Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Uploaded by
PREEVITHAA campus area network (CAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) located in close proximity, such as within a campus or building. It uses switched Ethernet backbone to connect buildings and parts of the campus. Key components of a CAN include high-performance switching, redundancy, virtualized and centralized servers, and server farms to provide resources to users. Network management is also an important aspect to monitor the network performance and security.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Design Scenario Chapter 5Document6 pagesDesign Scenario Chapter 5jtrillossNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1Document20 pagesChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1NURRUL ISMAILNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument7 pagesVirtualizationSusith KannanNo ratings yet
- Campus Infrastructure ModelDocument244 pagesCampus Infrastructure ModelxrasnaNo ratings yet
- Campus Area NetworkDocument4 pagesCampus Area NetworkanuyawellingNo ratings yet
- Network Security and Administration Group WorkDocument44 pagesNetwork Security and Administration Group WorkMunene KelvinNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NetworkingDocument99 pagesUnit 6 NetworkingtotoNo ratings yet
- Data Center Network InfrastructureDocument57 pagesData Center Network InfrastructureAnonymous kbmKQLe0JNo ratings yet
- A) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnDocument14 pagesA) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnRoebarNo ratings yet
- CISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewDocument10 pagesCISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewTarek HniediNo ratings yet
- Types of Distributed SystemsDocument21 pagesTypes of Distributed SystemsGARIMA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Jler-8eklr7 R6 enDocument16 pagesJler-8eklr7 R6 encarlosNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureDocument23 pagesProject Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureKavita KarkiNo ratings yet
- Student Guide FC 120 FC Basics LDocument66 pagesStudent Guide FC 120 FC Basics LVishal MulikNo ratings yet
- QN.2 ANS:-: The Main Network Set-Up in The Richmond Book Is Shown BelowDocument4 pagesQN.2 ANS:-: The Main Network Set-Up in The Richmond Book Is Shown BelowpoudelnNo ratings yet
- CSC 415 - NET-CENTRIC COMPUTING1 (Compatibility Mode)Document69 pagesCSC 415 - NET-CENTRIC COMPUTING1 (Compatibility Mode)ayomidekelly21No ratings yet
- Communication Part 1Document34 pagesCommunication Part 1panamasmasNo ratings yet
- LDoms - Knowledge SharingDocument32 pagesLDoms - Knowledge SharingselvanirmalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument21 pagesChapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsPro NebyuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document50 pagesChapter 02WilliamNo ratings yet
- MX-ONE User ManualDocument72 pagesMX-ONE User ManualAnisleidyNo ratings yet
- Bisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedDocument6 pagesBisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedvictorsebstarNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of Substation Process Lan: M. Perkov, D. - XudvrylüDocument4 pagesConceptual Design of Substation Process Lan: M. Perkov, D. - Xudvrylücastilho22No ratings yet
- 5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSDocument9 pages5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSShashank GosaviNo ratings yet
- Astu Network Design and Documentation PresentationDocument17 pagesAstu Network Design and Documentation PresentationllllllNo ratings yet
- SU Na Baze Internet PDFDocument7 pagesSU Na Baze Internet PDFT.AnithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3.1 Designing A Network TopologyDocument49 pagesChapter3.1 Designing A Network Topologyquoc.dx.62cnttNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Call Flow in A CDMA Network - CPT2Document21 pagesDemonstration of Call Flow in A CDMA Network - CPT2electricalbah100% (1)
- Chapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document92 pagesChap 2Iman KhoujaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition Standard EditionDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition Standard Editionchukkapalli69No ratings yet
- CSS12 Q3 Wk1Document11 pagesCSS12 Q3 Wk1jaimelovenaNo ratings yet
- CA - Ex - S4C1 - Introduction To WANs (Compatibility Mode)Document61 pagesCA - Ex - S4C1 - Introduction To WANs (Compatibility Mode)Hung LeNo ratings yet
- ITNE 3006 - AssignmentDocument13 pagesITNE 3006 - AssignmentSadia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- College Network ScenarioDocument18 pagesCollege Network ScenarioSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Tier Level Data Center RequirementsDocument7 pagesGlossary: Tier Level Data Center RequirementsJoson ChanNo ratings yet
- WorldSkills Junior 2019Document23 pagesWorldSkills Junior 2019DahayatNo ratings yet
- Secure Cloud Computing With A Virtualized Network InfrastructureDocument7 pagesSecure Cloud Computing With A Virtualized Network InfrastructureNeha AroraNo ratings yet
- Networkingglossary 2022Document17 pagesNetworkingglossary 2022osama.anwerNo ratings yet
- SYCSDocument3 pagesSYCSbhagyashribbsccsNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Chapter 8 + 9Document10 pagesStudy Notes - Chapter 8 + 9pmurphy24No ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution OverviewDocument20 pagesCisco Unified Wireless Network Solution OverviewPaul CherresNo ratings yet
- MCS-022 Operating System Concepts andDocument29 pagesMCS-022 Operating System Concepts andSumit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Uccx B Soldg-For-unified-ccx Chapter 0100Document14 pagesUccx B Soldg-For-unified-ccx Chapter 0100JayD77No ratings yet
- Cloud Enabling TechnologyDocument103 pagesCloud Enabling TechnologySahithi NamalaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Document9 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Jeffrey MacabareNo ratings yet
- Distributed Overlay Virtual Ethernet (DOVE) Networks: Renato Recio IBM Fellow & System Networking CTODocument27 pagesDistributed Overlay Virtual Ethernet (DOVE) Networks: Renato Recio IBM Fellow & System Networking CTORitu NathanNo ratings yet
- Campus DesignDocument9 pagesCampus DesignSaffanArainNo ratings yet
- Network & System Admin ch1 To 10.doc..bakDocument92 pagesNetwork & System Admin ch1 To 10.doc..bakDanny KirooNo ratings yet
- Revision 9608 Section 1.2Document20 pagesRevision 9608 Section 1.2Debasruti SahaNo ratings yet
- A WSN-Based Large Electrical - 2010Document6 pagesA WSN-Based Large Electrical - 2010Jeya RamanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CssDocument4 pagesReviewer CsstiamzoncasNo ratings yet
- Examining The Ciscoworks Lms ApplicationsDocument16 pagesExamining The Ciscoworks Lms ApplicationsEssou AmineNo ratings yet
- Day 5.2Document54 pagesDay 5.2Namrata PaudelNo ratings yet
- S.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFDocument7 pagesS.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFguimanolNo ratings yet
- Posted by Admin Labels: CCNA 4 Exams Answers, CCNA 4 Ver 4.0, CCNA Discovery 4Document7 pagesPosted by Admin Labels: CCNA 4 Exams Answers, CCNA 4 Ver 4.0, CCNA Discovery 4Keenan 'Monni' SharpeNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Network Operating SystemDocument10 pagesTopic 9 Network Operating SystemsimonnjauNo ratings yet
- Fibcom 6300NMS PDFDocument2 pagesFibcom 6300NMS PDFRaja SolaimalaiNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Surendran GunalanDocument25 pagesSurendran GunalanPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Python and Sublime ConfigurationDocument17 pagesPython and Sublime ConfigurationPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Mad-LT1 SignedDocument2 pagesMad-LT1 SignedPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5Document32 pagesChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Install Python Step by StepDocument2 pagesInstall Python Step by StepPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Muet PresentationDocument6 pagesMuet PresentationPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- DFN 40183: Open Source Server Administrator.: Final Assessment (Practical Test)Document12 pagesDFN 40183: Open Source Server Administrator.: Final Assessment (Practical Test)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Case Study - (PK)Document7 pagesCase Study - (PK)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Python and Mysql: Dfn40263 - Programming Essentials in PythonDocument28 pagesPython and Mysql: Dfn40263 - Programming Essentials in PythonPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Bahagian B: 45 MarkahDocument6 pagesBahagian B: 45 MarkahPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- PBT (PK)Document5 pagesPBT (PK)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Domain Name Service Agreement: Philippine Network Foundation Incorporated (PHNET) 12 May 2014Document5 pagesDomain Name Service Agreement: Philippine Network Foundation Incorporated (PHNET) 12 May 2014AubreyNo ratings yet
- Gea Matrix .Lon: Air Treatment DivisionDocument56 pagesGea Matrix .Lon: Air Treatment DivisionCosmin StroiaNo ratings yet
- 026 4144 Site Supervisor Controller Quick Setup Guide en Us 2188962Document11 pages026 4144 Site Supervisor Controller Quick Setup Guide en Us 2188962jrodNo ratings yet
- Opticube Training V2Document27 pagesOpticube Training V2Obinna ObiefuleNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 To 10: Web Technologies (Internet Technologies) Questions With Answers Set 1Document11 pagesQuestions 1 To 10: Web Technologies (Internet Technologies) Questions With Answers Set 1prabakaranNo ratings yet
- Systec MP 90 120 enDocument1 pageSystec MP 90 120 enDũng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cisco SwitchesDocument4 pagesCisco SwitchesrodolfocelisNo ratings yet
- Configuration Example To Migrate Spanning Tree From PVST+ To MST - CiscoDocument16 pagesConfiguration Example To Migrate Spanning Tree From PVST+ To MST - CiscoTomta FranckNo ratings yet
- IBwave Mobile User GuideDocument106 pagesIBwave Mobile User GuideEarl100% (1)
- VON Europe - Comments On ACMA's Consultation On Allocation and Charging of NumbersDocument4 pagesVON Europe - Comments On ACMA's Consultation On Allocation and Charging of NumbersVoice on the Net (VON) Coalition EuropeNo ratings yet
- Keyboard ShortcutsDocument9 pagesKeyboard ShortcutsakashdskyNo ratings yet
- RA 2114 Nutanix Enterprise Cloud For AIDocument66 pagesRA 2114 Nutanix Enterprise Cloud For AIDavid YehNo ratings yet
- Home - DOS Windows 32 & 64 Bit MAME Arcade Cabinet ConfiguratiDocument19 pagesHome - DOS Windows 32 & 64 Bit MAME Arcade Cabinet ConfiguratiLeo. D'Alençon R.No ratings yet
- Juniper EX Switches SNMPDocument5 pagesJuniper EX Switches SNMPRai Kashif JahangirNo ratings yet
- REU610Document68 pagesREU610mrithunNo ratings yet
- A FORTRAN 90 Numerical Library DownloadDocument1 pageA FORTRAN 90 Numerical Library DownloadAnonymous 1rLNlqUNo ratings yet
- Use Audio and Video Conferencing Tools To Share Ideas and Work With Others Online Week 7Document4 pagesUse Audio and Video Conferencing Tools To Share Ideas and Work With Others Online Week 7edwinoga80No ratings yet
- Hacking SCADADocument37 pagesHacking SCADAkonto27No ratings yet
- Remote Data Interface RDI 08-001A, Analog (MAN11641-11)Document38 pagesRemote Data Interface RDI 08-001A, Analog (MAN11641-11)justinNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 1Document7 pagesĐỀ 1Trà Dương PhươngNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Pnematic & Blautek PDFDocument40 pagesCatalogo Pnematic & Blautek PDFgustavoba7No ratings yet
- 03 Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide-BookDocument318 pages03 Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide-Booka.giacchettoNo ratings yet
- A MIL Q1M8 Teacher Copy FinalDocument22 pagesA MIL Q1M8 Teacher Copy FinalIvy BarnacheaNo ratings yet
- Ug EthernetDocument223 pagesUg EthernetshinhunoNo ratings yet
- CJ Programming ManualDocument434 pagesCJ Programming ManualjpgoasNo ratings yet
- FPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev ACDocument45 pagesFPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev ACMihaelNo ratings yet
- Edms Erd ManualDocument9 pagesEdms Erd ManualArjuna AnomNo ratings yet
- HL-3170cdw 2 Page Brochure FINAL 041013 PDFDocument2 pagesHL-3170cdw 2 Page Brochure FINAL 041013 PDFlleptirNo ratings yet
- Blockchain 2018Document16 pagesBlockchain 2018MoAzZam rAjpOotNo ratings yet
- Choi Midterm 1 PracticeDocument3 pagesChoi Midterm 1 PracticePhillip HsuNo ratings yet
Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Uploaded by
PREEVITHA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views17 pagesA campus area network (CAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) located in close proximity, such as within a campus or building. It uses switched Ethernet backbone to connect buildings and parts of the campus. Key components of a CAN include high-performance switching, redundancy, virtualized and centralized servers, and server farms to provide resources to users. Network management is also an important aspect to monitor the network performance and security.
Original Description:
Network Server
Original Title
CHAPTER 2 CAMPUS AREA NETWORK SERVER CONFIGURATIONS 2.1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA campus area network (CAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) located in close proximity, such as within a campus or building. It uses switched Ethernet backbone to connect buildings and parts of the campus. Key components of a CAN include high-performance switching, redundancy, virtualized and centralized servers, and server farms to provide resources to users. Network management is also an important aspect to monitor the network performance and security.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views17 pagesChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1
Uploaded by
PREEVITHAA campus area network (CAN) connects multiple local area networks (LANs) located in close proximity, such as within a campus or building. It uses switched Ethernet backbone to connect buildings and parts of the campus. Key components of a CAN include high-performance switching, redundancy, virtualized and centralized servers, and server farms to provide resources to users. Network management is also an important aspect to monitor the network performance and security.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
+
Campus Area Network
Server Configuration
+
Chapter 2 Objectives:
1. Understand Campus Area Network.
(CAN)
+
2.1 Campus Area Network
A campus network is an enterprise network consisting of
many LANs in one or more buildings, all connected and all
usually in the same geographic area.
As campus networks have grown and technologies have
matured, network engineers and architects have many more
options to consider than the hubs, Ethernet switches, and
routers traditionally put in place.
A company typically owns the entire campus network, as
well as the physical wiring.
+
2.1 Campus Area Network
Campus networks commonly consist of Ethernet, 802.11
wireless LANs, higher-speed Fast Ethernet, Fast
EtherChannel, and Gigabit Ethernet LANs.
Some campus networks also consist of legacy Token Ring
and FDDI.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
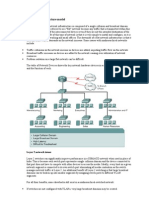
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
A) High Performance
---> like application performance must be provided at all times
throughout the campus.
---> A high-capacity, centralized server farm connects to the
backbone and provides internal server resources to users.
---> Moderate over subscription is common in the LAN access
layer but line-rate performance is highly desirable in the LAN
aggregation and core layers.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
B) Switched Backbone
---> called the campus backbone, that connects buildings and
different parts of the campus.
---> Network management is an important component in a
campus network design
---> A campus backbone must provide access to management
devices that support monitoring, logging, troubleshooting,
security, and other common management functions.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
C)Redundancy
***> Redundancy refer to the use of reliable backup methods to
protect against network failure ***
Refer to redundancy methods.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
D)Mirrored / Virtualization Servers
---> server virtualization is the masking of server resources,
including the number and identity of individual physical
servers, processors, and operating systems, from server users.
--->The server administrator uses a software application to divide
one physical server into multiple isolated virtual environments.
--->The virtual environments are sometimes called virtual private
servers, but they are also known as guests, instances,
containers, or emulations.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
D)Mirrored / Virtualization Servers
--->There are three popular approaches to server virtualization:
@}- The virtual machine model
@}- The paravirtual machine model
@}- virtualization at the operating system (OS) layer.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Components of Campus Area Network (CAN) topology:
E) Centralized Servers
---> type of network where all users connect to a central server,
which is the acting agent for all communications.
--->This server would store both the communications and the user
account information. Most public instant messaging , platform.
---> use a centralized network. Also called centralized server-
structure.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Server Farm Structure
*** Database management system (DBMS) that can respond to
queries from client machines formatted in the SQL language.
*** Two database management products
from Sybase and Microsoft. Both companies offer client-server
DBMS products called SQL Server.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Server Farm Structure
A group of enterprise servers along with their access and
distribution layer switches
A server farm can be made up of servers running applications
that are accessed by users from all across the enterprise.
The entire server farm can be identified as its own switch block
and given a layer of access switches uplinked to dual distribution
switches (multilayer).
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
Server Farm Structure
---> File server: a computer and storage
device dedicated to storing files. Any user on the network can
store files on the server.
---> Print server: a computer that manages one or more printers,
and a network server is a computer that manages network traffic.
---> Database server: A computer system that processes database
queries.
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
+ 2.1 Campus Area Network
You might also like
- Design Scenario Chapter 5Document6 pagesDesign Scenario Chapter 5jtrillossNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1Document20 pagesChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.1NURRUL ISMAILNo ratings yet
- VirtualizationDocument7 pagesVirtualizationSusith KannanNo ratings yet
- Campus Infrastructure ModelDocument244 pagesCampus Infrastructure ModelxrasnaNo ratings yet
- Campus Area NetworkDocument4 pagesCampus Area NetworkanuyawellingNo ratings yet
- Network Security and Administration Group WorkDocument44 pagesNetwork Security and Administration Group WorkMunene KelvinNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 NetworkingDocument99 pagesUnit 6 NetworkingtotoNo ratings yet
- Data Center Network InfrastructureDocument57 pagesData Center Network InfrastructureAnonymous kbmKQLe0JNo ratings yet
- A) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnDocument14 pagesA) (I) A Distributed Computer System Consists of Multiple Software Components That Are OnRoebarNo ratings yet
- CISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewDocument10 pagesCISCO Data Center Architecture OverviewTarek HniediNo ratings yet
- Types of Distributed SystemsDocument21 pagesTypes of Distributed SystemsGARIMA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Jler-8eklr7 R6 enDocument16 pagesJler-8eklr7 R6 encarlosNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureDocument23 pagesProject Report On Network Operating System: Strength To Client/Server ArchitectureKavita KarkiNo ratings yet
- Student Guide FC 120 FC Basics LDocument66 pagesStudent Guide FC 120 FC Basics LVishal MulikNo ratings yet
- QN.2 ANS:-: The Main Network Set-Up in The Richmond Book Is Shown BelowDocument4 pagesQN.2 ANS:-: The Main Network Set-Up in The Richmond Book Is Shown BelowpoudelnNo ratings yet
- CSC 415 - NET-CENTRIC COMPUTING1 (Compatibility Mode)Document69 pagesCSC 415 - NET-CENTRIC COMPUTING1 (Compatibility Mode)ayomidekelly21No ratings yet
- Communication Part 1Document34 pagesCommunication Part 1panamasmasNo ratings yet
- LDoms - Knowledge SharingDocument32 pagesLDoms - Knowledge SharingselvanirmalNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument21 pagesChapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsPro NebyuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document50 pagesChapter 02WilliamNo ratings yet
- MX-ONE User ManualDocument72 pagesMX-ONE User ManualAnisleidyNo ratings yet
- Bisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedDocument6 pagesBisf 2207 Past Paper RevisedvictorsebstarNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of Substation Process Lan: M. Perkov, D. - XudvrylüDocument4 pagesConceptual Design of Substation Process Lan: M. Perkov, D. - Xudvrylücastilho22No ratings yet
- 5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSDocument9 pages5.study Experiment On NOS and DOSShashank GosaviNo ratings yet
- Astu Network Design and Documentation PresentationDocument17 pagesAstu Network Design and Documentation PresentationllllllNo ratings yet
- SU Na Baze Internet PDFDocument7 pagesSU Na Baze Internet PDFT.AnithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3.1 Designing A Network TopologyDocument49 pagesChapter3.1 Designing A Network Topologyquoc.dx.62cnttNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Call Flow in A CDMA Network - CPT2Document21 pagesDemonstration of Call Flow in A CDMA Network - CPT2electricalbah100% (1)
- Chapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument23 pagesChapter Four Network Design and Implementations ConceptsBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document92 pagesChap 2Iman KhoujaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition Standard EditionDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition Standard Editionchukkapalli69No ratings yet
- CSS12 Q3 Wk1Document11 pagesCSS12 Q3 Wk1jaimelovenaNo ratings yet
- CA - Ex - S4C1 - Introduction To WANs (Compatibility Mode)Document61 pagesCA - Ex - S4C1 - Introduction To WANs (Compatibility Mode)Hung LeNo ratings yet
- ITNE 3006 - AssignmentDocument13 pagesITNE 3006 - AssignmentSadia AbdullahNo ratings yet
- College Network ScenarioDocument18 pagesCollege Network ScenarioSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Glossary: Tier Level Data Center RequirementsDocument7 pagesGlossary: Tier Level Data Center RequirementsJoson ChanNo ratings yet
- WorldSkills Junior 2019Document23 pagesWorldSkills Junior 2019DahayatNo ratings yet
- Secure Cloud Computing With A Virtualized Network InfrastructureDocument7 pagesSecure Cloud Computing With A Virtualized Network InfrastructureNeha AroraNo ratings yet
- Networkingglossary 2022Document17 pagesNetworkingglossary 2022osama.anwerNo ratings yet
- SYCSDocument3 pagesSYCSbhagyashribbsccsNo ratings yet
- Study Notes - Chapter 8 + 9Document10 pagesStudy Notes - Chapter 8 + 9pmurphy24No ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Wireless Network Solution OverviewDocument20 pagesCisco Unified Wireless Network Solution OverviewPaul CherresNo ratings yet
- MCS-022 Operating System Concepts andDocument29 pagesMCS-022 Operating System Concepts andSumit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Uccx B Soldg-For-unified-ccx Chapter 0100Document14 pagesUccx B Soldg-For-unified-ccx Chapter 0100JayD77No ratings yet
- Cloud Enabling TechnologyDocument103 pagesCloud Enabling TechnologySahithi NamalaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Document9 pagesComputer Systems Servicing: Self-Learning Module 2Jeffrey MacabareNo ratings yet
- Distributed Overlay Virtual Ethernet (DOVE) Networks: Renato Recio IBM Fellow & System Networking CTODocument27 pagesDistributed Overlay Virtual Ethernet (DOVE) Networks: Renato Recio IBM Fellow & System Networking CTORitu NathanNo ratings yet
- Campus DesignDocument9 pagesCampus DesignSaffanArainNo ratings yet
- Network & System Admin ch1 To 10.doc..bakDocument92 pagesNetwork & System Admin ch1 To 10.doc..bakDanny KirooNo ratings yet
- Revision 9608 Section 1.2Document20 pagesRevision 9608 Section 1.2Debasruti SahaNo ratings yet
- A WSN-Based Large Electrical - 2010Document6 pagesA WSN-Based Large Electrical - 2010Jeya RamanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CssDocument4 pagesReviewer CsstiamzoncasNo ratings yet
- Examining The Ciscoworks Lms ApplicationsDocument16 pagesExamining The Ciscoworks Lms ApplicationsEssou AmineNo ratings yet
- Day 5.2Document54 pagesDay 5.2Namrata PaudelNo ratings yet
- S.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFDocument7 pagesS.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFguimanolNo ratings yet
- Posted by Admin Labels: CCNA 4 Exams Answers, CCNA 4 Ver 4.0, CCNA Discovery 4Document7 pagesPosted by Admin Labels: CCNA 4 Exams Answers, CCNA 4 Ver 4.0, CCNA Discovery 4Keenan 'Monni' SharpeNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Network Operating SystemDocument10 pagesTopic 9 Network Operating SystemsimonnjauNo ratings yet
- Fibcom 6300NMS PDFDocument2 pagesFibcom 6300NMS PDFRaja SolaimalaiNo ratings yet
- Next-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsFrom EverandNext-Generation switching OS configuration and management: Troubleshooting NX-OS in Enterprise EnvironmentsNo ratings yet
- Surendran GunalanDocument25 pagesSurendran GunalanPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Python and Sublime ConfigurationDocument17 pagesPython and Sublime ConfigurationPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Mad-LT1 SignedDocument2 pagesMad-LT1 SignedPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5Document32 pagesChapter 2 Campus Area Network Server Configurations 2.5PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Install Python Step by StepDocument2 pagesInstall Python Step by StepPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Muet PresentationDocument6 pagesMuet PresentationPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- DFN 40183: Open Source Server Administrator.: Final Assessment (Practical Test)Document12 pagesDFN 40183: Open Source Server Administrator.: Final Assessment (Practical Test)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Case Study - (PK)Document7 pagesCase Study - (PK)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Python and Mysql: Dfn40263 - Programming Essentials in PythonDocument28 pagesPython and Mysql: Dfn40263 - Programming Essentials in PythonPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Bahagian B: 45 MarkahDocument6 pagesBahagian B: 45 MarkahPREEVITHANo ratings yet
- PBT (PK)Document5 pagesPBT (PK)PREEVITHANo ratings yet
- Domain Name Service Agreement: Philippine Network Foundation Incorporated (PHNET) 12 May 2014Document5 pagesDomain Name Service Agreement: Philippine Network Foundation Incorporated (PHNET) 12 May 2014AubreyNo ratings yet
- Gea Matrix .Lon: Air Treatment DivisionDocument56 pagesGea Matrix .Lon: Air Treatment DivisionCosmin StroiaNo ratings yet
- 026 4144 Site Supervisor Controller Quick Setup Guide en Us 2188962Document11 pages026 4144 Site Supervisor Controller Quick Setup Guide en Us 2188962jrodNo ratings yet
- Opticube Training V2Document27 pagesOpticube Training V2Obinna ObiefuleNo ratings yet
- Questions 1 To 10: Web Technologies (Internet Technologies) Questions With Answers Set 1Document11 pagesQuestions 1 To 10: Web Technologies (Internet Technologies) Questions With Answers Set 1prabakaranNo ratings yet
- Systec MP 90 120 enDocument1 pageSystec MP 90 120 enDũng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cisco SwitchesDocument4 pagesCisco SwitchesrodolfocelisNo ratings yet
- Configuration Example To Migrate Spanning Tree From PVST+ To MST - CiscoDocument16 pagesConfiguration Example To Migrate Spanning Tree From PVST+ To MST - CiscoTomta FranckNo ratings yet
- IBwave Mobile User GuideDocument106 pagesIBwave Mobile User GuideEarl100% (1)
- VON Europe - Comments On ACMA's Consultation On Allocation and Charging of NumbersDocument4 pagesVON Europe - Comments On ACMA's Consultation On Allocation and Charging of NumbersVoice on the Net (VON) Coalition EuropeNo ratings yet
- Keyboard ShortcutsDocument9 pagesKeyboard ShortcutsakashdskyNo ratings yet
- RA 2114 Nutanix Enterprise Cloud For AIDocument66 pagesRA 2114 Nutanix Enterprise Cloud For AIDavid YehNo ratings yet
- Home - DOS Windows 32 & 64 Bit MAME Arcade Cabinet ConfiguratiDocument19 pagesHome - DOS Windows 32 & 64 Bit MAME Arcade Cabinet ConfiguratiLeo. D'Alençon R.No ratings yet
- Juniper EX Switches SNMPDocument5 pagesJuniper EX Switches SNMPRai Kashif JahangirNo ratings yet
- REU610Document68 pagesREU610mrithunNo ratings yet
- A FORTRAN 90 Numerical Library DownloadDocument1 pageA FORTRAN 90 Numerical Library DownloadAnonymous 1rLNlqUNo ratings yet
- Use Audio and Video Conferencing Tools To Share Ideas and Work With Others Online Week 7Document4 pagesUse Audio and Video Conferencing Tools To Share Ideas and Work With Others Online Week 7edwinoga80No ratings yet
- Hacking SCADADocument37 pagesHacking SCADAkonto27No ratings yet
- Remote Data Interface RDI 08-001A, Analog (MAN11641-11)Document38 pagesRemote Data Interface RDI 08-001A, Analog (MAN11641-11)justinNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ 1Document7 pagesĐỀ 1Trà Dương PhươngNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Pnematic & Blautek PDFDocument40 pagesCatalogo Pnematic & Blautek PDFgustavoba7No ratings yet
- 03 Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide-BookDocument318 pages03 Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide-Booka.giacchettoNo ratings yet
- A MIL Q1M8 Teacher Copy FinalDocument22 pagesA MIL Q1M8 Teacher Copy FinalIvy BarnacheaNo ratings yet
- Ug EthernetDocument223 pagesUg EthernetshinhunoNo ratings yet
- CJ Programming ManualDocument434 pagesCJ Programming ManualjpgoasNo ratings yet
- FPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev ACDocument45 pagesFPRB Installation Manual For SPD Rev ACMihaelNo ratings yet
- Edms Erd ManualDocument9 pagesEdms Erd ManualArjuna AnomNo ratings yet
- HL-3170cdw 2 Page Brochure FINAL 041013 PDFDocument2 pagesHL-3170cdw 2 Page Brochure FINAL 041013 PDFlleptirNo ratings yet
- Blockchain 2018Document16 pagesBlockchain 2018MoAzZam rAjpOotNo ratings yet
- Choi Midterm 1 PracticeDocument3 pagesChoi Midterm 1 PracticePhillip HsuNo ratings yet