Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsChapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
bendermech kamelchapter-1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Nokia 1830 PSSDocument4 pagesNokia 1830 PSSGaetano CaccavoNo ratings yet
- Data Domain CommVault WhitepaperDocument15 pagesData Domain CommVault WhitepaperVinay KavalNo ratings yet
- SCCM Basic TroubleshootingDocument11 pagesSCCM Basic Troubleshootingsinghdeepak87100% (1)
- Nokia Siemens Networks Multicontroller Platform: Multicontroller BSC and Transcoder Multicontroller RNCDocument2 pagesNokia Siemens Networks Multicontroller Platform: Multicontroller BSC and Transcoder Multicontroller RNCkamaldesh sohelNo ratings yet
- Benefits of OTN in Transport SDNDocument9 pagesBenefits of OTN in Transport SDNGhallab AlsadehNo ratings yet
- 6500 Packet Optical Platform PBDocument9 pages6500 Packet Optical Platform PBIan Chris ValencerinaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data SheetDocument17 pagesVirtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data Sheet김경우No ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Platform: Grid SolutionsDocument4 pagesMDS Orbit Platform: Grid Solutionsoscar2102No ratings yet
- Parallel WI - 5G NRDocument10 pagesParallel WI - 5G NRRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Chap 1 - Modern NetworkingDocument18 pagesUnit 2-Chap 1 - Modern NetworkingTim CookNo ratings yet
- Technology Comparison: Cisco Overlay Transport Virtualization and Virtual Private LAN Service As Enablers of LAN ExtensionsDocument5 pagesTechnology Comparison: Cisco Overlay Transport Virtualization and Virtual Private LAN Service As Enablers of LAN ExtensionsMirko pugliniNo ratings yet
- Active Network Architecture: Name-A.Pavana Siddhartha Reddy USN-1PI07EC015 Seminar Guide-Mrs - Usha RaghunathDocument21 pagesActive Network Architecture: Name-A.Pavana Siddhartha Reddy USN-1PI07EC015 Seminar Guide-Mrs - Usha RaghunathSiddharth ReddyNo ratings yet
- 6500 Packet Optical Platform PBDocument7 pages6500 Packet Optical Platform PBsatyvan2003No ratings yet
- Designing Campus and Data Center NetworkDocument33 pagesDesigning Campus and Data Center NetworkBerihun Tenaye Ali100% (1)
- Demystifying NFV in Carrier NetworksDocument8 pagesDemystifying NFV in Carrier NetworksGabriel DarkNo ratings yet
- Nokia_NSP_datasheet_Data_Sheet_ENDocument16 pagesNokia_NSP_datasheet_Data_Sheet_ENAlexis SturmNo ratings yet
- WAN Optimization FrameworkDocument40 pagesWAN Optimization FrameworkVinamra KumarNo ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Cellular GEA-12740F PDFDocument8 pagesMDS Orbit Cellular GEA-12740F PDFFabian EspinozaNo ratings yet
- MCRNC Configuration PrinciplesDocument20 pagesMCRNC Configuration PrinciplesAshok DwivediNo ratings yet
- WP DriveNets Disaggregated Networks TCO-1Document6 pagesWP DriveNets Disaggregated Networks TCO-1OctavioNo ratings yet
- Networking Today and The FutureDocument10 pagesNetworking Today and The FutureSanjay RaviNo ratings yet
- Rakuten Cloud Native OrquestatorDocument4 pagesRakuten Cloud Native Orquestatoreng.viloriaNo ratings yet
- SCSA3Document7 pagesSCSA3naveenaNo ratings yet
- Seven Reasons To Use End-To-End Thinking When Building all-IP NetworksDocument12 pagesSeven Reasons To Use End-To-End Thinking When Building all-IP NetworksAjaykumar SinghNo ratings yet
- KCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 2Document25 pagesKCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 2Shailesh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BRKSDN 2063Document68 pagesBRKSDN 2063cool dude911No ratings yet
- Onecontrol Unified Management System: Data SheetDocument2 pagesOnecontrol Unified Management System: Data Sheetrobert adamsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Aspects NGNDocument44 pagesFundamental Aspects NGNwoody0No ratings yet
- Junos Containerized Routing Protocol Daemon: Product OverviewDocument3 pagesJunos Containerized Routing Protocol Daemon: Product Overviewchandrashekar_ganesanNo ratings yet
- Nortel CPLDocument6 pagesNortel CPLmcclaink06No ratings yet
- Keystone School of Engineering, Pune: Computer NetworksDocument19 pagesKeystone School of Engineering, Pune: Computer Networkssahil n phalleNo ratings yet
- Cloud BurstingDocument17 pagesCloud BurstingGarvit TyagiNo ratings yet
- 5g - DriversDocument51 pages5g - Driverspopescubianca2010No ratings yet
- 6CS029 Lecture 8 - SDNDocument36 pages6CS029 Lecture 8 - SDNdushantha.ellewalaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Technology NotesDocument6 pagesWireless Technology NotesSonali OramNo ratings yet
- Moyer Segment Routing For v1Document20 pagesMoyer Segment Routing For v1Anonymous NIkO5EI6No ratings yet
- Andromeda: Network Stack VirtualizationDocument16 pagesAndromeda: Network Stack VirtualizationMiguel PintoNo ratings yet
- RTU560 EnglishDocument16 pagesRTU560 EnglishrhomadonaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Densification With Juniper Mobile Backhaul SolutionDocument3 pagesMobile Network Densification With Juniper Mobile Backhaul Solutionyahya alrowniNo ratings yet
- CloudDocument32 pagesCloudSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Openran 5G NR: Whitebox - Flexible - Disaggregated - Small Cell PlatformDocument2 pagesOpenran 5G NR: Whitebox - Flexible - Disaggregated - Small Cell PlatformAbhishek BudhawaniNo ratings yet
- Ovum LTE450 PresentationDocument35 pagesOvum LTE450 Presentationnurys77No ratings yet
- Swishmem: Distributed Shared State Abstractions For Programmable SwitchesDocument8 pagesSwishmem: Distributed Shared State Abstractions For Programmable SwitchesIsaak ToviessiNo ratings yet
- Ciena OnePlanner - Unified - Design - System - DSDocument5 pagesCiena OnePlanner - Unified - Design - System - DSrobert adamsNo ratings yet
- Rohini 93532310129Document5 pagesRohini 93532310129pleasingprince123No ratings yet
- Form 4D Recloser Control: A Simple and Cost-Effective Solution For Everyday Protection RequirementsDocument4 pagesForm 4D Recloser Control: A Simple and Cost-Effective Solution For Everyday Protection RequirementsTuân MậpNo ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Platform GEA-12781F PDFDocument4 pagesMDS Orbit Platform GEA-12781F PDFMiguelNo ratings yet
- NEC 5G Open vRAN White Paper Flyer Rev1Document4 pagesNEC 5G Open vRAN White Paper Flyer Rev1Mo IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mem Overviewslideshare04142015 150420115259 Conversion Gate01Document16 pagesMem Overviewslideshare04142015 150420115259 Conversion Gate01l00pback63No ratings yet
- Ad Hoc WirelessDocument25 pagesAd Hoc WirelessABHISHEK TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- MBF MLMT - EdenNet Seminar v1.0Document82 pagesMBF MLMT - EdenNet Seminar v1.0Hồ Mạnh QuýNo ratings yet
- Vmware Nokia Solution OverviewDocument4 pagesVmware Nokia Solution OverviewEduardoNo ratings yet
- Google NetworkDocument15 pagesGoogle Networkanthony saddingtonNo ratings yet
- Manage Control and Plan DSDocument4 pagesManage Control and Plan DSPrasanna GanesanNo ratings yet
- NetWare 2013-SDN and Architectures v1.2 - August 25 - 2013Document118 pagesNetWare 2013-SDN and Architectures v1.2 - August 25 - 2013Boopathy PandiNo ratings yet
- Distributed Software Engineering: TEAM:20470,20471,20472,20473,20474Document22 pagesDistributed Software Engineering: TEAM:20470,20471,20472,20473,20474473Dharini IyerNo ratings yet
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasDocument30 pagesNetwork Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasBaraa EsamNo ratings yet
- Brochure Klerity Bringing Transparency To NetworksDocument4 pagesBrochure Klerity Bringing Transparency To Networksmore_nerdyNo ratings yet
- by Rso TX - 14-08-2014: 1 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014 For Internal Use OnlyDocument45 pagesby Rso TX - 14-08-2014: 1 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014 For Internal Use Onlysunilpanda08No ratings yet
- Intoduction To CloudDocument46 pagesIntoduction To CloudShagun DhimanNo ratings yet
- 1 Module: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument38 pages1 Module: Introduction To Cloud ComputingAsad AbbasNo ratings yet
- MC9S08DZ32 PDFDocument396 pagesMC9S08DZ32 PDFbandusNo ratings yet
- Upsc Epfo Eo: 50 Important Computer QuestionsDocument13 pagesUpsc Epfo Eo: 50 Important Computer QuestionsdeepthiNo ratings yet
- How To - Cannot Connect To Service Manager BiostarDocument5 pagesHow To - Cannot Connect To Service Manager BiostarDanish SaeedNo ratings yet
- VDR Maint ViewerDocument100 pagesVDR Maint ViewergorbachevrrrrNo ratings yet
- F2FS: A New File System For Flash StorageDocument15 pagesF2FS: A New File System For Flash StorageLuis KissNo ratings yet
- 18MCS13 R. V. College of Engineering: Time: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Instructions To CandidatesDocument3 pages18MCS13 R. V. College of Engineering: Time: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Instructions To CandidatesSAMARTH PATILNo ratings yet
- Ec2042 2 MarksDocument56 pagesEc2042 2 Marksanand_duraiswamyNo ratings yet
- Configurasi Ont Mdu Huawei 5612Document7 pagesConfigurasi Ont Mdu Huawei 5612Tri AgungNo ratings yet
- 7th Generation Core Mobile Processor Iot Platform BriefDocument6 pages7th Generation Core Mobile Processor Iot Platform BriefKukaneswaran Selva RajooNo ratings yet
- Memory SegmentationDocument38 pagesMemory SegmentationVinaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Omnipcx Install Manual PDFDocument964 pagesAlcatel Omnipcx Install Manual PDFmukiza ivanNo ratings yet
- Serial Do Windows XP Service Pack 2 e Service Pack 3Document3 pagesSerial Do Windows XP Service Pack 2 e Service Pack 3César augustoNo ratings yet
- ECE4680 Computer Organization and Architecture Memory HierarchyDocument7 pagesECE4680 Computer Organization and Architecture Memory HierarchySi Brian TohNo ratings yet
- Optmization in AlteryxDocument7 pagesOptmization in AlteryxLoan MotylNo ratings yet
- Dual Vios Upgrade Walk-Through Powervm Technical Webinar #12 For Customers/Bps/IbmersDocument31 pagesDual Vios Upgrade Walk-Through Powervm Technical Webinar #12 For Customers/Bps/IbmersAndrei AndreiuNo ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument2 pagesOperating System NotesAnkit bohraNo ratings yet
- Loading Contoso Demo Datafor Dynamics AX2009Document23 pagesLoading Contoso Demo Datafor Dynamics AX2009Kevin JonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Replace Lenovo Y510P Cache Drive With MyDigitalSSD Super Cache 2 SSDDocument14 pagesTutorial Replace Lenovo Y510P Cache Drive With MyDigitalSSD Super Cache 2 SSDPamela CoursonNo ratings yet
- ESA CREW Manual en 2 0Document1,469 pagesESA CREW Manual en 2 0DimitriNo ratings yet
- GO - General OutcomeDocument4 pagesGO - General OutcomeaymanaymanNo ratings yet
- Mastersaf DW Procedures Application PatchDocument11 pagesMastersaf DW Procedures Application Patchtyuhzinho0% (1)
- OS Chapter 2Document36 pagesOS Chapter 2maazali2735No ratings yet
- E2E Delay: R R R LDocument4 pagesE2E Delay: R R R Lspade0987No ratings yet
- Cs2100 12 Basic DatapathDocument50 pagesCs2100 12 Basic DatapathamandaNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Orako ProblemsDocument4 pagesBab 6 Orako ProblemsBilly Shan LastKagerooboroNo ratings yet
- Kvara Esa 200Document174 pagesKvara Esa 200DarkNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Module 3Document13 pagesMs Word Module 3R TECHNo ratings yet
- Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators (The Java™ Tutorials Learning The Java Language Language Basics)Document1 pageBitwise and Bit Shift Operators (The Java™ Tutorials Learning The Java Language Language Basics)YeNo ratings yet
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
bendermech kamel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pageschapter-1
Original Title
chapter-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentchapter-1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesChapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
bendermech kamelchapter-1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
mcRNC Basic Architecture Training
Ahmed Mohamed
Dec, 19 2012
Soc Classification level
1 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
Agenda
• mcRNC Product Overview
• mcRNC HW Architecture Overview
• mcRNC Capacity and Connectivity
• mcRNC Software Architecture Overview
• mcRNC Networking Solution Architecture
• mcRNC Network Connectivity
• mcRNC Availability and Reliability
• mcRNC Data Path and Traffic Flows
Soc Classification level
2 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
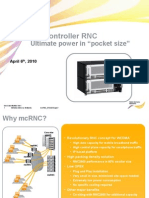
mcRNC Product Overview
Soc Classification level
3 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Product Overview
Multicontroller RNC
• Optimised for different radio
applications
• Ultra high packing density –
minimized site costs and overall
OPEX
CS + PS
• Maximum scalability – totally
new flexibility in operator’s
network building
RNC
• Very high availability with
advanced redundancy principles
• Integrated high capacity IP
transmission Scaling from low to very high capacities
just by adding modules
Controller role can be changed by loading
corresponding software – minimal or no
HW impact
Soc Classification level
4 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Architectural Principles Overview
Soc Classification level
5 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Compatibility and Portability
• mcRNC SW shall be compatible with cRNC application SW
– Co-siting of cRNC and mcRNC
mcRNC can be used to increase user plane capacity, unified transport etc
For example, control plane in cRNC and user plane in mcRNC shall be supported
• Portability of SW to be used with other processing architectures
shall be ensured.
– Libgen and PAL shall provided sufficient abstractions for the user plane
protocols to be used on multiple processor types.
Soc Classification level
6 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Availability
• Avoid single point of failure
• Redundancy based on the type of service offered
– Fault tolerance by replication
– Fault tolerance by redundancy
• Fault isolation and diagnosis without affecting working parts
• Avoid propagation of fault from source to other units
• Connectivity to other NEs and cell services protected ahead of
capacity in case of failure.
Soc Classification level
7 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Scalability
• Scalability in multiple dimensions
– Throughput
– Supported number of WBTS
– Transport connectivity
– Supported number of users
– Flexibility in configuring and optimizing the system in any dimension
• Possibility to stack more BCN modules without breaking the system
– BCN modules can be of varying processing capacities
– Newer processors providing higher processing capacity can be added
Over-provisioned internal backplane
• Less centralized processing and shared resources improves scalability
• Load balancing and multiple distribution points in design
– Incoming connections are distributed evenly
– Multiple points of distribution provide pipelined execution
Avoids pressure points
Soc Classification level
8 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Resource Management
• Homogeneous hardware for different processing enables resource
sharing between functions
– Dimensioning the system according to the traffic profile expected in the
network possible
Voice dominated networks and data dominated networks shall have different
composition of cores
Possible to modify the composition based on data traffic growth
Hardware modularity and software defined functions enable efficient use of
processing resources
• Co-located control and user plane improves performance
– Decentralized / localized decision making for resource allocation
Per call jump to centralized units for decision making and resource allocation
avoided
– Slow path escalation to centralized resource manager only in case of
overload or resource unavailability.
– Yet, location transparency of processing endpoints ensured
– Management of resources transparent to the user of the service
Soc Classification level
9 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
mcRNC Overload protection
• Ensure graceful degradation in overload mode
– Platform, Middleware and application specific overload control mechanisms
– Predictable behaviour under sustained load ensured by load shared
processing units and distribution schemes
Round-robin used in many distribution algorithms
Units in overload mode above higher threshold removed from participation list
Inclusion in the participation list on coming below lower threshold
Distribution entity does not maintain the list of participants
• List of eligible participants provided by different load monitors / managers
• Support for controlled switchover
• Access control at the earliest point
– Closer to boundary dropping of requests, when needed
Avoids wastage of internal resources when under load
Soc Classification level
10 © Nokia Siemens Networks Presentation / Author / Date
You might also like
- Nokia 1830 PSSDocument4 pagesNokia 1830 PSSGaetano CaccavoNo ratings yet
- Data Domain CommVault WhitepaperDocument15 pagesData Domain CommVault WhitepaperVinay KavalNo ratings yet
- SCCM Basic TroubleshootingDocument11 pagesSCCM Basic Troubleshootingsinghdeepak87100% (1)
- Nokia Siemens Networks Multicontroller Platform: Multicontroller BSC and Transcoder Multicontroller RNCDocument2 pagesNokia Siemens Networks Multicontroller Platform: Multicontroller BSC and Transcoder Multicontroller RNCkamaldesh sohelNo ratings yet
- Benefits of OTN in Transport SDNDocument9 pagesBenefits of OTN in Transport SDNGhallab AlsadehNo ratings yet
- 6500 Packet Optical Platform PBDocument9 pages6500 Packet Optical Platform PBIan Chris ValencerinaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data SheetDocument17 pagesVirtual Services Platform 4000 Series Data Sheet김경우No ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Platform: Grid SolutionsDocument4 pagesMDS Orbit Platform: Grid Solutionsoscar2102No ratings yet
- Parallel WI - 5G NRDocument10 pagesParallel WI - 5G NRRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Chap 1 - Modern NetworkingDocument18 pagesUnit 2-Chap 1 - Modern NetworkingTim CookNo ratings yet
- Technology Comparison: Cisco Overlay Transport Virtualization and Virtual Private LAN Service As Enablers of LAN ExtensionsDocument5 pagesTechnology Comparison: Cisco Overlay Transport Virtualization and Virtual Private LAN Service As Enablers of LAN ExtensionsMirko pugliniNo ratings yet
- Active Network Architecture: Name-A.Pavana Siddhartha Reddy USN-1PI07EC015 Seminar Guide-Mrs - Usha RaghunathDocument21 pagesActive Network Architecture: Name-A.Pavana Siddhartha Reddy USN-1PI07EC015 Seminar Guide-Mrs - Usha RaghunathSiddharth ReddyNo ratings yet
- 6500 Packet Optical Platform PBDocument7 pages6500 Packet Optical Platform PBsatyvan2003No ratings yet
- Designing Campus and Data Center NetworkDocument33 pagesDesigning Campus and Data Center NetworkBerihun Tenaye Ali100% (1)
- Demystifying NFV in Carrier NetworksDocument8 pagesDemystifying NFV in Carrier NetworksGabriel DarkNo ratings yet
- Nokia_NSP_datasheet_Data_Sheet_ENDocument16 pagesNokia_NSP_datasheet_Data_Sheet_ENAlexis SturmNo ratings yet
- WAN Optimization FrameworkDocument40 pagesWAN Optimization FrameworkVinamra KumarNo ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Cellular GEA-12740F PDFDocument8 pagesMDS Orbit Cellular GEA-12740F PDFFabian EspinozaNo ratings yet
- MCRNC Configuration PrinciplesDocument20 pagesMCRNC Configuration PrinciplesAshok DwivediNo ratings yet
- WP DriveNets Disaggregated Networks TCO-1Document6 pagesWP DriveNets Disaggregated Networks TCO-1OctavioNo ratings yet
- Networking Today and The FutureDocument10 pagesNetworking Today and The FutureSanjay RaviNo ratings yet
- Rakuten Cloud Native OrquestatorDocument4 pagesRakuten Cloud Native Orquestatoreng.viloriaNo ratings yet
- SCSA3Document7 pagesSCSA3naveenaNo ratings yet
- Seven Reasons To Use End-To-End Thinking When Building all-IP NetworksDocument12 pagesSeven Reasons To Use End-To-End Thinking When Building all-IP NetworksAjaykumar SinghNo ratings yet
- KCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 2Document25 pagesKCS 713 Unit 1 Lecture 2Shailesh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BRKSDN 2063Document68 pagesBRKSDN 2063cool dude911No ratings yet
- Onecontrol Unified Management System: Data SheetDocument2 pagesOnecontrol Unified Management System: Data Sheetrobert adamsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Aspects NGNDocument44 pagesFundamental Aspects NGNwoody0No ratings yet
- Junos Containerized Routing Protocol Daemon: Product OverviewDocument3 pagesJunos Containerized Routing Protocol Daemon: Product Overviewchandrashekar_ganesanNo ratings yet
- Nortel CPLDocument6 pagesNortel CPLmcclaink06No ratings yet
- Keystone School of Engineering, Pune: Computer NetworksDocument19 pagesKeystone School of Engineering, Pune: Computer Networkssahil n phalleNo ratings yet
- Cloud BurstingDocument17 pagesCloud BurstingGarvit TyagiNo ratings yet
- 5g - DriversDocument51 pages5g - Driverspopescubianca2010No ratings yet
- 6CS029 Lecture 8 - SDNDocument36 pages6CS029 Lecture 8 - SDNdushantha.ellewalaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Technology NotesDocument6 pagesWireless Technology NotesSonali OramNo ratings yet
- Moyer Segment Routing For v1Document20 pagesMoyer Segment Routing For v1Anonymous NIkO5EI6No ratings yet
- Andromeda: Network Stack VirtualizationDocument16 pagesAndromeda: Network Stack VirtualizationMiguel PintoNo ratings yet
- RTU560 EnglishDocument16 pagesRTU560 EnglishrhomadonaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Densification With Juniper Mobile Backhaul SolutionDocument3 pagesMobile Network Densification With Juniper Mobile Backhaul Solutionyahya alrowniNo ratings yet
- CloudDocument32 pagesCloudSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Openran 5G NR: Whitebox - Flexible - Disaggregated - Small Cell PlatformDocument2 pagesOpenran 5G NR: Whitebox - Flexible - Disaggregated - Small Cell PlatformAbhishek BudhawaniNo ratings yet
- Ovum LTE450 PresentationDocument35 pagesOvum LTE450 Presentationnurys77No ratings yet
- Swishmem: Distributed Shared State Abstractions For Programmable SwitchesDocument8 pagesSwishmem: Distributed Shared State Abstractions For Programmable SwitchesIsaak ToviessiNo ratings yet
- Ciena OnePlanner - Unified - Design - System - DSDocument5 pagesCiena OnePlanner - Unified - Design - System - DSrobert adamsNo ratings yet
- Rohini 93532310129Document5 pagesRohini 93532310129pleasingprince123No ratings yet
- Form 4D Recloser Control: A Simple and Cost-Effective Solution For Everyday Protection RequirementsDocument4 pagesForm 4D Recloser Control: A Simple and Cost-Effective Solution For Everyday Protection RequirementsTuân MậpNo ratings yet
- MDS Orbit Platform GEA-12781F PDFDocument4 pagesMDS Orbit Platform GEA-12781F PDFMiguelNo ratings yet
- NEC 5G Open vRAN White Paper Flyer Rev1Document4 pagesNEC 5G Open vRAN White Paper Flyer Rev1Mo IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mem Overviewslideshare04142015 150420115259 Conversion Gate01Document16 pagesMem Overviewslideshare04142015 150420115259 Conversion Gate01l00pback63No ratings yet
- Ad Hoc WirelessDocument25 pagesAd Hoc WirelessABHISHEK TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- MBF MLMT - EdenNet Seminar v1.0Document82 pagesMBF MLMT - EdenNet Seminar v1.0Hồ Mạnh QuýNo ratings yet
- Vmware Nokia Solution OverviewDocument4 pagesVmware Nokia Solution OverviewEduardoNo ratings yet
- Google NetworkDocument15 pagesGoogle Networkanthony saddingtonNo ratings yet
- Manage Control and Plan DSDocument4 pagesManage Control and Plan DSPrasanna GanesanNo ratings yet
- NetWare 2013-SDN and Architectures v1.2 - August 25 - 2013Document118 pagesNetWare 2013-SDN and Architectures v1.2 - August 25 - 2013Boopathy PandiNo ratings yet
- Distributed Software Engineering: TEAM:20470,20471,20472,20473,20474Document22 pagesDistributed Software Engineering: TEAM:20470,20471,20472,20473,20474473Dharini IyerNo ratings yet
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasDocument30 pagesNetwork Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasBaraa EsamNo ratings yet
- Brochure Klerity Bringing Transparency To NetworksDocument4 pagesBrochure Klerity Bringing Transparency To Networksmore_nerdyNo ratings yet
- by Rso TX - 14-08-2014: 1 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014 For Internal Use OnlyDocument45 pagesby Rso TX - 14-08-2014: 1 © Nokia Solutions and Networks 2014 For Internal Use Onlysunilpanda08No ratings yet
- Intoduction To CloudDocument46 pagesIntoduction To CloudShagun DhimanNo ratings yet
- 1 Module: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument38 pages1 Module: Introduction To Cloud ComputingAsad AbbasNo ratings yet
- MC9S08DZ32 PDFDocument396 pagesMC9S08DZ32 PDFbandusNo ratings yet
- Upsc Epfo Eo: 50 Important Computer QuestionsDocument13 pagesUpsc Epfo Eo: 50 Important Computer QuestionsdeepthiNo ratings yet
- How To - Cannot Connect To Service Manager BiostarDocument5 pagesHow To - Cannot Connect To Service Manager BiostarDanish SaeedNo ratings yet
- VDR Maint ViewerDocument100 pagesVDR Maint ViewergorbachevrrrrNo ratings yet
- F2FS: A New File System For Flash StorageDocument15 pagesF2FS: A New File System For Flash StorageLuis KissNo ratings yet
- 18MCS13 R. V. College of Engineering: Time: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Instructions To CandidatesDocument3 pages18MCS13 R. V. College of Engineering: Time: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Instructions To CandidatesSAMARTH PATILNo ratings yet
- Ec2042 2 MarksDocument56 pagesEc2042 2 Marksanand_duraiswamyNo ratings yet
- Configurasi Ont Mdu Huawei 5612Document7 pagesConfigurasi Ont Mdu Huawei 5612Tri AgungNo ratings yet
- 7th Generation Core Mobile Processor Iot Platform BriefDocument6 pages7th Generation Core Mobile Processor Iot Platform BriefKukaneswaran Selva RajooNo ratings yet
- Memory SegmentationDocument38 pagesMemory SegmentationVinaya SreeNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Omnipcx Install Manual PDFDocument964 pagesAlcatel Omnipcx Install Manual PDFmukiza ivanNo ratings yet
- Serial Do Windows XP Service Pack 2 e Service Pack 3Document3 pagesSerial Do Windows XP Service Pack 2 e Service Pack 3César augustoNo ratings yet
- ECE4680 Computer Organization and Architecture Memory HierarchyDocument7 pagesECE4680 Computer Organization and Architecture Memory HierarchySi Brian TohNo ratings yet
- Optmization in AlteryxDocument7 pagesOptmization in AlteryxLoan MotylNo ratings yet
- Dual Vios Upgrade Walk-Through Powervm Technical Webinar #12 For Customers/Bps/IbmersDocument31 pagesDual Vios Upgrade Walk-Through Powervm Technical Webinar #12 For Customers/Bps/IbmersAndrei AndreiuNo ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument2 pagesOperating System NotesAnkit bohraNo ratings yet
- Loading Contoso Demo Datafor Dynamics AX2009Document23 pagesLoading Contoso Demo Datafor Dynamics AX2009Kevin JonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Replace Lenovo Y510P Cache Drive With MyDigitalSSD Super Cache 2 SSDDocument14 pagesTutorial Replace Lenovo Y510P Cache Drive With MyDigitalSSD Super Cache 2 SSDPamela CoursonNo ratings yet
- ESA CREW Manual en 2 0Document1,469 pagesESA CREW Manual en 2 0DimitriNo ratings yet
- GO - General OutcomeDocument4 pagesGO - General OutcomeaymanaymanNo ratings yet
- Mastersaf DW Procedures Application PatchDocument11 pagesMastersaf DW Procedures Application Patchtyuhzinho0% (1)
- OS Chapter 2Document36 pagesOS Chapter 2maazali2735No ratings yet
- E2E Delay: R R R LDocument4 pagesE2E Delay: R R R Lspade0987No ratings yet
- Cs2100 12 Basic DatapathDocument50 pagesCs2100 12 Basic DatapathamandaNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Orako ProblemsDocument4 pagesBab 6 Orako ProblemsBilly Shan LastKagerooboroNo ratings yet
- Kvara Esa 200Document174 pagesKvara Esa 200DarkNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Module 3Document13 pagesMs Word Module 3R TECHNo ratings yet
- Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators (The Java™ Tutorials Learning The Java Language Language Basics)Document1 pageBitwise and Bit Shift Operators (The Java™ Tutorials Learning The Java Language Language Basics)YeNo ratings yet