Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsLecture, On
Lecture, On
Uploaded by
tempThe document discusses transformations of functions including translations, reflections, stretching, compressing, and families of functions. Key points include:
- Translations move the graph up/down or left/right by adding/subtracting a constant to the input or output.
- Reflections flip the graph across the x-axis or y-axis by replacing x with -x or multiplying the function by -1.
- Stretching and compressing make the graph vertically or horizontally taller/shorter by multiplying the function or input by a constant greater than or less than 1.
- Families of functions include linear, exponential, trigonometric, and polynomial functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Introduction to Time Series and Forecasting【solution manual 】Document46 pagesIntroduction to Time Series and Forecasting【solution manual 】Grey Baoyin79% (24)
- GraphsPolynomialFuncsSE PDFDocument3 pagesGraphsPolynomialFuncsSE PDFkyle garciaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul'S College: Multiple Choice QnsDocument14 pagesSt. Paul'S College: Multiple Choice Qns20/21-5B-(05) HoMeiYi/何美誼No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMDocument7 pagesLecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMSamiul Hasnat Taseen 2233054642No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 0.1 and 0.2 Introduction of Functions of Mat 120 of MTMDocument8 pagesLecture 1 0.1 and 0.2 Introduction of Functions of Mat 120 of MTMABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMDocument10 pagesLecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMDocument10 pagesLecture 3 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMSamiul Hasnat Taseen 2233054642No ratings yet
- Reviewer Alebra 1Document7 pagesReviewer Alebra 1jomhailcruz03No ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphDocument27 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityJohn LiamNo ratings yet
- Cronasia Foundation College, Inc.: Lesson 5-7 Grade 9 - Behiga Mathematics 9Document14 pagesCronasia Foundation College, Inc.: Lesson 5-7 Grade 9 - Behiga Mathematics 9queencyfaithNo ratings yet
- Transformations of FunctionsDocument35 pagesTransformations of FunctionsPHENYO SEICHOKONo ratings yet
- Introduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsDocument10 pagesIntroduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsbushraNo ratings yet
- Functions: What Is A Function?Document9 pagesFunctions: What Is A Function?Bilal AnwarNo ratings yet
- Graphs of FunctionsDocument13 pagesGraphs of FunctionsLennoxNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation and Quadratic EquationDocument30 pagesLinear Equation and Quadratic EquationAmz AlburoNo ratings yet
- Training Course 9 Senior Functions and TrigonometryDocument32 pagesTraining Course 9 Senior Functions and TrigonometryRichardoBrandonNo ratings yet
- Core RevisionDocument2 pagesCore RevisionMaasa AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuidegurpreetNo ratings yet
- Graphs Revision Sheet FinalDocument27 pagesGraphs Revision Sheet FinalLuumuno PeaceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 and 14 On 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical ShellsDocument11 pagesLecture 13 and 14 On 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical Shellsfaltu faltuNo ratings yet
- Illustrating Limit of A Function: Week 1Document12 pagesIllustrating Limit of A Function: Week 1Ynna Lyn ManaloNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions: General Mathematics O. OronceDocument55 pagesExponential Functions: General Mathematics O. Oroncecass dumpNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus PrimerDocument17 pagesPre Calculus PrimeracsimsNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Polynomial Functions and Applications - Mana-ItDocument12 pagesGraphs of Polynomial Functions and Applications - Mana-ItJenicel Mana-itNo ratings yet
- Function and PolynomialsDocument8 pagesFunction and PolynomialsJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- Transformations Final ReviewDocument18 pagesTransformations Final ReviewFrances Ijeoma ObiakorNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions: General MathematicsDocument55 pagesExponential Functions: General MathematicsStephany BartianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4KelleyNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document39 pagesCH 15iwouldwishforyouNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math 11 Lesson 4Document24 pagesGen. Math 11 Lesson 4Maricon SorongonNo ratings yet
- X2 Graph Sketching TransformationsDocument10 pagesX2 Graph Sketching TransformationsyddapNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument8 pagesQuadratic FunctionsJerome MirabuenosNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Exponential FunctionsDocument28 pagesModule1 - Exponential Functionsstepharry08No ratings yet
- Vertex Form of Quadratic FunctionsDocument12 pagesVertex Form of Quadratic FunctionspurplepinkNo ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Ma. Rica Mae Rosete100% (1)
- X InterceptDocument8 pagesX Interceptapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Sabreena RataniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Graphs of The Trigonometric Functions - Part 1Document48 pagesChapter 4 - Graphs of The Trigonometric Functions - Part 1Sharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- 1801 A Supp NotesDocument218 pages1801 A Supp NotesDodNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Graphs of Functions and RelationsDocument41 pagesAnalyzing Graphs of Functions and RelationsMohy SayedNo ratings yet
- CBR KalkulusDocument20 pagesCBR KalkulusYon setiawanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument25 pagesQuadratic FunctionCherry Grace Sagde EuldanNo ratings yet
- Inequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteDocument11 pagesInequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteKarenNo ratings yet
- MATH9 Q1 WEEK6 ForprintDocument15 pagesMATH9 Q1 WEEK6 Forprintryo.wolloh.27No ratings yet
- Week 2 BDocument24 pagesWeek 2 BMegane AlarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 3 - Graphs and FunctionsDocument26 pagesChapter 3 3 - Graphs and Functionsapi-263209117No ratings yet
- Math 8 Q2 Week 4Document11 pagesMath 8 Q2 Week 4Candy CastroNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Fungsi KuadratDocument37 pagesAplikasi Fungsi KuadratridwanawalianNo ratings yet
- Function of Two VariablesDocument50 pagesFunction of Two Variablesap021No ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionDocument55 pagesExponential FunctionPrin CessNo ratings yet
- Math Test 10Document11 pagesMath Test 10adhamjonnorkulov02No ratings yet
- Math Assignment Unit - 4Document9 pagesMath Assignment Unit - 4mdmokhlesh1993No ratings yet
- Common CurvesDocument9 pagesCommon CurvesTagore uNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Function Investigation - Maria AncutaDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Function Investigation - Maria Ancutaapi-515654558No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 3Document5 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 3freda licudNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Sec3Document59 pagesChap1 Sec3Naqeeb khanNo ratings yet
- A Polynomial Function of Degree N Has N Zeros, Provided Multiple Zeros Are Counted More Than Once and Provided Complex Zeros Are CountedDocument26 pagesA Polynomial Function of Degree N Has N Zeros, Provided Multiple Zeros Are Counted More Than Once and Provided Complex Zeros Are Countedbaifern24No ratings yet
- General Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Graphing - ExamplesDocument4 pagesTopic 6: Graphing - ExamplessaaskaphoneNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1Module6Document9 pagesMath8 Q1Module6iam_maria1997No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Proportional LogicDocument17 pagesProportional LogicBert SantosNo ratings yet
- Projection of PlanesDocument14 pagesProjection of PlanesHere Estrada100% (1)
- Why Stock Markets CrashDocument3 pagesWhy Stock Markets CrashMyfirstmillion FrugalNo ratings yet
- Ugmath2022 22may PDFDocument6 pagesUgmath2022 22may PDFManashree VyasNo ratings yet
- Ust Ms Cheme FlyerDocument2 pagesUst Ms Cheme Flyerjr_hernando_enal3852No ratings yet
- GMM Var StataDocument27 pagesGMM Var StataChahine BergaouiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Information Theory (Lecture Notes)Document101 pagesQuantum Information Theory (Lecture Notes)50_BMGNo ratings yet
- JOM 2023 SolutionDocument5 pagesJOM 2023 Solutionthairestaurant3No ratings yet
- 131911-3130704 - DF Nov-2019Document1 page131911-3130704 - DF Nov-2019APOLLO Sem 4 I.T.No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TV100% (1)
- R - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Document6 pagesR - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Srinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table CompletaDocument2 pagesLaplace Table CompletaAlexis Gianlvca Rodrigvez PereaNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument9 pagesCircles PDFbansallove2008No ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of An Unmanned Underwater VehicleDocument119 pagesModeling and Control of An Unmanned Underwater Vehiclearash501No ratings yet
- Modeling The Motion of A SpringDocument5 pagesModeling The Motion of A Springapi-253477911No ratings yet
- Looking For A Challenge 2 enDocument27 pagesLooking For A Challenge 2 enZaidNo ratings yet
- Java Code Lab)Document3 pagesJava Code Lab)peace_edafeNo ratings yet
- Mat495 Chapter 5Document10 pagesMat495 Chapter 5MuhamadSadiqNo ratings yet
- MSC MBA Prospectus Final Autumn-2020 PDFDocument47 pagesMSC MBA Prospectus Final Autumn-2020 PDFMuhammad AyazNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lec 8 CC p2-1Document17 pagesWeek 4 Lec 8 CC p2-1Sohaib KashmiriNo ratings yet
- Programs With Flowchart and AlgorithmDocument7 pagesPrograms With Flowchart and AlgorithmRadhika AjadkaNo ratings yet
- Adstock ModelDocument7 pagesAdstock ModelRachit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsDocument6 pagesQualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Race Car Damping - Some Food For ThoughtDocument30 pagesRace Car Damping - Some Food For ThoughtDionisis SpiliopoulosNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Skills TestDocument3 pagesBasic Math Skills TestKeri RossnerNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Skills Grade 5Document310 pagesBasic Math Skills Grade 5C A100% (2)
- Code ADocument10 pagesCode ATesfamichael FufaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Math QuizDocument5 pagesClass 12 Math Quizankita071291No ratings yet
Lecture, On
Lecture, On
Uploaded by
temp0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesThe document discusses transformations of functions including translations, reflections, stretching, compressing, and families of functions. Key points include:
- Translations move the graph up/down or left/right by adding/subtracting a constant to the input or output.
- Reflections flip the graph across the x-axis or y-axis by replacing x with -x or multiplying the function by -1.
- Stretching and compressing make the graph vertically or horizontally taller/shorter by multiplying the function or input by a constant greater than or less than 1.
- Families of functions include linear, exponential, trigonometric, and polynomial functions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses transformations of functions including translations, reflections, stretching, compressing, and families of functions. Key points include:
- Translations move the graph up/down or left/right by adding/subtracting a constant to the input or output.
- Reflections flip the graph across the x-axis or y-axis by replacing x with -x or multiplying the function by -1.
- Stretching and compressing make the graph vertically or horizontally taller/shorter by multiplying the function or input by a constant greater than or less than 1.
- Families of functions include linear, exponential, trigonometric, and polynomial functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesLecture, On
Lecture, On
Uploaded by
tempThe document discusses transformations of functions including translations, reflections, stretching, compressing, and families of functions. Key points include:
- Translations move the graph up/down or left/right by adding/subtracting a constant to the input or output.
- Reflections flip the graph across the x-axis or y-axis by replacing x with -x or multiplying the function by -1.
- Stretching and compressing make the graph vertically or horizontally taller/shorter by multiplying the function or input by a constant greater than or less than 1.
- Families of functions include linear, exponential, trigonometric, and polynomial functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Lecture, on Transformation, of functions, and families, of functions:
Seven Basic (Mother) curves:
1. The curve, of f of x equals x square, and 2. the curve, of f of x equals square root of x, and 3. the curve, of f of x equals absolute value of x
4. the curve, of f of x equals x cube, and 5. the curve, of f of x equals cubic root of x, and 6. The curve, of f of x equals 1 over x, and 7. the curve, of f of x equals 1 over x square, are shown.
Translations, and Drawing the graphs, of x square plus 2, and x square minus 2, and x plus 2, whole square, and x minus 2, whole square:
Operation, on y equals f of x, Mother curve: 1. add, a positive constant c, to f of x, 2. subtract, a positive constant c, from f of x, 3. Add, a positive constant c, to x, and 4. subtract, a positive constant c, from x.
New equation: 1. y equals f of x, plus c, and 2. y equals f of x, minus c, and 3. y equals f of (x plus c), and 4. y equals f of (x minus c).
Geometric effect: 1. translates the graph of y equals f of x, c units, up, and 2. translate the graph of y equals f of x, c units, down, and 3. translate the graph of y equals f of x, c units, left, and 4. translate the graph of y equals f of x, c units, right.
Examples: 1. mother curve is y equals x square, now, y equals x square plus 2, has been shifted 2 units up, And 2. mother curve is y equals x square, THEN y equals x square minus 2, has been shifted 2 units down. And 3. y equals x plus 2 whole square, has been shifted 2 units left, then 4. y equals x minus 2 whole square, has been shifted 2 units right, all of them are open up and u shape, details graphings shown.
Draw the graphs, of 1. y equals square root, of x minus 3, and 2. y equals square root, of x plus 3, And 3. y equals x square minus 4 x plus 5
Solution: First, Mother curve is f of x equals root x shown, then 1. f of x minus 3 equals, root over x minus 3, the mother curve shifts, 3 units to the right, And 2. f of x plus 3 equals, root over x plus 3, the mother curve shifts, 3 units to the left, are shown.
3. y equals x square minus 4 x plus 5 equals, x minus 2 whole square minus 2 square plus 5 equals, x minus 2 whole square plus 1, Here Mother curve, is f of x equals x square shown Then f of x minus 2 equals, x minus 2, whole square, the curve shifts, 2 units to the right, And finally,
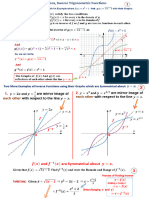
Reflections, and drawing the graphs, of square root, of minus x, and minus, square root, of x:
Operation, on f of x, Mother curve: 1. Replace, x by minus x, and 2. Multiply, f of x by minus 1.
new equation: 1. y equals f of minus x, and 2. y equals minus f of x.
geometric effect: 1. Reflects, the graph of y equals f of x, about the y axis, and 2. Reflects, the graph of y equals f of x, about the x axis.
Examples: 1. Mother curve y equals root x, then y equals root over, minus x reflects, about the y axis. And 2. Mother curve y equals root x, then y equals, minus root x reflects, about the x axis.
Draw the graphs, of 1. (a). y equals absolute value, of x minus 2, (b) y equals, minus absolute value of x minus 2, and (c) y equals, 4 minus absolute value of x minus 2, and 2. (a) y equals cubic root of x, (b) y equals cubic root, of minus x, and (c) y equals cubic root, of 2 minus x
Solution: First, Mother curve f of x equals, absolute value of x shown, Then 1.(a) y equals f of x minus 2 equals absolute value of x minus 2, the curve shifts, 2 units to the right, 1. (b) y equals, minus absolute value of x minus 2, curve reflects, about x axis, 1. (c) y equals, minus absolute value of x minus 2, plus 4, the previous curve shifts 4 units up along y axis.
2.(a) the curve, of f of x equals cubic root of x shown, then 2. (b) f of minus x equals cubic root, of minus x, the curve reflects, about y axis, 2. (c) if we consider f of x equals cubic root, of minus x, is mother curve, then f of x minus 2 equals cubic root, of minus, (x minus 2) equals, cubic root of 2 minus x, The previous curve cubic root of minus x called mother curve shifts, 2 units to the right, To get the graph, of cubic root of 2 minus x.
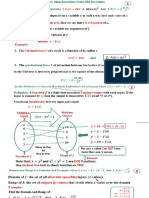
Stretching and Compressing
operation on f of x. Multiply f of x by c where c is greater than 1. Multiply f of x by c where 0 is less than c is less than 1. Multiply x by c where c is greater than 1. Multiply x by c where 0 is less than c is less than 1.
new equation. Y equals c into f of x. Y equals c into f of x. Y equals f of c into x. Y equals f of c into x.
geometric effect. Stretches the graph of y equals f of x vertically by a factor of c. Compresses the graph of y equals f of x vertically by a factor of 1 divided by c. Compresses the graph of y equals f of x horizontally by a factor of c. Stretches the graph of y equals f of x horizontally by a factor of 1 divided by c.
Example
In the first graph the base graph is y equals cos x but when we multiply cos x by 2 we can see the graph of y equals 2 cos x is stretched vertically by a factor of 2
In the second graph the base graph is y equals cos x but when we multiply cos x by half we can see the graph of y equals half cos x is compressed vertically by a factor of half
In the third graph the base graph is y equals cos x but when we multiply x by 2 we can see the graph of y equals cos 2 x is compressed horizontally by a factor of 2
In the fourth graph the base graph is y equals cos x but when we multiply x by half we can see the graph of y equals cos half x is stretched horizontally by a factor of half
Even and Odd Functions, with some examples, using two graphs:
Even function: A function f, is said to be an even function, if f of minus x equals f of x.
For example x square, x to the power four, x to the power 6, cos x, sine x square and e to the power x square so on.
Odd function: A function f, is said to be an odd function, if f of minus x equals minus f of x
For example, x cube, x to the power five, x to the power seven and sine x so on.
on the left side, A Graph, of an even function shown, which is symmetrical about y axis Where, f of minus x equals f of x, Then Another Graph of an odd function shown on the right side which is symmetrical about origin. where f of minus x equals minus f of x,
Families, of Functions
1. Families, of y equals m x plus b. for example y equals x, and y equals x plus 1 and y equals 2 x plus 1.
2. Families, of y equals x to the power n. for example y equals x, and y equals x square, and y equals x cube, and y equals x to the power 4 and y equals x to the power 5.
3. Families, of y equals x to the power minus n. for example y equals x to the power minus 2, and y equals x to the power minus 3, and y equals x to the power minus 4, and y equals x to the power minus 5.
4. Polynomials. For example y equals 3 plus 5 x, and y equals x square minus 3 x plus 1 and y equals 2 x cube minus 7.
5. Families, of y equals A into sine of bx minus c, and y equals a into cos of b x minus c.
for example, y equals 3 into sine of 2 pi x and y equals minus 2 into cos of pi x.
Graphs, of Families, of y equals m x plus b, for example y equals x, y equals x plus 1 and y equals 2 x plus 1.
The graph on the left side shows the family, of y equals m x plus b where b is fixed and m is varying, and The graph on the right side shows the family of y equals m x plus b where m is fixed and b is varying
Graphs, of Families, of y equals x to the power n. for example y equals x, y equals x square, y equals x cube, y equals x to the power 4 and y equals x to the power 5.
The First graph is y equals x, Second graph is y equals x square, And the third graph is y equals x cube
fourth graph is y equals x to the power 4 and the fifth graph is y equals x to the power 5
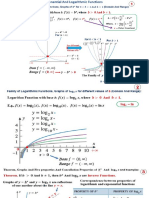
Graphs, of Families, of y equals x to the power minus n. for example y equals x to the power minus one, y equals x to the power minus 2, y equals x to the power minus 3, y equals x to the power minus 4 and y equals x to the power minus 5.
The graph on the left side shows, the family, of y equals 1 over x to the power n where n is even, and The graph on the right side shows the family of y equals 1 over x to the power n where n is odd
Graphs, of Polynomials. For example y equals 3 plus 5 x, y equals x square minus 3 x plus 1 and y equals 2 x cube minus 7
y equals 8 x to the power 4 minus 9 x cube plus 5 x minus 3 and y equals x to the power 5 plus x cube
The First graph has degree of two And The Second graph has degree of three
The Third graph has degree of four And the Fourth graph has degree of five
Graphs, of Families, of y equals a into sine of b x minus c, and y equals a into cos of b x minus c.
for example, y equals sine x comma y equals 2 into sine of 4 x
Here, absolute value of capital A is the amplitude and 2 pi divided by capital B indicates periods
There are two graphs together shown . The blue one indicates the graph of y equals sine x. The violate one indicates the graph of y equals 2 sine 4 x.
Practice Work:
1. Consider the function, f of x equals 2 minus square root of x plus 2. Graph the function and hence, find the domain and range of the function.
2. Draw the graph of f of x equals 3 minus square root of 2 minus x, and find the domain and range of f of x.
3. Sketch the graphs, of a. y equals 3 minus absolute value of 2x minus 4, and b. y equals 3 plus root over x plus 1, and c. k of x equals absolute value of x minus 3 plus 2, and hence write down the domain and range for each of them.
You might also like
- Introduction to Time Series and Forecasting【solution manual 】Document46 pagesIntroduction to Time Series and Forecasting【solution manual 】Grey Baoyin79% (24)
- GraphsPolynomialFuncsSE PDFDocument3 pagesGraphsPolynomialFuncsSE PDFkyle garciaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul'S College: Multiple Choice QnsDocument14 pagesSt. Paul'S College: Multiple Choice Qns20/21-5B-(05) HoMeiYi/何美誼No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMDocument7 pagesLecture 2 0.4 Inverse Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions of Mat 120 of MTMSamiul Hasnat Taseen 2233054642No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 0.1 and 0.2 Introduction of Functions of Mat 120 of MTMDocument8 pagesLecture 1 0.1 and 0.2 Introduction of Functions of Mat 120 of MTMABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMDocument10 pagesLecture 4 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMABU MASROOR AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMDocument10 pagesLecture 3 0.5 Exponential and Logarithmic Function of Mat 120 of MTMSamiul Hasnat Taseen 2233054642No ratings yet
- Reviewer Alebra 1Document7 pagesReviewer Alebra 1jomhailcruz03No ratings yet
- G9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphDocument27 pagesG9 Math Q1 - Week 6 - Quadratic Functions and Its GraphMechael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Community College of Gingoog CityJohn LiamNo ratings yet
- Cronasia Foundation College, Inc.: Lesson 5-7 Grade 9 - Behiga Mathematics 9Document14 pagesCronasia Foundation College, Inc.: Lesson 5-7 Grade 9 - Behiga Mathematics 9queencyfaithNo ratings yet
- Transformations of FunctionsDocument35 pagesTransformations of FunctionsPHENYO SEICHOKONo ratings yet
- Introduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsDocument10 pagesIntroduction: in Nearly Every Physical Phenomenon We Observe That One Quantity DependsbushraNo ratings yet
- Functions: What Is A Function?Document9 pagesFunctions: What Is A Function?Bilal AnwarNo ratings yet
- Graphs of FunctionsDocument13 pagesGraphs of FunctionsLennoxNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation and Quadratic EquationDocument30 pagesLinear Equation and Quadratic EquationAmz AlburoNo ratings yet
- Training Course 9 Senior Functions and TrigonometryDocument32 pagesTraining Course 9 Senior Functions and TrigonometryRichardoBrandonNo ratings yet
- Core RevisionDocument2 pagesCore RevisionMaasa AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuidegurpreetNo ratings yet
- Graphs Revision Sheet FinalDocument27 pagesGraphs Revision Sheet FinalLuumuno PeaceNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 and 14 On 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical ShellsDocument11 pagesLecture 13 and 14 On 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical Shellsfaltu faltuNo ratings yet
- Illustrating Limit of A Function: Week 1Document12 pagesIllustrating Limit of A Function: Week 1Ynna Lyn ManaloNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions: General Mathematics O. OronceDocument55 pagesExponential Functions: General Mathematics O. Oroncecass dumpNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus PrimerDocument17 pagesPre Calculus PrimeracsimsNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Polynomial Functions and Applications - Mana-ItDocument12 pagesGraphs of Polynomial Functions and Applications - Mana-ItJenicel Mana-itNo ratings yet
- Function and PolynomialsDocument8 pagesFunction and PolynomialsJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- Transformations Final ReviewDocument18 pagesTransformations Final ReviewFrances Ijeoma ObiakorNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions: General MathematicsDocument55 pagesExponential Functions: General MathematicsStephany BartianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4KelleyNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document39 pagesCH 15iwouldwishforyouNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math 11 Lesson 4Document24 pagesGen. Math 11 Lesson 4Maricon SorongonNo ratings yet
- X2 Graph Sketching TransformationsDocument10 pagesX2 Graph Sketching TransformationsyddapNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument8 pagesQuadratic FunctionsJerome MirabuenosNo ratings yet
- Module1 - Exponential FunctionsDocument28 pagesModule1 - Exponential Functionsstepharry08No ratings yet
- Vertex Form of Quadratic FunctionsDocument12 pagesVertex Form of Quadratic FunctionspurplepinkNo ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Ma. Rica Mae Rosete100% (1)
- X InterceptDocument8 pagesX Interceptapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Sabreena RataniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Graphs of The Trigonometric Functions - Part 1Document48 pagesChapter 4 - Graphs of The Trigonometric Functions - Part 1Sharmaine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- 1801 A Supp NotesDocument218 pages1801 A Supp NotesDodNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Graphs of Functions and RelationsDocument41 pagesAnalyzing Graphs of Functions and RelationsMohy SayedNo ratings yet
- CBR KalkulusDocument20 pagesCBR KalkulusYon setiawanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionDocument25 pagesQuadratic FunctionCherry Grace Sagde EuldanNo ratings yet
- Inequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteDocument11 pagesInequalities and Functions 2 - AdanteKarenNo ratings yet
- MATH9 Q1 WEEK6 ForprintDocument15 pagesMATH9 Q1 WEEK6 Forprintryo.wolloh.27No ratings yet
- Week 2 BDocument24 pagesWeek 2 BMegane AlarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 3 - Graphs and FunctionsDocument26 pagesChapter 3 3 - Graphs and Functionsapi-263209117No ratings yet
- Math 8 Q2 Week 4Document11 pagesMath 8 Q2 Week 4Candy CastroNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Fungsi KuadratDocument37 pagesAplikasi Fungsi KuadratridwanawalianNo ratings yet
- Function of Two VariablesDocument50 pagesFunction of Two Variablesap021No ratings yet
- Exponential FunctionDocument55 pagesExponential FunctionPrin CessNo ratings yet
- Math Test 10Document11 pagesMath Test 10adhamjonnorkulov02No ratings yet
- Math Assignment Unit - 4Document9 pagesMath Assignment Unit - 4mdmokhlesh1993No ratings yet
- Common CurvesDocument9 pagesCommon CurvesTagore uNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Function Investigation - Maria AncutaDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Function Investigation - Maria Ancutaapi-515654558No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Chapter 3Document5 pagesTrigonometry Chapter 3freda licudNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Sec3Document59 pagesChap1 Sec3Naqeeb khanNo ratings yet
- A Polynomial Function of Degree N Has N Zeros, Provided Multiple Zeros Are Counted More Than Once and Provided Complex Zeros Are CountedDocument26 pagesA Polynomial Function of Degree N Has N Zeros, Provided Multiple Zeros Are Counted More Than Once and Provided Complex Zeros Are Countedbaifern24No ratings yet
- General Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Graphing - ExamplesDocument4 pagesTopic 6: Graphing - ExamplessaaskaphoneNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q1Module6Document9 pagesMath8 Q1Module6iam_maria1997No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Proportional LogicDocument17 pagesProportional LogicBert SantosNo ratings yet
- Projection of PlanesDocument14 pagesProjection of PlanesHere Estrada100% (1)
- Why Stock Markets CrashDocument3 pagesWhy Stock Markets CrashMyfirstmillion FrugalNo ratings yet
- Ugmath2022 22may PDFDocument6 pagesUgmath2022 22may PDFManashree VyasNo ratings yet
- Ust Ms Cheme FlyerDocument2 pagesUst Ms Cheme Flyerjr_hernando_enal3852No ratings yet
- GMM Var StataDocument27 pagesGMM Var StataChahine BergaouiNo ratings yet
- Quantum Information Theory (Lecture Notes)Document101 pagesQuantum Information Theory (Lecture Notes)50_BMGNo ratings yet
- JOM 2023 SolutionDocument5 pagesJOM 2023 Solutionthairestaurant3No ratings yet
- 131911-3130704 - DF Nov-2019Document1 page131911-3130704 - DF Nov-2019APOLLO Sem 4 I.T.No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TV100% (1)
- R - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Document6 pagesR - (Z/R,) (1 + Ao o + E " (Z/R,) " (A. - Ib.)Srinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table CompletaDocument2 pagesLaplace Table CompletaAlexis Gianlvca Rodrigvez PereaNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument9 pagesCircles PDFbansallove2008No ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of An Unmanned Underwater VehicleDocument119 pagesModeling and Control of An Unmanned Underwater Vehiclearash501No ratings yet
- Modeling The Motion of A SpringDocument5 pagesModeling The Motion of A Springapi-253477911No ratings yet
- Looking For A Challenge 2 enDocument27 pagesLooking For A Challenge 2 enZaidNo ratings yet
- Java Code Lab)Document3 pagesJava Code Lab)peace_edafeNo ratings yet
- Mat495 Chapter 5Document10 pagesMat495 Chapter 5MuhamadSadiqNo ratings yet
- MSC MBA Prospectus Final Autumn-2020 PDFDocument47 pagesMSC MBA Prospectus Final Autumn-2020 PDFMuhammad AyazNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lec 8 CC p2-1Document17 pagesWeek 4 Lec 8 CC p2-1Sohaib KashmiriNo ratings yet
- Programs With Flowchart and AlgorithmDocument7 pagesPrograms With Flowchart and AlgorithmRadhika AjadkaNo ratings yet
- Adstock ModelDocument7 pagesAdstock ModelRachit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsDocument6 pagesQualitative Analysis On Second Order Neutral Delay Difference EquationsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Race Car Damping - Some Food For ThoughtDocument30 pagesRace Car Damping - Some Food For ThoughtDionisis SpiliopoulosNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Skills TestDocument3 pagesBasic Math Skills TestKeri RossnerNo ratings yet
- Basic Math Skills Grade 5Document310 pagesBasic Math Skills Grade 5C A100% (2)
- Code ADocument10 pagesCode ATesfamichael FufaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Math QuizDocument5 pagesClass 12 Math Quizankita071291No ratings yet