Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BE Unit 1
BE Unit 1
Uploaded by
Aarti PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Bank Statement 1 2024Document2 pagesBank Statement 1 2024joelschwartzllcNo ratings yet
- FInal Task Performance TNT ExpressDocument6 pagesFInal Task Performance TNT ExpressBea Catherine LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: The Task and Macro Environments of ManagementDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 3: The Task and Macro Environments of ManagementEunice Valeroso100% (1)
- Be 1Document48 pagesBe 1Sakshi ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Ebe Unit 1Document48 pagesEbe Unit 1ARJUNA.RNo ratings yet
- SM Unit 2Document85 pagesSM Unit 2Ashhar RashidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BE BBA ViiDocument51 pagesUnit 1 BE BBA ViiSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Organizational Environments & CulturesDocument32 pagesGroup 2 - Organizational Environments & CulturesYae'kult VIpincepe QuilabNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 2Document22 pages(Bea) 2Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document94 pagesUnit 2Riya jainNo ratings yet
- Business Environmental & AnalysisDocument51 pagesBusiness Environmental & AnalysisShreya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument71 pagesBusiness Environmentalexsin2112002No ratings yet
- Strategic Management PPT by Akshaya KumarDocument23 pagesStrategic Management PPT by Akshaya KumarAkshaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning ABBSDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning ABBSshashikiranl8580No ratings yet
- Strategy Management - LessonsDocument34 pagesStrategy Management - LessonsMaureen LobinNo ratings yet
- Environmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Document37 pagesEnvironmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Megha ThackerNo ratings yet
- Money Market in IndiaDocument39 pagesMoney Market in IndiaYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument20 pagesEnvironmental ScanningNeelabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning PPT'sDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning PPT'sSurbhi Aggarwal67% (3)
- 1 - Business - Environment With ScanningDocument71 pages1 - Business - Environment With ScanningNavneet Nanda0% (1)
- POM 003 Org Envrmt N CultureDocument30 pagesPOM 003 Org Envrmt N CultureRajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 1Document28 pages(Bea) 1Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Strategic ManagementDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Strategic ManagementSababegumNo ratings yet
- Business Environment For MBA.Document18 pagesBusiness Environment For MBA.keneyenanalioNo ratings yet
- Daft Chapter 3Document30 pagesDaft Chapter 3Ricky ThaungNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 3Document21 pages(Bea) 3Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Ch-Ii BPSMDocument31 pagesCh-Ii BPSMsadamhusen2551No ratings yet
- Strategic 2Document28 pagesStrategic 2Dianne VergaraNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument18 pagesEnvironmental ScanningShivangi DhamijaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Strategy NewDocument83 pagesAn Introduction To Strategy Newsehaj01No ratings yet
- External Environment AnalysisDocument21 pagesExternal Environment Analysisdivya aryaNo ratings yet
- Week1 2c Bpestel AnalysisDocument26 pagesWeek1 2c Bpestel AnalysisKyle Vladymir AyopNo ratings yet
- Antim Prahar 2024 Strategic ManagementDocument46 pagesAntim Prahar 2024 Strategic ManagementAbhay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Concept of Business EnvironmentDocument34 pagesUnit I: Concept of Business EnvironmentMegh Nath RegmiNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument44 pagesBusiness Environmentsshiva8812100% (14)
- POMDocument49 pagesPOMSouryatanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Strategy ImplementationDocument86 pagesStrategic Management: Strategy ImplementationBryan Joseph JumawidNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument31 pagesEnvironmental Scanningdrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Business EnvironmentDocument16 pagesApplied Economics: Business EnvironmentMariaAngelaAdanEvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intent and Environmental AppraisalDocument31 pagesStrategic Intent and Environmental AppraisalAshika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Economic PresentationDocument25 pagesEconomic PresentationARJUNA.RNo ratings yet
- MGT 1011-3rd ChapterDocument34 pagesMGT 1011-3rd ChapterThilinaNo ratings yet
- The General Environment: Strategic ManagementDocument20 pagesThe General Environment: Strategic Managementsonal jainNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument29 pagesBusiness EnvironmentRahul Paliya100% (1)
- Functional Policies 2Document11 pagesFunctional Policies 2Shivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Business Environment: by Nikunj Nayak Ganpat UniversityDocument28 pagesAn Overview of Business Environment: by Nikunj Nayak Ganpat UniversitypatelkkNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument25 pagesBusiness Environmenthasb97No ratings yet
- MM Mod 2Document5 pagesMM Mod 2Rahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - REVISION FOR TEST 2 - Unit 2 - 2.2 Evaluating The External Enviornment - Lecture SlidesDocument35 pagesWeek 14 - REVISION FOR TEST 2 - Unit 2 - 2.2 Evaluating The External Enviornment - Lecture SlidesNguyen Châu AnhNo ratings yet
- Bba BPSDocument21 pagesBba BPSNatural Mogli0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6Madhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Environment AnalyDocument18 pagesEnvironment AnalyPartha Pratim SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Document68 pagesLesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Neekah JoyNo ratings yet
- BBA-302 Business Policy & Strategy (I. P.University)Document39 pagesBBA-302 Business Policy & Strategy (I. P.University)Dipesh TekchandaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic 1.2 ENVIORNMENT SCANNING TECHNIQUESDocument35 pagesLecture Topic 1.2 ENVIORNMENT SCANNING TECHNIQUESKertik Singh100% (1)
- BBA473 Week 1 New EditionDocument44 pagesBBA473 Week 1 New EditionAfroj AlamNo ratings yet
- Environmental AnalysisDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Analysisanurag ranaNo ratings yet
- Implementing Ems: Erika S. NicolasDocument33 pagesImplementing Ems: Erika S. NicolasYka NicolasNo ratings yet
- Business Environment!Document140 pagesBusiness Environment!Hira LalNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University 2Document6 pagesLovely Professional University 2nashelegend7No ratings yet
- How to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationFrom EverandHow to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Robert L. Johnson: CAD $3.26 BillionDocument4 pagesRobert L. Johnson: CAD $3.26 BillionAnthonio MaraghNo ratings yet
- Starbucks1 - Situational Analysis and Marketing Plan For StarbucksDocument5 pagesStarbucks1 - Situational Analysis and Marketing Plan For StarbucksJimy PavelNo ratings yet
- Smart Accounting PSPM 20112017Document5 pagesSmart Accounting PSPM 20112017Nurfarhana JufriNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management Case StudiesDocument5 pagesWealth Management Case StudiesLeela Sri NaveenNo ratings yet
- Hilton Hhonors WorldwideDocument35 pagesHilton Hhonors Worldwidevivekchaubey67% (3)
- Module 9 - THC211Document5 pagesModule 9 - THC211LAURIO, LORA MAYNo ratings yet
- What Is The Zeitgeist MovementDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Zeitgeist MovementBrian M. HillNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Lecture 3Document78 pagesCost Accounting Lecture 3Fariya MemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Feasibility Analysis)Document41 pagesChapter 3 (Feasibility Analysis)AymanAlamNo ratings yet
- 102 Eabd Solved Sspu Qpapril2018Document18 pages102 Eabd Solved Sspu Qpapril2018Dr. Rakesh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Economics Classroom ResourcesDocument5 pagesEconomics Classroom Resourcesapi-455268050No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingDocument14 pagesChapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingElen LimNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: AnalysisDocument2 pagesCase Study 2 Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: AnalysisISHA AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Ayushi PDFDocument61 pagesAyushi PDFayushi kanoujiaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Purpose: GPA Is 3.57 (My GRE Score Is 306 and TOEFL90)Document2 pagesStatement of Purpose: GPA Is 3.57 (My GRE Score Is 306 and TOEFL90)haiqi wanNo ratings yet
- Module Week 4 Entrep For UploadDocument5 pagesModule Week 4 Entrep For Uploadゔ違でStrawberry milk100% (1)
- Module Outline SEM 1 2023-2024 FIN (1) (1) Updated Aug 28 2023 (4) FiinnnDocument5 pagesModule Outline SEM 1 2023-2024 FIN (1) (1) Updated Aug 28 2023 (4) FiinnnKristianNo ratings yet
- Immediate Payment NotificationDocument1 pageImmediate Payment Notificationgodswilludeme90No ratings yet
- Auditing The Expenditure CycleDocument35 pagesAuditing The Expenditure CycleodiledemonNo ratings yet
- IMCDocument88 pagesIMCRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Geetanjali Gems FinalDocument28 pagesCase Study On Geetanjali Gems FinalPuja BagriNo ratings yet
- HRM Case StudyDocument2 pagesHRM Case StudyAsfaq SumraNo ratings yet
- Changes in Kenyan Business Environment in The Last 2 DecadesDocument5 pagesChanges in Kenyan Business Environment in The Last 2 DecadesButo12003100% (5)
- Bonds CH08Document16 pagesBonds CH08Hendrickson Cruz SaludNo ratings yet
- D-Street Sees Best Samvat in 12 Years Little Risk For Coal Investors On Road To 2070Document30 pagesD-Street Sees Best Samvat in 12 Years Little Risk For Coal Investors On Road To 2070Ashu SinghNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airlines Project1Document19 pagesEmirates Airlines Project1akm_nhNo ratings yet
- Term Paper (PRAN Food and Beverage)Document16 pagesTerm Paper (PRAN Food and Beverage)Chowdhury Farsad AurangzebNo ratings yet
- Management - Definition - Functions - Nature - Management RolesDocument23 pagesManagement - Definition - Functions - Nature - Management RolesSakthirama VadiveluNo ratings yet
BE Unit 1
BE Unit 1
Uploaded by
Aarti PandeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BE Unit 1
BE Unit 1
Uploaded by
Aarti PandeyCopyright:
Available Formats
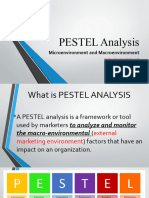
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT UNIT 1
Meaning of Business Environment Consist of all those factors that have a bearing on the business. Environment refer to all external forces which have a bearing on the functioning of business The survival and success of a business firm depends on its innate strength resources at its command, including physical resources, financial resources, human resources, skill & organization & its adaptability to the environment and the extent to which the environment is favorable to the development of the org. The survival and success of a firm, thus, depends on two sets of factors viz the internal factors the internal environment and the external factors the external environment
Internal Environment
Business Decision
External Environment
Characteristics of Contemporary Business
Transition
Competition
Information
Business
Opportunities
Technology
Globalization
Business Objectives
Business Decisions
Business Internal Factors
Business External Factors
Nature of Business Environment Direct relationship with the policy of business enterprise Impose several constraints on the enterprise income, supply and demand, price of products, fashion taste and preference, habit, season, government policies, rules and regulation, competitors strategy. The success of an enterprise depends to a very large extent on its adaptability to the environment. Shape opportunities and possess threats to the company. It changes frequently and affect the business of any organization
Significance of BE
To develop its broad strategies and long term policies
To analyze its competitors strategies and thereby formulate effective counter strategies.
To keep organization dynamic in approach.
To for see the impact of the socio economic changes at the national and international level on its stability.
To make the executives to adjust to the prevailing conditions and thus influence the environment in order to make it congenial to the business. Development of action plans to deal with technological advancements.
Scope and its relevance to Business Decision Making
To understand current and potential changes taking place in the task environment Provide inputs for strategic decision making. Facilitate and foster strategic thinking in organization
Challenging the current wisdom by bringing fresh view points into the organization.
The interaction Matrix of different environmental factors Micro Environment Customers Public Competitors Suppliers Marketing Intermediaries
Macro Environment Economic Environment Political Environment Socio Cultural Environment Natural Environment Global Environment Technological Environment
Environmental Analysis It is tracing of an opportunity or threat to its source. It involves breaking a whole into its parts to find its nature, function and relationship EA and diagnosis give strategists time to anticipate opportunities and to plan to take optional responses to these opportunities. It also helps strategists to develop an early warning system to prevent threats or to develop strategies which can turn a threat to the firms advantage.
Need for EA Due to constant change in environmental factors To cope up with recent changes in relation to production of goods and services. Opportunities and Threats Provide necessary and very useful picture of the important factors which influence the business Technological Forecasting Contribution in identification of risk Formulation of right strategies Modification in strategies Managers informed alert and often dynamic
Limitation of EA
Fails to for see future accurately Does not guarantee organizational effectiveness Potential of EA is often not realized because of how it is practiced Too much reliance on analysis makes a manager become complacent
Process of Environmental Scanning Environmental Analysis
Strategy Formulation
Strategy Implementation
Further Analysis for change evaluation and control
Process of Environmental Analysis Scanning Monitoring Forecasting Assessment
Basic Philosophies of Capitalism and Socialism Capitalism Stress the basic concept and philosophy of individualism believing in private ownership. Socialism - Here the tools of production are to be organized, managed and owned by the government with the benefits accruing to the public
You might also like
- Bank Statement 1 2024Document2 pagesBank Statement 1 2024joelschwartzllcNo ratings yet
- FInal Task Performance TNT ExpressDocument6 pagesFInal Task Performance TNT ExpressBea Catherine LaguitaoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: The Task and Macro Environments of ManagementDocument21 pagesCHAPTER 3: The Task and Macro Environments of ManagementEunice Valeroso100% (1)
- Be 1Document48 pagesBe 1Sakshi ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Ebe Unit 1Document48 pagesEbe Unit 1ARJUNA.RNo ratings yet
- SM Unit 2Document85 pagesSM Unit 2Ashhar RashidNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BE BBA ViiDocument51 pagesUnit 1 BE BBA ViiSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Organizational Environments & CulturesDocument32 pagesGroup 2 - Organizational Environments & CulturesYae'kult VIpincepe QuilabNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 2Document22 pages(Bea) 2Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document94 pagesUnit 2Riya jainNo ratings yet
- Business Environmental & AnalysisDocument51 pagesBusiness Environmental & AnalysisShreya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument71 pagesBusiness Environmentalexsin2112002No ratings yet
- Strategic Management PPT by Akshaya KumarDocument23 pagesStrategic Management PPT by Akshaya KumarAkshaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning ABBSDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning ABBSshashikiranl8580No ratings yet
- Strategy Management - LessonsDocument34 pagesStrategy Management - LessonsMaureen LobinNo ratings yet
- Environmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Document37 pagesEnvironmental Appraisal: 2 Year MBA Group 3Megha ThackerNo ratings yet
- Money Market in IndiaDocument39 pagesMoney Market in IndiaYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument20 pagesEnvironmental ScanningNeelabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning PPT'sDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Scanning PPT'sSurbhi Aggarwal67% (3)
- 1 - Business - Environment With ScanningDocument71 pages1 - Business - Environment With ScanningNavneet Nanda0% (1)
- POM 003 Org Envrmt N CultureDocument30 pagesPOM 003 Org Envrmt N CultureRajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 1Document28 pages(Bea) 1Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Strategic ManagementDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Strategic ManagementSababegumNo ratings yet
- Business Environment For MBA.Document18 pagesBusiness Environment For MBA.keneyenanalioNo ratings yet
- Daft Chapter 3Document30 pagesDaft Chapter 3Ricky ThaungNo ratings yet
- (Bea) 3Document21 pages(Bea) 3Rafika Hamidah HamdiNo ratings yet
- Ch-Ii BPSMDocument31 pagesCh-Ii BPSMsadamhusen2551No ratings yet
- Strategic 2Document28 pagesStrategic 2Dianne VergaraNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument18 pagesEnvironmental ScanningShivangi DhamijaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Strategy NewDocument83 pagesAn Introduction To Strategy Newsehaj01No ratings yet
- External Environment AnalysisDocument21 pagesExternal Environment Analysisdivya aryaNo ratings yet
- Week1 2c Bpestel AnalysisDocument26 pagesWeek1 2c Bpestel AnalysisKyle Vladymir AyopNo ratings yet
- Antim Prahar 2024 Strategic ManagementDocument46 pagesAntim Prahar 2024 Strategic ManagementAbhay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Concept of Business EnvironmentDocument34 pagesUnit I: Concept of Business EnvironmentMegh Nath RegmiNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument44 pagesBusiness Environmentsshiva8812100% (14)
- POMDocument49 pagesPOMSouryatanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Strategy ImplementationDocument86 pagesStrategic Management: Strategy ImplementationBryan Joseph JumawidNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScanningDocument31 pagesEnvironmental Scanningdrlov_20037767No ratings yet
- Applied Economics: Business EnvironmentDocument16 pagesApplied Economics: Business EnvironmentMariaAngelaAdanEvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intent and Environmental AppraisalDocument31 pagesStrategic Intent and Environmental AppraisalAshika MehtaNo ratings yet
- Economic PresentationDocument25 pagesEconomic PresentationARJUNA.RNo ratings yet
- MGT 1011-3rd ChapterDocument34 pagesMGT 1011-3rd ChapterThilinaNo ratings yet
- The General Environment: Strategic ManagementDocument20 pagesThe General Environment: Strategic Managementsonal jainNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument29 pagesBusiness EnvironmentRahul Paliya100% (1)
- Functional Policies 2Document11 pagesFunctional Policies 2Shivam SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Business Environment: by Nikunj Nayak Ganpat UniversityDocument28 pagesAn Overview of Business Environment: by Nikunj Nayak Ganpat UniversitypatelkkNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument25 pagesBusiness Environmenthasb97No ratings yet
- MM Mod 2Document5 pagesMM Mod 2Rahul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - REVISION FOR TEST 2 - Unit 2 - 2.2 Evaluating The External Enviornment - Lecture SlidesDocument35 pagesWeek 14 - REVISION FOR TEST 2 - Unit 2 - 2.2 Evaluating The External Enviornment - Lecture SlidesNguyen Châu AnhNo ratings yet
- Bba BPSDocument21 pagesBba BPSNatural Mogli0% (1)
- Chapter 6Document19 pagesChapter 6Madhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Environment AnalyDocument18 pagesEnvironment AnalyPartha Pratim SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Document68 pagesLesson IV. Analyzing The External Environment of The Firm & Lesson V Assessing The Internal Environment of The Firm 4252022 2Neekah JoyNo ratings yet
- BBA-302 Business Policy & Strategy (I. P.University)Document39 pagesBBA-302 Business Policy & Strategy (I. P.University)Dipesh TekchandaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Topic 1.2 ENVIORNMENT SCANNING TECHNIQUESDocument35 pagesLecture Topic 1.2 ENVIORNMENT SCANNING TECHNIQUESKertik Singh100% (1)
- BBA473 Week 1 New EditionDocument44 pagesBBA473 Week 1 New EditionAfroj AlamNo ratings yet
- Environmental AnalysisDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Analysisanurag ranaNo ratings yet
- Implementing Ems: Erika S. NicolasDocument33 pagesImplementing Ems: Erika S. NicolasYka NicolasNo ratings yet
- Business Environment!Document140 pagesBusiness Environment!Hira LalNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University 2Document6 pagesLovely Professional University 2nashelegend7No ratings yet
- How to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationFrom EverandHow to Enhance Productivity Under Cost Control, Quality Control as Well as Time, in a Private or Public OrganizationNo ratings yet
- Robert L. Johnson: CAD $3.26 BillionDocument4 pagesRobert L. Johnson: CAD $3.26 BillionAnthonio MaraghNo ratings yet
- Starbucks1 - Situational Analysis and Marketing Plan For StarbucksDocument5 pagesStarbucks1 - Situational Analysis and Marketing Plan For StarbucksJimy PavelNo ratings yet
- Smart Accounting PSPM 20112017Document5 pagesSmart Accounting PSPM 20112017Nurfarhana JufriNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management Case StudiesDocument5 pagesWealth Management Case StudiesLeela Sri NaveenNo ratings yet
- Hilton Hhonors WorldwideDocument35 pagesHilton Hhonors Worldwidevivekchaubey67% (3)
- Module 9 - THC211Document5 pagesModule 9 - THC211LAURIO, LORA MAYNo ratings yet
- What Is The Zeitgeist MovementDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Zeitgeist MovementBrian M. HillNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Lecture 3Document78 pagesCost Accounting Lecture 3Fariya MemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Feasibility Analysis)Document41 pagesChapter 3 (Feasibility Analysis)AymanAlamNo ratings yet
- 102 Eabd Solved Sspu Qpapril2018Document18 pages102 Eabd Solved Sspu Qpapril2018Dr. Rakesh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Economics Classroom ResourcesDocument5 pagesEconomics Classroom Resourcesapi-455268050No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingDocument14 pagesChapter 1 The Investment Environment: Fundamentals of InvestingElen LimNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: AnalysisDocument2 pagesCase Study 2 Salary Inequities at Acme Manufacturing: AnalysisISHA AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Ayushi PDFDocument61 pagesAyushi PDFayushi kanoujiaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Purpose: GPA Is 3.57 (My GRE Score Is 306 and TOEFL90)Document2 pagesStatement of Purpose: GPA Is 3.57 (My GRE Score Is 306 and TOEFL90)haiqi wanNo ratings yet
- Module Week 4 Entrep For UploadDocument5 pagesModule Week 4 Entrep For Uploadゔ違でStrawberry milk100% (1)
- Module Outline SEM 1 2023-2024 FIN (1) (1) Updated Aug 28 2023 (4) FiinnnDocument5 pagesModule Outline SEM 1 2023-2024 FIN (1) (1) Updated Aug 28 2023 (4) FiinnnKristianNo ratings yet
- Immediate Payment NotificationDocument1 pageImmediate Payment Notificationgodswilludeme90No ratings yet
- Auditing The Expenditure CycleDocument35 pagesAuditing The Expenditure CycleodiledemonNo ratings yet
- IMCDocument88 pagesIMCRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Geetanjali Gems FinalDocument28 pagesCase Study On Geetanjali Gems FinalPuja BagriNo ratings yet
- HRM Case StudyDocument2 pagesHRM Case StudyAsfaq SumraNo ratings yet
- Changes in Kenyan Business Environment in The Last 2 DecadesDocument5 pagesChanges in Kenyan Business Environment in The Last 2 DecadesButo12003100% (5)
- Bonds CH08Document16 pagesBonds CH08Hendrickson Cruz SaludNo ratings yet
- D-Street Sees Best Samvat in 12 Years Little Risk For Coal Investors On Road To 2070Document30 pagesD-Street Sees Best Samvat in 12 Years Little Risk For Coal Investors On Road To 2070Ashu SinghNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airlines Project1Document19 pagesEmirates Airlines Project1akm_nhNo ratings yet
- Term Paper (PRAN Food and Beverage)Document16 pagesTerm Paper (PRAN Food and Beverage)Chowdhury Farsad AurangzebNo ratings yet
- Management - Definition - Functions - Nature - Management RolesDocument23 pagesManagement - Definition - Functions - Nature - Management RolesSakthirama VadiveluNo ratings yet