Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Kcel Tumaliuan DassilThis document discusses metamorphism, which is the process by which rocks undergo changes due to heat, pressure, and chemical activity. There are two main types of metamorphism: contact metamorphism, which occurs near igneous intrusions, and regional metamorphism, which affects large areas. During metamorphism, minerals change, rocks recrystallize, and new minerals form through chemical reactions as temperatures and pressures increase with depth. Heat, pressure, fluids, time, and stress all influence metamorphic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Maximising Molecular Sieve Performance in Gas ProcessingDocument18 pagesMaximising Molecular Sieve Performance in Gas ProcessingAhmed ElShora100% (1)
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockABU SALEH MOHAMMAD RAFI100% (1)
- Introduction To Metamorphic PetrologyDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Metamorphic PetrologynsmpofuNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockYZKNo ratings yet
- Q2-Lesson 4 MetamorphismDocument34 pagesQ2-Lesson 4 MetamorphismBlesie-Lyn BautistaNo ratings yet
- MetamorphicDocument22 pagesMetamorphicJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Metamorphic RocksDocument27 pagesMetamorphic RocksCrafty JigyasaNo ratings yet
- 02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Document10 pages02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Eadaw100% (1)
- Black Doodle Group Project PresentationDocument26 pagesBlack Doodle Group Project PresentationJoseph BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Agents of MetamorphismDocument6 pagesAgents of MetamorphismZahid RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism NotesDocument2 pagesMetamorphism NotesMaria Pauline AsiNo ratings yet
- Phy. Geol. 8: Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument28 pagesPhy. Geol. 8: Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksSalman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Conditions of Metamorphism-1Document28 pagesConditions of Metamorphism-1sabreenaakhter099No ratings yet
- Engineering Geology For Civil EngineersDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology For Civil EngineersDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- G11 Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesG11 Earth ScienceAlthea RivadeloNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument39 pagesPhysical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksYeremia PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Earth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismDocument35 pagesEarth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismCj Padata100% (1)
- Metamorphism and MetastomatismDocument10 pagesMetamorphism and Metastomatismbilal ahmadNo ratings yet
- Solid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofDocument8 pagesSolid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofJahque LadaranNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document4 pagesWeek 4janice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Answer #4: Agents of MetamorphismDocument2 pagesAnswer #4: Agents of MetamorphismMujeeb Rahman DostNo ratings yet
- 24 MetamorphismDocument18 pages24 MetamorphismTyler PesterNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets Earth Science Grade 11 Quarter 2, Week 2BDocument8 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets Earth Science Grade 11 Quarter 2, Week 2BShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 12.2 Factors Controlling MetamorphismDocument14 pagesEarth Science SHS 12.2 Factors Controlling MetamorphismCamille AnibNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Metamorphism ReviewerDocument8 pagesGroup 7 Metamorphism ReviewermuhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- 6 - Metamorphic RocksDocument50 pages6 - Metamorphic Rocksloralara100% (1)
- MetamorphismDocument35 pagesMetamorphismjerry100% (1)
- Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument31 pagesChanging Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual instant download all chapterklausstubbax47No ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Metamorphic RocksDocument31 pagesLecture 05 Metamorphic RocksMuhammad Inam ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : MetamorphismDocument11 pagesEndogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : MetamorphismHannah LNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument31 pagesInstant Download PDF Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual Full Chaptersaiidimimic100% (5)
- LESSON 4 MetamorphismDocument3 pagesLESSON 4 Metamorphismjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- METAMORPHISM by Bhargav Arandhara-1Document15 pagesMETAMORPHISM by Bhargav Arandhara-1Bhargav ArandharaNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Process: Ms. Cherry Grace P. CuetoDocument23 pagesEndogenic Process: Ms. Cherry Grace P. CuetoJane Claire ManongsongNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The Earth S Relief Unit 10 21-22Document59 pagesThe Evolution of The Earth S Relief Unit 10 21-22miri21.02.06No ratings yet
- METAMORPHISMDocument42 pagesMETAMORPHISMResh GarciaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument6 pagesMetamorphic RocksrolandNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument7 pagesMetamorphismDustin LabsanNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument11 pagesMetamorphismRene Rey B. SulapasNo ratings yet
- Report Metamorphism FINALDocument67 pagesReport Metamorphism FINALKristine Joy ErangNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument10 pagesMetamorphism and Metamorphic RocksEduardo Romera JuberíasNo ratings yet
- L A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDocument52 pagesL A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDaniel JayapuraNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Process Part 2 PDFDocument35 pagesEndogenic Process Part 2 PDFIvan ZenitramNo ratings yet
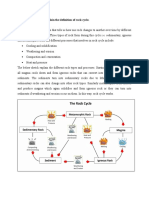
- in Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleDocument4 pagesin Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleGeology for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Curtis Williams E105 Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineral DepositsDocument8 pagesCurtis Williams E105 Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineral DepositsfvelasquezdNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument28 pagesMetamorphic Rocksapi-238589602No ratings yet
- ELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismDocument38 pagesELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Document22 pagesObjectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Akankwasa RonaldNo ratings yet
- CE-121 Metamorphic Rocks by Hamza SubhaniDocument44 pagesCE-121 Metamorphic Rocks by Hamza SubhaniMohammad RazaNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument12 pagesMetamorphismJelesa TabanginNo ratings yet
- 7.petrology MetamorphicrocksDocument65 pages7.petrology MetamorphicrocksClaudyo A Lerry MandeNo ratings yet
- Agent of MetamorphismDocument11 pagesAgent of MetamorphismMubashirKhattakNo ratings yet
- Types & MetamorphDocument7 pagesTypes & Metamorphreef_silverNo ratings yet
- 07 Metamorphic RocksDocument17 pages07 Metamorphic Rocksjcasafranca0% (1)
- Types of MetamorphismDocument8 pagesTypes of MetamorphismLuis Miguel Mogollon RamosNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rocks (Suman)Document34 pagesMetamorphic Rocks (Suman)Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- TypesmetamorphDocument7 pagesTypesmetamorphapi-19643403No ratings yet
- 5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core ConceptDocument8 pages5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core Conceptlandworth2450No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationlimr PozzolanaDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationlimr PozzolanaRaghu ThyagarajNo ratings yet
- Static and Seismic Design of One-Way and Two-Way JDocument17 pagesStatic and Seismic Design of One-Way and Two-Way JRAVIRAJ KARKENo ratings yet
- Wanchem Light Stabilizer 783Document1 pageWanchem Light Stabilizer 783Xuân Giang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutDocument2 pagesDura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutANILNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetJudi TurkNo ratings yet
- Strainer PDFDocument64 pagesStrainer PDFSanket SavlaNo ratings yet
- FeltDocument8 pagesFeltadhityaNo ratings yet
- Do 029 S2019Document6 pagesDo 029 S2019ZA TarraNo ratings yet
- Stressline Lintel Technical June 2016 Final - Digi - DownloadDocument4 pagesStressline Lintel Technical June 2016 Final - Digi - DownloadKovacs Zsolt-IstvanNo ratings yet
- Energy: Ivan Najdenov, Karlo T. Rai C, Gordana KokezaDocument9 pagesEnergy: Ivan Najdenov, Karlo T. Rai C, Gordana Kokeza......No ratings yet
- LedDocument20 pagesLedYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Index - 10000 ENDocument34 pagesIndex - 10000 ENAzmi Rizki LubisNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics Report 05Document8 pagesRock Mechanics Report 05Bernardo Baqueiro RiosNo ratings yet
- iNORGANIC Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesiNORGANIC Salt AnalysisNishant KaushikNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument6 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionsKyla AngelleNo ratings yet
- OX1272Document9 pagesOX1272Donatas BertasiusNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument12 pagesReferencesArul KirubakaranNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilsDocument13 pagesTypes of SoilsAaryan MoreNo ratings yet
- Crysytal Growth GelDocument18 pagesCrysytal Growth GelGnana SilviaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Specification Manual 45 MM SystemDocument46 pagesArchitectural Specification Manual 45 MM SystemHelmer Edgardo Monroy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Ps 6 - Material Balance With Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesPs 6 - Material Balance With Chemical ReactionsLizvel Keith TorresNo ratings yet
- Van Zyl 2017 JWSRT Evaluating The Pressure-Leakage Behaviour of Leaks in Water Pipes PDFDocument14 pagesVan Zyl 2017 JWSRT Evaluating The Pressure-Leakage Behaviour of Leaks in Water Pipes PDFguhmoroNo ratings yet
- Determination of Velocity Seal AreaDocument4 pagesDetermination of Velocity Seal AreaNajem A. SakorNo ratings yet
- Piping Slide ChartDocument36 pagesPiping Slide Charttandk1989100% (2)
- Phases Present in The Wrought Superalloy Udimet 700Document2 pagesPhases Present in The Wrought Superalloy Udimet 700Enary SalernoNo ratings yet
- 3 Kota Veheras of Sri LankaDocument6 pages3 Kota Veheras of Sri LankaPBG DISSANAYAKENo ratings yet
- WPS Format For ASME IX - PQR-AllDocument3 pagesWPS Format For ASME IX - PQR-AllThe Welding Inspections Community100% (1)
- Content of Watersoluble Sodium in Urban SoilsDocument1 pageContent of Watersoluble Sodium in Urban SoilsBosko BoskovskiNo ratings yet
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Kcel Tumaliuan Dassil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesThis document discusses metamorphism, which is the process by which rocks undergo changes due to heat, pressure, and chemical activity. There are two main types of metamorphism: contact metamorphism, which occurs near igneous intrusions, and regional metamorphism, which affects large areas. During metamorphism, minerals change, rocks recrystallize, and new minerals form through chemical reactions as temperatures and pressures increase with depth. Heat, pressure, fluids, time, and stress all influence metamorphic processes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses metamorphism, which is the process by which rocks undergo changes due to heat, pressure, and chemical activity. There are two main types of metamorphism: contact metamorphism, which occurs near igneous intrusions, and regional metamorphism, which affects large areas. During metamorphism, minerals change, rocks recrystallize, and new minerals form through chemical reactions as temperatures and pressures increase with depth. Heat, pressure, fluids, time, and stress all influence metamorphic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views18 pagesUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Kcel Tumaliuan DassilThis document discusses metamorphism, which is the process by which rocks undergo changes due to heat, pressure, and chemical activity. There are two main types of metamorphism: contact metamorphism, which occurs near igneous intrusions, and regional metamorphism, which affects large areas. During metamorphism, minerals change, rocks recrystallize, and new minerals form through chemical reactions as temperatures and pressures increase with depth. Heat, pressure, fluids, time, and stress all influence metamorphic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
WHAT I KNOW
Directions: Read and analyze each statement and choose the letter which corresponds to the
correct answer by writing it on your answer sheet/notebook.
1. Which of the following statements best describe metamorphosis?
a. change in the rock formation
b. process of rock formation
c. process which involves changes
d. change that takes place within body of rock once expose to different conditions
2. Which of the following metamorphism is affected by heat and reactive fluid?
a. contact only
b. regional only
c. both contact and regional
a. neither contact nor regional
3.Which of the following is an example of rock produced by a contact metamorphism
CHANGES IN MINERAL
COMPONENTS AND TEXTURE
OF ROCKS (METAMORPHISM)
METAMORPHISM
Is the change that takes place within a body of
rock as a result being subjected too conditions that
are different from those in which it is formed. It is
from Greek word “ meta” means change and
“morphe” means form.
METAMORPHIC ROCK
• Rocks that have been subjected to either enough heat
or pressure to cause the minerals in that rock to
undergo solid state chemical changes.
• Metamorphic rocks never melt- if they did they would
become igneous magma.This is why we say that the
changes are solid state.
CHANGES OCCURS DURING
METAMORPHISM
As rocks are subjected to great heat and pressure they begin to
undergo several changes
• Changes in the minerals
• Folding and bending of rocks causing change in its shape
• Recrystallization causes changes in minerals size and shape.
• Chemical reactions occur between the minerals to form new sets of
minerals that are more stable at the pressure and temperature of the
environment, and new minerals form as a result of polymorphic
phase transformations.
AGENTS AND FACTORS THAT
CONTROL METAMORPHISM
• Heat
• Pressure
• Chemical activity
• Fluid phase
HEAT
• Heat is the most important agent of metamorphism.
• Normally a geothermal gradient increases in temperature with depth at
about 30 degree Celsius per kilometer.
• The gradient is much higher in some areas, for example at the edges of
continents where one oceanic plate dives under another or where plutons
have become embedded in the crust.
• The first minerals that begin to change are clays , then others that are more
stable begin to change as the temperature increases.
• It usually takes burial to 20KM or more for feldspars to begin to
metamorphose.
PRESSURE
• Pressure increases with depth so that there is
1,000kg/cm2 at 4 km depth.
• Increased pressure may cause minerals to melt
or may cause atoms to move into
configurations that represent tighter packing.
TYPES OF PRESSURE
• CONFINING PRESSURE ( lithostatic )
- Equal pressure in all directions tends to cause objects to uniformly become
smaller.
• DIFFERENTIAL STRESS
- If the stress is not equal from all directions,then the stress is called a differential
stress.
• SHEAR STRESS
– causes objects to be smeared out in the direction of applied stress.
TIME
- Most metamorphic reactions occur very slowly.
Estimates of the growth rates of new minerals within a
rock during metamorphism suggest that new material is
added to the outside of mineral crystals at a rate of
approximately 1 mm per million years. Very slow
reaction rates make it difficult to study metamorphic
processes in a lab.
FLUID PHASE
• Water is the main fluid present within rocks
of the crust, and the only one considered
here. The presence of water is important for
two main reasons. First, water facilitates
the transfer of ions between minerals and
within minerals, and therefore increases the
rates at which metamorphic reactions take
place. This speeds the process up so
metamorphism might occur more rapidly, or
metamorphic processes that might not
otherwise have had time to be completed.
TYPES OF
METAMORPHISM
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Maximising Molecular Sieve Performance in Gas ProcessingDocument18 pagesMaximising Molecular Sieve Performance in Gas ProcessingAhmed ElShora100% (1)
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockABU SALEH MOHAMMAD RAFI100% (1)
- Introduction To Metamorphic PetrologyDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Metamorphic PetrologynsmpofuNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RockDocument47 pagesMetamorphic RockYZKNo ratings yet
- Q2-Lesson 4 MetamorphismDocument34 pagesQ2-Lesson 4 MetamorphismBlesie-Lyn BautistaNo ratings yet
- MetamorphicDocument22 pagesMetamorphicJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Metamorphic RocksDocument27 pagesMetamorphic RocksCrafty JigyasaNo ratings yet
- 02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Document10 pages02 Metamorphic Petrology - 1Eadaw100% (1)
- Black Doodle Group Project PresentationDocument26 pagesBlack Doodle Group Project PresentationJoseph BaclayoNo ratings yet
- Agents of MetamorphismDocument6 pagesAgents of MetamorphismZahid RahmanNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism NotesDocument2 pagesMetamorphism NotesMaria Pauline AsiNo ratings yet
- Phy. Geol. 8: Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument28 pagesPhy. Geol. 8: Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksSalman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Conditions of Metamorphism-1Document28 pagesConditions of Metamorphism-1sabreenaakhter099No ratings yet
- Engineering Geology For Civil EngineersDocument14 pagesEngineering Geology For Civil EngineersDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- G11 Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesG11 Earth ScienceAlthea RivadeloNo ratings yet
- Physical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument39 pagesPhysical Geology 2nd Ed Chapter 7 Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksYeremia PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Earth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismDocument35 pagesEarth-Science w2 l2 q2 MetamorphismCj Padata100% (1)
- Metamorphism and MetastomatismDocument10 pagesMetamorphism and Metastomatismbilal ahmadNo ratings yet
- Solid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofDocument8 pagesSolid Compaction Rock Mineral: Metamorphism, Mineralogical and Structural Adjustments ofJahque LadaranNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document4 pagesWeek 4janice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Answer #4: Agents of MetamorphismDocument2 pagesAnswer #4: Agents of MetamorphismMujeeb Rahman DostNo ratings yet
- 24 MetamorphismDocument18 pages24 MetamorphismTyler PesterNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets Earth Science Grade 11 Quarter 2, Week 2BDocument8 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets Earth Science Grade 11 Quarter 2, Week 2BShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 12.2 Factors Controlling MetamorphismDocument14 pagesEarth Science SHS 12.2 Factors Controlling MetamorphismCamille AnibNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Metamorphism ReviewerDocument8 pagesGroup 7 Metamorphism ReviewermuhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- 6 - Metamorphic RocksDocument50 pages6 - Metamorphic Rocksloralara100% (1)
- MetamorphismDocument35 pagesMetamorphismjerry100% (1)
- Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument31 pagesChanging Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual instant download all chapterklausstubbax47No ratings yet
- Lecture 05 Metamorphic RocksDocument31 pagesLecture 05 Metamorphic RocksMuhammad Inam ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : MetamorphismDocument11 pagesEndogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) : MetamorphismHannah LNo ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument31 pagesInstant Download PDF Changing Earth Exploring Geology and Evolution 7th Edition Monroe Solutions Manual Full Chaptersaiidimimic100% (5)
- LESSON 4 MetamorphismDocument3 pagesLESSON 4 Metamorphismjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- METAMORPHISM by Bhargav Arandhara-1Document15 pagesMETAMORPHISM by Bhargav Arandhara-1Bhargav ArandharaNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Process: Ms. Cherry Grace P. CuetoDocument23 pagesEndogenic Process: Ms. Cherry Grace P. CuetoJane Claire ManongsongNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of The Earth S Relief Unit 10 21-22Document59 pagesThe Evolution of The Earth S Relief Unit 10 21-22miri21.02.06No ratings yet
- METAMORPHISMDocument42 pagesMETAMORPHISMResh GarciaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument6 pagesMetamorphic RocksrolandNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument7 pagesMetamorphismDustin LabsanNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument11 pagesMetamorphismRene Rey B. SulapasNo ratings yet
- Report Metamorphism FINALDocument67 pagesReport Metamorphism FINALKristine Joy ErangNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism and Metamorphic RocksDocument10 pagesMetamorphism and Metamorphic RocksEduardo Romera JuberíasNo ratings yet
- L A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDocument52 pagesL A M P I R A N: Sumber: Batuan - HTMLDaniel JayapuraNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Process Part 2 PDFDocument35 pagesEndogenic Process Part 2 PDFIvan ZenitramNo ratings yet
- in Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleDocument4 pagesin Your Own Words Explain The Definition of Rock Cycle. Rock CycleGeology for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Curtis Williams E105 Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineral DepositsDocument8 pagesCurtis Williams E105 Hydrothermal Alteration and Mineral DepositsfvelasquezdNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic RocksDocument28 pagesMetamorphic Rocksapi-238589602No ratings yet
- ELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismDocument38 pagesELS-Q1-Week 4-Magmatism and MetamorphismRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- Objectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Document22 pagesObjectives: 7.0 Nature and Classification of Metamorphic Rocks 7.1Akankwasa RonaldNo ratings yet
- CE-121 Metamorphic Rocks by Hamza SubhaniDocument44 pagesCE-121 Metamorphic Rocks by Hamza SubhaniMohammad RazaNo ratings yet
- MetamorphismDocument12 pagesMetamorphismJelesa TabanginNo ratings yet
- 7.petrology MetamorphicrocksDocument65 pages7.petrology MetamorphicrocksClaudyo A Lerry MandeNo ratings yet
- Agent of MetamorphismDocument11 pagesAgent of MetamorphismMubashirKhattakNo ratings yet
- Types & MetamorphDocument7 pagesTypes & Metamorphreef_silverNo ratings yet
- 07 Metamorphic RocksDocument17 pages07 Metamorphic Rocksjcasafranca0% (1)
- Types of MetamorphismDocument8 pagesTypes of MetamorphismLuis Miguel Mogollon RamosNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic Rocks (Suman)Document34 pagesMetamorphic Rocks (Suman)Sameer ShaikhNo ratings yet
- TypesmetamorphDocument7 pagesTypesmetamorphapi-19643403No ratings yet
- 5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core ConceptDocument8 pages5500 Dynamics Colorwave Accent Rings Core Conceptlandworth2450No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationlimr PozzolanaDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationlimr PozzolanaRaghu ThyagarajNo ratings yet
- Static and Seismic Design of One-Way and Two-Way JDocument17 pagesStatic and Seismic Design of One-Way and Two-Way JRAVIRAJ KARKENo ratings yet
- Wanchem Light Stabilizer 783Document1 pageWanchem Light Stabilizer 783Xuân Giang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Dura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutDocument2 pagesDura. Grout: Non-Shrink Cementitious GroutANILNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetJudi TurkNo ratings yet
- Strainer PDFDocument64 pagesStrainer PDFSanket SavlaNo ratings yet
- FeltDocument8 pagesFeltadhityaNo ratings yet
- Do 029 S2019Document6 pagesDo 029 S2019ZA TarraNo ratings yet
- Stressline Lintel Technical June 2016 Final - Digi - DownloadDocument4 pagesStressline Lintel Technical June 2016 Final - Digi - DownloadKovacs Zsolt-IstvanNo ratings yet
- Energy: Ivan Najdenov, Karlo T. Rai C, Gordana KokezaDocument9 pagesEnergy: Ivan Najdenov, Karlo T. Rai C, Gordana Kokeza......No ratings yet
- LedDocument20 pagesLedYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Index - 10000 ENDocument34 pagesIndex - 10000 ENAzmi Rizki LubisNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics Report 05Document8 pagesRock Mechanics Report 05Bernardo Baqueiro RiosNo ratings yet
- iNORGANIC Salt AnalysisDocument12 pagesiNORGANIC Salt AnalysisNishant KaushikNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionsDocument6 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionsKyla AngelleNo ratings yet
- OX1272Document9 pagesOX1272Donatas BertasiusNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument12 pagesReferencesArul KirubakaranNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilsDocument13 pagesTypes of SoilsAaryan MoreNo ratings yet
- Crysytal Growth GelDocument18 pagesCrysytal Growth GelGnana SilviaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Specification Manual 45 MM SystemDocument46 pagesArchitectural Specification Manual 45 MM SystemHelmer Edgardo Monroy GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Ps 6 - Material Balance With Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesPs 6 - Material Balance With Chemical ReactionsLizvel Keith TorresNo ratings yet
- Van Zyl 2017 JWSRT Evaluating The Pressure-Leakage Behaviour of Leaks in Water Pipes PDFDocument14 pagesVan Zyl 2017 JWSRT Evaluating The Pressure-Leakage Behaviour of Leaks in Water Pipes PDFguhmoroNo ratings yet
- Determination of Velocity Seal AreaDocument4 pagesDetermination of Velocity Seal AreaNajem A. SakorNo ratings yet
- Piping Slide ChartDocument36 pagesPiping Slide Charttandk1989100% (2)
- Phases Present in The Wrought Superalloy Udimet 700Document2 pagesPhases Present in The Wrought Superalloy Udimet 700Enary SalernoNo ratings yet
- 3 Kota Veheras of Sri LankaDocument6 pages3 Kota Veheras of Sri LankaPBG DISSANAYAKENo ratings yet
- WPS Format For ASME IX - PQR-AllDocument3 pagesWPS Format For ASME IX - PQR-AllThe Welding Inspections Community100% (1)
- Content of Watersoluble Sodium in Urban SoilsDocument1 pageContent of Watersoluble Sodium in Urban SoilsBosko BoskovskiNo ratings yet