Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ER Diagram
ER Diagram
Uploaded by
Joy Boy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views23 pagesThe document discusses the components of an Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram including entities, attributes, relationships, and types of relationships. It provides examples of each component and their representations in an ER diagram. Key points include: Entities can be objects, people, or places and are represented by rectangles. Attributes describe entity properties and are represented by ellipses. Relationships show relations between entities and are represented by diamonds. Relationship types include one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many.
Original Description:
Original Title
ER diagram.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the components of an Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram including entities, attributes, relationships, and types of relationships. It provides examples of each component and their representations in an ER diagram. Key points include: Entities can be objects, people, or places and are represented by rectangles. Attributes describe entity properties and are represented by ellipses. Relationships show relations between entities and are represented by diamonds. Relationship types include one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views23 pagesER Diagram
ER Diagram
Uploaded by
Joy BoyThe document discusses the components of an Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram including entities, attributes, relationships, and types of relationships. It provides examples of each component and their representations in an ER diagram. Key points include: Entities can be objects, people, or places and are represented by rectangles. Attributes describe entity properties and are represented by ellipses. Relationships show relations between entities and are represented by diamonds. Relationship types include one-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-one, and many-to-many.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 23
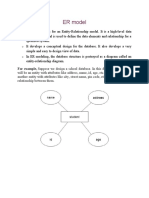
ER diagram
• ER model stands for an Entity-Relationship model. It is a high-level
data model. This model is used to define the data elements and
relationship for a specified system.
• It develops a conceptual design for the database. It also develops a
very simple and easy to design view of data.
• In ER modeling, the database structure is portrayed as a diagram
called an entity-relationship diagram.
• For example, Suppose we design a school database. In this database,
the student will be an entity with attributes like address, name, id,
age, etc. The address can be another entity with attributes like city,
street name, pin code, etc and there will be a relationship between
them.
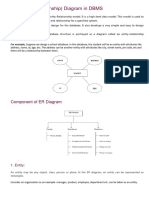
Component of ER diagram
1. Entity:
• An entity may be any object, class, person or place. In the ER diagram,
an entity can be represented as rectangles.
• Consider an organization as an example- manager, product, employee,
department etc. can be taken as an entity.
a. Weak Entity
An entity that depends on another entity called a weak entity. The
weak entity doesn't contain any key attribute of its own. The weak
entity is represented by a double rectangle.
2. Attribute
The attribute is used to describe the property of an entity. Eclipse is
used to represent an attribute.
For example, id, age, contact number, name, etc. can be attributes of a
student.
a. Key Attribute
The key attribute is used to represent the main characteristics of an
entity. It represents a primary key. The key attribute is represented by
an ellipse with the text underlined.
b. Composite Attribute
• An attribute that composed of many other attributes is known as a
composite attribute. The composite attribute is represented by an
ellipse, and those ellipses are connected with an ellipse.
c. Multivalued Attribute
• An attribute can have more than one value. These attributes are
known as a multivalued attribute. The double oval is used to
represent multivalued attribute.
• For example, a student can have more than one phone number.
d. Derived Attribute
• An attribute that can be derived from other attribute is known as a
derived attribute. It can be represented by a dashed ellipse.
• For example, A person's age changes over time and can be derived
from another attribute like Date of birth.
3. Relationship
• A relationship is used to describe the relation between entities.
Diamond or rhombus is used to represent the relationship.
Types of relationship are as follows:
a. One-to-One Relationship
• When only one instance of an entity is associated with the
relationship, then it is known as one to one relationship.
• For example, A female can marry to one male, and a male can marry
to one female.
b. One-to-many relationship
• When only one instance of the entity on the left, and more than one
instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship then
this is known as a one-to-many relationship.
• For example, Scientist can invent many inventions, but the invention
is done by the only specific scientist.
c. Many-to-one relationship
• When more than one instance of the entity on the left, and only one
instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship then
it is known as a many-to-one relationship.
• For example, Student enrolls for only one course, but a course can
have many students.
d. Many-to-many relationship
• When more than one instance of the entity on the left, and more than
one instance of an entity on the right associates with the relationship
then it is known as a many-to-many relationship.
• For example, Employee can assign by many projects and project can
have many employees.
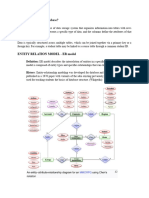
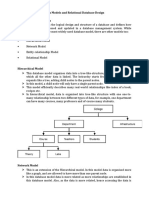
ER diagram of University Management
System
Advantages of ER diagram
• The ER model is easy to build.
• This model is widely used by database designers for communicating
their ideas.
• This model can easily convert to any other model like network model,
hierarchical model etc.
• It is integrated with the dominant relational model.
Disadvantages of ER diagram
• There is no industry standard for developing an ER model.
• Information might be lost or hidden in the ER model.
• There is no Data Manipulation Language (DML).
• There is limited relationship representation.
MCQ
The descriptive property possessed by each entity set is _________
a) Entity
b) Attribute
c) Relation
d) Model
MCQ
The attribute AGE is calculated from DATE_OF_BIRTH. The attribute
AGE is
a) Single valued
b) Multi valued
c) Composite
d) Derived
In an Entity-Relationship Diagram “Ellipses” represents?
Attributes
Weak entity set
Relationship sets
Multi-valued attributes
Every weak entity set can be converted into a strong entity set
by………
using generalization
adding appropriate attributes
using aggregation
none of the above
You might also like
- Data Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandData Structures & Algorithms Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Sans Gcih Certification Guide v2Document15 pagesSans Gcih Certification Guide v2ziptiedNo ratings yet
- Iso 27001Document3 pagesIso 27001nebojsami100% (1)
- ER Model: Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The StudentDocument10 pagesER Model: Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The StudentHaider SultanNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument5 pagesER ModelHarpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- DatamodelingDocument8 pagesDatamodelingRakshita NathawatNo ratings yet
- ER Model: Component of ER DiagramDocument9 pagesER Model: Component of ER Diagramprerana sheteNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ErDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Erkalik goyalNo ratings yet
- ER Model: For Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The StudentDocument7 pagesER Model: For Example, Suppose We Design A School Database. in This Database, The Studentpyari mohanNo ratings yet
- DBMS ER Model Concept Unit2Document6 pagesDBMS ER Model Concept Unit2Surya PalNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Database Design: Er Model & Er DiagramsDocument81 pagesUnit-Ii Database Design: Er Model & Er DiagramsSneha IgnatiousNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE3001 ETH VL2020210504489 Reference Material II 01-Mar-2021 System ModelsDocument24 pagesWINSEM2020-21 CSE3001 ETH VL2020210504489 Reference Material II 01-Mar-2021 System ModelsBody SoDaNo ratings yet
- Data Modeling Using Entity-Relationship Model: Unit 2 Chapter 3Document42 pagesData Modeling Using Entity-Relationship Model: Unit 2 Chapter 3Rahul V SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - ER Diagram in DBMSDocument32 pagesLecture 5 - ER Diagram in DBMSNjemax PanasheNo ratings yet
- 5.1 (B) ER ModelDocument10 pages5.1 (B) ER Model2002746.it.cecNo ratings yet
- VND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2Document42 pagesVND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - Presentationml.presentation&rendition 1 2fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- S-Database Design U 2Document67 pagesS-Database Design U 2Sukesh KrNo ratings yet
- 3DBMS ER Model Concept - Javatpoint PDFDocument6 pages3DBMS ER Model Concept - Javatpoint PDFriddhi chavanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Data Modeling - UpdatedDocument51 pagesUnit 1 Data Modeling - Updatedsahish pandavNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument14 pagesER ModelShobhaNo ratings yet
- Types of DatabasesDocument35 pagesTypes of DatabasesrosaliaNo ratings yet
- Se Lab NotesDocument32 pagesSe Lab NotesRushmitha SelvarajNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Unit II)Document33 pagesDBMS (Unit II)Abhay KNo ratings yet
- 10.ER ModelDocument51 pages10.ER ModelAditya AnandNo ratings yet
- Co1 Session3Document18 pagesCo1 Session3Jayavarapu Karthik JNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship DiagramDocument20 pagesEntity Relationship DiagramTynan SokNo ratings yet
- Entity - Relationship Model - CH2Document65 pagesEntity - Relationship Model - CH2Divit wadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Data Models ER UpdatedDocument28 pagesData Models ER UpdatedSudhanshu Raj TiwariNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram: Ruben A. Parazo Faculty, Department of Computer StudiesDocument30 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram: Ruben A. Parazo Faculty, Department of Computer StudiesPaula Rodalyn MateoNo ratings yet
- Da Tabase Management System: Hassan KhanDocument11 pagesDa Tabase Management System: Hassan KhanHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- 3ac8acd1 1700887751396Document30 pages3ac8acd1 1700887751396arshmehak2313No ratings yet
- ER (Entity Relationship) DiagramDocument13 pagesER (Entity Relationship) DiagramRutuja KadamNo ratings yet
- Relational Databases - 3rd SemesterDocument23 pagesRelational Databases - 3rd SemesterErdemtugs ErdenetogtokhNo ratings yet
- Anish GuptaDocument14 pagesAnish GuptaSatyam MallickNo ratings yet
- DBMS ER DiagramDocument11 pagesDBMS ER DiagramAayushi ChowlaNo ratings yet
- Data Models - ER2Document48 pagesData Models - ER2Rohan jhaNo ratings yet
- Data Models 2Document45 pagesData Models 2VenuNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram - KameshwariDocument12 pagesER Diagram - KameshwariKameshwari PurusothmanNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Database DesignDocument77 pagesDBMS - Database Designsteffinamorin LNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - ModelsDocument45 pagesLecture 2 - Modelsjubairahmed1678No ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument9 pagesER ModelDhyan PatelNo ratings yet
- Relational Data Model: Chapter ThreeDocument19 pagesRelational Data Model: Chapter Threesahan instituteNo ratings yet
- Dbms-Module - 2 Updated at 07-02-2023Document107 pagesDbms-Module - 2 Updated at 07-02-2023edrickwitch01No ratings yet
- Data-Models DBMSDocument30 pagesData-Models DBMSKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Database ManagementDocument22 pagesDatabase Managementresearcher-690955No ratings yet
- E-R DiagramDocument11 pagesE-R DiagramAaruni BattaNo ratings yet
- Airport Mangement SystemDocument11 pagesAirport Mangement SystemHarsh tandelNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Data Models - ER ModelDocument9 pages5.1 Data Models - ER Model2002746.it.cecNo ratings yet
- Data or ER ModelsDocument74 pagesData or ER ModelsShivanshu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Data Models 1Document33 pagesData Models 1Vamsi PradeepNo ratings yet
- ER ModelDocument46 pagesER ModelMd. Minhajul Abedin 171-15-1386No ratings yet
- Presentation Group 3Document35 pagesPresentation Group 3Marian NyamukondaNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram Part 1Document22 pagesER Diagram Part 1Dev BabbarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Data ModelsDocument83 pagesUnit 1 Data ModelsAdarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Data Models 1Document33 pagesData Models 1radwanNo ratings yet
- Se CH 3Document16 pagesSe CH 3Jack Chetty (Lion gaming)No ratings yet
- CH 3Document37 pagesCH 3Ashenafi EliasNo ratings yet
- DBMS - Data Models and Relational Database Design NotesDocument48 pagesDBMS - Data Models and Relational Database Design NotesKomal Ramteke100% (1)
- Lec3 - Relational Database Design ERDDocument33 pagesLec3 - Relational Database Design ERDSonu SachdevNo ratings yet
- A Simple ER Diagram:: 1) Explain Design of Entity Relational ModalDocument18 pagesA Simple ER Diagram:: 1) Explain Design of Entity Relational Modalchaithu goudNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document41 pagesUnit 2adityahada00No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 DbmsDocument17 pagesLecture 5 DbmsMohd AhadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0 INT306Document38 pagesLecture 0 INT306Joy BoyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document164 pagesUnit 1Joy BoyNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument24 pagesSoftwareJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document130 pagesUnit 2Joy BoyNo ratings yet
- Work Plan For Alternative Food ResourcesDocument1 pageWork Plan For Alternative Food ResourcesJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Zero Lecture MTH401 2Document27 pagesZero Lecture MTH401 2Joy BoyNo ratings yet
- TCL QueriesDocument1 pageTCL QueriesJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Elevator PitchDocument21 pagesElevator PitchJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- DCL AdminDocument1 pageDCL AdminJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- DCL QueriesDocument1 pageDCL QueriesJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Programs On Functions - Parameter Passing Mechanisms - RecursionDocument10 pagesPrograms On Functions - Parameter Passing Mechanisms - RecursionJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- DDL QueriesDocument1 pageDDL QueriesJoy BoyNo ratings yet
- Mec107 Unit 1Document55 pagesMec107 Unit 1Joy BoyNo ratings yet
- Internet Programming Final ReportDocument36 pagesInternet Programming Final ReportMUKKOTI JANANI,CSE(19-23) Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument13 pagesDBMStigerNo ratings yet
- DBAS Assignment Spring 2024 - Winter 2024 (6750)Document5 pagesDBAS Assignment Spring 2024 - Winter 2024 (6750)swanhtetthu456No ratings yet
- ArcSDE® Administration Command ReferenceDocument263 pagesArcSDE® Administration Command Referenceelproper100% (2)
- On Car Sales System: Mini Project ReportDocument41 pagesOn Car Sales System: Mini Project ReportAnandhu VsNo ratings yet
- Android SQLite Database and Content Provider - TutorialDocument25 pagesAndroid SQLite Database and Content Provider - TutorialRaj Kumar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Rosoka General 2015Document20 pagesRosoka General 2015swTechieNo ratings yet
- DIT 0204 Object OrientationDocument2 pagesDIT 0204 Object Orientationkipkoecharonz korirNo ratings yet
- Navigating To The File Using CMDDocument18 pagesNavigating To The File Using CMDforex masterNo ratings yet
- Emc Unity Family Emc Unity All Flash, Emc Unity Hybrid, Emc UnityvsaDocument33 pagesEmc Unity Family Emc Unity All Flash, Emc Unity Hybrid, Emc UnityvsaMortimer EchavarriaNo ratings yet
- SLT (SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server) in SAP HANADocument5 pagesSLT (SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server) in SAP HANAsatishsapbiwNo ratings yet
- H4 Chapter1Document12 pagesH4 Chapter1Rhea BadanaNo ratings yet
- Resume of Experienced Data ScientistDocument7 pagesResume of Experienced Data ScientistDevarshi MishraNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Securing User-ID Deployments Palo Alto Networks LiveDocument2 pagesBest Practices For Securing User-ID Deployments Palo Alto Networks LiveChau NguyenNo ratings yet
- RMA Case StudyDocument8 pagesRMA Case StudyJohnny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bridge TablesDocument6 pagesBridge TablesLawal Mobolaji MNo ratings yet
- Names: Gakuru James Reg: 2011453 Topic: Library Management System Advanced Web Programming Project Index - HTMLDocument19 pagesNames: Gakuru James Reg: 2011453 Topic: Library Management System Advanced Web Programming Project Index - HTMLKabahizi JoelNo ratings yet
- Ppa Unit-1Document12 pagesPpa Unit-1NobitaNo ratings yet
- Citra LogDocument18 pagesCitra LogDarma yasaNo ratings yet
- ADF Code Corner: 92. Caching ADF Web Service Results For In-Memory FilteringDocument11 pagesADF Code Corner: 92. Caching ADF Web Service Results For In-Memory FilteringRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDocument31 pagesChapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDiamond MindglanceNo ratings yet
- MC081Document385 pagesMC081Siddu BalaganurNo ratings yet
- Wreetika Adhikary Pranaya Mishra Yashwanth Bhanu Trisha George Mehal Batavia Ashray PandeyDocument7 pagesWreetika Adhikary Pranaya Mishra Yashwanth Bhanu Trisha George Mehal Batavia Ashray PandeyYaswanth MalepatiNo ratings yet
- 4C4 22 SQL LAB AssignmentDocument8 pages4C4 22 SQL LAB AssignmentABCNo ratings yet
- Mrpii CaseDocument9 pagesMrpii CaseRasel777No ratings yet
- 1.1 Linux-Commands - 101Document11 pages1.1 Linux-Commands - 101Bharath KumarNo ratings yet
- BdedeployDocument6 pagesBdedeployjessicacaetanoNo ratings yet
- 10 - Proof of Concept Project CloseOut Presentation - CRMDocument12 pages10 - Proof of Concept Project CloseOut Presentation - CRMBalavignesh VenugopalNo ratings yet