Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsLesson 6 Nerve Cells
Lesson 6 Nerve Cells
Uploaded by
Ellen leeThis document discusses nerve cells (neurons). It defines key terms like synapse, neurotransmitters, and the three main types of neurons. It notes that neurons communicate chemically or electrically at synapses using neurotransmitters. Motor neurons connect the brain to muscles, sensory neurons allow sensation, and interneurons connect neurons. The document lists signs of nerve damage like numbness and lists that damaged peripheral neurons can regrow but spinal cord neurons have limited regeneration due to scar tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CH 06 Nervous System (MS)Document63 pagesCH 06 Nervous System (MS)alyssa bananNo ratings yet
- Simbio Lab 1Document11 pagesSimbio Lab 1samantha davidsonNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- SCIENCE VI Module 10Document5 pagesSCIENCE VI Module 10JHUDIELLE ANNE JANSOLNo ratings yet
- Coordination HDocument9 pagesCoordination HmatinNo ratings yet
- What Is A Neuron Diagrams, Types, Function, and More PDFDocument1 pageWhat Is A Neuron Diagrams, Types, Function, and More PDFSantiago BarbosaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument17 pagesNerve CellCathy C DNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesNeuroscienceZerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- What Are NeuronsDocument3 pagesWhat Are NeuronsNancy Medina CabalunaNo ratings yet
- RBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsDocument16 pagesRBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsFelixdino09No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument31 pagesNervous System NotesEMILIA VELEZ RESTREPONo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscDocument60 pagesGrade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscScience Teacher100% (1)
- Biology - Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesBiology - Coordination and ResponseMiguel HallNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Control System of The BodyDocument31 pagesWelcome To The Control System of The BodypadiosNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination and ResponseDocument11 pagesNervous Coordination and ResponseJashya NoorNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - The Nervous System& NeuronsDocument14 pagesBio Project - The Nervous System& Neuronskaungthit51188No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesThe Nervous SystemMaia MohammedNo ratings yet
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocument7 pagesHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Neuroscience Week 2Document6 pagesNeuroscience Week 2Naima AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kep InggrisDocument18 pagesKep InggrisArif RimbunNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Nervecell-10Document4 pagesScience Lesson Nervecell-10Strawberry MilkeuNo ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Document21 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions - Chapter 2Document6 pagesDiscussion Questions - Chapter 2nlenz94No ratings yet
- Wires Really Crossed Teacher 1EDocument5 pagesWires Really Crossed Teacher 1EEllie EllaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemHans Festin-DiazNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 9Document29 pagesAP Psychology Module 9Klein ZhangNo ratings yet
- Bio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyDocument10 pagesBio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyNancy Medina CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpDocument3 pages3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpJana De LiñaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemGraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- K00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesK00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemNixon ErnestNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Letter 2Document3 pagesLetter 2NorrisRyanNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit of The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesBasic Unit of The Nervous SystemsarohlimNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Neuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNeuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous Systemwellskyle891No ratings yet
- Case Studies in NeurologyDocument3 pagesCase Studies in NeurologyOnline WriterNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- 2 ReactionsDocument43 pages2 ReactionsTrixie Anne CordovaNo ratings yet
- 2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument5 pages2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oCasey HachilesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet
Lesson 6 Nerve Cells
Lesson 6 Nerve Cells
Uploaded by
Ellen lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesThis document discusses nerve cells (neurons). It defines key terms like synapse, neurotransmitters, and the three main types of neurons. It notes that neurons communicate chemically or electrically at synapses using neurotransmitters. Motor neurons connect the brain to muscles, sensory neurons allow sensation, and interneurons connect neurons. The document lists signs of nerve damage like numbness and lists that damaged peripheral neurons can regrow but spinal cord neurons have limited regeneration due to scar tissue.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lesson-6-Nerve-Cells.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses nerve cells (neurons). It defines key terms like synapse, neurotransmitters, and the three main types of neurons. It notes that neurons communicate chemically or electrically at synapses using neurotransmitters. Motor neurons connect the brain to muscles, sensory neurons allow sensation, and interneurons connect neurons. The document lists signs of nerve damage like numbness and lists that damaged peripheral neurons can regrow but spinal cord neurons have limited regeneration due to scar tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesLesson 6 Nerve Cells
Lesson 6 Nerve Cells
Uploaded by
Ellen leeThis document discusses nerve cells (neurons). It defines key terms like synapse, neurotransmitters, and the three main types of neurons. It notes that neurons communicate chemically or electrically at synapses using neurotransmitters. Motor neurons connect the brain to muscles, sensory neurons allow sensation, and interneurons connect neurons. The document lists signs of nerve damage like numbness and lists that damaged peripheral neurons can regrow but spinal cord neurons have limited regeneration due to scar tissue.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
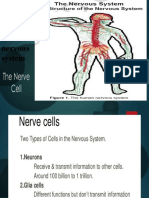
Lesson 6: Nerve Cell
Objectives:
1. identify different parts and
functions of nerve cell; and
2. cite some consequences of
neurons death and damage.
If you lost or damaged your
sense of sight, what would be
very hard for you to do? What
would be more challenging for
you to do but you could still do
it?
Activity Time
What is synapse? Neurons communicate with one another at junctions
called synapses. At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target
neuron—another cell. Most synapses are chemical; these synapses
communicate using chemical messengers. Other synapses are electrical; in
these synapses, ions flow directly between cells.
What are neurotransmitters? Neurotransmitters are chemical
messengers that your body can't function without. Their job is to carry
chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next
target cell. The next target cell can be another nerve cell, a muscle cell
or a gland.
Three classifications of neurons according to the direction of the message or impulse they carry.
Motor neurons make the connection
between the brain and muscles
throughout the body.
Sensory neurons are neurons that
let us feel sensation.
Interneurons are the nerve cells that
connect motor neurons to other
motor neurons and sensory neurons
to other sensory neurons.
Are you experiencing numbness in your hands or sometimes in your legs? What do
you think is the cause of numbness?
Signs of Nerve Damage
1. Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
2. Feeling like you're wearing a tight glove or sock.
3. Muscle weakness, especially in your arms or
legs.
4. Regularly dropping objects that you're holding.
5. Sharp pains in your hands, arms, legs, or feet.
6. A buzzing sensation that feels like a mild
electrical shock.
Can damaged neurons be repaired?
Damaged nerve cells in a finger will
regrow, but those in the spinal cord
do not. Nerve cells in the spinal
cord still can grow even many
weeks after an injury. However, the
regeneration is prevented by scar
tissue created after the injury
occurs.
You might also like
- CH 06 Nervous System (MS)Document63 pagesCH 06 Nervous System (MS)alyssa bananNo ratings yet
- Simbio Lab 1Document11 pagesSimbio Lab 1samantha davidsonNo ratings yet
- Science-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Document5 pagesScience-10 Q3 Module-3 Week-3Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Neurons Elements of BehaviourDocument3 pagesNeurons Elements of Behaviourchantefraser8No ratings yet
- SCIENCE VI Module 10Document5 pagesSCIENCE VI Module 10JHUDIELLE ANNE JANSOLNo ratings yet
- Coordination HDocument9 pagesCoordination HmatinNo ratings yet
- What Is A Neuron Diagrams, Types, Function, and More PDFDocument1 pageWhat Is A Neuron Diagrams, Types, Function, and More PDFSantiago BarbosaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellDocument17 pagesNerve CellCathy C DNo ratings yet
- NeuroscienceDocument6 pagesNeuroscienceZerica JohnNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Notes #2Document7 pagesNervous System Notes #2LeoNo ratings yet
- What Are NeuronsDocument3 pagesWhat Are NeuronsNancy Medina CabalunaNo ratings yet
- RBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsDocument16 pagesRBA Lesson 1 Reflexes and ReactionsFelixdino09No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesNervous SystemSatrioNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument31 pagesNervous System NotesEMILIA VELEZ RESTREPONo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscDocument60 pagesGrade 5 Nervous System PPT DiscScience Teacher100% (1)
- Biology - Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesBiology - Coordination and ResponseMiguel HallNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Control System of The BodyDocument31 pagesWelcome To The Control System of The BodypadiosNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesModule 5 Nervous TissueHermione MalfoyNo ratings yet
- Nervous Coordination and ResponseDocument11 pagesNervous Coordination and ResponseJashya NoorNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - The Nervous System& NeuronsDocument14 pagesBio Project - The Nervous System& Neuronskaungthit51188No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesThe Nervous SystemMaia MohammedNo ratings yet
- Histology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureDocument7 pagesHistology: Neuron Cells Types and StructureAli HayderNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Neuroscience Week 2Document6 pagesNeuroscience Week 2Naima AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kep InggrisDocument18 pagesKep InggrisArif RimbunNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Nervecell-10Document4 pagesScience Lesson Nervecell-10Strawberry MilkeuNo ratings yet
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Document21 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Denver TamayoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions - Chapter 2Document6 pagesDiscussion Questions - Chapter 2nlenz94No ratings yet
- Wires Really Crossed Teacher 1EDocument5 pagesWires Really Crossed Teacher 1EEllie EllaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemAnonymous iOaluenhNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Nervous SystemHans Festin-DiazNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Module 9Document29 pagesAP Psychology Module 9Klein ZhangNo ratings yet
- Bio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyDocument10 pagesBio612 Writtenreport Cabaluna NancyNancy Medina CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpDocument3 pages3.2.2.2. The Human Nervous System Conceptual Check UpJana De LiñaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesThe Nervous System868.CapalotNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : The Nervous SystemGraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- K00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesK00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemNixon ErnestNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 pagesNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807No ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Letter 2Document3 pagesLetter 2NorrisRyanNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit of The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesBasic Unit of The Nervous SystemsarohlimNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Neuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNeuro-Network: A Presentation About The Nervous Systemwellskyle891No ratings yet
- Case Studies in NeurologyDocument3 pagesCase Studies in NeurologyOnline WriterNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesModule 7 Nervous SystemMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- 2 ReactionsDocument43 pages2 ReactionsTrixie Anne CordovaNo ratings yet
- 2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument5 pages2.voluntary Body Movements: o o o o o o o o o o o o o o oCasey HachilesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Nscelec4-Week 15Document23 pagesNscelec4-Week 15Jeune Kristine OngNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSecond Quarter Grade 10 - Science HANDOUT No.2 On Neurons, Reflex, Reflex Arc & Brain General Information About The Nervous SystemMartin ReaporNo ratings yet