Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine Pharmacology
Endocrine Pharmacology
Uploaded by
gim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesThis document discusses several hormones involved in the endocrine system and their functions:
- Thyroid stimulating hormone is used for diagnostic purposes to determine thyroid gland issues and thyroxine replacement is used to treat deficiencies.
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone promotes the secretion of TSH and prolactin. It is used to distinguish primary from secondary hypothyroidism.
- Prolactin develops lactation after birth and is inhibited by dopamine. Its levels are measured to diagnose hyperprolactinemia.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several hormones involved in the endocrine system and their functions:
- Thyroid stimulating hormone is used for diagnostic purposes to determine thyroid gland issues and thyroxine replacement is used to treat deficiencies.
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone promotes the secretion of TSH and prolactin. It is used to distinguish primary from secondary hypothyroidism.
- Prolactin develops lactation after birth and is inhibited by dopamine. Its levels are measured to diagnose hyperprolactinemia.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesEndocrine Pharmacology
Endocrine Pharmacology
Uploaded by
gimThis document discusses several hormones involved in the endocrine system and their functions:
- Thyroid stimulating hormone is used for diagnostic purposes to determine thyroid gland issues and thyroxine replacement is used to treat deficiencies.
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone promotes the secretion of TSH and prolactin. It is used to distinguish primary from secondary hypothyroidism.
- Prolactin develops lactation after birth and is inhibited by dopamine. Its levels are measured to diagnose hyperprolactinemia.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
Endocrine pharmacology
Thyroid stimulating hormone
• Used for diagnostic purposes to determine cause of
hyperthyroidism (pituitary vs. thyroid gland failure) –
• Not used for treatment, deficiencies are treated by giving
thyroxine itself
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
• Promotes secretion of TSH –
• Promotes release of Prolactin
• -Used for tests to distinguish primary from secondary
hypothyroidism
Prolactin
• To develop lactation after birth
• Inhibits release of GnRH (Increases during stress)
• Inhibited by dopamine
• Release is stimulated by oxytocin
• Synthesis is enhanced by Estradiol
• Serum levels are measured to diagnose hyperprolactinemia
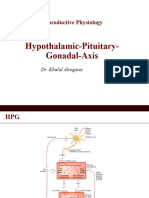
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogs
• -Stimulates secretion of LH & FSH
• Feedback inhibition: testosterone & progesterone
• Inhibited by: dopamine, endorphin & prolactin
• Positive feedback: estradiol
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
• -Development of ovarian follicles (follicular phase of
menstrual cycle)
• Required for estrogen synthesis
• -Inhibin controls its release
Progesterone
• Suppresses ovulation (Negative feedback on release of LH &
FSH)
• -Basis for oral contraceptives
Estradiol
• Enhances prolactin synthesis
• Positive feedback on GnRH (triggers ovulation)
Oxytocin
• Stimulates myoepithelial contractions (in uterus during
parturition & mammary gland during lactation)
• Milk ejection from lactating mammary gland
• Uterine contractions
Estrogen
• Decreases bone resorption
• Treatment of hypercalcemia
• Given to postmenopausal women with primary
hyperparathyroidism
Estrogen Replacement Therapy
• Increases bone density
• Prophylactic regimen of osteoporosis at the onset of
menopause
• Decreases risk of colon cancer
• Decreased vaginal atrophy
You might also like
- Female Reproductive System DrugsDocument84 pagesFemale Reproductive System DrugsPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones & Inhibitors Contraceptives: DR Dhoro Clinical PharmacologyDocument34 pagesGonadal Hormones & Inhibitors Contraceptives: DR Dhoro Clinical PharmacologykelvinNo ratings yet
- Oestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensDocument58 pagesOestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensTandin Sonam100% (1)
- Drug Acting On Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesDrug Acting On Reproductive SystemRoshann Marcus MamaysonNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDocument57 pagesAnesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDoc SabNo ratings yet
- Vety Endocrine PharmaDocument59 pagesVety Endocrine PharmaSunilNo ratings yet
- OVARIAN STIMULANTS AND OXYTOCICS - PPTX - 22.04.2021 - Dr. SSDocument43 pagesOVARIAN STIMULANTS AND OXYTOCICS - PPTX - 22.04.2021 - Dr. SSRashitha NalarangaNo ratings yet
- SajanDocument28 pagesSajanSajan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones and InhibitorsDocument8 pagesGonadal Hormones and InhibitorsMarianne CruzNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument9 pagesContraceptionmayafayez021No ratings yet
- Hormones of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesHormones of The Reproductive Systemkarthickmech1987No ratings yet
- SEX HORMONES AND DRUGS EditedDocument44 pagesSEX HORMONES AND DRUGS Editednalubwamasarah163No ratings yet
- Infertility NirwenDocument55 pagesInfertility Nirwenpok yeahNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument46 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormonespramod bhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian CycleDocument78 pagesOvarian CyclefasicaregroupNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Female Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesDrugs Affecting The Female Reproductive SystemPatrick Jayson Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic & Pituitary Hormone DrugsDocument29 pagesHypothalamic & Pituitary Hormone DrugsDylan MansillaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Gonadal Hormones-3Document197 pages2019 Gonadal Hormones-3Vishwajeet RaneNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormones PDFDocument54 pagesSex Hormones PDFmohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Reproductive Pharmacology-By:Dr. DHIREN BHOIDocument77 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Pharmacology-By:Dr. DHIREN BHOIdrdhirenvet100% (9)
- Gonadal Hormones and InhibitorsDocument14 pagesGonadal Hormones and InhibitorsbluesumNo ratings yet
- 1 Pituitary and Thyroid PharmacologyDocument64 pages1 Pituitary and Thyroid PharmacologyZaina MasriNo ratings yet
- Hormones in Reproduction: Presented To: Dr. Akhtar Rasool Presented By: M Tayyab 2012-VA-300Document17 pagesHormones in Reproduction: Presented To: Dr. Akhtar Rasool Presented By: M Tayyab 2012-VA-300javeria choudharyNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The FemaleDocument32 pagesDrugs Affecting The FemaleLule Allan PhillipNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle: Dr. Milvan Hadi, M. Ked (Og), SpogDocument41 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle: Dr. Milvan Hadi, M. Ked (Og), SpogEvi Liana BahriahNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Jason Ryan, MD, MPHDocument47 pagesPituitary Gland: Jason Ryan, MD, MPHmisfa044No ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesPharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Reproductive SystemShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic and Pituitary Drugs (Autosaved)Document41 pagesHypothalamic and Pituitary Drugs (Autosaved)mug ashNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture 9 Gonadal Hormones and Drugs (Pod Pharm DR Thatcher 2022)Document46 pages01 Lecture 9 Gonadal Hormones and Drugs (Pod Pharm DR Thatcher 2022)sahilaminNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progestin, ContraceptionDocument53 pagesEstrogen, Progestin, ContraceptionDebby Astasya AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland IntroDocument40 pagesPituitary Gland IntroSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and ReleaseDocument36 pagesEndocrine System: Endocrine: Which Have No Duct and Releasedr_saleh77No ratings yet
- Lec-4 The Anterior Pituitary Gland-IIDocument32 pagesLec-4 The Anterior Pituitary Gland-IIMowlidAbdirahman Ali madaaleNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument27 pagesThe Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Male Sex Hormones FunctionsDocument18 pagesMale Sex Hormones FunctionsPermanand BheemsinNo ratings yet
- Hormonal BiochemistryDocument82 pagesHormonal BiochemistryRuthNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and HypophysisDocument32 pagesHypothalamus and HypophysisAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Sex HarmoneDocument22 pagesSex Harmonesuyash jainNo ratings yet
- 3 - Hypothalam - Anterior PituitaryDocument22 pages3 - Hypothalam - Anterior PituitaryAbboodNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism: Group OneDocument22 pagesHypopituitarism: Group OneSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Preparation of HormonesDocument23 pagesSynthetic Preparation of HormonesSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- Female Sex HormonesDocument28 pagesFemale Sex HormonesAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- Estrogens and Antiestrogens: Dr. D. K. Brahma Associate Professor of Pharmacology NEIGRIHMS, ShillongDocument24 pagesEstrogens and Antiestrogens: Dr. D. K. Brahma Associate Professor of Pharmacology NEIGRIHMS, ShillongdrfatimarizNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sex HormonesDocument6 pagesPharmacology of Sex Hormonesarnold23456100% (4)
- Gonadotrphs and Corticotrophes 6Document6 pagesGonadotrphs and Corticotrophes 6nananqNo ratings yet
- Psychosomatics: Endocrine System: Miguel Agustin ST Francisco, RPM, Mpsy CandDocument23 pagesPsychosomatics: Endocrine System: Miguel Agustin ST Francisco, RPM, Mpsy CandRalph Christian ZorillaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Reproductive Health: Estrogen and ProgestinDocument41 pagesDrugs Used in Reproductive Health: Estrogen and ProgestindrfatimarizNo ratings yet
- Hyopthalamus and PituitaryDocument45 pagesHyopthalamus and PituitaryJalil HaddadinNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument136 pagesEndocrinologyShiela Torres100% (9)
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Drugs in PregnancyDocument52 pagesDrugs in Pregnancydarboeb265100% (2)
- Steroids JenniferKettelDocument25 pagesSteroids JenniferKettelvinay0717No ratings yet
- Kuliah MenstruasiDocument44 pagesKuliah MenstruasidocbayNo ratings yet
- 1,4) HPG and Physiology of AndrogensDocument46 pages1,4) HPG and Physiology of AndrogensBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument57 pagesHORMONESRAMA ABO SAMRANo ratings yet
- Female Sex HormonesDocument30 pagesFemale Sex HormonesMagdy El-GammalNo ratings yet
- ENDODocument141 pagesENDOearldem1996No ratings yet
- Farmacoendocrino 2008Document58 pagesFarmacoendocrino 2008Eduardo ValdezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemAkshat RastogiNo ratings yet
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthFrom EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Genital System & Congenital Anomalies: Kenbon S. (MS) January 30,2021Document56 pagesEmbryology of Genital System & Congenital Anomalies: Kenbon S. (MS) January 30,2021gimNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Female Reproductive OrgansDocument26 pagesPhysiology of The Female Reproductive Organsgim100% (1)
- Infertility: by Kenbon SDocument58 pagesInfertility: by Kenbon SgimNo ratings yet
- AmenorrheaDocument70 pagesAmenorrheagimNo ratings yet