Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Background Case Description
Background Case Description
Uploaded by
Arli Surya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageA 65-year-old male presented with low back pain radiating to his lumbar region for 6 months. MRI revealed a mass in his lumbar region. He underwent lumbar stabilization decompression and removal of the tumor via anterior approach. Pathology revealed a low-grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) positive for S100. MPNST often develops in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 from benign plexiform neurofibromas. Definitive diagnosis requires histopathologic examination and imaging like MRI/FDG-PET. Surgical resection aims to achieve negative margins and prognosis depends on factors like metastasis, grade, size, location, margins, and presence of NF1.
Original Description:
Original Title
RI.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA 65-year-old male presented with low back pain radiating to his lumbar region for 6 months. MRI revealed a mass in his lumbar region. He underwent lumbar stabilization decompression and removal of the tumor via anterior approach. Pathology revealed a low-grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) positive for S100. MPNST often develops in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 from benign plexiform neurofibromas. Definitive diagnosis requires histopathologic examination and imaging like MRI/FDG-PET. Surgical resection aims to achieve negative margins and prognosis depends on factors like metastasis, grade, size, location, margins, and presence of NF1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBackground Case Description
Background Case Description
Uploaded by
Arli SuryaA 65-year-old male presented with low back pain radiating to his lumbar region for 6 months. MRI revealed a mass in his lumbar region. He underwent lumbar stabilization decompression and removal of the tumor via anterior approach. Pathology revealed a low-grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) positive for S100. MPNST often develops in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 from benign plexiform neurofibromas. Definitive diagnosis requires histopathologic examination and imaging like MRI/FDG-PET. Surgical resection aims to achieve negative margins and prognosis depends on factors like metastasis, grade, size, location, margins, and presence of NF1.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour
A Case Reports
Rico Ikhsani1 , Roni Eka Saputra2
1
General Surgery Resident Faculty of Medicine Andalas University – Dr. M. Djamil Hospital
2
Orthopedy and Traumatology Department Staff Faculty of Medicine Andalas University – Dr. M. Djamil Hospital
BACKGROUND CASE DESCRIPTION
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor A 65-year-old male with symptomps low back pain
(MPNST) is a locally aggressive soft for 6 months. Pain was radiate from lumbar joint
tissue sarcoma. It is characterized by especially when walking or when bending down.
Physical examination on thoracolumbar region
differen-tiation of the nerve sheath and found limitation of joint motion. On a radiological
has a high tendency to metastasize. In imaging, MRI study have shown mass on lumbar
addition, MPNST often accompanies region. Patient were assessed to lumbal
adults with neurofibroma type 1 (NF1) stabilitation decompression following removal
and usually develops from benign tumor with anterior approach. Pathology anatomy
plexiform neurofibroma. examination showed a MPNST Low Grade with
S100 (+).
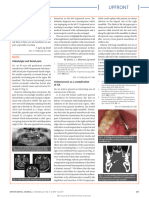
DOCUMENTATION
DISCUSSION CONCLUSION
MPNST is a malignancy that often presents with
neurofibroma type 1. Clinical manifestations in
MPNST are dependent on tumor location and
invasion or compression of the tumor mass to the Patients with neurofibroma type 1 who have a
nerve plexus will cause neurological symptoms. significantly enlarged mass that was
Histopatho-logic examination is required in the previously asymptomatic should be suspected
definitive diagnosis in addition to MRI and FDG-PET. of malignancy. In addition to mass
The definitive management of MPNST is by surgical enlargement, patients usually complain of
resection, where surgery aims to achieve negative paresthesias, pain, weakness, and local
surgical margins. The prognosis of MPNST is
influenced by several things such as the presence or
neurologic deficits.
absence of metastasis, tumor grade, size, location,
surgical margins, and the presence of NF1.
You might also like
- Introduction To Orthopaedic OncologyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Orthopaedic OncologyKikiMaria100% (1)
- Mock Exam 1-50Document7 pagesMock Exam 1-50mike_steven12No ratings yet
- Multimodality Imaging For Malignant Transformation Assessment Inneurofibromatosis Type 1 2167 7964 1000e135Document2 pagesMultimodality Imaging For Malignant Transformation Assessment Inneurofibromatosis Type 1 2167 7964 1000e135Usman Agus PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions in Foot and Ankle Foo and RabyDocument25 pagesTumors and Tumor-Like Lesions in Foot and Ankle Foo and RabyICNo ratings yet
- SNP Envolvimento em Doentes Com Neoplasia Lancet 2007Document12 pagesSNP Envolvimento em Doentes Com Neoplasia Lancet 2007Gonçalo CabralNo ratings yet
- EPOSTER PABI Dr. Defri HeryadiDocument1 pageEPOSTER PABI Dr. Defri HeryadiSeptia Pristi RahmahNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve TumorsDocument33 pagesPeripheral Nerve TumorsMariah BasemNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of An Appendiceal Neurofibroma in A Neurofibromatosis-1 Patient Case ReviewDocument8 pagesSurgical Management of An Appendiceal Neurofibroma in A Neurofibromatosis-1 Patient Case ReviewJack PierNo ratings yet
- Osteoradionecrosis of The Upper Cervical Spine - MR Imaging Following Radiotherapy For Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaDocument7 pagesOsteoradionecrosis of The Upper Cervical Spine - MR Imaging Following Radiotherapy For Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaakreditasiNo ratings yet
- Npaa 051Document7 pagesNpaa 051Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- The Long Term Outcome After Resection Of.20 PDFDocument9 pagesThe Long Term Outcome After Resection Of.20 PDFDragos IftimieNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookDocument6 pagesVeterinary Oncology, A Short TextbookMacarena Beatriz Piña ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Sca IDocument8 pagesSca IAlfredo Enrique Marin AliagaNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Multiple Benign Schwannomas of Left Foot A Case ReportDocument7 pagesRecurrent Multiple Benign Schwannomas of Left Foot A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Current Diagnostic Criteria and Advances in MRI DiagnosticsDocument5 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Current Diagnostic Criteria and Advances in MRI DiagnosticsGeorgios StathisNo ratings yet
- Orbital Peripheral Nerve SheathDocument15 pagesOrbital Peripheral Nerve SheathChavdarNo ratings yet
- Spindle Cell Sarcoma of The Vagus Nerve Presenting As A Neck Lump - Case ReportDocument2 pagesSpindle Cell Sarcoma of The Vagus Nerve Presenting As A Neck Lump - Case Reportahmed_ateegNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors - A Review of Current and Future Treatment StrategiesDocument10 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors - A Review of Current and Future Treatment StrategiesSachin RajaNo ratings yet
- Fonc 12 881665Document10 pagesFonc 12 881665Raul Matute MartinNo ratings yet
- Artigo Image Dogs DOIDocument4 pagesArtigo Image Dogs DOIrebsbvetNo ratings yet
- Ircmj 16 11423Document4 pagesIrcmj 16 11423jenifer paathNo ratings yet
- Paraneoplastic SyndromesDocument8 pagesParaneoplastic SyndromesAndres F AristizabalNo ratings yet
- 5 - Tumorlike Lesions and Benign Tumors of The Hand and Wrist-PlateDocument13 pages5 - Tumorlike Lesions and Benign Tumors of The Hand and Wrist-PlatedouglasNo ratings yet
- Seorang Laki-Laki Dengan Tumor Mediastinum Posterior (: Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor)Document9 pagesSeorang Laki-Laki Dengan Tumor Mediastinum Posterior (: Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor)Alif riadiNo ratings yet
- Metástasis Leptomeningea en Tumores SólidosDocument16 pagesMetástasis Leptomeningea en Tumores SólidosElis EscobarNo ratings yet
- KLP 10 - Jurnal - MeningiomaDocument11 pagesKLP 10 - Jurnal - Meningiomawahy udiNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan Penunjang Onkologi Pada MataDocument29 pagesPemeriksaan Penunjang Onkologi Pada MatamazidahzulfaNo ratings yet
- 2011-Sonographic Appearances of Morton's Neuroma - UMBDocument6 pages2011-Sonographic Appearances of Morton's Neuroma - UMBAsim AliNo ratings yet
- Neurofibromatosis 1: Practical GeneticsDocument8 pagesNeurofibromatosis 1: Practical GeneticsEccoNo ratings yet
- Rosai-Dorfman Desease With Infra - Tentorial Localization - A Case ReportDocument2 pagesRosai-Dorfman Desease With Infra - Tentorial Localization - A Case Reportfawad mughalNo ratings yet
- Orbital Tumours and Tumour-Like Lesions: Exploring The Armamentarium of Multiparametric ImagingDocument26 pagesOrbital Tumours and Tumour-Like Lesions: Exploring The Armamentarium of Multiparametric ImagingNobita CutterNo ratings yet
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders.15Document33 pagesNeuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders.15Marco Macavilca CruzNo ratings yet
- ZJ 4852Document10 pagesZJ 4852Christopher BermeoNo ratings yet
- 5 4 126 654 Meralgia ParestheticaDocument5 pages5 4 126 654 Meralgia Parestheticachandrasen chaughuleNo ratings yet
- Intradural Extramedullary TumorsDocument10 pagesIntradural Extramedullary TumorsFaizyab Ahmed100% (1)
- Metastatic Spinal Cord CompressionDocument3 pagesMetastatic Spinal Cord CompressionAjibaskoro Prayogi IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor With Rhabdomyosarcomatous Differentiation (Malignant Triton Tumor)Document4 pagesMalignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor With Rhabdomyosarcomatous Differentiation (Malignant Triton Tumor)NIck MenzelNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Sheng-Po Hao, MD, Facs, Fics Ngan-Ming Tsang, MD, DSCDocument9 pagesSurgical Management of Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Sheng-Po Hao, MD, Facs, Fics Ngan-Ming Tsang, MD, DSCMirzaulin LeonaviriNo ratings yet
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Metastases: Lisa M. D AngelisDocument13 pagesLeukemia and Lymphoma Metastases: Lisa M. D AngelisjaquelineartNo ratings yet
- Vol-1, Issue-1 Prospective Study of Peripheral Nerve Tumors Over A Period of 2 YearsDocument4 pagesVol-1, Issue-1 Prospective Study of Peripheral Nerve Tumors Over A Period of 2 YearsijhrmimsNo ratings yet
- IJCP Neurofibroma FinalDocument5 pagesIJCP Neurofibroma FinalFatima Al ZahraNo ratings yet
- JNS Role of Electrophysiology in Guiding Near Total Resection For Preservation of Facial Nerve Function in The Surgical Treatment of Large Vestibular SchwannomasDocument8 pagesJNS Role of Electrophysiology in Guiding Near Total Resection For Preservation of Facial Nerve Function in The Surgical Treatment of Large Vestibular SchwannomasAlejandro CheritNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging of Spinal Canal StenosisDocument17 pagesNeuroimaging of Spinal Canal Stenosisrulitoss_41739No ratings yet
- Transforaminal LP3Document6 pagesTransforaminal LP3Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- RG 2017160077Document23 pagesRG 2017160077Imagenologia Hospital de ClinicasNo ratings yet
- Chap 18 Brain Metastase ENNDocument34 pagesChap 18 Brain Metastase ENNspiritNo ratings yet
- ACNRSO10 21 Neurosurgery PDFDocument4 pagesACNRSO10 21 Neurosurgery PDFriandhaniNo ratings yet
- Sca IiDocument8 pagesSca IiAlfredo Enrique Marin AliagaNo ratings yet
- Sarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasDocument3 pagesSarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasCharlie65129No ratings yet
- Intradural Spinal Tumors in Adults - Update On Management and OutcomeDocument18 pagesIntradural Spinal Tumors in Adults - Update On Management and OutcomeSuciatije PenelitianNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cystic SchwannomaDocument3 pagesSpinal Cystic SchwannomahelenNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis With Predominant Pyramidal - 2006 - Magnetic ResoDocument7 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis With Predominant Pyramidal - 2006 - Magnetic Resotejas1578No ratings yet
- Case Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalDocument84 pagesCase Report Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor of SinonasalAyunita ArifinNo ratings yet
- Compressive and Traumatic Myelopathies: Jeremy L. Fogelson, William KraussDocument18 pagesCompressive and Traumatic Myelopathies: Jeremy L. Fogelson, William KraussGian CarloNo ratings yet
- Laminectomy With Fusion Versus Young LaminoplastyDocument6 pagesLaminectomy With Fusion Versus Young Laminoplasty7w7dzjhgbqNo ratings yet
- InvestigationsDocument28 pagesInvestigationsAndrei BulgariuNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tumor: Zelin Sun MD, PH.DDocument28 pagesSpinal Tumor: Zelin Sun MD, PH.DMargaret ThatcherNo ratings yet
- Cancer, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) : Statpearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) : Statpearls Publishing 2020 JanDocument11 pagesCancer, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) : Statpearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) : Statpearls Publishing 2020 JanikaNo ratings yet
- SJ BDJ 2017 386Document1 pageSJ BDJ 2017 3862907tranthaonguyenNo ratings yet
- Payer 2015Document10 pagesPayer 2015esinsubozatliNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Ultrasound Management of Pancreatic Lesions: From Diagnosis to TherapyFrom EverandEndoscopic Ultrasound Management of Pancreatic Lesions: From Diagnosis to TherapyAntonio FacciorussoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesWendel Jonn L. AbaraNo ratings yet
- Modutec Ceiling Supply UnitsDocument16 pagesModutec Ceiling Supply Unitsabouali najafNo ratings yet
- APHAKIADocument20 pagesAPHAKIAAmitabh SatsangiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Odontogenic CystsDocument4 pagesSurgical Management of Odontogenic CystsHana FauziyahNo ratings yet
- He 2016Document5 pagesHe 2016Anonymous 44bTHDeHkbNo ratings yet
- Basic OtolaryngologyDocument13 pagesBasic OtolaryngologyPhilippe Ceasar C. Basco100% (1)
- Compass Hinge Knee STDocument12 pagesCompass Hinge Knee STDJGGNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of An Amputated Finger: Case ReportDocument5 pagesProsthetic Rehabilitation of An Amputated Finger: Case ReportSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Journal-Appraisal - Pgmi Del Prado, RockyDocument14 pagesJournal-Appraisal - Pgmi Del Prado, Rockyrockson del PradoNo ratings yet
- Extensive Maxillary Odontomas in 2 Dogs: Diagnosis, Pathology, and ManagementDocument9 pagesExtensive Maxillary Odontomas in 2 Dogs: Diagnosis, Pathology, and ManagementAlejandro Estrada RiosNo ratings yet
- Empyema Thoracis: Ain Najwa BT Abd Rahim (090100457) MARDHIAH BT MARZUKI (090100470)Document22 pagesEmpyema Thoracis: Ain Najwa BT Abd Rahim (090100457) MARDHIAH BT MARZUKI (090100470)Dumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument4 pagesUnknownmohammadrezahajian12191No ratings yet
- Cv-Update For DoctorDocument2 pagesCv-Update For DoctorRATANRAJ SINGHDEONo ratings yet
- Dental Update - May 2022Document88 pagesDental Update - May 2022Ahmed Abou FoulNo ratings yet
- TMJ PrintDocument135 pagesTMJ PrintAsmaa RagabNo ratings yet
- The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative DentistryDocument8 pagesThe International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative DentistryBagis Emre GulNo ratings yet
- Procedure AssignmentDocument12 pagesProcedure AssignmentMubarek UmerNo ratings yet
- Amanda Collier Agacnp-Bc Resume 3-2020Document2 pagesAmanda Collier Agacnp-Bc Resume 3-2020api-555316862No ratings yet
- Types of BedDocument42 pagesTypes of BedS AnthonyNo ratings yet
- KatarakDocument28 pagesKatarakBimo Nugroho SaktiNo ratings yet
- CHILD HEALTH NURSING Unit I Stuents Notes NotesDocument13 pagesCHILD HEALTH NURSING Unit I Stuents Notes Noteskarthicpraveen100% (1)
- NABH Certified Entry Level HospitalsDocument46 pagesNABH Certified Entry Level HospitalsADDECC INFO INDIANo ratings yet
- Hearing With Bone-Anchored Hearing Aid BAHA PDFDocument8 pagesHearing With Bone-Anchored Hearing Aid BAHA PDFpro4ksaNo ratings yet
- E231008 FullDocument2 pagesE231008 Fullandrew timanta brahmanaNo ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)Document2 pagesFrequently Asked Questions (FAQ)TrishaNo ratings yet
- Varicocele TreatmentDocument3 pagesVaricocele TreatmentJebakumar720No ratings yet
- Greetings: Pushpagiri College of Dental SciencesDocument27 pagesGreetings: Pushpagiri College of Dental SciencesDilu DavisNo ratings yet
- Urethral InjuryDocument7 pagesUrethral InjuryIoannis ValioulisNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Malocclusion On Masticatory Performance A Systematic Review-Magalhaes IB Et AlDocument7 pagesThe Influence of Malocclusion On Masticatory Performance A Systematic Review-Magalhaes IB Et AlAnggiswariNo ratings yet