Professional Documents
Culture Documents
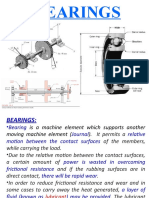
Roller Bearings
Roller Bearings
Uploaded by
21B65A0347 THARIGOPULA SAI KUMAR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views21 pagesRolling contact bearings use balls or rollers to reduce friction between moving parts. Common types include ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings. Design considerations for selecting the proper bearing include load type and magnitude, speed, environment, and desired life. Materials for balls and races include high carbon chromium steel for strength. Lubrication is important to reduce wear and prevent corrosion. Load ratings and calculations of equivalent load determine the bearing size needed to support the application loads over the required life.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRolling contact bearings use balls or rollers to reduce friction between moving parts. Common types include ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings. Design considerations for selecting the proper bearing include load type and magnitude, speed, environment, and desired life. Materials for balls and races include high carbon chromium steel for strength. Lubrication is important to reduce wear and prevent corrosion. Load ratings and calculations of equivalent load determine the bearing size needed to support the application loads over the required life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views21 pagesRoller Bearings
Roller Bearings
Uploaded by
21B65A0347 THARIGOPULA SAI KUMARRolling contact bearings use balls or rollers to reduce friction between moving parts. Common types include ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings. Design considerations for selecting the proper bearing include load type and magnitude, speed, environment, and desired life. Materials for balls and races include high carbon chromium steel for strength. Lubrication is important to reduce wear and prevent corrosion. Load ratings and calculations of equivalent load determine the bearing size needed to support the application loads over the required life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
SYLLABUS-UNIT-2
• Rolling contact Bearings: Ball
and Roller bearings- Static
load- Dynamic load-
Equivalent radial load-
Design and selection of Ball
&Roller Bearings.
Rolling contact bearings
• Rolling contact bearings are also called anti -friction bearings or simply
ball bearings.
• Rolling elements, such as balls or rollers, are introduced between the
surfaces that are in relative motion.
• Sliding friction is replaced by rolling friction.
• Applications: Automobiles,Agriculture m/c,Fans ,Motors,M/ c
tools,Air-crafts.
Types of Rolling contact Bearings
• Two types.
• Ball bearings & Roller bearings.
• Rolling elements are in the form of spherical
balls.
• Rolling elements are in the form of roller,
which may be cylindrical,conical,spherical or
needle form.
Ball and Roller Bearing Elements
Rolling contact Bearing-Material
• Ball bearings (inner ring, outer ring &balls)High
carbon chromium steel-is through hardened to
Rockwell C 58-63.
• Factors to be considered: Space, type &amount of
load,Speed,alignment,Environmental conditions.
• Main components – Outer ring,Inner ring,Balls or
rollers, retainers.
• Material-Ballraces made of high carbon chromium
steel for high compressive strength.
• Cages- Seperators low carbon steel .
Roller bearings-materials
• Rolling elements & races are subjected to high local stresses
of varying magnitude, therefore the material(steel) should
be of high quality. The balls are made of high carbon
chromium steel. Roller bearings are usually fabricated of
case hardened steels- hardened to Rockwell C 58-63.
• The balls are manufactured by hot forging on hammers from
steel rods. They are then heat-treated, ground &polished
• Ball separators(cages) made of low carbon steel.
• Seals of made of low carbon steel. Shields that are used to
retain grease and to prevent chips, dirt made of low .c.
steels.
Types of Rolling contact Bearings
• Deep groove.
• Cylindrical roller.
• Angular contact.
• Self –aligning.
• Spherical roller.
• Taper roller bearing.
• Thrust ball bearing.
Types of Roller Bearings
• Cylinder roller bearing –have shorter rollers guided in a cage.
Relatively rigid against radial motion. They have low
coefficient of friction. Used in high speed service.
• Spherical roller bearing: self –aligning bearing. Self –aligning
feature is achieved by grinding one of the races in the form
of sphere.it can tolerate angular mis alignment of +/_1
1/2deg.
• Needle roller bearing: relatively slender.used when heavy loads.
• Tapered roller bearing: the rollers and race ways are
truncated .capable of carrying both radial and thrust loads.
Lubrication of Ball & Roller bearing
-The main purpose of lubrication is:
-To reduce friction &wear of the parts.
-To prevent rusting or corrosion of the bearing
surfaces.
-To protect the bearing surfaces from water &
dirt.
-To dissipate the heat.
Lubricating material for Ball & Roller
Bearings
Oil, light grease.
Pure mineral oil, Calcium –base Grease.
If moisture content, Potassium and Sodium
based grease used.
Advantage of grease is that it forms a seal
to keep out dirt or any foreign substance.
Classifications of Roller Bearings
Classification based on the nature of
loads
• Single row deep groove ball bearing-radial loads
&can carry thrust loads in either direction.
• Double row ball bearings-radial and angular
contact between the balls and races.
• Angular contact ball bearing-to resist combined
radial and thrust loads depending on contact
angle. Bearings having large contact angles can
support heavier thrust loads.
• Self-aligning ball bearing-
Standard designation of ball bearing
Selection of Bearing size
• Criteria for selection :-
• load carrying Capacity
• Life
• Reliability the Bearing
Types of roller bearing
Design terms of bearing
(C0):depends on bearing material, no .of
Static load rating
rows of rolling elements, bearing contact angle, ball
or roller diameter.
When the bearings are to rotate at very slow
speeds or to be stationary under load.
When heavy shock loads at short duration acting on
a rotating bearing.
Basic dynamic load rating(C): is used for dynamically stressed
bearings i.e a bearing which is rotating under load.
Load rating of a bearing
• Basic Static load rating( ): is the load acting on a non- rotating bearing
under which a permanent deformation should appear in balls or race ways.
• Basic dynamic load rating(C): is the actual or real load acting on the rolling
contact bearing during running conditions.
• Equivalent load(P): defined as the constant stationary load which is applied
to a bearing with rotating inner ring & stationary outer ring would give the
same life as that which the bearing would attain under the actual condition
of load and rotation.
• P=(V. X. +Y. )S
• P=equivalent load, V=Race rotation factor,
• Fr=radial load, Fa= actual load,
• X=radial load factor ,Y=axial load factor,
• S=service factor.
Life of the Rolling bearing
• The life of a rolling is defined as the number of revolutions
which the bearing is capable of enduring before the first
evidence of fatigue, i.e developed in the material of either rings
or rolling elements.
• The dynamic load carrying capacity recommended in
catalogues is based on life attained or exceed by 90% of
identical bearings under identical working conditions. This is
called normal or rated life.
• The rated life is based on 90% survival rate or 10% failure rate.
• To meet the requirements of manufactures ,they provide
reliability factors.
Reliability and load carrying capacity
Selection procedure for rolling bearing
• Determine the radial and axial forces from the
working conditions.
• Select the type of bearing such as Ball or
Roller bearing etc. from load conditions.
• Calculate the working life of bearing.
• Find the dynamic load capacity ‘C’
• C = XP
• L=life in hrs*r.p.m*60/10^6
You might also like
- Automotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MoreFrom EverandAutomotive Machining: A Guide to Boring, Decking, Honing & MoreRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Nissan Com Engine Qg15 Sfi System Ecu of Terminal Pinout DiagramDocument5 pagesNissan Com Engine Qg15 Sfi System Ecu of Terminal Pinout DiagramRodrigo Salas62% (13)
- TM 10-3930-669-20 Forklift Truck 6K Drexel R60SL-DC Part 1Document408 pagesTM 10-3930-669-20 Forklift Truck 6K Drexel R60SL-DC Part 1Advocate100% (1)
- Service Sm2000 enDocument32 pagesService Sm2000 enTony TarzNo ratings yet
- Hi-7 and Hi-8 Race Ignition Systems: Battery ConsiderationsDocument8 pagesHi-7 and Hi-8 Race Ignition Systems: Battery ConsiderationssphinxxxxNo ratings yet
- Bearings: IndexDocument9 pagesBearings: IndextanmayNo ratings yet
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Yanmar 6AYM WET Datasheet 3Document2 pagesYanmar 6AYM WET Datasheet 3adamzlamet33% (3)
- 1971 Chevy Overhaul ManualDocument505 pages1971 Chevy Overhaul ManualCharlie Moretti100% (1)
- BearingsDocument35 pagesBearingsmahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact Bearings PDFDocument15 pagesRolling Contact Bearings PDFnaufal labibNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Me-305: TH THDocument118 pagesMachine Design Me-305: TH THTAHAAHMED KHANNo ratings yet
- DMM 2 JBDocument27 pagesDMM 2 JB21B65A0347 THARIGOPULA SAI KUMARNo ratings yet
- Bearing IntroductionDocument62 pagesBearing IntroductionsbkulkNo ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingDocument31 pagesRolling Contact Bearingpotnuru JaivanthNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument63 pagesBearingsYeabsraNo ratings yet
- Bearings: BEARING: It Is Device WhichDocument23 pagesBearings: BEARING: It Is Device WhichPranjal Dogra100% (1)
- Rolling Bearing: by Dr. Atul KumarDocument25 pagesRolling Bearing: by Dr. Atul KumarAtul KumarNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument48 pagesBearingsgaurav tiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Bearing PDFDocument41 pagesChapter 4 Bearing PDFMaitri ViratNo ratings yet
- Bearings and Selection of Bearing From Manufacturers CatalogDocument29 pagesBearings and Selection of Bearing From Manufacturers CatalogUddhav S100% (1)
- 1 3 Rolling Contact Bearings RNR 25012021Document31 pages1 3 Rolling Contact Bearings RNR 25012021potnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- Group#02Document29 pagesGroup#02amir zia100% (1)
- Roller Bearings DME M046Document22 pagesRoller Bearings DME M046prathamchawla1301No ratings yet
- Rolling Contact BearingsDocument37 pagesRolling Contact BearingsErik BaltssNo ratings yet
- Bearing Selection: IntrdouctionDocument4 pagesBearing Selection: IntrdouctionMuneeb JavedNo ratings yet
- BearingDocument41 pagesBearingTejesh ShamiNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearing Design Classes 2021Document75 pagesBall Bearing Design Classes 2021Apurba barmanNo ratings yet
- Dte - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesDte - Rolling Contact Bearingspotnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- Also Called Anti Friction Bearing (Misnomer) Consists 4 Parts 2. Outer Race 3. Rolling Elements (Balls, Roller, Needle) 4. CageDocument37 pagesAlso Called Anti Friction Bearing (Misnomer) Consists 4 Parts 2. Outer Race 3. Rolling Elements (Balls, Roller, Needle) 4. Cagerahil100% (1)
- 4.0 Shaft, Axle & BearingDocument75 pages4.0 Shaft, Axle & BearingphyrdowsNo ratings yet
- Types, Installation Principles, Maintenance.: Port Service Basic TrainingDocument30 pagesTypes, Installation Principles, Maintenance.: Port Service Basic TrainingMouwadine MoussaNo ratings yet
- Antifriction Bearings - 230131 - 143447Document61 pagesAntifriction Bearings - 230131 - 143447hassan aliNo ratings yet
- Bearings: Heart of The MachineDocument51 pagesBearings: Heart of The MachinevarunNo ratings yet
- Bearing NomenclaturDocument64 pagesBearing NomenclaturSachin DixitNo ratings yet
- Bearings: By: Jagdish Singh Mehta Uttrakhand Graphic Era Hill UniversityDocument61 pagesBearings: By: Jagdish Singh Mehta Uttrakhand Graphic Era Hill UniversityJagdish Singh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rolling Element Bearing-16!9!21Document38 pagesKami Export - Rolling Element Bearing-16!9!21Dr Atul WaghmareNo ratings yet
- What Loads or Movements Will The Bearing Need To Support or Allow?Document1 pageWhat Loads or Movements Will The Bearing Need To Support or Allow?SarvagnaMNNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Bearing & It's Types - For StudentsDocument29 pagesLecture-Bearing & It's Types - For StudentsMuhammad Junaid RasoolNo ratings yet
- Rolling BearingDocument39 pagesRolling BearingashaNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore: Name: Hanzlah Naseer Roll No:2018-Me-136 Submitted To: Sir Ahmed NaveedDocument19 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology, Lahore: Name: Hanzlah Naseer Roll No:2018-Me-136 Submitted To: Sir Ahmed NaveedHanzlah NaseerNo ratings yet
- BearingDocument1 pageBearingproxywarNo ratings yet
- Section 5Document80 pagesSection 5pattan madhuNo ratings yet
- Sliding Contact and Rolling Contact BearingDocument45 pagesSliding Contact and Rolling Contact BearingorgasandreyNo ratings yet
- Bearings - Seals V 3.3Document115 pagesBearings - Seals V 3.3Martin Andre SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Rolling BearingsDocument22 pagesRolling BearingsFully YoursNo ratings yet
- Bearings - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument34 pagesBearings - Rolling Contact BearingsRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Bearings-An Introduction-NPTIDocument59 pagesBearings-An Introduction-NPTISakthi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Bearings: Nizwa College of TechnologyDocument22 pagesBearings: Nizwa College of Technologyparth bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: 1.1 Bearing HistoryDocument24 pagesTechnical Information: 1.1 Bearing HistoryMohammed KapasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document17 pagesChapter 6mohamedbadawyNo ratings yet
- Cuscinetti Bearings-Engineering CollegeDocument23 pagesCuscinetti Bearings-Engineering CollegeantoniodellisantiNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearing: Ball (Bearing) Rolling-Element Bearing Balls Bearing Radial AxialDocument6 pagesBall Bearing: Ball (Bearing) Rolling-Element Bearing Balls Bearing Radial AxialMuhamad PriyatnaNo ratings yet
- Spherical and Spherical Thrust BearingsDocument21 pagesSpherical and Spherical Thrust BearingsSumit GhosalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document27 pagesLecture 6Carlos Aguilar RodríguezNo ratings yet
- M.E.I.M. 2017 365 Powder Bearings (PM)Document28 pagesM.E.I.M. 2017 365 Powder Bearings (PM)rohanNo ratings yet
- Bearing GuideDocument176 pagesBearing GuideJay_CRENo ratings yet
- Plant MaintenanceDocument37 pagesPlant MaintenanceAli khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Antifriction BearingsDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Antifriction BearingsTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document11 pagesWa0001onkar nikamNo ratings yet
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsFrom EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Turning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.From EverandTurning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.No ratings yet
- Descriptive Pamphlet of the Richmond Mill Furnishing WorksFrom EverandDescriptive Pamphlet of the Richmond Mill Furnishing WorksNo ratings yet
- How To Mountain Bike: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Mountain BikingFrom EverandHow To Mountain Bike: Your Step-By-Step Guide To Mountain BikingRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesFrom EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 107-b00 - Manual OperacionDocument12 pages107-b00 - Manual OperacionJuan David Triana SalazarNo ratings yet
- Steering System Principles: Chapter ObjectivesDocument23 pagesSteering System Principles: Chapter ObjectivesJithendra SaiNo ratings yet
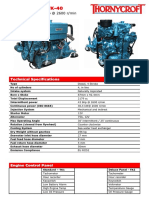
- Thornycroft Tk-40: 4-Cylinders in Line 43 BHP at 2600 R/minDocument2 pagesThornycroft Tk-40: 4-Cylinders in Line 43 BHP at 2600 R/minGilnad WilsonNo ratings yet
- Offshore Piping Design CriteriaDocument1 pageOffshore Piping Design CriteriaDhakshina K100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Cooling System: 1. SpecificationsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Cooling System: 1. SpecificationsMaz Ariez EkaNo ratings yet
- Dominar 400 Spare Parts CatalogueDocument82 pagesDominar 400 Spare Parts CatalogueAkshayaNo ratings yet
- Engine Analysis-Capstone ReportDocument13 pagesEngine Analysis-Capstone ReportAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Skoda Octavia Mk1 04 Heating Air ConditioningDocument118 pagesSkoda Octavia Mk1 04 Heating Air Conditioningdaliborjaro80% (5)
- Conquest Lathe Manual PDFDocument47 pagesConquest Lathe Manual PDFHaitham Mohammad100% (1)
- Lighting & Power Layout Vicinity Map: Chedule of LoadsDocument1 pageLighting & Power Layout Vicinity Map: Chedule of Loadsjohndean urbanozoNo ratings yet
- Small Engine SimulationDocument20 pagesSmall Engine SimulationAhmed SajitNo ratings yet
- Anka Catalogue 2011 WebDocument352 pagesAnka Catalogue 2011 WebMustafa Serdar YAZICINo ratings yet
- Air XXXXDocument2 pagesAir XXXXardianalimNo ratings yet
- OM673L3Document34 pagesOM673L3dromascoNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Spare Part List FOR: JULY - 2011 PUBLICATION NO. 6H.561.11.0.01Document79 pagesIllustrated Spare Part List FOR: JULY - 2011 PUBLICATION NO. 6H.561.11.0.01Sunil ThackerNo ratings yet
- Steering and Fan System 844 Wheel Tractor Hydraulic SchematicDocument2 pagesSteering and Fan System 844 Wheel Tractor Hydraulic SchematicAlexis ReyesNo ratings yet
- Eee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - AssignmentDocument4 pagesEee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - AssignmentchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- M250-C47E Turboshaft: Powering The World's Newest Light HelicoptersDocument2 pagesM250-C47E Turboshaft: Powering The World's Newest Light HelicoptersOleksandr BalychevNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Turbine, Generator and Governing SystemDocument21 pagesModeling of Turbine, Generator and Governing SystemdanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Drive Axle and Differential Assembly Repair (Wet Brake - NMHG)Document66 pagesDrive Axle and Differential Assembly Repair (Wet Brake - NMHG)Dashzeveg BayrsaikhanNo ratings yet
- VSP 266 - Lycoming Service Instruction No. 1498B, Recommended Engine Procedures For Purge of Vapor During Ground Operations' 2019-01-10 RecomendationDocument3 pagesVSP 266 - Lycoming Service Instruction No. 1498B, Recommended Engine Procedures For Purge of Vapor During Ground Operations' 2019-01-10 RecomendationAlexander GraytrousesNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine BearingsDocument44 pagesSteam Turbine Bearingsbalajieee88100% (1)
- Kenr6225 01Document68 pagesKenr6225 01Boris BabicNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Induction Motor and Special MachinesDocument29 pagesSingle Phase Induction Motor and Special MachinesAlisha DasNo ratings yet