Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAE Architecture
SAE Architecture
Uploaded by
Adnaan Sulaiman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views7 pagesThe SAE architecture is the core network architecture for 3GPP's LTE wireless standard. It uses a simplified architecture with flat IP-based networking and includes the Evolved Node B and Access Gateway. The SAE architecture allows interworking with other wireless technologies through additional entities. Key components are the Mobility Management Entity for tracking users and handovers, the Serving Gateway for routing packets and mobility, and the PDN Gateway for connecting to external networks.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe SAE architecture is the core network architecture for 3GPP's LTE wireless standard. It uses a simplified architecture with flat IP-based networking and includes the Evolved Node B and Access Gateway. The SAE architecture allows interworking with other wireless technologies through additional entities. Key components are the Mobility Management Entity for tracking users and handovers, the Serving Gateway for routing packets and mobility, and the PDN Gateway for connecting to external networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views7 pagesSAE Architecture
SAE Architecture
Uploaded by
Adnaan SulaimanThe SAE architecture is the core network architecture for 3GPP's LTE wireless standard. It uses a simplified architecture with flat IP-based networking and includes the Evolved Node B and Access Gateway. The SAE architecture allows interworking with other wireless technologies through additional entities. Key components are the Mobility Management Entity for tracking users and handovers, the Serving Gateway for routing packets and mobility, and the PDN Gateway for connecting to external networks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
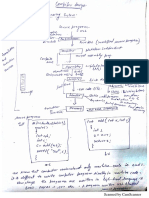
SAE Architecture
SAE
It is the core network architecture of mobile communication
protocol group 3GGP’s LTE wireless communication standard
SAE is the evolution of the GPRS Core Network, but with a
simplified architecture with an all-Network
It has support for higher throughput, lower latency radio access
network, support for mobility for heterogeneous access network
including LTE, LTE-Adv and 3GPP
SAE Architecture
• The SAE architecture is flat architecture similar to other
IP-based communication network. SAE uses an ENB
and Access Gateway (aGW)
• SAE also includes entities to allow full inter-working
with other related wireless technology (WCDMA,
WiMAX, WLAN)
• These entities can manage and permit the non-3GPP
technologies to interface directly with the network
SAE Architecture
Diagram
MME
It is the mobility management entity which is an important
controller node in the LTE network.
Some of the features of MME are:-
● Idle mode UE tracking
● Intra-LTE handover
● User authentication with HSS
● Paging procedure such as tr-transmission
SGW
The main function of the serving gateway is routing and forwarding of
user packets.
It is also responsible for the inter-eNB handovers in the U-Plane and
provides mobility between LTE and other types of network.
The SGW keeps context information such IP bearer and routing
information, and stores the UE contexts when paging happens. It is also
responsible for replicating user traffic for lawful interception.
PDN
The PDN Gateway is the connecting node between the UE’s and the
external networks.
In order to access multiple PDNs the UE can connect to several SGW at
the same time.
Functions are:-
● Policy enforcement
● Packet filtering
● Charging station
You might also like
- CloudHub 2.0 Discovery Form Template v1-20221116Document35 pagesCloudHub 2.0 Discovery Form Template v1-20221116Ashish TiwariNo ratings yet
- MIS TechNeoDocument137 pagesMIS TechNeoAditi ChanganNo ratings yet
- DBMS Easy Solution PDFDocument59 pagesDBMS Easy Solution PDFChinmay Gawde100% (2)
- Problem Solving Using C KCA-102: Introduction To CourseDocument36 pagesProblem Solving Using C KCA-102: Introduction To CourseVarun AroraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document15 pagesAssignment 2ZIX326No ratings yet
- Algorithms & Data Structure: Kiran WaghmareDocument20 pagesAlgorithms & Data Structure: Kiran WaghmareGayatri aptilNo ratings yet
- RTS SyllabusDocument3 pagesRTS SyllabusthejasNo ratings yet
- ADBMS Techknowledge Rev-2019 SearchableDocument90 pagesADBMS Techknowledge Rev-2019 SearchablerahqansayeedNo ratings yet
- Data Structures (Handwritten Notes)Document123 pagesData Structures (Handwritten Notes)Prince TyagiNo ratings yet
- Operating System Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniya PDFDocument232 pagesOperating System Notes 3 - TutorialsDuniya PDFKhalid RehmanNo ratings yet
- DLCA - TechNeoDocument132 pagesDLCA - TechNeoBhumi Avhad100% (1)
- DWM Mini ProjectDocument14 pagesDWM Mini ProjectHarish PawarNo ratings yet
- Unit7-Mobiliy and Handover Management in Mobile NetworksDocument54 pagesUnit7-Mobiliy and Handover Management in Mobile NetworkstesfuNo ratings yet
- DCE Techmax PDFDocument145 pagesDCE Techmax PDFBhakti PatilNo ratings yet
- CSS EasyDocument123 pagesCSS EasyRushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics GTU Book (3130006) by JS Chitode, IA DhotreDocument262 pagesProbability and Statistics GTU Book (3130006) by JS Chitode, IA DhotreSHAH YASH RAMESHBHAINo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing TechneoDocument103 pagesCloud Computing TechneoSETA40 Atharva MoreNo ratings yet
- DMBI Easy SolutionDocument48 pagesDMBI Easy SolutionKanishk Jain100% (1)
- Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesDocument75 pagesComputer Networking: A Top Down Approach: A Note On The Use of These PPT SlidesTajammul NasiriNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design QuantumDocument175 pagesCompiler Design QuantumArch SharNo ratings yet
- Operating System (Decode)Document117 pagesOperating System (Decode)OLLURI ROHITNo ratings yet
- Lecture On 06-10-2020Document27 pagesLecture On 06-10-2020neemarawat11No ratings yet
- Signal Coding and Estimation Theory PracticalDocument11 pagesSignal Coding and Estimation Theory Practicalrohit_vishwakarma786100% (2)
- ParallelDocument13 pagesParallelashiNo ratings yet
- Real Time System 12 Philip A Laplante 2nd EditionDocument34 pagesReal Time System 12 Philip A Laplante 2nd Editionanshuljain7750% (2)
- Sree Vahini: Codetect Financial Fraud Detection With Anomaly Feature DetectionDocument26 pagesSree Vahini: Codetect Financial Fraud Detection With Anomaly Feature DetectionkkvprasadNo ratings yet
- Mis Techmax UpdatedDocument137 pagesMis Techmax UpdatedtusharNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year Syllabus 2020-21Document36 pages3rd Year Syllabus 2020-21HarshitNo ratings yet
- NongatebookDocument2,245 pagesNongatebookLakshay Kakkar100% (1)
- Computer Networks Notes - TutorialsDuniyaDocument129 pagesComputer Networks Notes - TutorialsDuniyaquotes motivationalNo ratings yet
- INP MOD2 JavaScriptDocument15 pagesINP MOD2 JavaScriptMs. Noah NaomiNo ratings yet
- Vtu 6TH Sem Cse Computer Networks 2 Notes 10CS64Document72 pagesVtu 6TH Sem Cse Computer Networks 2 Notes 10CS64EKTHATIGER633590100% (8)
- Compiler Design Handwritten NotesDocument93 pagesCompiler Design Handwritten NotesAdityaNo ratings yet
- EmtlDocument295 pagesEmtlMallikarjuna raoNo ratings yet
- FAFLDocument136 pagesFAFLHariprasad MutalikdesaiNo ratings yet
- B.Tech EC Syllabus 3rd YearDocument35 pagesB.Tech EC Syllabus 3rd Yearpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Tech SeminarDocument13 pagesTech SeminarAnil Reddy Pochampally100% (1)
- Project ReportDocument8 pagesProject Reportramakant.savranNo ratings yet
- E Wheelz AbstractDocument5 pagesE Wheelz AbstractTelika RamuNo ratings yet
- AlgoPrep's 151 Problems SheetDocument6 pagesAlgoPrep's 151 Problems Sheettanijain1501No ratings yet
- Difference Between DFA NFA - NFA Vs DFA Automata - Engineer's PortalDocument3 pagesDifference Between DFA NFA - NFA Vs DFA Automata - Engineer's PortalprofBalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Lecture On 07-10-2020Document30 pagesLecture On 07-10-2020neemarawat11No ratings yet
- Unit-4 & 5Document21 pagesUnit-4 & 5neemarawat11No ratings yet
- MCSE-103 by Mohd AbdullahDocument9 pagesMCSE-103 by Mohd AbdullahabhayNo ratings yet
- Dsip Topper Solution 2020Document56 pagesDsip Topper Solution 2020asdNo ratings yet
- Deadline: 09 November 2021 On or Before 2359 Hours. Late Submissions Are NOT PermittedDocument12 pagesDeadline: 09 November 2021 On or Before 2359 Hours. Late Submissions Are NOT PermittedSnr Berel ShepherdNo ratings yet
- About Skyess: Problems CrushedDocument11 pagesAbout Skyess: Problems CrushedshaikNo ratings yet
- Data-Parallel Architectures andDocument27 pagesData-Parallel Architectures andAmeed UddinNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument621 pagesComputer NetworkCBSE UGC NET EXAMNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors NotesDocument65 pagesMicroprocessors NoteswizardvenkatNo ratings yet
- Network Layer: Delivery, Forwarding, and RoutingDocument62 pagesNetwork Layer: Delivery, Forwarding, and RoutingAarti KhareNo ratings yet
- WN TechmaxDocument172 pagesWN Techmaxavani ganatraNo ratings yet
- Final MergedDocument946 pagesFinal Mergedstrawberry shortcakeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Auto Selection and Auto Tuning of Machine Learning Models For Cloud Network Analytics SynopsisDocument9 pagesDynamic Auto Selection and Auto Tuning of Machine Learning Models For Cloud Network Analytics Synopsissudhakar kethanaNo ratings yet
- 6CS5 DS Unit-4Document64 pages6CS5 DS Unit-4CHIRAG GUPTA PCE19IT010No ratings yet
- Lab Assignment: EXPERIMENT 1: Study of Socket Programming and Client - Server ModelDocument4 pagesLab Assignment: EXPERIMENT 1: Study of Socket Programming and Client - Server ModelAkash PalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ethical Hacking TechmaxDocument33 pagesUnit 1 Ethical Hacking TechmaxakshayNo ratings yet
- LTE Architecture OverviewDocument19 pagesLTE Architecture OverviewVikramKumarNo ratings yet
- MC M6Document32 pagesMC M6vaidehi1713No ratings yet
- Lte BasicDocument2 pagesLte BasicKurnia Chris Pradana WicaksonoNo ratings yet