Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Ergun Manto Lodos
Formula Ergun Manto Lodos
Uploaded by
ReinaldoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Ergun Manto Lodos
Formula Ergun Manto Lodos
Uploaded by
ReinaldoCopyright:
Available Formats
H2 O
CE4003
Water Treatment
Hydraulics of Filtration
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Filtration Hydraulics
• Filter Design
– Very empirical
• Modelling Removal
– Need pilot plant tests
– No generally applicable models
• Head loss and backwashing
– Some things can be predicted
– Need pilot tests for effect of deposition
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Head Loss in a Clean Filter
Kozeny Equation (Kozeny-Carmen)
Hagen-Poiseuille Equation
Hydraulic radius
For a filter
Hydraulic radius = pore volume/grain surface area
CE4003 -Water Treatment
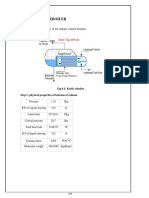
H2 O Hydraulic radius for a Filter
Consider unit volume of filter
Pore volume =
V : volume of one grain
A : surface area of one grain
N : number of grains per unit volume
Solid volume = 1-
Total Grain surface = NA
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Kozeny Equation
K is a constant, typically about 4-5
For spheres of diameter dg
If sphericity is
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Kozeny Equation
Valid for Reynolds number less than 10
For a uniform bed of depth L
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Stratified bed
d1 p1L
d2 p2L
dn pnL
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Alternative form of Kozeny Equation
ff : friction factor
Ergun equation
Stratified bed
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Example 1
Data: Kozeny Equation
L 0.67 m
K 4.5
0.00102 Nms-2
998.2 kgm-3
g 9.81ms-2
0 0.4
0.85 Ergun Equation
dg 0.0004 m
u 0.001389 ms-1
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Backwashing
Backwashing fluidises the bed
Head loss counterbalanced by effective weight of bed
A : X-sectional area
Le : Expanded depth of bed
e : porosity of expanded bed
g : density of grains
Effective weight of fluidised bed = effective weight of packed bed
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Backwashing
Pressure = force per unit area
Using the Ergun equation
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Alternative Procedure
Fair & Geyer
Porosity of expanded bed can be related to settling velocity vt
Need to calculate terminal settling velocity
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Example
Data: Ergun Equation
L 0.67 m
K 4.5 u = 0.008887 ms-1
0.00102 Nms-2 = 32 mh-1
998.2 kgm-3
g 9.81ms-2 Fair & Geyer
0 0.4
u = 0.009879 ms-1
0.85 = 35.6 mh-1
dg 0.0004 m
u 0.001389 ms-1
g 2650 kgm-3
e 0.65
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Design Considerations
• Aim for expanded bed porosity of 0.6 to 0.7
• Expanded depth 1.2 to 1.55 times original
• Ensure no loss of media
• Choose size and densities in multimedia to
minimize intermixing.
• Loading Rates
– < 8 g Al/(m2h)
– < 6 g Al/(m2h) for low alkalinity water
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Loading Rates
• Often expressed in terms of
– g Al/(m2h)
• Filter loading = coagulant dose x filtration rate
• 1 g/m3 Al = 6.3 g/m3 Al2(SO4)3
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Stratified Bed - Backwashing
• Minimum fluidisation velocity
– Calculate fluidisation velocity for each fraction
– Take maximum value
• Bed Expansion
– Calculate expanded bed length for each fraction
– Add up values
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Example
Packed bed porosity = 0.42 Backwash velocity 40 m/h
Packed bed depth = 0.70 m
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Minimum fluidisation velocity
Maximum fluidisation velocity will be for largest grains
Put e=0.42
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Bed Expansion
Backwash velocity = 40 m/h =0.01111 m/s
Size 0.78
Fraction 18%
vt 0.135 m/s
L0 = 0.18 x 0.70 = 0.126 m
Expanded porosity
Expanded bed length
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Bed Expansion
Size 0.66
Fraction 59%
vt 0.115 m/s
L0 = 0.59 x 0.70 = 0.413 m
Expanded porosity
Expanded bed length
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Bed Expansion
Size 0.55
Fraction 23%
vt 0.095 m/s
L0 = 0.23 x 0.70 = 0.161 m
Expanded porosity
Expanded bed length
CE4003 -Water Treatment
H2 O Totals
Expanded bed depth = 0.173 + 0.596 + 0.248 = 1.017
Expanded porosity
Expanded depth ratio
CE4003 -Water Treatment
You might also like
- Tube Settler - CalculationDocument3 pagesTube Settler - CalculationJai Kumar89% (18)
- KST ServoGun Basic 31 enDocument214 pagesKST ServoGun Basic 31 enRáfaga CoimbraNo ratings yet
- Tank Sizing CalculationDocument13 pagesTank Sizing CalculationMythili BysaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Hydraulic ConductivityDocument31 pages7 Hydraulic ConductivityDarya Memon100% (2)
- 123Document7 pages123Jennifer Damasco100% (2)
- Azenkot A. Irrigation DesignDocument86 pagesAzenkot A. Irrigation DesignJay MartinNo ratings yet
- EPC Challenges and Hot Topics - Huawei SingleEPC Solution - QI Workshop 12July2011-Part1 PDFDocument64 pagesEPC Challenges and Hot Topics - Huawei SingleEPC Solution - QI Workshop 12July2011-Part1 PDFFiras Ibrahim Al-Hamdany100% (1)
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument11 pagesFalling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportLee Z QiNo ratings yet
- H H T T A Al K Ty Permeabili: 3.0 TheoryDocument9 pagesH H T T A Al K Ty Permeabili: 3.0 TheorycrizelNo ratings yet
- SEDIMENTATION PresentationDocument45 pagesSEDIMENTATION PresentationShai Sta CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Input Required Data in Yellow Field OnlyDocument5 pagesInput Required Data in Yellow Field OnlyKrishna PATELNo ratings yet
- Double Effect EvapDocument32 pagesDouble Effect EvapJubell MogoteNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability Test Lab ReportDocument8 pagesFalling Head Permeability Test Lab Reportmr_sam91100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document40 pagesChapter 4Addison Juttie100% (1)
- Falling Head PermeabilityDocument13 pagesFalling Head PermeabilitySitiNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control Technology - FinalDocument28 pagesAir Pollution Control Technology - FinalBobNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2 Last Date of Submission: 14 April, 2014Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2 Last Date of Submission: 14 April, 2014Joy RavalNo ratings yet
- Anion ExchengerDocument12 pagesAnion Exchengerdewi permatasari p.aNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering (New) PDFDocument3 pagesChemical Engineering (New) PDFAman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 pagesFalling Head Permeability TestFaeez Zain83% (6)
- Groundwater Basics: (Calculation)Document16 pagesGroundwater Basics: (Calculation)Rahat fahimNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangDocument19 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangValium MorphineNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityRîkèñ PâtélNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Engineering Assignment-Week 3 Number of Questions: 12 Total Mark: 12 X 1 12Document7 pagesHydraulic Engineering Assignment-Week 3 Number of Questions: 12 Total Mark: 12 X 1 12gowricivilNo ratings yet
- Where, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedDocument43 pagesWhere, The Temperature Ratio, Capacity Ratio, R A Value of 0.8 Is Generally Not AcceptedAditya DeokarNo ratings yet
- Energy Loss Due To Friction in A PipelineDocument7 pagesEnergy Loss Due To Friction in A PipelineAbdullah al-amerNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Guid To Design of Evaporator PRDocument40 pagesToaz - Info Guid To Design of Evaporator PRDivyamNo ratings yet
- Geo TechnicalDocument105 pagesGeo TechnicalSigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Osborne Reynold ApparatusDocument10 pagesExp 3 Osborne Reynold ApparatusnileshNo ratings yet
- Ce467 Fall 2019 2020finalDocument3 pagesCe467 Fall 2019 2020finalfarajelmabroukNo ratings yet
- Report Salma Ahmed NewDocument6 pagesReport Salma Ahmed NewSuhaila AhmedNo ratings yet
- PPP 5Document4 pagesPPP 5Smit patelNo ratings yet
- Water Adsorption Desorption On Aluminum SurfaceDocument6 pagesWater Adsorption Desorption On Aluminum SurfacemakfirsefaNo ratings yet
- ProbSet-5-Thermodynamics-and-FluidsansDocument6 pagesProbSet-5-Thermodynamics-and-FluidsansdiegoNo ratings yet
- Ie5b02555 Si 001Document15 pagesIe5b02555 Si 001Akshay PatelNo ratings yet
- Iecep - Geas MCQDocument11 pagesIecep - Geas MCQMel Kee100% (1)
- For Online Practice Exam Visit Us atDocument12 pagesFor Online Practice Exam Visit Us atscribd scribdNo ratings yet
- EVAPORATIONDocument52 pagesEVAPORATIONRica Marie MarilaoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics (Water Distribution System)Document11 pagesHydraulics (Water Distribution System)Saurav GhimireNo ratings yet
- Quizzers EliminationDocument63 pagesQuizzers EliminationFuture HazeNo ratings yet
- Falling Head Permeability TestDocument9 pagesFalling Head Permeability TestPasindu MalithNo ratings yet
- Name of Work:: NTR Telugu Ganga Project Package - 12 Design ReportDocument15 pagesName of Work:: NTR Telugu Ganga Project Package - 12 Design ReportVaraPrasadNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Transport ProcessesDocument3 pagesExercise - Transport ProcessesJan Mark FongfarNo ratings yet
- Abstraction of PrecipitationDocument36 pagesAbstraction of PrecipitationRiot AyaseNo ratings yet
- Cive 514 Exam Cheat SheatDocument10 pagesCive 514 Exam Cheat SheatKhumo Ezekiel MoraNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger1Document19 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger1Lily NurdianaNo ratings yet
- 21CH54Document6 pages21CH54RochakNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science and Engineering: Baltazar, Daniel Janz Envi - A41Document4 pagesEnvironmental Science and Engineering: Baltazar, Daniel Janz Envi - A41Lucienne IrianaNo ratings yet
- Therefore The Required Heat Transfer Area, A 303.44 m2: in Out in OutDocument7 pagesTherefore The Required Heat Transfer Area, A 303.44 m2: in Out in OutHsein WangNo ratings yet
- Broad Crested WeirDocument7 pagesBroad Crested Weirrancid100% (1)
- Buoyancy ProblemsDocument20 pagesBuoyancy ProblemsairaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Pumps and Hydraulics: Instructor GuideDocument9 pagesBasics of Pumps and Hydraulics: Instructor Guideعمار ياسرNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1Marcky Reacher100% (1)
- Feed Drum/ Vessel General Design Considerations Basis or AssumptionsDocument9 pagesFeed Drum/ Vessel General Design Considerations Basis or AssumptionsLouie GresulaNo ratings yet
- LE2 Review PDFDocument2 pagesLE2 Review PDFJulian de LaraNo ratings yet
- Ground Water HydrologyDocument18 pagesGround Water HydrologyChanako DaneNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 5: Evaporation & TranspirationDocument20 pagesHydrology 5: Evaporation & TranspirationAve de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Design of An Absorption Tower For The Separation of Acrylonitrile in - IndustryDocument9 pagesDesign of An Absorption Tower For The Separation of Acrylonitrile in - IndustryLouell Nikki HipulanNo ratings yet
- Hydro 2 Evaporation LectureDocument19 pagesHydro 2 Evaporation Lecturebsnow5325No ratings yet
- Case Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesFrom EverandCase Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesNo ratings yet
- Conbraco LP Sight Glasses PDFDocument16 pagesConbraco LP Sight Glasses PDFRICARDO MAMANI GARCIANo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management SystemDocument6 pagesRelational Database Management SystemYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- App 34Document4 pagesApp 34kagisokhoza000No ratings yet
- PSoC™ Designer: C Language Compiler User GuideDocument74 pagesPSoC™ Designer: C Language Compiler User Guidetuandt2_1415No ratings yet
- Applied Statistics SyllabusDocument7 pagesApplied Statistics SyllabusPaul Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- AI - AI417DE01 Lab - Week 09-22102363Document8 pagesAI - AI417DE01 Lab - Week 09-22102363thinhbui1907No ratings yet
- Investigating The PH of The 11 Basic Substances Lab PhetDocument3 pagesInvestigating The PH of The 11 Basic Substances Lab PhetVeronica Leroux0% (1)
- Data Structures With C++Document169 pagesData Structures With C++Rachna BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Detail Tangga Mockup PDFDocument1 pageDetail Tangga Mockup PDFanicoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: E V Praveenesh Reddy Sap Bi/Bw Consultant CONTACT NO: +91-8142114031Document4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: E V Praveenesh Reddy Sap Bi/Bw Consultant CONTACT NO: +91-8142114031harish2212No ratings yet
- AC TO DC CONVERTERS Paper 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAC TO DC CONVERTERS Paper 1 PDFDonigoNo ratings yet
- Installation of Sonic Pipe - QCR-9212-2015Document2 pagesInstallation of Sonic Pipe - QCR-9212-2015Zaky PrawiraNo ratings yet
- 304 Chromic Acid AnodizingDocument6 pages304 Chromic Acid AnodizingPuguh Cahpordjo BaeNo ratings yet
- Asmiv T I Dwgs For 3keDocument14 pagesAsmiv T I Dwgs For 3kePSI Guillermo Francisco RuizNo ratings yet
- The Amazingly: Flexible FlexarDocument6 pagesThe Amazingly: Flexible FlexarrialmdrdNo ratings yet
- The Implementation of Photovoltaic System and DC-DC Converter For The Production Process of Hydrogen Gas Through ElectrolysisDocument8 pagesThe Implementation of Photovoltaic System and DC-DC Converter For The Production Process of Hydrogen Gas Through ElectrolysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall U Wall Type Estimate With Box PushingDocument8 pagesRetaining Wall U Wall Type Estimate With Box PushingApurva ParikhNo ratings yet
- Homework Help Geometry HoltDocument8 pagesHomework Help Geometry Holtafnofbfqearczc100% (1)
- Grade 9 QuestionsDocument18 pagesGrade 9 Questionsutariq002277No ratings yet
- Autonomy Support, Need Satisfaction, and Motivation For Support Among Adults With Intellectual Disability: Testing A Self-Determination Theory ModelDocument17 pagesAutonomy Support, Need Satisfaction, and Motivation For Support Among Adults With Intellectual Disability: Testing A Self-Determination Theory ModelIntan HumaerohNo ratings yet
- Ppe Unit 1Document118 pagesPpe Unit 1Vbalaji VaithiyanathanNo ratings yet
- HTK (v.3.1) : Basic Tutorial: ContentDocument18 pagesHTK (v.3.1) : Basic Tutorial: ContentJanković MilicaNo ratings yet
- Mca 105Document2 pagesMca 105kola0123No ratings yet
- Setup Sheet Report: Mill DefaultDocument5 pagesSetup Sheet Report: Mill DefaultGandi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Infra-Red CAR-KEY Transmitter: OM1058 in Case SO-8Document4 pagesInfra-Red CAR-KEY Transmitter: OM1058 in Case SO-8José SilvaNo ratings yet
- Gateway Quiz Mid-Term - Section - 1: Webwork (/webwork2)Document6 pagesGateway Quiz Mid-Term - Section - 1: Webwork (/webwork2)Areesha Imam BakshNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument37 pagesFutureBT20EEE052 KhushalNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ReportDocument6 pagesDiagnostic ReportChigasumiNo ratings yet