Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit V - 7BCD Counter
Unit V - 7BCD Counter
Uploaded by
Thiriveedhi Subbarayudu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesA BCD counter counts from 0000 to 1001 in decimal using binary-coded decimal and then resets to 0000. It does not have a regular counting pattern like a binary counter due to returning to 0000 after 9. The excitation table shows the input conditions for the T flip-flops to count from state to state or reset, with an output that enables the next decade when the counter reaches 1001.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA BCD counter counts from 0000 to 1001 in decimal using binary-coded decimal and then resets to 0000. It does not have a regular counting pattern like a binary counter due to returning to 0000 after 9. The excitation table shows the input conditions for the T flip-flops to count from state to state or reset, with an output that enables the next decade when the counter reaches 1001.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesUnit V - 7BCD Counter
Unit V - 7BCD Counter
Uploaded by
Thiriveedhi SubbarayuduA BCD counter counts from 0000 to 1001 in decimal using binary-coded decimal and then resets to 0000. It does not have a regular counting pattern like a binary counter due to returning to 0000 after 9. The excitation table shows the input conditions for the T flip-flops to count from state to state or reset, with an output that enables the next decade when the counter reaches 1001.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
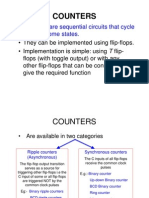
BCD Counter
A BCD counter counts in binary-coded
decimal from 0000 to 1001 and back to
0000.
Because of the return of 0 after a count of
9, a BCD counter does not have a regular
pattern as in a straight binary count.
The excitation table of a BCD counter is
shown below.
BCD Counter
BCD Counter
The excitation for the T flip-flops is obtained
from the present and next state conditions.
An output y is also shown in the table. This
output is equal to 1 when the counter present
state is 1001.
In this way, y can enable the count of the
next higher-order decade while the same
pulse switches the present decade from 1001
to 0000.
BCD Counter
The flip-flop input functions from the
excitation table can be simplified by
means of maps.
The unused states for minterms 10 to 15
are taken as don’t-care terms.
The simplified functions are
BCD Counter
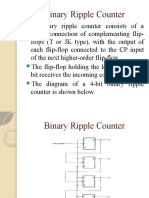
The circuit can be easily drawn with four
T flip-flops, five AND gates, and one OR
gate.
Synchronous BCD counters can be
cascaded to form a counter for decimal
numbers of any length.
You might also like
- Unit V - 3BCD Ripple CounterDocument13 pagesUnit V - 3BCD Ripple CounterThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 2Document20 pagesDigital Assignment 2Anup PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 DPCO 2nd HalfDocument26 pagesUnit 2 DPCO 2nd Halfmitopof121No ratings yet
- Eee 122 CH 6 CountersDocument26 pagesEee 122 CH 6 Countersjayacomp100% (1)
- Digital Pulse Counter - Two Digits: DescriptionDocument7 pagesDigital Pulse Counter - Two Digits: DescriptionAsgher KhattakNo ratings yet
- Counter, Shifts and DecoderDocument20 pagesCounter, Shifts and DecoderLuís Ki-llahNo ratings yet
- Pattern Shifting With Different Frequencies - ReportDocument19 pagesPattern Shifting With Different Frequencies - ReportChristopher EarnshawNo ratings yet
- (Counter) Paper - 1 - 7967 - 163 PDFDocument57 pages(Counter) Paper - 1 - 7967 - 163 PDFmaprofNo ratings yet
- 2-Lecture Notes Lesson5 3Document7 pages2-Lecture Notes Lesson5 3kstu1112No ratings yet
- Four-Bit Modulo-16 D-Flipflop Counter: Play Around With The Circuit To See That It WorksDocument4 pagesFour-Bit Modulo-16 D-Flipflop Counter: Play Around With The Circuit To See That It WorksFajri NaomiNo ratings yet
- Exp10 BCDAdderDocument4 pagesExp10 BCDAddervk2you009No ratings yet
- Report TextDocument7 pagesReport TextVica Azka Novalya IINo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: Part A 20 Marks Each Carry Two MarksDocument9 pagesDigital Electronics: Part A 20 Marks Each Carry Two MarksN. A. KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (1) Physics EngineeringDocument26 pagesUnit 1 (1) Physics EngineeringShiny ShinyNo ratings yet
- DPCO Unit 1Document45 pagesDPCO Unit 1Laks SadeeshNo ratings yet
- VivaDocument18 pagesVivaSumaya ShinosNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. A Simple Ripple Counter Consisting of J-K Flip-FlopsDocument1 pageFigure 1. A Simple Ripple Counter Consisting of J-K Flip-FlopsSatyanarayan BhanjaNo ratings yet
- Counters & Shifters: by Dr. Alok Kumar Rastogi Professor of Physics Department of Physics & Electronics IEHE, BhopalDocument45 pagesCounters & Shifters: by Dr. Alok Kumar Rastogi Professor of Physics Department of Physics & Electronics IEHE, BhopalKritiiNo ratings yet
- Ring JohnsonDocument31 pagesRing JohnsonBharadwaja PisupatiNo ratings yet
- 9 Counter CircuitsDocument9 pages9 Counter CircuitsWaseem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document21 pagesWeek 7İBRAHİM YÜMLÜNo ratings yet
- Lecture 55Document8 pagesLecture 55Anuj SainiNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 1-Sequential Circuit CountersDocument20 pagesDigital Electronics 1-Sequential Circuit CountersSatyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- DLD - Module IIDocument21 pagesDLD - Module IIChaitanya J S ReddyNo ratings yet
- Counters 1Document11 pagesCounters 1Jenifer StalinNo ratings yet
- Digital Pre Lab 5Document2 pagesDigital Pre Lab 5Martin DelNo ratings yet
- Decimal AdderDocument6 pagesDecimal AdderAsfand Yar AkramNo ratings yet
- Shift RegisterDocument21 pagesShift RegisterPurva ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 4 Bit BCD AdderDocument7 pages4 Bit BCD AdderJagnur SinghNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design 6 CountersDocument37 pagesDigital Logic Design 6 CountersMurad QəhramanovNo ratings yet
- Count Down CounterDocument2 pagesCount Down CounterJose GarciaNo ratings yet
- Counters and RegistersDocument16 pagesCounters and Registersamury kgNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 2binary Ripple CounterDocument11 pagesUnit V - 2binary Ripple CounterThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document18 pagesWeek 4İBRAHİM YÜMLÜNo ratings yet
- Counters: Compiled By: Afaq Alam KhanDocument28 pagesCounters: Compiled By: Afaq Alam KhanRajeshwari SNo ratings yet
- Digital Principles and Application by Leach & Malvino ExportDocument69 pagesDigital Principles and Application by Leach & Malvino ExportOfficial KillerNo ratings yet
- Counter 1Document11 pagesCounter 1royal brotherNo ratings yet
- Parallel Binary Adders: ScriptDocument9 pagesParallel Binary Adders: Scriptirfan ansariNo ratings yet
- Circuit Can Be Used For Many PurposesDocument1 pageCircuit Can Be Used For Many PurposesAszhar Al AmbaryNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document57 pagesCH 12Juju salehNo ratings yet
- 07 Registers and CountersDocument28 pages07 Registers and CountersChandravadhana NarayananNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument25 pagesCountersSonam SoniNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument6 pagesDatasheetUlma HudinNo ratings yet
- 09 CountersDocument58 pages09 CountersWu JingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Counters: Ee 202 Digital ElectronicsDocument59 pagesChapter 5: Counters: Ee 202 Digital ElectronicsSyazreen RahmanNo ratings yet
- A 4-Stage Johnson Counter Divides by 8Document13 pagesA 4-Stage Johnson Counter Divides by 8PrashantNirmalNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sequential CircuitsDocument2 pagesAssignment Sequential CircuitsPavan SaiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 8Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 8ashish_jiitNo ratings yet
- Week 4pdf PDFDocument23 pagesWeek 4pdf PDFwael mahfouzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08 - Registers and CountersDocument27 pagesLecture 08 - Registers and CountersMohammed ZaitounNo ratings yet
- Counting Using BinaryDocument58 pagesCounting Using BinaryblueskyderNo ratings yet
- LOGSWCH Lab1Document3 pagesLOGSWCH Lab1topherskiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implement A Four Bit Adder Using Logic Gate ICsDocument10 pagesDesign and Implement A Four Bit Adder Using Logic Gate ICsahsan khanNo ratings yet
- CS302LecturewiseQuestions PDFDocument96 pagesCS302LecturewiseQuestions PDFattiqueNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1jixxy jaxNo ratings yet
- Circuit Contador en Reversa LDocument6 pagesCircuit Contador en Reversa LcastilloNo ratings yet
- CountersDocument16 pagesCountersgargraghav82No ratings yet
- Module 5 Part ADocument8 pagesModule 5 Part AHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- DLD SimpleDocument62 pagesDLD SimpleSanaAzharKhanNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 3BCD Ripple CounterDocument13 pagesUnit V - 3BCD Ripple CounterThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 5binary CounterDocument7 pagesUnit V - 5binary CounterThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 2binary Ripple CounterDocument11 pagesUnit V - 2binary Ripple CounterThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document211 pagesUnit 1Thiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 4synchronous CountersDocument2 pagesUnit V - 4synchronous CountersThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument79 pagesUnit IiThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Unit V - 1ripple CountersDocument2 pagesUnit V - 1ripple CountersThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Consensus TheoremDocument3 pagesConsensus TheoremThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet
- Code ConversionDocument10 pagesCode ConversionThiriveedhi SubbarayuduNo ratings yet