Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Center of Gravity and Moment of Force
Center of Gravity and Moment of Force
Uploaded by
Leonidas Rocks0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views17 pagesThe document discusses the concept of center of gravity. It defines center of gravity as the point at which all the mass of a body seems to be concentrated. It can be found using a plumb bob. An object will remain upright if its center of gravity is over its base, but will topple if the center of gravity extends beyond the base. Stability depends on the position of the center of gravity. The document also provides examples of solving problems involving center of gravity using the principle of moments.
Original Description:
Original Title
4._center_of_gravity_and_moment_of_force
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the concept of center of gravity. It defines center of gravity as the point at which all the mass of a body seems to be concentrated. It can be found using a plumb bob. An object will remain upright if its center of gravity is over its base, but will topple if the center of gravity extends beyond the base. Stability depends on the position of the center of gravity. The document also provides examples of solving problems involving center of gravity using the principle of moments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views17 pagesCenter of Gravity and Moment of Force
Center of Gravity and Moment of Force
Uploaded by
Leonidas RocksThe document discusses the concept of center of gravity. It defines center of gravity as the point at which all the mass of a body seems to be concentrated. It can be found using a plumb bob. An object will remain upright if its center of gravity is over its base, but will topple if the center of gravity extends beyond the base. Stability depends on the position of the center of gravity. The document also provides examples of solving problems involving center of gravity using the principle of moments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
Center of Gravity
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Center of Gravity
Center of gravity is often called the
“Center of Mass” and is defined as the
point at which all mass seems be
concentrated.
Center of Gravity is a balance point.
You can use a plumb bob to find the center
of gravity
Alta High Conceptual Physics
High Jumper
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Toppling
When an object’s center of gravity is
over its base it will remain upright,
however if the center of gravity extends
beyond the base it will topple.
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Center of Gravity Center of Gravity
over Base – will outside Base –
stay upright will topple
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Stability
Base Alta High Conceptual Physics
of Support
Stability
When an object is balanced so that any
displacement lowers its center of gravity it
is in an unstable equilibrium.
Center of
Gravity
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Stability
Which object is most stable?
Alta High Conceptual Physics
State of Principle of Equilibrium
The state of Principle of Equilibrium of a body at rest
will depend on the position of the center of gravity of
a body. This is an imaginary point in the body where
its weight seems to be concentrated. The state of
principle of equilibrium may be classified as stable,
unstable and neutral.
1. Stable Equilibrium. A body is said to be in a state
of stable equilibrium if, after being slightly disturbed,
it returns to its original position of rest because the
center of gravity is relatively in its lowest position.
2. Unstable Equilibrium. A body is said to be in a
state of unstable equilibrium if, after being slightly
disturbed and released, it moves further away from
Alta High Conceptual Physics
position of rest because the center of gravity is in
highest position.
3. Neutral Equilibrium. A body is said to be a state of
neutral equilibrium if, after being slightly pushed,
there will be no tendency for the top to return to its
original of rest because the center of gravity is
neither raised nor lowered when the top is slightly
pushed.
Alta High Conceptual Physics
The condition required for equilibrium when a
number of forces and moments act on a body.
If the resultant of all the forces acting on a body is
zero, all forces balance, and the body I said to be in
equilibrium. The body will remain at rest if it is
originally at rest before the forces are applied.
The torque produced by a force about any axis is
also called the moment of the force about that same
axis.
Alta High Conceptual Physics
The factors which govern the stability
and over turning of a box.
1. Weight
2. Area of the base
3. Location of the center of gravity
Alta High Conceptual Physics
The balance of forces and the
center gravity of a straight lever.
If there is no rotation, the sum of all the clockwise
moments must be equal to the sum of all the counter
clockwise moments. This is known as the Second
Condition for Equilibrium. In a seesaw, the weights
of the two persons who are trying to balance the
seesaw is supported is known as the fulcrum. A
balance can be obtained, even with unequal weights,
by a proper choice of the lever arm.
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Applying the Law of Moments.
M1 = M 2
F1d1 = F2d2
Where: M - Moment
F - Force or Weight
d - distance
Playing in a seesaw is an example of balance
moments. The product of the weight and distance
from the fulcrum of the left side should be equal to
that of the other side.
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Solved Problem 1:
Juan weighs 250 N sits at one end of a 4-meter
seesaw. And Pedro sits opposite side of Juan 1.5
meters away from the fulcrum and they balance each
other. What is the weight of Pedro?
Given:
Weight of Juan, WJ = 250 N
Distance of Juan from the fulcrum, dJ = 2 m
Distance of Pedro from the fulcrum, dP = 1.5 m
Required:
Weight of Pedro, WP
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Solution:
Formula:
MJ = MP
WJ dJ= WP dP
WP = WJ dJ / dP
WP = 250 N( 2 m ) / 1.5 m
WP = 333 N
Alta High Conceptual Physics
Solved Problem 2:
A two-sided pulley serves as a cargo-carrier in a certain vessel.
One of the cargo is 40 kg and is located 0.6 meter from the
center, and the other cargo is 60 kg is at the second side. How
far from the center must be massive object be located on the
opposite side?
Given: W1 = 40 kg; d1 = 0.6 m
W2 = 60 kg
Solution:
W1d1 = W2d2
d2 = W1d1 / W2
= 40 kg ( 0.6 m ) / 60 kg
= 0.4 meter
Alta High Conceptual Physics
You might also like
- How to Achieve Glowing Health and Vitality: The Wisdom of YoganandaFrom EverandHow to Achieve Glowing Health and Vitality: The Wisdom of YoganandaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ELEC1010 Homework 3Document3 pagesELEC1010 Homework 3Yuen Hei Max Lee100% (2)
- Centre of GravityDocument6 pagesCentre of GravityPiyan HashimNo ratings yet
- Moment of A Force JLLA YR 10Document20 pagesMoment of A Force JLLA YR 10michealshodeinde994No ratings yet
- Mat Phy CH 1 To 5Document20 pagesMat Phy CH 1 To 5Kamran SaleemNo ratings yet
- 8 Rotation TorqueDocument3 pages8 Rotation TorqueJerome BedañoNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaDocument42 pagesGeneral Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaLADY SUZETTE LANDICHONo ratings yet
- Center of GravityDocument21 pagesCenter of GravityAwais Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityDocument18 pagesUnit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Center of GravityDocument28 pagesCenter of GravityLeon LawnNo ratings yet
- Turning Effect of ForcesDocument7 pagesTurning Effect of ForcesSyed M HassanNo ratings yet
- Cog and ComDocument7 pagesCog and ComSrikant AichNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity1Document28 pagesCenter of Gravity1Leon LawnNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity and EquilibriumDocument2 pagesCenter of Gravity and EquilibriumHarrison Cabreros100% (1)
- Makalah Kesetimbangan Da ElastisitasDocument20 pagesMakalah Kesetimbangan Da ElastisitasRirinNo ratings yet
- Group: 2: 1. Define The Following: A. Moment of A ForceDocument3 pagesGroup: 2: 1. Define The Following: A. Moment of A ForceJea CansinoNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4 (Laws of Motion)Document14 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4 (Laws of Motion)Shubhrojyoti MitraNo ratings yet
- Energy DiagramsDocument40 pagesEnergy DiagramsEljay Manuel CabactulanNo ratings yet
- General Physics PDFDocument5 pagesGeneral Physics PDFsimi sanuNo ratings yet
- 2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFDocument3 pages2 Center of Gravity, Stability and Equilibrium PDFPhilip Moore100% (2)
- Balance and Stability PowerpointDocument36 pagesBalance and Stability PowerpointCzarina Amor CabilleteNo ratings yet
- Turning Effects of Forces MomentsDocument7 pagesTurning Effects of Forces Momentsanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Forces and MotionDocument88 pagesChapter - 3: Forces and MotionAlisha QaziNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3065761028398401936Document21 pagesInbound 3065761028398401936Eric Alvarado SaludaresNo ratings yet
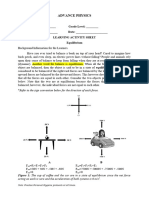
- Solution: Sigmatau 0 (40N) (0.5+X) + (150N) (X) (50N) (0.5-X) 20+40X+150X 25-50X 20+190X 25-50X 190X+50X 25-20 240X 5240 240X 0.0208MDocument2 pagesSolution: Sigmatau 0 (40N) (0.5+X) + (150N) (X) (50N) (0.5-X) 20+40X+150X 25-50X 20+190X 25-50X 190X+50X 25-20 240X 5240 240X 0.0208MJosephine Julia KoNo ratings yet
- Stability Experiment 2 UpdateDocument7 pagesStability Experiment 2 UpdateApostrophe Fareez ImprezzaNo ratings yet
- Center of Gravity Vs Center of MassDocument25 pagesCenter of Gravity Vs Center of Massguptafamily1992No ratings yet
- Centripetal Forces Lab ReportDocument4 pagesCentripetal Forces Lab Reportapi-315606787No ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument3 pagesBuoyancyharoonNo ratings yet
- 10 Lecture Newton's Laws Sum12Document10 pages10 Lecture Newton's Laws Sum12Jay Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument5 pagesNewton's LawsHasib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document42 pagesLesson 2Tr. PrincessNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium & TypesDocument10 pagesEquilibrium & TypesRahulNo ratings yet
- TorqueDocument3 pagesTorquerf08dNo ratings yet
- Phy SS2 Acad Week 4Document2 pagesPhy SS2 Acad Week 4ohakwekosiNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6Document43 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6himeshs298No ratings yet
- Forces I: The Basics: Ms. Mikaela Irene Fudolig Physics 71Document30 pagesForces I: The Basics: Ms. Mikaela Irene Fudolig Physics 71Keith SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Equilibrium and Stability of The Human BodyDocument23 pagesChapter 1. Equilibrium and Stability of The Human BodyNermeinKhattabNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument47 pagesCHAPTER 7 - Newtons Laws of Motionoman92870164No ratings yet
- Newton Laws.Document30 pagesNewton Laws.Xixi XixiNo ratings yet
- 6 - Mass, Weight and C.GDocument17 pages6 - Mass, Weight and C.GRafayNo ratings yet
- HILADO Laboratory Report 1 (Individual)Document1 pageHILADO Laboratory Report 1 (Individual)ChristopherHiladoNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Concept Notes On Laws of Motion For NEET. CB1198675309Document57 pagesDisha Publication Concept Notes On Laws of Motion For NEET. CB1198675309ZIA UR REHMAN33% (3)
- Advance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumDocument27 pagesAdvance Physics: Forces in EquilibriumMilcah Shane Niones SarenNo ratings yet
- Educational MaterialsDocument5 pagesEducational MaterialsTula DhimitraNo ratings yet
- Physics 101 Chapter 2Document39 pagesPhysics 101 Chapter 2Andrew GoolsbyNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics Chapter 4 NotesDocument4 pages9th Physics Chapter 4 NotesHassan Arslan85% (20)
- Centre of Gravity, Stability & EquilibriumDocument6 pagesCentre of Gravity, Stability & EquilibriumA BarrettNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Laws of MotionDocument40 pagesChapter - 5 Laws of MotionNafees FarheenNo ratings yet
- Force Notes Class 10Document4 pagesForce Notes Class 10Hostellers creationsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Turning Effects: - Learning ObjectivesDocument67 pagesChapter 4 Turning Effects: - Learning Objectivesceline chungNo ratings yet
- Biomechanical Bases 18Document28 pagesBiomechanical Bases 18769znkc99dNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TheoryDocument25 pagesUnit 1 TheoryparthibankNo ratings yet
- Antonio Gabriel Mesa Activity 2.1Document4 pagesAntonio Gabriel Mesa Activity 2.1Daniel Rupert PilapilNo ratings yet
- 4 BphysicsDocument12 pages4 BphysicsLeigh DevezaNo ratings yet
- Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7Document8 pagesSystems of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 7Mehak ShireenNo ratings yet
- EqulibriumDocument43 pagesEqulibriumSidnee MadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Physics of the Human Body Lose Weight for GoodFrom EverandPhysics of the Human Body Lose Weight for GoodRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- An Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Physics For Engineer: Work, Energy and PowerDocument35 pagesPhysics For Engineer: Work, Energy and PowerLee TalierNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument3 pagesEarthGavinNo ratings yet
- What Is Mathematics - An Overview: ResearchDocument5 pagesWhat Is Mathematics - An Overview: ResearchBeloved DhinaNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Calculus Single Variable 7th by Eury PeraltaDocument8 pagesSolucionario Calculus Single Variable 7th by Eury PeraltaKaren PonceNo ratings yet
- Band Broadening and Column Efficiency 2020 PDFDocument23 pagesBand Broadening and Column Efficiency 2020 PDFSalix MattNo ratings yet
- Gear Transmission Error Outside The Normal Path of Contact Due To Corner and Top Contact PDFDocument12 pagesGear Transmission Error Outside The Normal Path of Contact Due To Corner and Top Contact PDFsuchul kimNo ratings yet
- Atlantis - The Lost Continent Finally FoundDocument337 pagesAtlantis - The Lost Continent Finally FoundOff White100% (1)
- Science of Cooking NotesDocument2 pagesScience of Cooking NotesjuanNo ratings yet
- Newton Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesNewton Lesson Planapi-283344745No ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of An Aircraft WingDocument25 pagesVibration Analysis of An Aircraft WingRan Bag100% (1)
- GLASSDocument1 pageGLASSGizelle B NuñezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamits: MC Graw HillDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Aerodynamits: MC Graw HillHunny VermaNo ratings yet
- Sma Ode 2Document13 pagesSma Ode 2SHAWN TAKAONANo ratings yet
- OMAE2019-95477: Baseline Design of The Deep Turbine Installation-Floating, A New Floating Wind ConceptDocument9 pagesOMAE2019-95477: Baseline Design of The Deep Turbine Installation-Floating, A New Floating Wind ConceptJordi SerretNo ratings yet
- 18 Inch 9 5 MM Combo (MFL+CLP+IMU) (Ver Data Sheet Pàg. 8) PDFDocument19 pages18 Inch 9 5 MM Combo (MFL+CLP+IMU) (Ver Data Sheet Pàg. 8) PDFOscar Miguel Fuquen SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Literatur Grundfos NBDocument250 pagesLiteratur Grundfos NBShil HammiyNo ratings yet
- Quadcopter Control Project ReportDocument76 pagesQuadcopter Control Project Reportmudit vermaNo ratings yet
- Modern Vehicle TechnologyDocument11 pagesModern Vehicle Technologymehmet nedimNo ratings yet
- MELCS-General MathematicsDocument3 pagesMELCS-General MathematicsLiedi BrigetteNo ratings yet
- EP 440L-enUS-ASTMDocument1 pageEP 440L-enUS-ASTMAndersonNo ratings yet
- Formal Proofs of The Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesFormal Proofs of The Pythagorean TheoremLauren EricksonNo ratings yet
- Bell 1 Engine Flush: Applications / BenefitsDocument1 pageBell 1 Engine Flush: Applications / BenefitsTommy OetomoNo ratings yet
- 19 098 Nuclear Physics and Radiation Edit2Document67 pages19 098 Nuclear Physics and Radiation Edit2Danish Fitri RoslanNo ratings yet
- Astm 351 GR - CF 8Document6 pagesAstm 351 GR - CF 8Rajnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Part 1 Earth Science - History of The EarthDocument5 pagesModule 3 Part 1 Earth Science - History of The EarthJam AicaNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQDocument7 pagesChem MCQDeepa SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022024813002820 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0022024813002820 Main PDFSamah SamahNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic Mechanical Vapor Compression Refrigeration (MVCR) Cycle (Part 1)Document16 pages02 Basic Mechanical Vapor Compression Refrigeration (MVCR) Cycle (Part 1)VinNo ratings yet
- Metoda Magnetik Dalam Eksplorasi Geothermal - ITERA 8 Sep 2021Document28 pagesMetoda Magnetik Dalam Eksplorasi Geothermal - ITERA 8 Sep 2021AditNo ratings yet