemReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Human Bodies Only For FemaleDocument26 pagesHuman Bodies Only For FemaleArnold S DumapatNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument9 pagesHealthNadia NoorNo ratings yet
- Exposicion InglesDocument6 pagesExposicion InglesManuel FLORESNo ratings yet
- Different Glands of The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesDifferent Glands of The Endocrine SystemNovie Roycell Fernandez RueloNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Glands, Hormones, and Functions (Hypothalamus-Pancreas)Document31 pagesEndocrine System: Glands, Hormones, and Functions (Hypothalamus-Pancreas)Ace Vincent LunaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Lesson 1Document44 pagesThe Endocrine System Lesson 1Heaven Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System LessonDocument47 pagesEndocrine System LessonMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument17 pagesHuman PhysiologySharanya BasakNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ReportDocument21 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM ReportAdelfa LibanonNo ratings yet
- Loi 1Document26 pagesLoi 1nivedita.warrierNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument20 pagesEndocrine Systemchankatrina011No ratings yet
- Anatomy: Pineal GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy: Pineal GlandJoshua LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesEndocrine SystemAtteya Mogote AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands and HormonesDocument6 pagesEndocrine Glands and HormoneshaileyNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Document5 pagesMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Aries SungaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument15 pagesEndocrineapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Physiology 3 ExercisesDocument21 pagesPhysiology 3 ExercisesLeo II LacadenNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System PDFDocument27 pagesThe Endocrine System PDFpratiksha.bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument29 pagesEndocrine SystemNiño Adan CadagNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reference ReportingDocument16 pagesPharma Reference ReportingMa. Andrea B. PALOMONo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesEndocrine SystemYenny AcostaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Group 6Document43 pagesEndocrine System: Group 6Redona Audrey RoseNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument24 pagesEndocrine Systempromisefo65No ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- ReportDocument3 pagesReportShams BlitzerNo ratings yet
- UNIT13 CompressedDocument27 pagesUNIT13 Compressedemerald CasinilloNo ratings yet
- 1D - Thyroid Gland AssessmentDocument35 pages1D - Thyroid Gland AssessmentSadeem AbbasNo ratings yet
- Congenital HypothyroidismDocument5 pagesCongenital HypothyroidismGuia Dolor Denosta100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CushingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of CushingAj MacotoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesThyroid StormAnjelika Eurelle Caliboso MapiliNo ratings yet
- J. O. Ogunbiyi Department of Pathology University College Hospital Ibadan, NigeriaDocument13 pagesJ. O. Ogunbiyi Department of Pathology University College Hospital Ibadan, Nigeriaibnbasheer100% (3)
- Dr. Harsinen SubjectDocument222 pagesDr. Harsinen SubjectFaridah LailiNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Document33 pagesEndocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15 Endocrinology - Lecture Notes 12,13,14,15Omed Zarifi100% (1)
- Primary HyperparathyroidismDocument5 pagesPrimary HyperparathyroidismAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDocument21 pagesHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesCh-2 Human ReproductionShivam Kumar100% (1)
- Dental Management in Thyroid PatientDocument8 pagesDental Management in Thyroid PatientSidhartha KumarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of HormonMuhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Gonadotropin Releasing HormoneDocument9 pagesGonadotropin Releasing HormoneNTA UGC-NETNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyAliah PanondiNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle: Sevag OuzounianDocument20 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle: Sevag OuzounianBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- G 10 Biology, 6th Work Sheet On Endocrine Glands and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesG 10 Biology, 6th Work Sheet On Endocrine Glands and HomeostasishannahNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disorder in Chusing SyndromeDocument18 pagesMetabolic Disorder in Chusing Syndromeronald marbunNo ratings yet
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone: Glycoprotein Hormones, Alpha PolypeptideDocument6 pagesFollicle-Stimulating Hormone: Glycoprotein Hormones, Alpha PolypeptideNTA UGC-NETNo ratings yet
- FT3Document26 pagesFT3Florea RodicaNo ratings yet
- MiliariasisDocument4 pagesMiliariasisperpesanan100% (1)
- Final: LPL - Suvprabhat Pathology Lab Near Hospitsl Chowk (In Front of Zonal Hospital), Janakpur NepalDocument2 pagesFinal: LPL - Suvprabhat Pathology Lab Near Hospitsl Chowk (In Front of Zonal Hospital), Janakpur NepalAjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of SecretionDocument14 pagesPhysiology of Secretionrozha100% (2)
- Nuclear Thyroid - DR Siegel 2017Document414 pagesNuclear Thyroid - DR Siegel 2017AHNo ratings yet
- Med Surg EndocrineDocument13 pagesMed Surg EndocrineTeresa TorreonNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Endocrine DisordersDocument33 pagesPediatrics Endocrine DisordersfatimaNo ratings yet
- Hipertiroid Guideline, ATADocument54 pagesHipertiroid Guideline, ATAHashini VjkmrNo ratings yet
- Calcium Metabolism: Preparation byDocument18 pagesCalcium Metabolism: Preparation byAbhijeet KanjeNo ratings yet