Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Treponema
Treponema
Uploaded by
قاسم اليوسفي0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesThe document summarizes information about Treponema, including that it is a genus of bacteria that includes the pathogen that causes syphilis, T. pallidum. It describes the morphology and difficulties culturing Treponema. It also outlines the stages of syphilis infection, from primary to secondary to latent to tertiary syphilis. Congenital syphilis transmission from mother to fetus is also discussed. The document concludes with sections on diagnosis of syphilis through direct detection or antibody assays and treatment with penicillin G.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes information about Treponema, including that it is a genus of bacteria that includes the pathogen that causes syphilis, T. pallidum. It describes the morphology and difficulties culturing Treponema. It also outlines the stages of syphilis infection, from primary to secondary to latent to tertiary syphilis. Congenital syphilis transmission from mother to fetus is also discussed. The document concludes with sections on diagnosis of syphilis through direct detection or antibody assays and treatment with penicillin G.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesTreponema
Treponema
Uploaded by
قاسم اليوسفيThe document summarizes information about Treponema, including that it is a genus of bacteria that includes the pathogen that causes syphilis, T. pallidum. It describes the morphology and difficulties culturing Treponema. It also outlines the stages of syphilis infection, from primary to secondary to latent to tertiary syphilis. Congenital syphilis transmission from mother to fetus is also discussed. The document concludes with sections on diagnosis of syphilis through direct detection or antibody assays and treatment with penicillin G.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Treponema
•The genus Treponema belongs to the family of
Spirochaetaceae and includes several significant
human pathogen species and subspecies. T.
pallidum, is the syphilis pathogen.
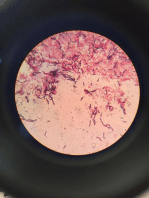
•Morphology and culture: These organisms are slender
bacteria, 0.2 µ wide and 5–15 µ long; they feature 10–20
primary windings and move by rotating around their
lengthwise axis. Their small width makes it difficult to
render them visible by staining. They can be observed in
vivo using dark field microscopy. Invitro culturing has
not yet been achieved.
•Pathogenesis and clinical picture: Syphilis
affects only humans. The disease is normally
transmitted by sexual intercourse. .The
incubation period is two to four weeks. Left
untreated, the disease manifests in several
stages:
• Stage I (primary syphilis): Hard painless
lesion, later infiltration and ulceration, called
hard chancre. The accompanied by regional
lymphadenitis, also painless. Treponemes can
be detected in the ulcer.
• StageII (secondarysyphilis): Generalization
of the disease occurs four to eight weeks after
primary syphilis. Clinical symptoms include
macular or popular skin and mucus membrane
eruption.
• Latent syphilis: Stage of the disease in which
no clinical symptoms are manifested, but the
pathogens are present in the body and serum
antibody tests are positive.
• Stage III (tertiary or late syphilis):
manifestations in skin, mucosa, and various
organs. Tissue disintegration is frequent.
Lesions are hardly infectious.
• Congenital Syphilis: Transmission of the
pathogen from mother to fetus after the fourth
month of pregnancy. It leads to miscarriage or
birth of severely diseased infant with
numerous treponemes in its organs.
Diagnosis:
•Pathogen identification: Only detectable in
fluid pressed out of primary chancre, in the
secretions of seeping stage II or in lymph node
biopsies. Methods: dark field microscopy, direct
immunofluorescence.
•Antibody assays: Two antibody groups can
be identified
1)Anti-lipoidal antibodies (reagain
antibodies): The antigen used is cardiolipin, a
lipid extract from the heart muscle of cattle.
1)Anti-treponema antibodies:
a.Treponema pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA): The
antigens (treated suspension of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain,
cultured in rabbit testicles) are coupled to particles or erythrocytes.
b.Immunofluorescence test:
c. Treponema pallidum immobilization test (TPI test). Living
treponemes (Nichols strain) are immobilized by antibodies in the
patient serum.
Therapy
•:Penicillin G is the antibiotic agent of choice.
You might also like
- Syphilis: Dr. Sachin PatelDocument36 pagesSyphilis: Dr. Sachin PatelAakash PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-X SyphilisDocument44 pagesChapter-X SyphilisD PharmaNo ratings yet
- It 38 Microbiology in Obgyn 24Document146 pagesIt 38 Microbiology in Obgyn 24dhjekwkwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.4 Family SpirochaetaceaeDocument27 pagesChapter 3.4 Family SpirochaetaceaecimdesadesuNo ratings yet
- 13 Treponema - Borrelia.leptospira 1Document26 pages13 Treponema - Borrelia.leptospira 1Jaydeep ThummarNo ratings yet
- ID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Document20 pagesID-Micro L9 (Atypical Bacteria)Oraco1No ratings yet
- Syphilis: Michelle LinardiDocument20 pagesSyphilis: Michelle Linardimichelle95No ratings yet
- ChlamydiaDocument47 pagesChlamydiaAmmarNo ratings yet
- Lab Diagnosis of TreponemaDocument3 pagesLab Diagnosis of Treponemayam pdNo ratings yet
- Family Spirochaetaceae and Leptospiraceae-1Document29 pagesFamily Spirochaetaceae and Leptospiraceae-1temesgensemahegn55No ratings yet
- SpirochaetesDocument14 pagesSpirochaetesCaroline NgabuNo ratings yet
- Treponema SPPDocument45 pagesTreponema SPPDavid lufafaNo ratings yet
- Rep 1Document50 pagesRep 1bbbbbvvvvv1No ratings yet
- SPIROCHETESDocument11 pagesSPIROCHETESShujat Razaq100% (1)
- Mti Notes Stds-1Document24 pagesMti Notes Stds-1Mahmoud KhelfaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical SpirochaetalesDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Medical SpirochaetalesAngelic khanNo ratings yet
- ChlamydiaeDocument47 pagesChlamydiaeshravaniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityDocument51 pagesDr. Dalia El-Shafei: Assistant Professor, Community Medicine Department, Zagazig UniversityArpit MahoreNo ratings yet
- Spirochetes: Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument99 pagesSpirochetes: Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Syphilislecturepp 180719075049Document30 pagesSyphilislecturepp 180719075049EndaleNo ratings yet
- Group of Communicable Diseases in Which Sexual Contact Is The Most Important Mode of TransmissionDocument57 pagesGroup of Communicable Diseases in Which Sexual Contact Is The Most Important Mode of TransmissionJovelyn Silapan ManalangNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 19sexually Transmitted Infection 1Document50 pagesCHAPTER 19sexually Transmitted Infection 1Nick Martin RequejoNo ratings yet
- 12 - SpirochetesDocument55 pages12 - SpirochetesJohanna Kate DiestroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document31 pagesLecture 17Me TooNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesAhmed HajiNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Disease STDDocument47 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease STDSurya DoleyNo ratings yet
- CDC Part 2Document297 pagesCDC Part 2fdamissieNo ratings yet
- Syphilislecturepp 180719075049Document32 pagesSyphilislecturepp 180719075049abdellatifNo ratings yet
- Syphilislecturepp 180719075049Document32 pagesSyphilislecturepp 180719075049EndaleNo ratings yet
- Treponema Pallidum: Human PathogensDocument27 pagesTreponema Pallidum: Human PathogensGeorgeNecoarăNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyBeyins TiuNo ratings yet
- SPIROCHETESDocument5 pagesSPIROCHETESJOVELYN GARCIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 31Document10 pagesLesson 31Abdelraouf ElmanamaNo ratings yet
- Genera:: Treponema & BorreiliaDocument25 pagesGenera:: Treponema & BorreiliaKhalifa Sifaw Ghenghesh100% (1)
- Imo SpirocheteDocument43 pagesImo SpirocheteGelvia AwaehNo ratings yet
- Part-2-ParasitologyDocument33 pagesPart-2-ParasitologyAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 9Document24 pagesLecture - 9ASADULLAH AL GALIBNo ratings yet
- TreponemaDocument16 pagesTreponemakanubhushan2018No ratings yet
- Spirochetes 2023Document42 pagesSpirochetes 2023Ahmed khanNo ratings yet
- Spirochetes and Curved RodsDocument54 pagesSpirochetes and Curved RodsDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Remaining BacteriaDocument66 pagesRemaining BacteriaRonelene GatoNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative SpirochetesDocument50 pagesGram Negative SpirochetesYeshiwas FelekeNo ratings yet
- Lection 8 SyphilisDocument39 pagesLection 8 SyphilisAtawna AtefNo ratings yet
- Family Spirochaetaceae AND LeptospiraceaeDocument33 pagesFamily Spirochaetaceae AND Leptospiraceaeyosef awokeNo ratings yet
- Agent: Defining Characteristics Clinical Diseases Laboratory Diagnosis Treatment SpirochetesDocument6 pagesAgent: Defining Characteristics Clinical Diseases Laboratory Diagnosis Treatment SpirochetesEd Daniel DavisNo ratings yet
- Treponema PallidumDocument26 pagesTreponema PallidumprincejhaNo ratings yet
- All 45 BugsDocument26 pagesAll 45 Bugsroboat96No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Therapeutics IIDocument54 pagesTuberculosis: Therapeutics IIdstu20No ratings yet
- Chlamydia by Rosemary C. AgboDocument24 pagesChlamydia by Rosemary C. AgboRosemaryNo ratings yet
- 7 Spirochetes TrponemaDocument7 pages7 Spirochetes TrponemaShama Al-ShadidiNo ratings yet
- Infection & Specific Wound InfectionsDocument39 pagesInfection & Specific Wound InfectionsAhmed ShorshNo ratings yet
- Syphilis - ReportDocument4 pagesSyphilis - ReportAnna CahucomNo ratings yet
- 11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Document61 pages11 Spirochetes 130520112830 Phpapp02Manisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Microbial Infections (Bacteria) : Presented byDocument116 pagesMicrobial Infections (Bacteria) : Presented byamitpubsinghNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Brief Diagnostic Parasitology Notes FACS: Flagellates, Amoebae, Ciliates, SporozoaDocument10 pagesMicrobiology: Brief Diagnostic Parasitology Notes FACS: Flagellates, Amoebae, Ciliates, Sporozoapieterinpretoria391No ratings yet
- MBIO 4823 Final Review XDocument3 pagesMBIO 4823 Final Review Xuberjunk426801No ratings yet
- Syphilis (Is)Document31 pagesSyphilis (Is)Khalid SeliaNo ratings yet
- Seminar2ischemia 180315152816Document124 pagesSeminar2ischemia 180315152816قاسم اليوسفيNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - IHDDocument29 pagesLecture 3 - IHDقاسم اليوسفيNo ratings yet
- Histotechniques For Medical Laboratory (Lab 1)Document15 pagesHistotechniques For Medical Laboratory (Lab 1)قاسم اليوسفيNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Acetone DioxaneDocument15 pagesDehydration: Acetone Dioxaneقاسم اليوسفيNo ratings yet
- Lecture One of Analytical Chemistry 1Document15 pagesLecture One of Analytical Chemistry 1قاسم اليوسفيNo ratings yet
- General Properties & Classification of ParasitesDocument33 pagesGeneral Properties & Classification of Parasitesraanja2100% (1)
- Communicable Disease - Community Health NursingDocument49 pagesCommunicable Disease - Community Health Nursinggelean payod100% (1)
- Mylonakis 2016Document10 pagesMylonakis 2016Mariano ErcoleNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Projoec1Document7 pagesScience Investigatory Projoec1Alfred RegalaNo ratings yet
- Bartholomew - Japanese Nobel Candidates in The First Half of The Twentieth CenturyDocument48 pagesBartholomew - Japanese Nobel Candidates in The First Half of The Twentieth CenturyYagtaliNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Hepatitis BDocument20 pagesResearch Paper On Hepatitis Bjamaica_maglinteNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Study Guide 2023-IvDocument7 pagesDermatology Study Guide 2023-IvUnknown ManNo ratings yet
- Textbook Infectious Diseases Emergencies 1St Edition Bissonette Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Infectious Diseases Emergencies 1St Edition Bissonette Ebook All Chapter PDFaline.pacheo873100% (15)
- Role of MIS in National Rural Health Mission, OrissaDocument17 pagesRole of MIS in National Rural Health Mission, OrissaAbhinav RaajNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease 2 AnswersDocument14 pagesCommunicable Disease 2 AnswersRika MaeNo ratings yet
- Quinolones: Prof. Anuradha NischalDocument42 pagesQuinolones: Prof. Anuradha Nischalsekprodi profesifkyarsiNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of COVIDDocument6 pagesSide Effects of COVIDKamran Ali AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Transes RespiratoryDocument17 pagesMedsurg Transes RespiratoryAprille Kaye TayoneNo ratings yet
- Viral Gastroenteritis - Lancet (2024)Document15 pagesViral Gastroenteritis - Lancet (2024)Ricardo GarzaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology SummaryDocument38 pagesBacteriology SummaryMohsen HaleemNo ratings yet
- Gilead 7th HIV Summi AgendaDocument8 pagesGilead 7th HIV Summi Agendaayaks uuNo ratings yet
- Public Health Microbiology - 3rd EdDocument175 pagesPublic Health Microbiology - 3rd EdYolandia WNo ratings yet
- Yellow Fever Disease PamphletDocument2 pagesYellow Fever Disease Pamphletapi-551984674No ratings yet
- Practice 50 2022Document5 pagesPractice 50 2022Thảo Bùi Thị HươngNo ratings yet
- Mip MCQ 4Document4 pagesMip MCQ 4nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Fmge Dec 2021 PSM Questions WMDocument5 pagesFmge Dec 2021 PSM Questions WMAbinashmishraNo ratings yet
- 2.13 - NemathelminthesDocument4 pages2.13 - NemathelminthesLunaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Dread AkataDocument3 pagesAdvanced Dread AkataAaron RichterNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Salmonella TyphiDocument4 pagesThesis On Salmonella Typhikimberlyreyessterlingheights100% (2)
- L3, Jonas SalkDocument5 pagesL3, Jonas SalkKhương VũNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck NCPDocument2 pagesHead and Neck NCPAngelo AbiganiaNo ratings yet
- Name: Deborah V. Insepido Code/Subject: NCM 113 (3679)Document2 pagesName: Deborah V. Insepido Code/Subject: NCM 113 (3679)Deborah InsepidoNo ratings yet
- No Jab For Me: Did You Know?Document13 pagesNo Jab For Me: Did You Know?Jamie RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Public Health UnitDocument2 pagesPublic Health UnitMark Emil BautistaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Covid 19Document2 pagesReflection Covid 19Hello KittyNo ratings yet