Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geological Basin of Pakistan
Geological Basin of Pakistan
Uploaded by
Sajjad Aziz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views19 pagesThe document summarizes the source rocks and reservoir rocks of the major sedimentary basins in Pakistan. It discusses that the Upper Indus Basin, Central Indus Basin, Lower Indus Basin, Pishin Basin, and Balochistan Basin each contain various source rocks such as shales and reservoir rocks such as sandstones and carbonates that trap oil and gas. Key source rocks mentioned include the Patala Formation in the Upper Indus Basin and Sember and Ranikot formations in the Lower Indus Basin. Major fields produced from reservoirs like the Khewra sandstone, Wargal carbonates, and Sui Main Limestone are also outlined.
Original Description:
Engineering Geology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the source rocks and reservoir rocks of the major sedimentary basins in Pakistan. It discusses that the Upper Indus Basin, Central Indus Basin, Lower Indus Basin, Pishin Basin, and Balochistan Basin each contain various source rocks such as shales and reservoir rocks such as sandstones and carbonates that trap oil and gas. Key source rocks mentioned include the Patala Formation in the Upper Indus Basin and Sember and Ranikot formations in the Lower Indus Basin. Major fields produced from reservoirs like the Khewra sandstone, Wargal carbonates, and Sui Main Limestone are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views19 pagesGeological Basin of Pakistan
Geological Basin of Pakistan
Uploaded by
Sajjad AzizThe document summarizes the source rocks and reservoir rocks of the major sedimentary basins in Pakistan. It discusses that the Upper Indus Basin, Central Indus Basin, Lower Indus Basin, Pishin Basin, and Balochistan Basin each contain various source rocks such as shales and reservoir rocks such as sandstones and carbonates that trap oil and gas. Key source rocks mentioned include the Patala Formation in the Upper Indus Basin and Sember and Ranikot formations in the Lower Indus Basin. Major fields produced from reservoirs like the Khewra sandstone, Wargal carbonates, and Sui Main Limestone are also outlined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Sedimentary Basins of Pakistan
and their source rocks and
reservoir rocks
Source Rock
Source rock refers to rocks in which hydrocarbons have been
generated or capable of being generated.
They are organic-rich sediments that may have been
deposited in a variety of environments including deep water
marine, lacustrine and deltaic.
Typical source rocks, usually shales contain about 1% organic
matter
Rocks of marine origin tend to be oil-prone, whereas terrestrial
source rocks (such as coal) tend to be gas-prone.
Under the right conditions, source rocks may also be reservoir
rocks, as in the case of shale gas reservoirs.
A source rock is formed by the:
Sedimentation in areas of high organic productivity.
Preservation of organic matter in sediment.
Reservoir Rocks
A reservoir rock is a rock body that must be:
1. Porous
2. Permeable
3. Covered with a cap rock (Trap)
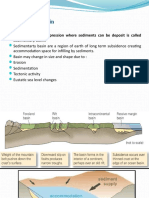
Sedimentary Basin of Pakistan
Basin is region of the earth of long-term subsidence
creating accommodation space for infilling by
sediments.
Sedimentary Basin of Pakistan
Pakistan comprises three sedimentary basins.
Indus Basin:
(1) Upper Indus Basin
(2) Central Indus Basin
(3) Lower Indus Basin
Balochistan Basin
Pishin or kakar khorasan Basin
Upper Indus Basin: The Upper Indus Basin (UIB)is the
area covering Potwar-Kohat plateau in Punjab and
Khyber-Pathtunkhawa provinces in Northern Pakistan
(districts, Jhelum, Chakwal, Rawalpindi, Islamabad,
Attock,Kohat, Karak area).
Sedimentary Basin of Pakistan
Central Indus Basin:
• The central indus basin is separated from upper indus
basin by the Sargodha high and pezu uplift in the
north.
• It is bounded by indian shield in the east, marginal
zone of Indian Plate in the west, and Sukker Riftin
the south.
Lower Indus Basin:
• The south indus basin is bounded by the indian
shield to the east and the marginal zone of Inian
plate to the west.
Sedimentary Basin of Pakistan
Pishin basin:
• It is also called kakar khorasan basin.
• Kakar khorasan basin is located between Chaman fault
in the north and northwest and obducted ophiolitic
margin of Indian Plate in the south.
Balochistan basin:
• In the east Balochistan basin is separated from Indus
basin by chaman fault, whereas the western part
extend into Iran.
Basin Map Of Pakistan
Source Rock Of Upper Indus Basin
The Paleocene Patala Formation appears to be the primary
source of hydrocarbons.
There are several potential source rocks in the Kohat-Potwar
geologic province. These include the Late Proterozoic–Lower
Cambrian Salt Range; Permian Wargal, Sardhai, and Chhidru;
Paleocene Lockhart; and Eocene Patala Formations (OGDC, 1996;
Quadri and Quadri, 1996).
Chichali and Lumshiwal Formations may be the youngest mature
rocks with source potential throughout most of the Kohat Plateau.
Reservoir Rock Of Upper Indus basin
In the Upper Indus basin, oil or gas has been produced from the
following formations:
Cambrian Kherwa, Kussak, and Jutana;
Permian Tobra, Amb, and Wargal;
Jurassic Datta;
Cretaceous Lumshiwal;
Paleocene Khairabad, Lockhart, Patala, and Nammal;
Eocene Bhadrar, Chorgali, and Margala Hill Limestone;
Miocene Murree (Khan and others, 1986; Petroconsultants,
1996).
Oil and Gas Field
The Potwar thrust belt has been known for oil production since 1915
when Khaur field was discovered in district Attock about 100 miles
south of Rawalpindi.
The oldest reservoir for oil, gas and condensate is Khewra
formation’s sandstone of Early Cambrian age in Adhi field near
Gujar Khan district Rawalpindi in Potwar Basin.
The carbonates of Chorgali-Sakesar Formation of Eocene age are the
biggest reservoir in Potwar Basin. The major fields where Eocene
fractured carbonates are reservoirs, Dhulian, Meyal, Pindori, Pariwali,
Dhurnal, Dakhni, Balkassar, Chak naurang, Adhi, Bhangali and Fim
Kasser.
Missa Kiswal and Rajian field are also producing oil from Khewra
sandstone; both located not far away from Adhi field.
Late Permain carbonates of Wargal Formation is the reservoir in
Dhurnal field. This reservoir is natural fractured. Dhurnal field is also
located in Potwar Basin near Khaur field.
Source Rock Of Lower Indus basin
Total area of lower indus basin is 169,000 sq.ml.
Sember (Cretaceous) and Ranikot (Paleocene) are main source
rock.
Environment of deposition of Sember and ranikot is marine
environment.
But there are units with Lower Goru, Ranikot and Ghazij
Formation to be source rock as well.
There are other known and potential source rocks.
Permian Dandot and Tredian Formations,
Triassic Jurassic Datta Formation,
Eocene Ghazij Formation,
lower Miocene shales.
Reservoir Rock Of Lower Indus basin
In Kirthar Range mostly Pab sandstone is the reservoir.
Lower Goru Sands (Lower Cretaceous) are the main reservoir
for oil and gas.
Habib Rahi limestone (Eocene ) is the gas reservoir in the giant
Mari Field.
These fields produce from Sui Main Limestone (SML, Eocene),
Ranikot sands, Dungan limestone (Paleocene) and the Pab
sandstone ( Late Cretaceous).
Oil and Gas Field
Lower Goru Formation Upper sands and Basal sands are oil
bearing in more than 50 fields in the Badin area in the districts
Mirpurkhas, Hyderabad, Badin and Sanghar in Sindh Province.
(Khaskheli, matli, Tando Adam, Turk, Duphri, Kato, Lashari,
Bhatti fields, etc)
Source is Sembar, Reservoir is Sui Main Limestone (Sui,
Kandhkot, Loti, Kandra, Bhadra fields).
Habib Rahi limestone (Mari gas field).
Along Kirthar Range (Mazarani, Mehar, Zamzama, Bhit, Badhra
gas fields) Pab is the reservoir for gas.
Source Rocks Of Balochistan basin
Balochistan basin is a least explored area.
Panjgur formation (Miocene) is considered as a reservoir.
Hoshab and Parkana formation has also ability as reservoir rock
in balochistab basin.
Reservoir Rocks Of Balochistan basin
Talar sand stone has high porosity act as reservoir rock.
You might also like
- Shipsheds of The Ancient MediterraneanDocument4 pagesShipsheds of The Ancient MediterraneanPere Garcia0% (1)
- Petroleum Geology of Pakistan-FinalDocument93 pagesPetroleum Geology of Pakistan-Finalsheikhjana100% (1)
- DGCA Nav QuestionDocument137 pagesDGCA Nav QuestionCHANDAN KUMAR100% (4)
- Reservior Rock of Indus BasinDocument22 pagesReservior Rock of Indus BasinJahangir MalikNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Rocks in PakistanDocument3 pagesReservoir Rocks in PakistanWaqas Arif100% (1)
- Sedimentary Basin: A Low Lying Area/depression Where Sediments Can Be Deposit Is Called Sedimentary BasinDocument13 pagesSedimentary Basin: A Low Lying Area/depression Where Sediments Can Be Deposit Is Called Sedimentary Basinomair babarNo ratings yet
- Source RockDocument8 pagesSource RockAhmed KazmiNo ratings yet
- Oil Fields For StudentsDocument20 pagesOil Fields For StudentsAbhinav ShahiNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology of Lower Indus BasinDocument5 pagesPetroleum Geology of Lower Indus BasinMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Onshore and Offshore Petroliferous Basins of IndiaDocument14 pagesOnshore and Offshore Petroliferous Basins of IndiaKukiMonjori BoruahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Niaz HussanNo ratings yet
- Petroleum System of The Lower Indus BasinDocument19 pagesPetroleum System of The Lower Indus Basinasadali100% (1)
- Digboi OilfieldDocument24 pagesDigboi OilfieldPurushottam Gupta100% (2)
- Economic Geology Lecture Spring 17 AM 3Document6 pagesEconomic Geology Lecture Spring 17 AM 3mohsin maqsoodNo ratings yet
- Geology of Salt RangeDocument18 pagesGeology of Salt RangeAdil KhanNo ratings yet
- Source Rocks Are Commonly Shales and Lime MudstonesDocument12 pagesSource Rocks Are Commonly Shales and Lime MudstonesZahid MalikNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Basins of IndiaDocument90 pagesSedimentary Basins of IndiaSrikanta Khuntia100% (6)
- Phanerozoic Petrol BasinDocument16 pagesPhanerozoic Petrol BasinKanika SinghNo ratings yet
- Shale Oil Exploration From Paleocene EarDocument19 pagesShale Oil Exploration From Paleocene EarSK FIROJ ALINo ratings yet
- Assam Basin IntroductionDocument6 pagesAssam Basin IntroductionrijindiNo ratings yet
- General Geology of PakistanDocument14 pagesGeneral Geology of PakistanSpangle StarNo ratings yet
- Tectonics of PakistanDocument26 pagesTectonics of Pakistanmarzia hussainNo ratings yet
- Assam & Assam Arakan BasinDocument29 pagesAssam & Assam Arakan BasinSahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Bombay Offshore BasinDocument10 pagesBombay Offshore BasinSangita100% (2)
- Malanjkhend Report Raj Veer Singh CHATEN BHOPALDocument53 pagesMalanjkhend Report Raj Veer Singh CHATEN BHOPALvidhya associateNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Basins of IndiaDocument31 pagesSedimentary Basins of Indianilay05100% (2)
- Document PDFDocument25 pagesDocument PDFTariq ZamanNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document7 pagesBook 1attiqueNo ratings yet
- 1914 - Petroliferous Basins of India PDFDocument25 pages1914 - Petroliferous Basins of India PDFIshita MongaNo ratings yet
- Significance of Reef Limestones As Oil and Gas Reservoirs in The Middle East and North AfricaDocument29 pagesSignificance of Reef Limestones As Oil and Gas Reservoirs in The Middle East and North AfricabehrangarefNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Salt RangeDocument197 pagesPresentation of Salt RangeSamiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Ganga Basin: Presented By: Barsha Rani Das Roll. No: PE 04/16 Petroleum Engineering, 6 SemesterDocument20 pagesGanga Basin: Presented By: Barsha Rani Das Roll. No: PE 04/16 Petroleum Engineering, 6 SemesterAbu ikhtiarNo ratings yet
- Department of Earthsciences (Bs Geology) : Assignment TopicDocument26 pagesDepartment of Earthsciences (Bs Geology) : Assignment TopicsalahudinNo ratings yet
- Geology of IndiaDocument6 pagesGeology of IndiaJay Prakash Singh100% (1)
- MDSW Orissa01Document190 pagesMDSW Orissa01miningnova1No ratings yet
- Economic Geology of PakistanDocument8 pagesEconomic Geology of Pakistanimran salarianNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Salt Range, PakistanDocument199 pagesPresentation of Salt Range, PakistanSamiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Oil - Producing - Basin - IndiaDocument12 pagesOil - Producing - Basin - IndiaSK FIROJ ALINo ratings yet
- Art 41Document11 pagesArt 41Aneesh KRNo ratings yet
- Coal Deposits in KPK PakistanDocument3 pagesCoal Deposits in KPK Pakistanmuhammad tahirNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Potential of The Trans Indus Ranges: 10.1 SummaryDocument28 pagesHydrocarbon Potential of The Trans Indus Ranges: 10.1 Summaryjawad khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1: Geo TectonicsDocument10 pagesAssignment No 1: Geo TectonicssanaNo ratings yet
- Cu Deposits in PakistanDocument5 pagesCu Deposits in PakistanZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Geological History of IndiaDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Geological History of IndiaGerald TanNo ratings yet
- Team 13 (Assam-Arakan Basin) - 1Document20 pagesTeam 13 (Assam-Arakan Basin) - 1jai donNo ratings yet
- Reef LimestoneDocument17 pagesReef LimestoneHeart TrackerNo ratings yet
- Evaporites Formation and Its Depositional Environmentwith Reference To PakistanDocument25 pagesEvaporites Formation and Its Depositional Environmentwith Reference To PakistanMuhammad Harris KhanNo ratings yet
- Malkanietal 2010 ExplanatoryNoteofGeologicalMapofFortMunroquad 39-G-13Document6 pagesMalkanietal 2010 ExplanatoryNoteofGeologicalMapofFortMunroquad 39-G-13Zia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Bundelkhand and Bastar CratonDocument32 pagesBundelkhand and Bastar CratonGirijesh Pandey100% (4)
- Gondwana Supergroup: Seminar OnDocument29 pagesGondwana Supergroup: Seminar OnTEN TV100% (1)
- Basin - Assam Arakan BasinDocument5 pagesBasin - Assam Arakan BasinParush VermaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentAmna SadiqNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources in PakistanDocument5 pagesNatural Resources in PakistanSohaib ENo ratings yet
- Abstracts 91Document1 pageAbstracts 91Ayaz GulNo ratings yet
- Natural TopographyDocument12 pagesNatural TopographyAsad Ali100% (1)
- Huma Sattar TectonicsDocument21 pagesHuma Sattar Tectonicsshehriyaroffice47No ratings yet
- Evidence of Ancient Glaciation in Jharkhand State - of India.Document5 pagesEvidence of Ancient Glaciation in Jharkhand State - of India.Dr. Nitish PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- School Book Read Up 36Document12 pagesSchool Book Read Up 36Deep HansNo ratings yet
- Oil Fields in IndiaDocument7 pagesOil Fields in IndiaAn Open LetterNo ratings yet
- Nature of Basins in GhanaDocument4 pagesNature of Basins in GhanaAcheampong SamuelNo ratings yet
- Formation of PetroleumDocument19 pagesFormation of PetroleumSajjad AzizNo ratings yet
- Dip & StrikeDocument20 pagesDip & StrikeSajjad AzizNo ratings yet
- Star Delta Numerical Problems by SajjadDocument15 pagesStar Delta Numerical Problems by SajjadSajjad AzizNo ratings yet
- ECL Special Course 2020Document53 pagesECL Special Course 2020Sajjad AzizNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Kesesuaian Lahan Untuk Tanaman Kedelai Pada Bentuk Lahan Fluvial Batang Salido Kecamatan Empat Jurai Kabupaten Pesisir SelatanDocument8 pagesTingkat Kesesuaian Lahan Untuk Tanaman Kedelai Pada Bentuk Lahan Fluvial Batang Salido Kecamatan Empat Jurai Kabupaten Pesisir Selatansuci ktp48No ratings yet
- Tài Liệu Đi Kèm Khóa HọcDocument6 pagesTài Liệu Đi Kèm Khóa HọcĐăng HảiNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson Plan Template 3: Ivana Cortez 3 Grade Social Studies Geography LandformsDocument4 pagesSiop Lesson Plan Template 3: Ivana Cortez 3 Grade Social Studies Geography Landformsapi-548183213No ratings yet
- From The Spring Flowers Own - "The Morning After - Poetry FoundationDocument9 pagesFrom The Spring Flowers Own - "The Morning After - Poetry FoundationNazuk Iftikhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Final English Exam Viii: July 27thDocument3 pagesFinal English Exam Viii: July 27throber4mamaniNo ratings yet
- The Fungal Caverns v.02Document1 pageThe Fungal Caverns v.02hotel DumortNo ratings yet
- GG G1 Ans Gate2023Document2 pagesGG G1 Ans Gate2023Niranjan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Parambikulam-Aliyar Project (Regulation of Water-Supply) Act, 1993Document5 pagesParambikulam-Aliyar Project (Regulation of Water-Supply) Act, 1993Latest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- Chart and Compass (London Zetetic Society)Document8 pagesChart and Compass (London Zetetic Society)tjmigoto@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Assam - WikipediaDocument32 pagesAssam - WikipediaNazrul IslamNo ratings yet
- PASSAGE PLAN Batam To SangattaDocument4 pagesPASSAGE PLAN Batam To SangattaTERAS HYDRA100% (1)
- Branches of GeographyDocument3 pagesBranches of GeographyShadman Sadik100% (1)
- Las Vegas: Mixed Use Overlay DistrictDocument1 pageLas Vegas: Mixed Use Overlay DistrictZNo ratings yet
- Our Country IndiaDocument8 pagesOur Country IndiaShalini Mohan PandeyNo ratings yet
- South America (Fondly Names With Flags)Document4 pagesSouth America (Fondly Names With Flags)Sherlene Voluntad100% (1)
- Vocabulary Word List: Reading 1: Because of Winn-DixieDocument2 pagesVocabulary Word List: Reading 1: Because of Winn-DixieLolitNo ratings yet
- Beato Angelico Building Analysis:: Geographical ContextDocument15 pagesBeato Angelico Building Analysis:: Geographical ContextChesella Kaye LungayNo ratings yet
- 2022 Uci World Championships Wollongong Aus RR Men Elite Map FullDocument1 page2022 Uci World Championships Wollongong Aus RR Men Elite Map FullTáber SeguraNo ratings yet
- Equipment List For Resection and IntersectionDocument6 pagesEquipment List For Resection and IntersectionDiegoNo ratings yet
- CH 600.00Document1 pageCH 600.00NILRATAN SARKARNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 in Review Subject: Algebra, Trigo (Plane and Spherical)Document1 pageQuiz 1 in Review Subject: Algebra, Trigo (Plane and Spherical)Noxian TelicNo ratings yet
- Northern EuropeDocument58 pagesNorthern EuropeAngel TamboboyNo ratings yet
- Details Bali Geography As Its UniquenessDocument2 pagesDetails Bali Geography As Its UniquenessDayu JeniNo ratings yet
- By Dr. A Jon Kimerling, Professor Emeritus, Oregon State UniversityDocument3 pagesBy Dr. A Jon Kimerling, Professor Emeritus, Oregon State Universitymailmaverick8167No ratings yet
- CESURVE Mod 02 Surveying Measurements Angles and DirectionsDocument41 pagesCESURVE Mod 02 Surveying Measurements Angles and DirectionsPetero BlancNo ratings yet
- 2022 Minnesota Congressional MapsDocument5 pages2022 Minnesota Congressional MapsinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Australia OdtDocument3 pagesAustralia OdtHedvika TomkováNo ratings yet
- Mountain Park Brochure FinalDocument77 pagesMountain Park Brochure FinalMostafa ElghifaryNo ratings yet