Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Endjerriekha Dela cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views28 pages Here are the steps to plot the points and connect them with line segments on the Cartesian coordinate plane:
1. Use a pencil and ruler to draw the x- and y-axes on the graph paper, labeling the axes.
2. Plot the points provided one at a time by marking their coordinates on the graph. For example, plot point A at (-3, 4).
3. Use a colored pencil to draw a line segment between the points in the order they are given, connecting each new point to the prior one(s).
4. Continue drawing line segments until all points have been connected in a closed path or paths.
5. Optional: Label each point with its letter for clarity.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Here are the steps to plot the points and connect them with line segments on the Cartesian coordinate plane:
1. Use a pencil and ruler to draw the x- and y-axes on the graph paper, labeling the axes.
2. Plot the points provided one at a time by marking their coordinates on the graph. For example, plot point A at (-3, 4).
3. Use a colored pencil to draw a line segment between the points in the order they are given, connecting each new point to the prior one(s).
4. Continue drawing line segments until all points have been connected in a closed path or paths.
5. Optional: Label each point with its letter for clarity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views28 pagesUntitled
Untitled
Uploaded by
Endjerriekha Dela cruz Here are the steps to plot the points and connect them with line segments on the Cartesian coordinate plane:
1. Use a pencil and ruler to draw the x- and y-axes on the graph paper, labeling the axes.
2. Plot the points provided one at a time by marking their coordinates on the graph. For example, plot point A at (-3, 4).
3. Use a colored pencil to draw a line segment between the points in the order they are given, connecting each new point to the prior one(s).
4. Continue drawing line segments until all points have been connected in a closed path or paths.
5. Optional: Label each point with its letter for clarity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 28
The name cartesian comes from the
French mathematician and philosopher
René Descartes (Latin: Cartesius), who
worked to merge algebra and Euclidean
geometry. This work was important in
creating calculus and cartography.
• The idea of this system was developed in 1637 in two works
by Descartes. In part two of his Discourse on Method,
Descartes explains plotting the position of a point or object on
a surface, using two perpendicular axes as measuring guides.
In La Géométrie, he further explores these ideas.
1. A(5,1)
2. B(-1, 2)
3. C(3,-2)
4. D(0,4)
5. E(-3,-2)
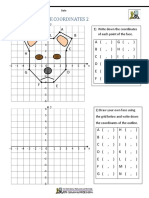
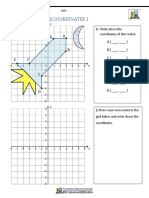
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A
2. B
E
B 3. C
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B
E
B 3. C
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3, 4) - Q II
2. B (-3, 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3, 4) - Q II
2. B (-3, 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3, 4) - Q II
2. B (-3, 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5, -2) - Q III
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3, 4) - Q II
2. B (-3, 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5, -2) - Q III
H 4. D
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3, 4) - Q II
2. B (-3, 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5, -2) - Q III
H 4. D (-1, -1) - Q III
5. E
D F 6. F
C 7. G
I 8. H
J 9. I
10. J
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F
J 7. G
8. H
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G
8. H
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G
8. H
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G (4 , 4) - Q I
8. H
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G (4 , 4) - Q I
8. H (5 , 0) - x-axis
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G (4 , 4) - Q I
8. H (5 , 0) - x-axis
Write the coordinates of
G each letter and identify
A
the quadrant.
1. A (-3 , 4) - Q II
2. B (-3 , 1) - Q II
E
B 3. C (-5 , -2) - Q
H III
4. D (-1 , -1) - Q
D F III
C 5. E (2 , 2) - Q I
I 6. F (2 , -1) - Q IV
J 7. G (4 , 4) - Q I
8. H (5 , 0) - x-axis
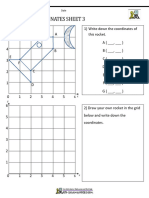
OUTPUT #1 – Cartesian Coordinate
Materials:
1. Graphing Paper
2. Pencil
3. Colors
4. Ruler
Direction: Plot the points on the graph below, connect the points with lines
segments as you plot them, keep connecting the points until you see line ends,
then start the next group.
You might also like
- Coordenadas en El Plano 4Document2 pagesCoordenadas en El Plano 4Maria Fernanda QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Graphs and It'S ExamplesDocument19 pagesGraphs and It'S Examplessumi kannaNo ratings yet
- Plot The Coordinates 3Document2 pagesPlot The Coordinates 3evermath123No ratings yet
- CPM Practise QuestionsDocument2 pagesCPM Practise Questionsnadeem ahmadNo ratings yet
- Ab C D E F G H I J K: English Test (1) A Trace The Letter A - MDocument6 pagesAb C D E F G H I J K: English Test (1) A Trace The Letter A - MLai Hui FangNo ratings yet
- Co Ordinate Geometry: XYZ XYZDocument7 pagesCo Ordinate Geometry: XYZ XYZarvindshukla123No ratings yet
- Problems On Network Diagram CPM 2Document1 pageProblems On Network Diagram CPM 2Asima Huma0% (1)
- Img 20230711 0002Document3 pagesImg 20230711 0002Merun BoseNo ratings yet
- CPM322E Exercise 2Document2 pagesCPM322E Exercise 2ayman sobhyNo ratings yet
- Graphing Ordered Pairs 2Document2 pagesGraphing Ordered Pairs 2Luis AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Practice Practice Coordinate PlaneDocument4 pagesPractice Practice Coordinate PlaneChuuNo ratings yet
- PH-6 - Adv - Answers - PhysicsDocument6 pagesPH-6 - Adv - Answers - Physicstanu15048No ratings yet
- Plotting Points On A Coordinate Grid (1st Quadrant Only) : Grade 4 Geometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesPlotting Points On A Coordinate Grid (1st Quadrant Only) : Grade 4 Geometry WorksheetMUHAMMAD ARIFFUDDIN BIN SUKIAT MoeNo ratings yet
- ამოცანა ქსელურ გრაფიკზეDocument3 pagesამოცანა ქსელურ გრაფიკზეsmv smvNo ratings yet
- Sheet (2) Project Time Planning and SchedulingDocument8 pagesSheet (2) Project Time Planning and SchedulingmohamedNo ratings yet
- Angles WorksheetDocument2 pagesAngles WorksheetJayzel BangotNo ratings yet
- CCN2024 Logic & Reasoning Semester Two 2015/2016: Tutorial 6 CP and IP (Ch. 5)Document4 pagesCCN2024 Logic & Reasoning Semester Two 2015/2016: Tutorial 6 CP and IP (Ch. 5)sio kuan laoNo ratings yet
- Line BalancingDocument6 pagesLine BalancingAlejandra FernándezNo ratings yet
- Schedules and Activities of Some Projects Are Shown BelowDocument1 pageSchedules and Activities of Some Projects Are Shown BelowAbdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Rahaf HudaibNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 Project ManagementDocument5 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 Project ManagementpatriquembeleonokokoNo ratings yet
- WSIIAAUIS2Document4 pagesWSIIAAUIS2beshahashenafe20No ratings yet
- Depth First Search Analysis: Conclusion: For This Particular Example BSF Search Is Faster But It Requires MoreDocument1 pageDepth First Search Analysis: Conclusion: For This Particular Example BSF Search Is Faster But It Requires MoreSaroj KatwalNo ratings yet
- Answer KeysDocument3 pagesAnswer Keysryanne jeffrey pandiNo ratings yet
- 0206ph PKDocument12 pages0206ph PKRana HazemNo ratings yet
- Principals of MusicDocument15 pagesPrincipals of MusicThilina GomisNo ratings yet
- MT 4 P 2 Key ADocument1 pageMT 4 P 2 Key AAnkit BansalNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: I I T - J E E, 2 0 1 9Document1 pageFiitjee: I I T - J E E, 2 0 1 9Ankit BansalNo ratings yet
- Describe Position QuestionsDocument6 pagesDescribe Position Questionsranj19869No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument4 pagesEnglishDipti Mahadeorao HatwarNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: I I T - J E E, 2 0 1 9Document1 pageFiitjee: I I T - J E E, 2 0 1 9Ankit BansalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Review WSDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Review WSLuis Abonce-LlanosNo ratings yet
- BIO435 Biological Modeling and Simulation: Spring 2021 Dr. Qaiser ChaudryDocument69 pagesBIO435 Biological Modeling and Simulation: Spring 2021 Dr. Qaiser ChaudryadeenNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 18 KruskalDocument31 pagesLecture17 18 KruskalMr. Hussain SarganaNo ratings yet
- Final Period: Jhaymie Rose B. Alfonso CA4-A1 CM4Document1 pageFinal Period: Jhaymie Rose B. Alfonso CA4-A1 CM4Jhaymie AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Linear Graphing PDFDocument40 pagesLinear Graphing PDFestherfe rafaelaNo ratings yet
- Span TreeDocument74 pagesSpan TreeLiela Borganio GardoseNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercise-Network Diagram Project Duration (CPM)Document12 pagesPractice Exercise-Network Diagram Project Duration (CPM)Samar PratapNo ratings yet
- Tarea ConjuntosDocument6 pagesTarea ConjuntosZayde Hdz.G.No ratings yet
- STA3022 Tut 5 Cluster Analysis and MDS SolutionsDocument7 pagesSTA3022 Tut 5 Cluster Analysis and MDS SolutionsalutakaundaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Function (Exercise) Module-2Document11 pagesInverse Trigonometric Function (Exercise) Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- PDM - HW 3Document2 pagesPDM - HW 3Ahmad Al-HawadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6:coordinate Geometry: X X y yDocument20 pagesChapter 6:coordinate Geometry: X X y yTee Pei LengNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Textbook PracticeDocument1 page1.4 Textbook PracticeGarima Rohit SalujaNo ratings yet
- AOA DiagramDocument3 pagesAOA DiagramMarium RazaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Date: Name: Time: FormDocument51 pagesMathematics: Date: Name: Time: Formnsiu1234No ratings yet
- Critical Path Method Analysis: Practice Questions: Q1. Activity Immediate Predecessor DurationDocument2 pagesCritical Path Method Analysis: Practice Questions: Q1. Activity Immediate Predecessor Durationaa61353No ratings yet
- Single Answer Questions: Level-ViDocument25 pagesSingle Answer Questions: Level-Vimohd atifNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SPR Emp WordDocument9 pagesQuadrilateral SPR Emp WordMario Labastida AyubanNo ratings yet
- 405 Straight Line: 5.1 Basic of A Straight Line Distance Between Two PointDocument12 pages405 Straight Line: 5.1 Basic of A Straight Line Distance Between Two PointatikahNo ratings yet
- PH 1 PhysicsDocument8 pagesPH 1 PhysicsdevilogywinsNo ratings yet
- Essentials of College Algebra 11th Edition Lial Test BankDocument26 pagesEssentials of College Algebra 11th Edition Lial Test BankJoanSmithrgqb100% (58)
- Letter, Symbol Series, and Pattrens: A - B. C. DDocument6 pagesLetter, Symbol Series, and Pattrens: A - B. C. Darjunmba119624No ratings yet
- Hi Alc Ltaee: 1. Standard 2. Application of TraverseDocument10 pagesHi Alc Ltaee: 1. Standard 2. Application of TraverseDerry ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Aits 10718 FT VII Paper 1 Sol2Document13 pagesAits 10718 FT VII Paper 1 Sol2architNo ratings yet
- Ielts Journal Tips For IELTS ReadingDocument11 pagesIelts Journal Tips For IELTS ReadingBehrokh SatarnejadNo ratings yet
- Find and Plot 1 PDFDocument2 pagesFind and Plot 1 PDFJavzanlkham VanchinbazarNo ratings yet
- Classifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92From EverandClassifying Spaces for Surgery and Corbordism of Manifolds. (AM-92), Volume 92No ratings yet
- Mesh BasicsDocument45 pagesMesh BasicsS.M. Atiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 06 PDFNisa ArpyantiNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegrationDocument32 pagesDefinite IntegrationsanagavarapuNo ratings yet
- Levi Civita Etc PDFDocument6 pagesLevi Civita Etc PDFAmalendu PramanickNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument21 pagesHYPERBOLARALPH RICHMOND CENONNo ratings yet
- PreCal Quarter 1 Module 1Document37 pagesPreCal Quarter 1 Module 1PRINCESS CLARIZZ JOY SALUDESNo ratings yet
- 3.coordinate GeometryDocument12 pages3.coordinate GeometryDebNo ratings yet
- SymGeoAnal Template 2022Document1 pageSymGeoAnal Template 2022Adel DelloumNo ratings yet
- From Brans-Dicke Theory To A Newtonian GravityDocument4 pagesFrom Brans-Dicke Theory To A Newtonian GravitycrocoaliNo ratings yet
- 03 Conic SectionsDocument49 pages03 Conic SectionsmeheheheNo ratings yet
- Parabola: Definitions of Various Important TermsDocument11 pagesParabola: Definitions of Various Important Termsno nameNo ratings yet
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument6 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- ConicSectionsTreatedGeometrically 10440007Document300 pagesConicSectionsTreatedGeometrically 10440007rachealhantukumane52No ratings yet
- 3D Geometry BasicsDocument9 pages3D Geometry Basicsmath2727No ratings yet
- The Plane Through Three Points: R Such That MDocument70 pagesThe Plane Through Three Points: R Such That Mprica_adrianNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAdrian PachecoNo ratings yet
- Final Ellipse - JEE MAINS Prev. Year Qs - V-Math PDFDocument26 pagesFinal Ellipse - JEE MAINS Prev. Year Qs - V-Math PDFVickyNo ratings yet
- Topics in Finite Element AnalysisDocument9 pagesTopics in Finite Element Analysischeung ka lungNo ratings yet
- 12 Practical 7 - 10Document4 pages12 Practical 7 - 10Piyush ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Flipped-Class 3 - Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsDocument11 pagesFlipped-Class 3 - Graphs of Quadratic FunctionsReign droppingNo ratings yet
- TocDocument3 pagesTocAndrea ScapellatoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 PDFsarangaNo ratings yet
- 3D - GeometryDocument9 pages3D - GeometryMadhav GoelNo ratings yet
- Bernhard Riemann's LifeDocument2 pagesBernhard Riemann's LifeBrenda BastidasNo ratings yet
- The EllipseDocument9 pagesThe Ellipsesifogax112No ratings yet
- 2.5 Pressure Force On Curved SurfaceDocument5 pages2.5 Pressure Force On Curved SurfaceW GangenathNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids by Crandall, Dahl, LardnerDocument79 pagesMechanics of Solids by Crandall, Dahl, Lardnerpurijatin100% (6)
- Brigidine 2000 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument12 pagesBrigidine 2000 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsomhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- A. Wipf - Introduction To SupersymmetryDocument268 pagesA. Wipf - Introduction To Supersymmetrynom nomNo ratings yet
- CENG 1104 - Lec 9 - Moments About An AxisDocument17 pagesCENG 1104 - Lec 9 - Moments About An AxisJaleel SammsNo ratings yet