Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsChapter 2 Slides
Chapter 2 Slides
Uploaded by
Nour El Houda ChaibiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Vic 2019 CatalogDocument893 pagesVic 2019 CatalogAnna Mae Marantan100% (1)
- SB10 Chapter 8 AnswersDocument16 pagesSB10 Chapter 8 Answersanna jones20% (5)
- OutlookDocument53 pagesOutlookAvi Kense100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Chapter 2Document41 pagesLecture 2 - Chapter 2Wei NingNo ratings yet
- Seventeenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument44 pagesSeventeenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDenis OgingaNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis17 PPT Ch02Document40 pagesLaudon Mis17 PPT Ch02Samar sarahnaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document22 pagesCH 02atikanabilazahraNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Infor Systems in Global Business TodayDocument43 pagesCh01 Infor Systems in Global Business TodayHusha ArjunanNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument50 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationjuhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument42 pagesChapter 2-Global E-Business and CollaborationSarah Al ZaabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document62 pagesLecture 2sofeaNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument34 pagesGlobal E-Business and CollaborationAlexandra Ping HeangNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch02 KL CE, Global E-B & CollaborationDocument36 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch02 KL CE, Global E-B & Collaborationnajib.shamlan2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 1Document43 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 1Wei NingNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document39 pagesCH 02YESSICA CECILIA SINAGANo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument39 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionKaisoo KadiNo ratings yet
- Inf Sys in Org Chapter2Document33 pagesInf Sys in Org Chapter2Oliver TaukNo ratings yet
- Managing Information Systems: Seventh Canadian EditionDocument34 pagesManaging Information Systems: Seventh Canadian EditionJayson KingNo ratings yet
- Fourteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument49 pagesFourteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationSabelo RonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 3Document30 pagesLecture 3 - Chapter 3Wei NingNo ratings yet
- Laudon Ess16e ch01Document51 pagesLaudon Ess16e ch01Dalal KwtNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch12 KL CEDocument35 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch12 KL CEGhiyats Thariq Al-HaqNo ratings yet
- MIS - Chapter 2Document37 pagesMIS - Chapter 2poneNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument41 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and Collaborationaadhya guptaNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Information Systems, Organizations, and StrategyDocument51 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Information Systems, Organizations, and Strategyaadhya guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1ruba.nour.33No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Nourhan AfifiNo ratings yet
- Minggu 2 - CH2-Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument34 pagesMinggu 2 - CH2-Global E-Business and CollaborationRIANA IRAWATINo ratings yet
- Laudon PPT ch02Document36 pagesLaudon PPT ch02opadasadlehNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT ch02 KL CEDocument40 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT ch02 KL CEVân HảiNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument33 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionsynwithgNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Jane P. Laudon Kenneth C. Laudon Prentice-Hall IncDocument29 pagesManagement Information Systems: Jane P. Laudon Kenneth C. Laudon Prentice-Hall IncAnargya WidyatamaNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch03 KL CEDocument53 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch03 KL CEKgaogeloNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document28 pagesCH 09Samah AyadNo ratings yet
- Mis - CH1 EsDocument30 pagesMis - CH1 EsDwi HandokoNo ratings yet
- Laudon ITBV ch02Document31 pagesLaudon ITBV ch02mahmudNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Is Week 3Document23 pagesFundamentals of Is Week 3vmera23No ratings yet
- Management Information System - BUS 252Document237 pagesManagement Information System - BUS 252GhadaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IS in Global Business TodayDocument35 pagesCH 1 IS in Global Business Todaykhwaish jaanNo ratings yet
- Laudon Emis13 PPT C01Document49 pagesLaudon Emis13 PPT C01sjowiserNo ratings yet
- U01 Information Systems 2022 July 7Document44 pagesU01 Information Systems 2022 July 7Noppon SETTASATIENNo ratings yet
- Siste MeDocument457 pagesSiste MeStefan VasileNo ratings yet
- ISM-25 BI and Decision MakingDocument25 pagesISM-25 BI and Decision Makingminaf47No ratings yet
- باور بوينت شابتر 1 مقدمةDocument41 pagesباور بوينت شابتر 1 مقدمةوديع علاء مطلق عسافNo ratings yet
- ISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Document48 pagesISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Abhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument37 pagesGlobal E-Business and CollaborationDerry TannamaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MIS2023 SpringDocument52 pagesCH 1 MIS2023 SpringshajibayliNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument36 pagesSixteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationMohamedNo ratings yet
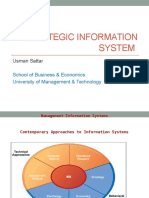
- Strategic Information System: Usman Sattar School of Business & Economics University of Management & TechnologyDocument33 pagesStrategic Information System: Usman Sattar School of Business & Economics University of Management & TechnologyRaaied JafferNo ratings yet
- Per 2 SimDocument49 pagesPer 2 SimjordyNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and Collaboration-CHP2Document39 pagesGlobal E-Business and Collaboration-CHP2Nurul Aisyah MisranNo ratings yet
- Management of DataDocument25 pagesManagement of DataSujal ManandharNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition: Information Systems in Global Business TodayDocument34 pagesSixteenth Edition: Information Systems in Global Business TodayHAMDAH HASSAN ALHARBINo ratings yet
- ch09 PPTDocument29 pagesch09 PPTjeff8272No ratings yet
- Lesson - 2 - Global Business CollaborationDocument22 pagesLesson - 2 - Global Business CollaborationBronwyn BammNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT ch02Document35 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT ch02Vita VitrianingrumNo ratings yet
- ch01 MIS 2024Document36 pagesch01 MIS 2024Mariem JabberiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Information Systems in Business ProcessesDocument40 pagesThe Use of Information Systems in Business ProcessesZyra MediosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Nourhan AfifiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information System: Usman SattarDocument42 pagesStrategic Information System: Usman SattarRaaied Jaffer100% (1)
- Chapter 01 Information System in The Digital AgeDocument32 pagesChapter 01 Information System in The Digital Agefennie lohNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document15 pagesCH 01Md Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- IT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureFrom EverandIT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureNo ratings yet
- INT4300 2reportDocument4 pagesINT4300 2reportNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- INT4300 1st ProgressreportDocument4 pagesINT4300 1st ProgressreportNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- GBU Ethics Case 4Document1 pageGBU Ethics Case 4Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Internship Placement FormDocument2 pagesInternship Placement FormNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Veneroo - POD&POPDocument1 pageVeneroo - POD&POPNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- INT 4301 SyllabusDocument9 pagesINT 4301 SyllabusNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior ProjectDocument7 pagesConsumer Behavior ProjectNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- EMP Skills Development TipsDocument45 pagesEMP Skills Development TipsNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report EnglishDocument30 pagesInternship Report EnglishNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Types of Entrepreneurship and Moroccan Ecosystem 6Document45 pagesTypes of Entrepreneurship and Moroccan Ecosystem 6Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Light House Tool-VF-1Document4 pagesLight House Tool-VF-1Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: The Biggest Threat of The Century 1Document8 pagesGlobal Warming: The Biggest Threat of The Century 1Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Porn Addiction - The Non Sexual Reasons - Pornography AddictionDocument1 pagePorn Addiction - The Non Sexual Reasons - Pornography Addictiona_berger6684No ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTDocument12 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTAGM S&M-CMNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Earth's ProcessesDocument4 pages1.3 Earth's ProcessesRufo FelixNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 pagesHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFK Cor100% (1)
- Bongabon Senior High School Brgy. Sinipit, Bongabon, Nueva Ecija, 3128Document2 pagesBongabon Senior High School Brgy. Sinipit, Bongabon, Nueva Ecija, 3128Cire HerreraNo ratings yet
- 131 Lesson PlansDocument3 pages131 Lesson PlansleahmnortonNo ratings yet
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Flow Characteristics of External Gear Pumps ConsidDocument10 pagesFlow Characteristics of External Gear Pumps ConsidThar GyiNo ratings yet
- Ud 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesDocument27 pagesUd 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesLola FrancoNo ratings yet
- NFCDocument12 pagesNFCDUDIMETLA SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- Admission Letter CsabDocument1 pageAdmission Letter Csabsuraj mohantyNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentDocument7 pagesG.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentMaria AndresNo ratings yet
- HP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.20 What's New and Release NotesDocument13 pagesHP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.20 What's New and Release NotesDavid SaralidzeNo ratings yet
- Time Cost Trade OffDocument22 pagesTime Cost Trade Offtulsi pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Structural Excavation and BackfillDocument3 pagesStructural Excavation and BackfillBillal BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ReviewDocument10 pagesChapter 23 ReviewThanat MilinthachindaNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksDocument29 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksFirdausi FauziNo ratings yet
- Ansi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Document17 pagesAnsi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Boris AguilarNo ratings yet
- Prinsip-Prinsip EkonomiDocument11 pagesPrinsip-Prinsip EkonomiRev AwNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Flogocid Cream - Google SearchDocument1 pageFlogocid Cream - Google SearchAyesha SohailNo ratings yet
- An4221 I2c Protocol Used in The stm32 Bootloader StmicroelectronicsDocument60 pagesAn4221 I2c Protocol Used in The stm32 Bootloader StmicroelectronicsmegatornadoNo ratings yet
- Ben MunteanDocument3 pagesBen MunteanBen MunteanNo ratings yet
- TDS BLR 896 EN ScreenDocument1 pageTDS BLR 896 EN ScreenLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Memory OrganizationDocument32 pagesLecture9 Memory Organizationecevitmert1453No ratings yet
- PCB Chassis Mount AC SSRDocument2 pagesPCB Chassis Mount AC SSRjbhupiNo ratings yet
Chapter 2 Slides
Chapter 2 Slides
Uploaded by
Nour El Houda Chaibi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views42 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views42 pagesChapter 2 Slides
Chapter 2 Slides
Uploaded by
Nour El Houda ChaibiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 42
Essentials of Management
Information Systems
Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Chapter 2
Global E-business and
Collaboration
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Learning Objectives
2.1 What major features of a business are important for
understanding the role of information systems?
2.2 How do systems serve different management groups in a
business, and how do systems that link the enterprise
improve organizational performance?
2.3 Why are systems for collaboration and social business
so important, and what technologies do they use?
2.4 What is the role of the information systems function in a
business?
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Organizing a Business: Basic
Business Functions (1 of 2)
• Business: formal organization that makes products or
provides a service in order to make a profit
• Four basic business functions
– Manufacturing and production
– Sales and marketing
– Finance and accounting
– Human resources
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Organizing a Business: Basic
Business Functions (2 of 2)
• Five basic business entities
– Suppliers
– Customers
– Employees
– Invoices/payments
– Products and services
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.1 The Four Major Functions
of a Business
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Business Processes
• Logically related set of tasks that define how specific
business tasks are performed
– The tasks each employee performs, in what order, and on
what schedule
– E.g., Steps in hiring an employee
• Some processes tied to functional area
– Sales and marketing: identifying customers
• Some processes are cross-functional
– Fulfilling customer order
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.2 The Order Fulfillment
Process
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
How IT Enhances Business
Processes
• Automation of manual processes
• Change the flow of information
• Replace sequential processes with simultaneous activity
• Transform how a business works
• Drive new business models
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Managing a Business and Firm
Hierarchies
• Firms coordinate work of employees by developing
hierarchy in which authority is concentrated at top.
– Senior management
– Middle management
– Operational management
– Knowledge workers
– Data workers
– Production or service workers
• Each group has different needs for information.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.3 Levels in a Firm
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
The Business Environment
• Businesses depend heavily on their environments for
capital, labor, supplies, and more.
• Global environment
– Technology and science, economy, politics, international
change
• Immediate environment
– Customers, suppliers, competitors, regulations, stockholders
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.4 The Business Environment
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
The Role of Information Systems in a
Business
• Firms invest in information systems in order to:
– Achieve operational excellence
– Develop new products and services
– Attain customer intimacy and service
– Improve decision making
– Promote competitive advantage
– Ensure survival
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Systems for Different Management
Groups
• Transaction processing systems (TPS)
– Keep track of basic activities and transactions of
organization
• Systems for business intelligence
– Address decision-making needs of all levels of management
Management information systems (MIS)
Decision support systems (DSS)
Executive support systems (ESS)
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Transaction Processing Systems
• Serve operational managers
• Principal purpose is to answer routine questions and to
track the flow of transactions through the organization
– E.g., inventory questions, granting credit to customer
• Monitor status of internal operations and firm’s relationship
with external environment
• Major producers of information for other systems
• Highly central to business operations and functioning
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.5 A Payroll TPS
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Management Information Systems
• Provide middle managers with reports on firm’s
performance, to help monitor firm and predict future
performance
• Summarize and report on basic operations using data from
TPS
• Provide weekly, monthly, annual results, but may enable
drilling down into daily or hourly data
• Typically not very flexible systems with little analytic
capability
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.6 How MIS Obtain Their Data
from the Organization’s TPS
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.7 Sample MIS Report
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Decision Support Systems
• Serve middle managers
• Support nonroutine decision making
– Example: What is impact on production schedule if
December sales double?
• Often use external information as well from TPS and MI S
• Model driven DSS
– Voyage-estimating systems
• Data driven DS S
– Intrawest’s marketing analysis systems
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.8 Voyage-Estimating
Decision Support System
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Executive Support Systems
• Serve senior managers
• Address strategic issues and long-term trends
– E.g., what products should we make in five years?
• Address nonroutine decision making
• Provide generalized computing capacity that can be
applied to changing array of problems
• Draw summarized information from M I S, DSS, and data
from external events
• Typically use portal with web interface, or digital
dashboard, to present content
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
A Digital Dashboard
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Systems for Linking the Enterprise
• Enterprise applications
– Systems that span functional areas, focus on executing
business processes across the firm, and include all levels of
management
• Four major types
– Enterprise systems
– Supply chain management systems
– Customer relationship management systems
– Knowledge management systems
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.9 Enterprise Application
Architecture
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Enterprise Systems
• Also called enterprise resource planning (ERP ) systems
• Integrate data from key business processes into single
system
• Speed communication of information throughout firm
• Enable greater flexibility in responding to customer
requests, greater accuracy in order fulfillment
• Enable managers to assemble overall view of operations
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Supply Chain Management (SCM )
Systems
• Manage relationships with suppliers, purchasing firms,
distributors, and logistics companies
• Manage shared information about orders, production,
inventory levels, and so on
– Goal is to move correct amount of product from source to
point of consumption as quickly as possible and at lowest
cost
• Type of interorganizational system
– Automating flow of information across organizational
boundaries
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Customer Relationship Management
(CRM ) Systems
• Help manage relationship with customers
• Coordinate business processes that deal with customers in
sales, marketing, and customer service
• Goals:
– Optimize revenue
– Improve customer satisfaction
– Increase customer retention
– Identify and retain most profitable customers
– Increase sales
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Knowledge Management Systems
• Manage processes for capturing and applying knowledge
and expertise
• Collect relevant knowledge and make it available wherever
needed in the enterprise to improve business processes
and management decisions
• Link firm to external sources of knowledge
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Intranets and Extranets
• Technology platforms that increase integration and
expedite the flow of information
• Intranets:
– Internal networks based on Internet standards
– Often are private access area in company’s website
• Extranets:
– Company websites accessible only to authorized vendors
and suppliers
– Facilitate collaboration
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
E-Business, E-Commerce, and E-
Government
• E-business:
– Use of digital technology and Internet to drive major
business processes
• E-commerce:
– Subset of e-business
– Buying and selling goods and services through Internet
• E-government:
– Using Internet technology to deliver information and
services to citizens, employees, and businesses
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
What is Collaboration?
• Growing importance of collaboration:
– Changing nature of work
– Growth of professional work
– Changing organization of the firm
– Changing scope of the firm
– Emphasis on innovation
– Changing culture of work and business
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
What is Social Business?
• Use of social networking platforms to engage employees,
customers, suppliers
• Conversations to strengthen bonds
• Requires information transparency
• Seen as way to drive operational efficiency, spur
innovation, accelerate decision making
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Business Benefits of Collaboration
and Social Business
• Investment in collaboration technology can return large
rewards, especially in sales and marketing, research and
development.
• Productivity: sharing knowledge and resolving problems
• Quality: faster resolution of quality issues
• Innovation: more ideas for products and services
• Customer service: complaints handled more rapidly
• Financial performance: generated by improvements in
factors above
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.10 Requirements for
Collaboration
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Tools and Technologies for
Collaboration and Teamwork
• Email and instant messaging (I M )
• Wikis
• Virtual worlds
• Collaboration and social business environments
– Virtual meeting systems (telepresence)
– Cloud collaboration services
Google Drive, Dropbox
– Microsoft SharePoint and IBM Notes
– Enterprise social networking tools
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Evaluating and Selecting
Collaboration Tools
1. What are your firm’s collaboration challenges?
2. What kinds of solutions are available?
3. Analyze available products’ cost and benefits.
4. Evaluate security risks.
5. Consult users for implementation and training issues.
6. Select candidate tools and evaluate vendors.
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.11 The Time/Space
Collaboration and Social Tool Matrix
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Systems for Knowledge Management
• Structured vs. tacit knowledge
• Systems for knowledge management
– Enterprise Content Management (ECM) Systems
– Locating and sharing expertise
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Figure 2.12 Enterprise Content
Management System
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
The Information Systems Department
• Programmers
• Systems analysts
– Principle liaisons to rest of firm
• Information systems managers
– Leaders of teams of programmers and analysts, project
managers, physical facility managers, telecommunications
managers, database specialists, managers of computer
operations, and data entry staff
• Senior managers: CI O, CPO, CSO, CKO, CDO
• End users
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
Information Systems Services
• Computing services
• Telecommunications services
• Data management services
• Application software services
• Physical facilities management services
• IT management services
• IT standards services
• IT educational services
• IT research and development services
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Ltd.
You might also like
- Vic 2019 CatalogDocument893 pagesVic 2019 CatalogAnna Mae Marantan100% (1)
- SB10 Chapter 8 AnswersDocument16 pagesSB10 Chapter 8 Answersanna jones20% (5)
- OutlookDocument53 pagesOutlookAvi Kense100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Chapter 2Document41 pagesLecture 2 - Chapter 2Wei NingNo ratings yet
- Seventeenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument44 pagesSeventeenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDenis OgingaNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis17 PPT Ch02Document40 pagesLaudon Mis17 PPT Ch02Samar sarahnaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document22 pagesCH 02atikanabilazahraNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Infor Systems in Global Business TodayDocument43 pagesCh01 Infor Systems in Global Business TodayHusha ArjunanNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument50 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationjuhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument42 pagesChapter 2-Global E-Business and CollaborationSarah Al ZaabiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document62 pagesLecture 2sofeaNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument34 pagesGlobal E-Business and CollaborationAlexandra Ping HeangNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch02 KL CE, Global E-B & CollaborationDocument36 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch02 KL CE, Global E-B & Collaborationnajib.shamlan2020No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 1Document43 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 1Wei NingNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document39 pagesCH 02YESSICA CECILIA SINAGANo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument39 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionKaisoo KadiNo ratings yet
- Inf Sys in Org Chapter2Document33 pagesInf Sys in Org Chapter2Oliver TaukNo ratings yet
- Managing Information Systems: Seventh Canadian EditionDocument34 pagesManaging Information Systems: Seventh Canadian EditionJayson KingNo ratings yet
- Fourteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument49 pagesFourteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationSabelo RonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 3Document30 pagesLecture 3 - Chapter 3Wei NingNo ratings yet
- Laudon Ess16e ch01Document51 pagesLaudon Ess16e ch01Dalal KwtNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch12 KL CEDocument35 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch12 KL CEGhiyats Thariq Al-HaqNo ratings yet
- MIS - Chapter 2Document37 pagesMIS - Chapter 2poneNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument41 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Global E-Business and Collaborationaadhya guptaNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Information Systems, Organizations, and StrategyDocument51 pagesSixteenth Edition - Global Edition: Information Systems, Organizations, and Strategyaadhya guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1ruba.nour.33No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Nourhan AfifiNo ratings yet
- Minggu 2 - CH2-Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument34 pagesMinggu 2 - CH2-Global E-Business and CollaborationRIANA IRAWATINo ratings yet
- Laudon PPT ch02Document36 pagesLaudon PPT ch02opadasadlehNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT ch02 KL CEDocument40 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT ch02 KL CEVân HảiNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument33 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionsynwithgNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems: Jane P. Laudon Kenneth C. Laudon Prentice-Hall IncDocument29 pagesManagement Information Systems: Jane P. Laudon Kenneth C. Laudon Prentice-Hall IncAnargya WidyatamaNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT Ch03 KL CEDocument53 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT Ch03 KL CEKgaogeloNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document28 pagesCH 09Samah AyadNo ratings yet
- Mis - CH1 EsDocument30 pagesMis - CH1 EsDwi HandokoNo ratings yet
- Laudon ITBV ch02Document31 pagesLaudon ITBV ch02mahmudNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Is Week 3Document23 pagesFundamentals of Is Week 3vmera23No ratings yet
- Management Information System - BUS 252Document237 pagesManagement Information System - BUS 252GhadaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 IS in Global Business TodayDocument35 pagesCH 1 IS in Global Business Todaykhwaish jaanNo ratings yet
- Laudon Emis13 PPT C01Document49 pagesLaudon Emis13 PPT C01sjowiserNo ratings yet
- U01 Information Systems 2022 July 7Document44 pagesU01 Information Systems 2022 July 7Noppon SETTASATIENNo ratings yet
- Siste MeDocument457 pagesSiste MeStefan VasileNo ratings yet
- ISM-25 BI and Decision MakingDocument25 pagesISM-25 BI and Decision Makingminaf47No ratings yet
- باور بوينت شابتر 1 مقدمةDocument41 pagesباور بوينت شابتر 1 مقدمةوديع علاء مطلق عسافNo ratings yet
- ISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Document48 pagesISM-06-07 (Global E-Business and Collaboration)Abhishek PatilNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument37 pagesGlobal E-Business and CollaborationDerry TannamaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MIS2023 SpringDocument52 pagesCH 1 MIS2023 SpringshajibayliNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationDocument36 pagesSixteenth Edition: Global E-Business and CollaborationMohamedNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information System: Usman Sattar School of Business & Economics University of Management & TechnologyDocument33 pagesStrategic Information System: Usman Sattar School of Business & Economics University of Management & TechnologyRaaied JafferNo ratings yet
- Per 2 SimDocument49 pagesPer 2 SimjordyNo ratings yet
- Global E-Business and Collaboration-CHP2Document39 pagesGlobal E-Business and Collaboration-CHP2Nurul Aisyah MisranNo ratings yet
- Management of DataDocument25 pagesManagement of DataSujal ManandharNo ratings yet
- Sixteenth Edition: Information Systems in Global Business TodayDocument34 pagesSixteenth Edition: Information Systems in Global Business TodayHAMDAH HASSAN ALHARBINo ratings yet
- ch09 PPTDocument29 pagesch09 PPTjeff8272No ratings yet
- Lesson - 2 - Global Business CollaborationDocument22 pagesLesson - 2 - Global Business CollaborationBronwyn BammNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis16 PPT ch02Document35 pagesLaudon Mis16 PPT ch02Vita VitrianingrumNo ratings yet
- ch01 MIS 2024Document36 pagesch01 MIS 2024Mariem JabberiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Information Systems in Business ProcessesDocument40 pagesThe Use of Information Systems in Business ProcessesZyra MediosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Nourhan AfifiNo ratings yet
- Strategic Information System: Usman SattarDocument42 pagesStrategic Information System: Usman SattarRaaied Jaffer100% (1)
- Chapter 01 Information System in The Digital AgeDocument32 pagesChapter 01 Information System in The Digital Agefennie lohNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document15 pagesCH 01Md Ali AshrafNo ratings yet
- IT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureFrom EverandIT Governance to Drive High Performance: Lessons from AccentureNo ratings yet
- INT4300 2reportDocument4 pagesINT4300 2reportNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- INT4300 1st ProgressreportDocument4 pagesINT4300 1st ProgressreportNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- GBU Ethics Case 4Document1 pageGBU Ethics Case 4Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Internship Placement FormDocument2 pagesInternship Placement FormNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Veneroo - POD&POPDocument1 pageVeneroo - POD&POPNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- INT 4301 SyllabusDocument9 pagesINT 4301 SyllabusNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior ProjectDocument7 pagesConsumer Behavior ProjectNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- EMP Skills Development TipsDocument45 pagesEMP Skills Development TipsNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Internship Report EnglishDocument30 pagesInternship Report EnglishNour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Types of Entrepreneurship and Moroccan Ecosystem 6Document45 pagesTypes of Entrepreneurship and Moroccan Ecosystem 6Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Light House Tool-VF-1Document4 pagesLight House Tool-VF-1Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: The Biggest Threat of The Century 1Document8 pagesGlobal Warming: The Biggest Threat of The Century 1Nour El Houda ChaibiNo ratings yet
- Porn Addiction - The Non Sexual Reasons - Pornography AddictionDocument1 pagePorn Addiction - The Non Sexual Reasons - Pornography Addictiona_berger6684No ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTDocument12 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTAGM S&M-CMNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Earth's ProcessesDocument4 pages1.3 Earth's ProcessesRufo FelixNo ratings yet
- Hand Hygiene and HandwashingDocument7 pagesHand Hygiene and HandwashingFaith Dianasas RequinaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFK Cor100% (1)
- Bongabon Senior High School Brgy. Sinipit, Bongabon, Nueva Ecija, 3128Document2 pagesBongabon Senior High School Brgy. Sinipit, Bongabon, Nueva Ecija, 3128Cire HerreraNo ratings yet
- 131 Lesson PlansDocument3 pages131 Lesson PlansleahmnortonNo ratings yet
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Flow Characteristics of External Gear Pumps ConsidDocument10 pagesFlow Characteristics of External Gear Pumps ConsidThar GyiNo ratings yet
- Ud 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesDocument27 pagesUd 6 Naturales 2º - Tools and MachinesLola FrancoNo ratings yet
- NFCDocument12 pagesNFCDUDIMETLA SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- Admission Letter CsabDocument1 pageAdmission Letter Csabsuraj mohantyNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentDocument7 pagesG.R. No. 200233 JULY 15, 2015 LEONILA G. SANTIAGO, Petitioner, People of The Philippines, RespondentMaria AndresNo ratings yet
- HP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.20 What's New and Release NotesDocument13 pagesHP Smart Update Firmware DVD 9.20 What's New and Release NotesDavid SaralidzeNo ratings yet
- Time Cost Trade OffDocument22 pagesTime Cost Trade Offtulsi pokhrelNo ratings yet
- Structural Excavation and BackfillDocument3 pagesStructural Excavation and BackfillBillal BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 ReviewDocument10 pagesChapter 23 ReviewThanat MilinthachindaNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksDocument29 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksFirdausi FauziNo ratings yet
- Ansi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Document17 pagesAnsi Scte74 2003 Ipssp001Boris AguilarNo ratings yet
- Prinsip-Prinsip EkonomiDocument11 pagesPrinsip-Prinsip EkonomiRev AwNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Flogocid Cream - Google SearchDocument1 pageFlogocid Cream - Google SearchAyesha SohailNo ratings yet
- An4221 I2c Protocol Used in The stm32 Bootloader StmicroelectronicsDocument60 pagesAn4221 I2c Protocol Used in The stm32 Bootloader StmicroelectronicsmegatornadoNo ratings yet
- Ben MunteanDocument3 pagesBen MunteanBen MunteanNo ratings yet
- TDS BLR 896 EN ScreenDocument1 pageTDS BLR 896 EN ScreenLuis Angel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture9 Memory OrganizationDocument32 pagesLecture9 Memory Organizationecevitmert1453No ratings yet
- PCB Chassis Mount AC SSRDocument2 pagesPCB Chassis Mount AC SSRjbhupiNo ratings yet