Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PE Grade 9
PE Grade 9
Uploaded by
Josh Laurenz Romero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views30 pages Here are my guesses for the pictures based on the clues:
K N E E I N J U R Y
H E A T E X H A U S T I O N
F R A C T U R E
D I S L O C A T I O N
C R A M P
Original Description:
Original Title
PE-grade-9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Here are my guesses for the pictures based on the clues:
K N E E I N J U R Y
H E A T E X H A U S T I O N
F R A C T U R E
D I S L O C A T I O N
C R A M P
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views30 pagesPE Grade 9
PE Grade 9
Uploaded by
Josh Laurenz Romero Here are my guesses for the pictures based on the clues:
K N E E I N J U R Y
H E A T E X H A U S T I O N
F R A C T U R E
D I S L O C A T I O N
C R A M P
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 30
Injury
It is a general term that refers to
harm caused by accidents, falls, hits,
weapons, and more. These injuries
range from minor to life- threatening.
Injuries can happen at work or play,
indoors or outdoors, driving a car, or
walking across the streets.
First aid
It is an immediate and temporary care
given to a person who has been injured
or suddenly taken ill. It includes self- help
and home care if medical assistance is
not available or delayed. The two main
objectives of first aid are: to alleviate
suffering; and to prevent added/further
injury or danger.
7 Seven Common
Injuries with its
Basic First Aid.
1. Cramps
➢ It is a sudden and involuntary contraction of
one or more muscles. Though generally
harmless, muscle cramps can make it
temporarily impossible to use the affected
muscle.
First Aid:
1. Stretch and massage. Stretch the cramped muscle
and gently rub it to help it relax. For a calf cramp,
put your weight on your cramped leg and bend your
knee slightly. If you are unable to stand, sit on the
floor or in a chair with your affected leg extended.
2. Apply heat or cold. Use a warm towel or heating
the pad on tense or tight muscles. Taking a warm
bath or directing the stream of hot shower onto the
cramped muscle also can help. Alternatively,
massaging the cramped muscle with ice may relieve
pain.
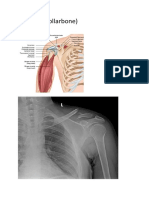
2. Dislocations
➢ It is when the two bones that come together to form a
joint become separated, the joint is described as dislocated.
➢ Contact sports such as football, basketball, and lacrosse,
as well as high impact sports that can result in excessive
stretching or falling, cause the majority dislocations.
➢ A dislocated joint is an emergency that requires medical
treatment.
First Aid:
1. Call 999 or 112 for emergency help if you cannot take
them yourself.
2. Advise the casualty to stay still. Help them to support
their dislocated joint in the most comfortable position.
Do not try to put the dislocated bone back in to its socket,
as this may cause further injury.
3. Stop the joint from moving.
If you think they have dislocated their shoulder or elbow,
support the injured arm using a sling. To give extra support,
tie a broad- fold bandage (wide bandage) around the chest
and the sling. If a hand or arm is injured, remove any rings,
or watches in case of swelling.
If you think they have dislocated their
ankle, knee, or hip joint, support the
injured leg using padding and broad- fold
bandages.
4. While waiting for help, treat for shock if
necessary. Monitor their level of response.
Do not raise an injured leg. Only raise the
uninjured leg.
5. Check the circulation beyond any
bandages every 10 minutes and loosen if
necessary.
3. Fractures
➢ A fracture is a break in the bone that can occur from
either a quick, one- time injury to the bone (acute fracture)
or from repeated stress to the bone over time (stress
fracture).
➢ The most common symptom of a stress fracture is pain at
the site that worsens with weight bearing activities.
➢ Tenderness and swelling often accompany the pain.
First Aid:
1. Apply the R.I.C.E (Rest, Ice,
Compression, Elevation) method.
2. Keep the limb in the position you
found it and place soft padding around
the broken bones. Splint the injury
with something rigid, such as rolled up
newspaper or magazines, to prevent
the bones from shifting.
Do not move the broken bones.
Splints must be long enough to extend
beyond joints above and below the
fracture.
3. If there is an open fracture, cover it
with a clean gauze pad. Apply
pressure to control bleeding. Do not
try to push the bone back into the
wound and do not attempt to clean it.
4. Get medical attention
immediately. Fractures of the
femur and pelvis may cause severe
internal bleeding.
5. Don't give the person anything
to eat or drink in case surgery is
needed.
4. Heat Exhaustion
➢ It is a response to heat
characterized by fatigue, weakness
and collapse due to inadequate intake
of water to compensate for loss of
fluids during sweating.
First Aid:
1. Have the victim lie down with his/her feet
elevated.
2. Keep the victim cool.
3. Give him/her electrolyte beverages to sip or
make a salted drink.
4. Monitor the victim for signs of shock.
5. If the victim starts having seizures, protect
him/her from injury and give first aid for
convulsions.
6. If the victim loses consciousness, give first
aid for unconsciousness.
5. Knee Injuries
➢ It is a result from a blow or twist to the knee, from improper
landing after jump or from running too hard, too much or without
proper warm up.
➢ Knee injuries can range from mild to severe.
➢ Less severe would be tendinitis, patella femoral compression
syndrome, iliotibial band syndrome and bursitis.
➢ Major injuries are common to the Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL),
Meniscus injuries, Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), Medical collateral
ligament (MCL), and the Lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
First Aid:
1. Stop your activity immediately.
Do not ‘work through’ the pain.
2. Rest the joint at first.
3. Reduce pain, swelling and
internal bleeding with icepacks,
applied for 15 minutes every
couple of hours.
4. Bandage the knee firmly and
extend the wrapping down the
lower leg.
5. Elevate the injured leg.
6. Do not apply the heat to the
joint.
7. Do not massage the joint, as this
encourages bleeding and swelling.
6. Sprain
➢ It is a stretch or tear of a ligament, the band of
connective tissues that joins the end of one bone
with another.
➢ Sprains are caused by trauma such as a fall or a
blow to the body that knocks a joint out of position
and, in the worst case, ruptures the supporting
ligament.
➢ Sprains can range from first
degree (minor) to third degree (the
worst).
➢ Ankles, knees, and wrists are
parts of the body vulnerable to
sprain.
➢ Swelling and bruising are some
signs and symptoms.
First Aid:
1. Remove any clothing or jewelry around
the joint.
2. Apply cold compress at once.
3. Elevate the affected joint.
4. The victim’s physician may recommend
an over the counter anti- inflammatory
medication (aspirin, ibuprofen)
appropriate for the victims’ general
health.
7. Strain
➢ It is a twist, pull or tear of a muscle or tendon—a
cord of tissue connecting muscle to the bone.
➢ It is an acute, non- contact injury that results from
over stretching or over contraction.
➢ Symptoms of strain include pain, muscle spasm,
and loss of strength.
First Aid:
1. Apply ice right away to reduce
swelling. Wrap the ice in cloth. Do not
place ice directly on the skin. Apply
ice for 10 to 15 minutes every 1 hour
for the first day and every 3 to 4
hours after that.
2. Use ice for the first 3 days. After 3
days, either heat or ice may be
helpful if you still have pain.
3. Rest the pulled muscle for at
least a day. If possible, keep the
pulled muscle raised above your
heart.
4. Try not to use a strained muscle
while it is still painful. When the
pain starts to go away, you can
slowly increase activity by gently
stretching the injured muscle.
PICTURE PICTURE!
Guess what is being
shown in each picture
K N ___ ___ I N ___ ___ R __ E S
H E ___ ___ E X ___ A ___ S T ___ O ___
___ R ___ ___ T U ___ E
___ I S ___ O ___ ___ T I ___ N
C___ A M ___ ___
You might also like
- CXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFDocument17 pagesCXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFSayyid Muhammad Aqeed AabidiNo ratings yet
- The Philippine FestivalsDocument33 pagesThe Philippine FestivalsKYCIE FIDELICIONo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument39 pagesSports InjuriesKYCIE FIDELICIONo ratings yet
- Fix Me I'm Broken (On First Aid)Document21 pagesFix Me I'm Broken (On First Aid)Romar LagunaNo ratings yet
- MAPEH ReportingDocument18 pagesMAPEH ReportingKurt Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Sprain Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EDocument2 pagesFirst Aid For Sprain Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EbokanegNo ratings yet
- Week 2 PeDocument20 pagesWeek 2 PeJulie AnneNo ratings yet
- Importance of First AidDocument20 pagesImportance of First AidHeroe SedicoNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 9 Q1 Week 3 P.EDocument10 pagesMAPEH 9 Q1 Week 3 P.EJohn AgnerNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Physical EducationDocument4 pagesHandouts in Physical EducationjjkOT7No ratings yet
- P.E First AidDocument33 pagesP.E First AidMarc Robert SandovalNo ratings yet
- Sports InjuriesDocument2 pagesSports InjuriesGuwayNo ratings yet
- PE9 SLeM1 Q1Document9 pagesPE9 SLeM1 Q1Joemer SiplocNo ratings yet
- Mark Bonnin Jara 8-Edison P.E. History of Basketball: Springfield, Massachusetts James NaismithDocument5 pagesMark Bonnin Jara 8-Edison P.E. History of Basketball: Springfield, Massachusetts James NaismithMark Bonnin JaraNo ratings yet
- Bone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingDocument30 pagesBone Joint and Muscle Injuries SplintingHesedh Jireh MartinNo ratings yet
- Pe9 Q1 W1-1Document11 pagesPe9 Q1 W1-1PaulaNo ratings yet
- PE M2 Dance Injuries and First AidDocument22 pagesPE M2 Dance Injuries and First AidKeith Emerich FermaNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument22 pagesBasic First AidApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Injuries and Its First Aid ProcedureDocument4 pagesKinds of Injuries and Its First Aid ProcedureVergie Fernandez ParungaoNo ratings yet
- InjuryDocument34 pagesInjuryenajejohn9No ratings yet
- Cramps: Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EDocument4 pagesCramps: Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EKenkoi SanchezNo ratings yet
- Hfe Note SportsDocument2 pagesHfe Note SportsbharathNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument15 pagesFirst AidEden Martirez-VillalonNo ratings yet
- Pe1 First AidDocument17 pagesPe1 First AidAllan VillelaNo ratings yet
- Bone, Joint and Muscle Injuries: Freida Michelle Bonnit-Taja, RN, ManDocument45 pagesBone, Joint and Muscle Injuries: Freida Michelle Bonnit-Taja, RN, ManFreida Michelle BonnitNo ratings yet
- Follow The Instructions For R.I.C.EDocument2 pagesFollow The Instructions For R.I.C.Eayatolla ayatollaTMNo ratings yet
- 1q.pe Sprain Strain Fracture DislocateDocument57 pages1q.pe Sprain Strain Fracture DislocateCheius AcostaNo ratings yet
- Question? What Will You Do If The Following Situations Happened To You?Document37 pagesQuestion? What Will You Do If The Following Situations Happened To You?Emiliano PlantillaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Sports InjuriesDocument11 pagesFirst Aid Sports Injuriesjlemmon1979No ratings yet
- Slem P e 9 Week 5 Q 1 FinalDocument14 pagesSlem P e 9 Week 5 Q 1 FinalRongeluaymail.com GeluaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Safety Practices in Outdoor RecreationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Safety Practices in Outdoor RecreationJham LayoutsNo ratings yet
- Appropriate First Aid Injuries and Emergency Situations in Physical ActivityDocument4 pagesAppropriate First Aid Injuries and Emergency Situations in Physical ActivityJanine JanineNo ratings yet
- PE 2 AssignmentDocument1 pagePE 2 Assignmentyancypachoco0404No ratings yet
- Health Group3Document29 pagesHealth Group3Angela OrenseNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument40 pagesFirst AidRegina Starla DizonNo ratings yet
- Common Sports InjuriesDocument35 pagesCommon Sports InjuriesRizalyn TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Different Sports InjuriesDocument11 pagesDifferent Sports InjuriesregineNo ratings yet
- DislocationsDocument3 pagesDislocationsDIANA ROMERO MEDINANo ratings yet
- Yrc Project Presented byDocument4 pagesYrc Project Presented byShruti SurlakarNo ratings yet
- Cast CareDocument4 pagesCast CareRogelyn PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Injries in SportsDocument17 pagesPhysiology & Injries in Sportsashvirchatha3No ratings yet
- First AidDocument6 pagesFirst AidLeary John TambagahanNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries Involved in RecreationDocument36 pagesCommon Injuries Involved in RecreationJoshua CullaNo ratings yet
- PE9 Q1 - LP5 MELCsDocument5 pagesPE9 Q1 - LP5 MELCsWilson MoralesNo ratings yet
- Bones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesDocument14 pagesBones, Joints, & Muscle InjuriesAngela YlaganNo ratings yet
- Wrist Injury at SiteDocument10 pagesWrist Injury at SiteClark Angelo JuanNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument4 pagesCommon Injuries of The Musculoskeletal SystemJoniele Angelo AninNo ratings yet
- Contusions, Sprains, StrainsDocument14 pagesContusions, Sprains, StrainsKaryn Joy LamisNo ratings yet
- Pathfit2 Midterm Safety TipsDocument58 pagesPathfit2 Midterm Safety TipsNICKO PACLEBNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan University Philippines: FracturesDocument21 pagesWesleyan University Philippines: Fracturesjeneva029No ratings yet
- Bones Notes MbbsDocument35 pagesBones Notes MbbsFatimaNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument5 pagesSoft Tissue InjuriesLizaEllagaNo ratings yet
- Traumeel Com Patientenbooklet en 14823Document13 pagesTraumeel Com Patientenbooklet en 14823Eduardo DutraNo ratings yet
- Physical Education 10 Las No.2 Week 3 4 Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesPhysical Education 10 Las No.2 Week 3 4 Fourth Quarterasdfubepruhf asdfubepruhfNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument2 pagesFracturelucky_b0iNo ratings yet
- CRI 089 Midterm NotesDocument39 pagesCRI 089 Midterm Notesdebroah280No ratings yet
- Nursing Splinting Skills in Powerpoint PresentationDocument23 pagesNursing Splinting Skills in Powerpoint Presentationpearlannesanford1995No ratings yet
- Peh 1 Handout 3Document5 pagesPeh 1 Handout 3julie jane arcillaNo ratings yet
- Sports Injuries 2Document28 pagesSports Injuries 2Nicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Sprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSprain and Strains, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Achilles Tendinitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandAchilles Tendinitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument6 pagesTutorial QuestionsEribeta TeiaNo ratings yet
- K.L.P. Mishra (FLAT)Document434 pagesK.L.P. Mishra (FLAT)Piyush Joshi43% (7)
- Studying in The LibraryDocument9 pagesStudying in The Libraryapi-253420500No ratings yet
- The Princess, The Dragon, and The Very Bad Knight PDFDocument14 pagesThe Princess, The Dragon, and The Very Bad Knight PDFleonns1No ratings yet
- 011 - Descriptive Writing - UpdatedDocument39 pages011 - Descriptive Writing - UpdatedLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Action PlanDocument2 pagesPractical Research 2 - Action Plananon_186395269100% (1)
- DLL Mapeh-5 Q3 W7Document9 pagesDLL Mapeh-5 Q3 W7Diana Rose AcupeadoNo ratings yet
- Overview Six Sigma PhasesDocument3 pagesOverview Six Sigma Phaseshans_106No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Learning Principles and Applications 8th Edition Stephen B KleinDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Learning Principles and Applications 8th Edition Stephen B KleinTonyRamosriqzf100% (36)
- RFC OperationDocument13 pagesRFC OperationRicky DasNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam in Mapeh 10Document4 pages1st Quarter Exam in Mapeh 10Dhan Mark Barlintangco100% (1)
- BM Wed Wild LordDocument2 pagesBM Wed Wild Lordcori sabauNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Loans and Advances ofDocument85 pagesA Comparative Study of Loans and Advances ofRohan MhatreNo ratings yet
- FCE Unit 3 TestDocument4 pagesFCE Unit 3 Testconny100% (1)
- India Since Independence NotesDocument8 pagesIndia Since Independence NotesDilip PanchalNo ratings yet
- What Is Dance?Document2 pagesWhat Is Dance?Lavapie ZcheT8No ratings yet
- Group1 - Final Exam 2023 Budget of Work Plan 1 1Document6 pagesGroup1 - Final Exam 2023 Budget of Work Plan 1 1HennessyNo ratings yet
- Liver Biopsy: Mary Raina Angeli Fujiyoshi, MDDocument10 pagesLiver Biopsy: Mary Raina Angeli Fujiyoshi, MDRaina FujiyoshiNo ratings yet
- A Linguistic History of Arabic - TextDocument164 pagesA Linguistic History of Arabic - TextDNo ratings yet
- Javascript - FormsDocument3 pagesJavascript - FormspapuNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Raymundo Castro Vs BustosDocument13 pagesHeirs of Raymundo Castro Vs Bustosautumn moonNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument4 pagesDefinition of TermsAgnes Francisco50% (2)
- Neuropathic Ulcers For StudentsDocument23 pagesNeuropathic Ulcers For Studentsbusiness911No ratings yet
- Solution Science-X T 2 POW reducesupportMaterialSolution To Science-IX T2 POW Solutions PDFDocument138 pagesSolution Science-X T 2 POW reducesupportMaterialSolution To Science-IX T2 POW Solutions PDFSumeet AroraNo ratings yet
- Arni University::: B.Tech Mechanical II SEMESTERDocument3 pagesArni University::: B.Tech Mechanical II SEMESTERNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- CommInsights Issue6 It S All About ContentDocument40 pagesCommInsights Issue6 It S All About ContentLucijano Andreas SoftićNo ratings yet
- ICD X Kes HajiDocument2 pagesICD X Kes Hajiyasin_rsdk67% (3)
- Factfulness Book Review #2: Taehoon KimDocument3 pagesFactfulness Book Review #2: Taehoon KimTaehoon KimNo ratings yet
- General Financial Accounting TestDocument9 pagesGeneral Financial Accounting TestDuas and Urdu Dramas/Movies100% (1)