Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsWeek 3 PolarCoordinates
Week 3 PolarCoordinates
Uploaded by
LULUHBELLE L. CRUZThe document discusses polar coordinates and converting between rectangular and polar coordinate systems. It provides examples of converting points between the two systems, as well as examples of analyzing sinusoidal functions by identifying their amplitude, period, phase shift, domain and range based on their equations or graphs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Measurement, Area, Surface Area and Volume - SeriesJ2 - SDocument10 pagesMeasurement, Area, Surface Area and Volume - SeriesJ2 - SJames Buchan50% (2)
- Intervals From Graphs WorksheetDocument4 pagesIntervals From Graphs WorksheetMcmustacheNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3Document5 pagesPre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3aggieNo ratings yet
- TFN Module 1 & 2Document10 pagesTFN Module 1 & 2A CNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson Three Notes Guided NotesDocument14 pagesModule Seven Lesson Three Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Unit 3 Intro To Trig Functions 1Document19 pagesPrecalculus Unit 3 Intro To Trig Functions 1api-287816312No ratings yet
- 112 Graphing 7.6 7.8 PDFDocument4 pages112 Graphing 7.6 7.8 PDFJavzanlkham VanchinbazarNo ratings yet
- 10 ClassworkDocument2 pages10 Classworktreehouse52906No ratings yet
- Function Lesson 1 FormativeDocument2 pagesFunction Lesson 1 FormativeJack BarbutoNo ratings yet
- Lab 04: Network Theorems: Experiment 04Document7 pagesLab 04: Network Theorems: Experiment 04Umer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument17 pagesCircle TheoremdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Pre Calc NotesDocument6 pagesPre Calc NotesAditya PaluriNo ratings yet
- Part C-Instructional MaterialsDocument11 pagesPart C-Instructional Materialsapi-326255121No ratings yet
- Surveying 1 Laboratory Elementary and Higher Surveying: Reciprocal LevelingDocument5 pagesSurveying 1 Laboratory Elementary and Higher Surveying: Reciprocal LevelingCarlo Miguel MagalitNo ratings yet
- Notes and Worksheets - Polar FunctionsDocument15 pagesNotes and Worksheets - Polar FunctionsranjidsarhanNo ratings yet
- Week 12 BodePlotsDocument7 pagesWeek 12 BodePlotsAhmad Hassan FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson Two Notes Guided NotesDocument7 pagesModule Seven Lesson Two Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Prefinal ExamDocument3 pagesPrefinal ExamDiamante ArasNo ratings yet
- 2010 Algebra II Trig Review 13.4-13.6Document2 pages2010 Algebra II Trig Review 13.4-13.6Alice DwyerNo ratings yet
- U08 D10Classwork+B-+Domain+and+Range+Inequality+vs+Interval+NotationDocument4 pagesU08 D10Classwork+B-+Domain+and+Range+Inequality+vs+Interval+Notationmelissa blancoNo ratings yet
- Ps1calculus Domain and RangeDocument3 pagesPs1calculus Domain and Rangepao.felix1021No ratings yet
- Analysis& Approaches Graphing Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Day 2Document6 pagesAnalysis& Approaches Graphing Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Day 2ethanNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson One Notes Guided NotesDocument25 pagesModule Seven Lesson One Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Review With Sample ProblemsDocument16 pagesMath 2 Review With Sample Problemsapi-297398947No ratings yet
- Lab#2 - Cie 111Document11 pagesLab#2 - Cie 111Biblee ChasNo ratings yet
- Pairs of Angles Lesson 1Document2 pagesPairs of Angles Lesson 1api-338888247No ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewDocument12 pagesGR 10 ReviewHoda RagabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 NotessmwhitmanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus HandoutDocument4 pagesPre-Calculus Handoutluluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- Mathlab 9Document2 pagesMathlab 9fftemmmNo ratings yet
- Geo Unit 1Document25 pagesGeo Unit 1Grace QiuNo ratings yet
- Formula List For AP Calculus BCDocument6 pagesFormula List For AP Calculus BCRuchi GuptaNo ratings yet
- APC 4.5 Notes Day 1 2018Document2 pagesAPC 4.5 Notes Day 1 2018Krishna KolluriNo ratings yet
- ANGLESDocument4 pagesANGLESCatherine GaloteraNo ratings yet
- I. Basic Information: St. Paul University System Gen. Luna ST.Document6 pagesI. Basic Information: St. Paul University System Gen. Luna ST.Ma Faustina GeronaNo ratings yet
- Oscillating Mass Lab: Review: Characterizing A SpringDocument8 pagesOscillating Mass Lab: Review: Characterizing A SpringFrancis DayanNo ratings yet
- Graphing Ellipse With Center at (H, K)Document3 pagesGraphing Ellipse With Center at (H, K)Diaz KaneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercises No.7Document4 pagesLaboratory Exercises No.7Rica Mae Garcia OberoNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Task Topic 4 - 3 CosmologyDocument2 pagesAstronomy Task Topic 4 - 3 CosmologyprabathoopsNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigDocument7 pagesAlgebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigSmart StudyManNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Supplementary Angles 90: If The Sum of Their Measures Equal ToDocument1 pageComplementary and Supplementary Angles 90: If The Sum of Their Measures Equal ToGlydel Mae Villamora - SaragenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewDocument2 pages2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewAbigail WileyNo ratings yet
- Daniel R. Aguinaldo National High SchoolDocument2 pagesDaniel R. Aguinaldo National High SchoolChris TinNo ratings yet
- Weirs Notch Report PDFDocument62 pagesWeirs Notch Report PDFMaxwell RejilNo ratings yet
- Nets and Surface Area Class ActivityDocument4 pagesNets and Surface Area Class ActivitySTEPHEN MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GeoTest PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 GeoTest PDFStephanie ValienteNo ratings yet
- Online Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDocument8 pagesOnline Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 NotesDocument2 pages1.4 NotesHetti arachchige pamith PereraNo ratings yet
- 9 16 2016 Domain RangeDocument1 page9 16 2016 Domain Rangeapi-327140356No ratings yet
- Form Operasional Genset Kemenko Marves Perkins 1500 KvaDocument1 pageForm Operasional Genset Kemenko Marves Perkins 1500 KvaArdee LEDNo ratings yet
- 10.2 - 10.4 - Characteristics - and - Translations - of - Functions - Practice - Worksheet (1) DoneDocument2 pages10.2 - 10.4 - Characteristics - and - Translations - of - Functions - Practice - Worksheet (1) DonesohiNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision BookletDocument4 pagesWaves Revision BookletAsif Zubayer PalakNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Learning Targets Sheet NewDocument3 pagesUnit 8 Learning Targets Sheet Newapi-704050165No ratings yet
- Algebra Two NotesDocument12 pagesAlgebra Two NotesShiline NguyenNo ratings yet
- St. Marks: Child Development Center, IncDocument3 pagesSt. Marks: Child Development Center, IncNoli CalderonNo ratings yet
- Test On Sections 1-1, 1-2, and 1-4 (Pre-Calc Honors)Document5 pagesTest On Sections 1-1, 1-2, and 1-4 (Pre-Calc Honors)RiveraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 03 Math 8Document2 pagesQuiz 03 Math 8Jeddah Joy OperarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Vocabulary Term Definition ExampleDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Vocabulary Term Definition ExampleScotty MalcolmNo ratings yet
- Elt Systems Service Information Letter: Date: May 6, 2020 Number: SIL4013Document4 pagesElt Systems Service Information Letter: Date: May 6, 2020 Number: SIL4013Nitesh PalNo ratings yet
- Mw61a Ti All Sv6.01a enDocument11 pagesMw61a Ti All Sv6.01a enpradeepNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills:: Types of Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument9 pagesListening Skills:: Types of Non-Verbal CommunicationMustafa DagiaNo ratings yet
- NewSmartTransformerStation STS 6000K H1Document2 pagesNewSmartTransformerStation STS 6000K H1Juan BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Market Systems Development: Sustainable Growth For EveryoneDocument53 pagesInclusive Market Systems Development: Sustainable Growth For EveryoneFarai MandisodzaNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Second Law: Driving Question - ObjectiveDocument6 pagesNewton'S Second Law: Driving Question - ObjectiveRKNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday Lesson Plan Copy GRADE ONEDocument5 pagesCatch Up Friday Lesson Plan Copy GRADE ONEJancel Añasco Tabliga100% (1)
- Form 4 SowDocument4 pagesForm 4 SowNAJWA ZAHIDAH BINTI RAZALI MoeNo ratings yet
- DTC Production Design 101.4 - MOODBOARD-AFDA.2.0Document17 pagesDTC Production Design 101.4 - MOODBOARD-AFDA.2.0NatoNo ratings yet
- Princeton University Press Eros The BittersweetDocument5 pagesPrinceton University Press Eros The BittersweetI.M.C.No ratings yet
- 08-Risk Control TechniqueDocument15 pages08-Risk Control TechniqueMubarak Noor AzliNo ratings yet
- Soal Pendalaman Materi XiiDocument16 pagesSoal Pendalaman Materi Xiihaifa marsya luthfiaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Notes - 18ME734.Document17 pagesModule 1 Notes - 18ME734.SANTOSH0% (1)
- 2023 Basics and Biopsychosocial Model - Stage 1 PsychologyDocument27 pages2023 Basics and Biopsychosocial Model - Stage 1 Psychologyapi-642709499No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesPlate TectonicsJericho Luiz Sipin RamosNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Literature Review Jennifer RowleyDocument6 pagesConducting A Literature Review Jennifer Rowleyafdtwudac100% (1)
- Lenton CouplersDocument20 pagesLenton CouplersSherief MagdyNo ratings yet
- Sound Absorption Prediction Software: Absorber Is A Computer Program ForDocument1 pageSound Absorption Prediction Software: Absorber Is A Computer Program Forchristian atauje garciaNo ratings yet
- Landform Cards 19 ADocument100 pagesLandform Cards 19 ANina StratukNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument3 pagesProbabilitynoer_rizalNo ratings yet
- Sorting Variables by Using Informative Vectors As A Strategy For Feature Selection in Multivariate RegressionDocument17 pagesSorting Variables by Using Informative Vectors As A Strategy For Feature Selection in Multivariate RegressionALDO JAVIER GUZMAN DUXTANNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Logic - Module 4Document3 pagesPhilosophy and Logic - Module 4Vijanes BeltransNo ratings yet
- Rubrica Writing A2 - B1Document2 pagesRubrica Writing A2 - B1Ivette CepedaNo ratings yet
- The Consistency Approach For The Quality Control of VaccinesDocument5 pagesThe Consistency Approach For The Quality Control of VaccinesauiiiNo ratings yet
- Tech 1 34Document34 pagesTech 1 34Mohamed JaleelNo ratings yet
- Transformation - Making Software Engineering Accountable For SustainabilityDocument8 pagesTransformation - Making Software Engineering Accountable For SustainabilityNICOL FRANCISCA NAVARRO SEPULVEDANo ratings yet
- Mathematics PDFDocument198 pagesMathematics PDFBakari HamisiNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment 1 202020212Document2 pagesGroup Assignment 1 202020212satish chandranNo ratings yet
- DC SystemDocument230 pagesDC Systemsalemg82No ratings yet
Week 3 PolarCoordinates
Week 3 PolarCoordinates
Uploaded by
LULUHBELLE L. CRUZ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views27 pagesThe document discusses polar coordinates and converting between rectangular and polar coordinate systems. It provides examples of converting points between the two systems, as well as examples of analyzing sinusoidal functions by identifying their amplitude, period, phase shift, domain and range based on their equations or graphs.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses polar coordinates and converting between rectangular and polar coordinate systems. It provides examples of converting points between the two systems, as well as examples of analyzing sinusoidal functions by identifying their amplitude, period, phase shift, domain and range based on their equations or graphs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views27 pagesWeek 3 PolarCoordinates
Week 3 PolarCoordinates
Uploaded by
LULUHBELLE L. CRUZThe document discusses polar coordinates and converting between rectangular and polar coordinate systems. It provides examples of converting points between the two systems, as well as examples of analyzing sinusoidal functions by identifying their amplitude, period, phase shift, domain and range based on their equations or graphs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 27
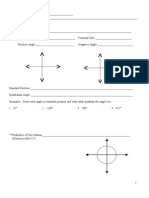
Polar Coordinates
For each point in polar
coordinates given below plot
the point and then give two
additional expressions for the
point, one of which has r > 0
and the other with r < 0.
For each point in polar coordinates given
below plot the point and then give two
additional expressions for the point, one of
which has r > 0 and the other with r < 0.
For each point in polar coordinates given
below plot the point and then give two
additional expressions for the point, one of
which has r > 0 and the other with r < 0.
For each point in polar coordinates given
below plot the point and then give two
additional expressions for the point, one of
which has r > 0 and the other with r < 0.
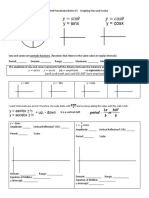
CONVERSION BETWEEN RECTANGULAR AND POLAR COORDINATES
CONVERSION BETWEEN RECTANGULAR AND POLAR COORDINATES
Suppose P is represented in rectangular coordinates as and in
polar coordinates as . Then:
Convert each point in rectangular coordinates given
below into polar coordinates with and .
Convert each point in rectangular coordinates given
below into polar coordinates with and .
Convert each point in rectangular coordinates given
below into polar coordinates with and .
Convert the point from polar coordinates into rectangular
coordinates.
Convert the point from polar coordinates into rectangular
coordinates.
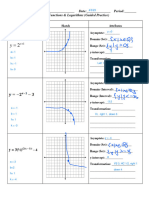
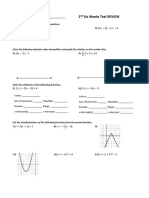
Example 3: Without graphing give the amplitude, period,
phase shift, domain and range for each of the following
functions.
+3
𝑦 =2 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 + (
𝜋
3 )
Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
− 1Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
𝑦 =3 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( 2 𝜃 − 𝜋 ) +5 Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
-1 Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
(
𝑦 =− 𝑠𝑖𝑛 2 𝜃 −
𝜋
3
+2 )
Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
𝑦 =3 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( 4 𝜃+ 𝜋 ) +2 Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
𝑟𝑎𝑝h : 𝑦 = − 2 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜃 − ( )
𝜋 Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
2 Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
𝑟𝑎𝑝h : 𝑦= 4 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( 𝜃 + 𝜋 ) Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
𝑟𝑎𝑝h : 𝑦= 3 𝑠𝑖𝑛 ( 2 𝜃 − 𝜋 ) Amplitude: ________________ Domain:
Period: ________________ ________________
Phase shift:________________ Range: ________________
Vertical Translation: Reflection:
________________ ____________________
Example 4: Write the equation of the cosine function with
the following characteristics:
1. amplitude = 4, period = , phase shift=0
2. amplitude = 1, period =, phase shift=
Example 5: Determine two functions for each sinusoidal function based on the
given graph.
Example 6: Determine two functions for each sinusoidal function based on the
given graph.
Example 7: Determine two functions for each sinusoidal function based on the
given graph.
You might also like
- Measurement, Area, Surface Area and Volume - SeriesJ2 - SDocument10 pagesMeasurement, Area, Surface Area and Volume - SeriesJ2 - SJames Buchan50% (2)
- Intervals From Graphs WorksheetDocument4 pagesIntervals From Graphs WorksheetMcmustacheNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3Document5 pagesPre-Calc CH 4 Review Quiz 4.1-4.3aggieNo ratings yet
- TFN Module 1 & 2Document10 pagesTFN Module 1 & 2A CNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson Three Notes Guided NotesDocument14 pagesModule Seven Lesson Three Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Unit 3 Intro To Trig Functions 1Document19 pagesPrecalculus Unit 3 Intro To Trig Functions 1api-287816312No ratings yet
- 112 Graphing 7.6 7.8 PDFDocument4 pages112 Graphing 7.6 7.8 PDFJavzanlkham VanchinbazarNo ratings yet
- 10 ClassworkDocument2 pages10 Classworktreehouse52906No ratings yet
- Function Lesson 1 FormativeDocument2 pagesFunction Lesson 1 FormativeJack BarbutoNo ratings yet
- Lab 04: Network Theorems: Experiment 04Document7 pagesLab 04: Network Theorems: Experiment 04Umer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument17 pagesCircle TheoremdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- Pre Calc NotesDocument6 pagesPre Calc NotesAditya PaluriNo ratings yet
- Part C-Instructional MaterialsDocument11 pagesPart C-Instructional Materialsapi-326255121No ratings yet
- Surveying 1 Laboratory Elementary and Higher Surveying: Reciprocal LevelingDocument5 pagesSurveying 1 Laboratory Elementary and Higher Surveying: Reciprocal LevelingCarlo Miguel MagalitNo ratings yet
- Notes and Worksheets - Polar FunctionsDocument15 pagesNotes and Worksheets - Polar FunctionsranjidsarhanNo ratings yet
- Week 12 BodePlotsDocument7 pagesWeek 12 BodePlotsAhmad Hassan FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson Two Notes Guided NotesDocument7 pagesModule Seven Lesson Two Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Prefinal ExamDocument3 pagesPrefinal ExamDiamante ArasNo ratings yet
- 2010 Algebra II Trig Review 13.4-13.6Document2 pages2010 Algebra II Trig Review 13.4-13.6Alice DwyerNo ratings yet
- U08 D10Classwork+B-+Domain+and+Range+Inequality+vs+Interval+NotationDocument4 pagesU08 D10Classwork+B-+Domain+and+Range+Inequality+vs+Interval+Notationmelissa blancoNo ratings yet
- Ps1calculus Domain and RangeDocument3 pagesPs1calculus Domain and Rangepao.felix1021No ratings yet
- Analysis& Approaches Graphing Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Day 2Document6 pagesAnalysis& Approaches Graphing Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Day 2ethanNo ratings yet
- Module Seven Lesson One Notes Guided NotesDocument25 pagesModule Seven Lesson One Notes Guided NotesJazmyn DavisNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Review With Sample ProblemsDocument16 pagesMath 2 Review With Sample Problemsapi-297398947No ratings yet
- Lab#2 - Cie 111Document11 pagesLab#2 - Cie 111Biblee ChasNo ratings yet
- Pairs of Angles Lesson 1Document2 pagesPairs of Angles Lesson 1api-338888247No ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewDocument12 pagesGR 10 ReviewHoda RagabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 NotessmwhitmanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus HandoutDocument4 pagesPre-Calculus Handoutluluhbelle cruzNo ratings yet
- Mathlab 9Document2 pagesMathlab 9fftemmmNo ratings yet
- Geo Unit 1Document25 pagesGeo Unit 1Grace QiuNo ratings yet
- Formula List For AP Calculus BCDocument6 pagesFormula List For AP Calculus BCRuchi GuptaNo ratings yet
- APC 4.5 Notes Day 1 2018Document2 pagesAPC 4.5 Notes Day 1 2018Krishna KolluriNo ratings yet
- ANGLESDocument4 pagesANGLESCatherine GaloteraNo ratings yet
- I. Basic Information: St. Paul University System Gen. Luna ST.Document6 pagesI. Basic Information: St. Paul University System Gen. Luna ST.Ma Faustina GeronaNo ratings yet
- Oscillating Mass Lab: Review: Characterizing A SpringDocument8 pagesOscillating Mass Lab: Review: Characterizing A SpringFrancis DayanNo ratings yet
- Graphing Ellipse With Center at (H, K)Document3 pagesGraphing Ellipse With Center at (H, K)Diaz KaneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercises No.7Document4 pagesLaboratory Exercises No.7Rica Mae Garcia OberoNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Task Topic 4 - 3 CosmologyDocument2 pagesAstronomy Task Topic 4 - 3 CosmologyprabathoopsNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigDocument7 pagesAlgebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigSmart StudyManNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Supplementary Angles 90: If The Sum of Their Measures Equal ToDocument1 pageComplementary and Supplementary Angles 90: If The Sum of Their Measures Equal ToGlydel Mae Villamora - SaragenaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewDocument2 pages2nd Six Weeks Test ReviewAbigail WileyNo ratings yet
- Daniel R. Aguinaldo National High SchoolDocument2 pagesDaniel R. Aguinaldo National High SchoolChris TinNo ratings yet
- Weirs Notch Report PDFDocument62 pagesWeirs Notch Report PDFMaxwell RejilNo ratings yet
- Nets and Surface Area Class ActivityDocument4 pagesNets and Surface Area Class ActivitySTEPHEN MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GeoTest PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 GeoTest PDFStephanie ValienteNo ratings yet
- Online Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDocument8 pagesOnline Lab - Me Lab1 Expt 2 Area MeasurementDessa GuditoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 NotesDocument2 pages1.4 NotesHetti arachchige pamith PereraNo ratings yet
- 9 16 2016 Domain RangeDocument1 page9 16 2016 Domain Rangeapi-327140356No ratings yet
- Form Operasional Genset Kemenko Marves Perkins 1500 KvaDocument1 pageForm Operasional Genset Kemenko Marves Perkins 1500 KvaArdee LEDNo ratings yet
- 10.2 - 10.4 - Characteristics - and - Translations - of - Functions - Practice - Worksheet (1) DoneDocument2 pages10.2 - 10.4 - Characteristics - and - Translations - of - Functions - Practice - Worksheet (1) DonesohiNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision BookletDocument4 pagesWaves Revision BookletAsif Zubayer PalakNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Learning Targets Sheet NewDocument3 pagesUnit 8 Learning Targets Sheet Newapi-704050165No ratings yet
- Algebra Two NotesDocument12 pagesAlgebra Two NotesShiline NguyenNo ratings yet
- St. Marks: Child Development Center, IncDocument3 pagesSt. Marks: Child Development Center, IncNoli CalderonNo ratings yet
- Test On Sections 1-1, 1-2, and 1-4 (Pre-Calc Honors)Document5 pagesTest On Sections 1-1, 1-2, and 1-4 (Pre-Calc Honors)RiveraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 03 Math 8Document2 pagesQuiz 03 Math 8Jeddah Joy OperarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Vocabulary Term Definition ExampleDocument13 pagesChapter 1: Vocabulary Term Definition ExampleScotty MalcolmNo ratings yet
- Elt Systems Service Information Letter: Date: May 6, 2020 Number: SIL4013Document4 pagesElt Systems Service Information Letter: Date: May 6, 2020 Number: SIL4013Nitesh PalNo ratings yet
- Mw61a Ti All Sv6.01a enDocument11 pagesMw61a Ti All Sv6.01a enpradeepNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills:: Types of Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument9 pagesListening Skills:: Types of Non-Verbal CommunicationMustafa DagiaNo ratings yet
- NewSmartTransformerStation STS 6000K H1Document2 pagesNewSmartTransformerStation STS 6000K H1Juan BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Market Systems Development: Sustainable Growth For EveryoneDocument53 pagesInclusive Market Systems Development: Sustainable Growth For EveryoneFarai MandisodzaNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Second Law: Driving Question - ObjectiveDocument6 pagesNewton'S Second Law: Driving Question - ObjectiveRKNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday Lesson Plan Copy GRADE ONEDocument5 pagesCatch Up Friday Lesson Plan Copy GRADE ONEJancel Añasco Tabliga100% (1)
- Form 4 SowDocument4 pagesForm 4 SowNAJWA ZAHIDAH BINTI RAZALI MoeNo ratings yet
- DTC Production Design 101.4 - MOODBOARD-AFDA.2.0Document17 pagesDTC Production Design 101.4 - MOODBOARD-AFDA.2.0NatoNo ratings yet
- Princeton University Press Eros The BittersweetDocument5 pagesPrinceton University Press Eros The BittersweetI.M.C.No ratings yet
- 08-Risk Control TechniqueDocument15 pages08-Risk Control TechniqueMubarak Noor AzliNo ratings yet
- Soal Pendalaman Materi XiiDocument16 pagesSoal Pendalaman Materi Xiihaifa marsya luthfiaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Notes - 18ME734.Document17 pagesModule 1 Notes - 18ME734.SANTOSH0% (1)
- 2023 Basics and Biopsychosocial Model - Stage 1 PsychologyDocument27 pages2023 Basics and Biopsychosocial Model - Stage 1 Psychologyapi-642709499No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesPlate TectonicsJericho Luiz Sipin RamosNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Literature Review Jennifer RowleyDocument6 pagesConducting A Literature Review Jennifer Rowleyafdtwudac100% (1)
- Lenton CouplersDocument20 pagesLenton CouplersSherief MagdyNo ratings yet
- Sound Absorption Prediction Software: Absorber Is A Computer Program ForDocument1 pageSound Absorption Prediction Software: Absorber Is A Computer Program Forchristian atauje garciaNo ratings yet
- Landform Cards 19 ADocument100 pagesLandform Cards 19 ANina StratukNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument3 pagesProbabilitynoer_rizalNo ratings yet
- Sorting Variables by Using Informative Vectors As A Strategy For Feature Selection in Multivariate RegressionDocument17 pagesSorting Variables by Using Informative Vectors As A Strategy For Feature Selection in Multivariate RegressionALDO JAVIER GUZMAN DUXTANNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Logic - Module 4Document3 pagesPhilosophy and Logic - Module 4Vijanes BeltransNo ratings yet
- Rubrica Writing A2 - B1Document2 pagesRubrica Writing A2 - B1Ivette CepedaNo ratings yet
- The Consistency Approach For The Quality Control of VaccinesDocument5 pagesThe Consistency Approach For The Quality Control of VaccinesauiiiNo ratings yet
- Tech 1 34Document34 pagesTech 1 34Mohamed JaleelNo ratings yet
- Transformation - Making Software Engineering Accountable For SustainabilityDocument8 pagesTransformation - Making Software Engineering Accountable For SustainabilityNICOL FRANCISCA NAVARRO SEPULVEDANo ratings yet
- Mathematics PDFDocument198 pagesMathematics PDFBakari HamisiNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment 1 202020212Document2 pagesGroup Assignment 1 202020212satish chandranNo ratings yet
- DC SystemDocument230 pagesDC Systemsalemg82No ratings yet