Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geology and Rock Cycle
Geology and Rock Cycle
Uploaded by
Michael Akinola0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesGeology is the study of the Earth, its composition, structure, and processes. There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary rocks which form near the surface, metamorphic rocks which form from heat and pressure, and igneous rocks which form when magma cools. Igneous rocks specifically form when magma cools and crystallizes. Erosion removes material from one location and transports it elsewhere while weathering removes material but keeps it in the same place.
Original Description:
Original Title
2. Geology and Rock Cycle (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGeology is the study of the Earth, its composition, structure, and processes. There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary rocks which form near the surface, metamorphic rocks which form from heat and pressure, and igneous rocks which form when magma cools. Igneous rocks specifically form when magma cools and crystallizes. Erosion removes material from one location and transports it elsewhere while weathering removes material but keeps it in the same place.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views13 pagesGeology and Rock Cycle
Geology and Rock Cycle
Uploaded by
Michael AkinolaGeology is the study of the Earth, its composition, structure, and processes. There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary rocks which form near the surface, metamorphic rocks which form from heat and pressure, and igneous rocks which form when magma cools. Igneous rocks specifically form when magma cools and crystallizes. Erosion removes material from one location and transports it elsewhere while weathering removes material but keeps it in the same place.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
What is Geology?
The Earth (As A Whole)
The Earth is complex. Most people look at it
externally, but there’s a complex internal process.
Geology, Defined
Geology - The study of the Earth, the materials it is
made of, the structure of materials on Earth, and the
processes which alter and create them.
Geology (Rocks!), I
Within geology, there are three types of rocks:
1. Sedimentary rocks
2. Metamorphic rocks
3. Igneous rocks
Geology (Rocks!), II
Types of Rocks
Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary – Form at or near the Earth’s surface
through low temperatures and pressures.
Examples: sandstone, limestone, shale.
Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic – Form when sedimentary or
igneous undergo intense heat/pressure in the Earth’s
crust. Example: marble, gneiss, schist.
Igneous Rocks
Igneous – Form when magma cools and creates
crystals. Examples: granite, basalt, obsidian.
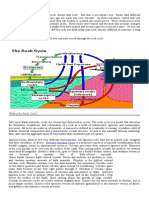
The Rock Cycle
Forces of Change
Erosion (by water, wind, or ice) – the process that removes
soil, rock, or material from one spot and takes it to another.
Weathering (by water, wind, or ice) – the process that
removes soil, rock, or material from one spot but remains
where it is.
Deposition (by water, wind, or ice) – when soil, rock, or
material are added to a landmass.
Compaction (by rock, ice, or other sediment) – when
sediments are buried due to overlay pressure.
Cementation (when the sediment is “cemented” into the
rock) – the hardening of sediment together.
Forces of Change
Questions
What are the three types of rocks?
What type of rock is made when it encounters magma?
What’s the difference between erosion and weathering?
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Module SCI101 EARTH SCI ROCKSDocument8 pagesModule SCI101 EARTH SCI ROCKSLarah Jane MaravilesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Rocks)Document8 pagesModule 2 (Rocks)JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- Earth MaterialsDocument32 pagesEarth MaterialsalexandereugeneleguaNo ratings yet
- HW-1 (Rock Cycle)Document10 pagesHW-1 (Rock Cycle)Tiarra MojelNo ratings yet
- Earthmaterials Rock Cycle StemscopediaDocument6 pagesEarthmaterials Rock Cycle Stemscopediaapi-506851645100% (2)
- Three Main Categories of RocksDocument4 pagesThree Main Categories of RocksJess MCDNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle Rocks Are The Most Common Material On Earth. They Are Naturally OccurringDocument2 pagesThe Rock Cycle Rocks Are The Most Common Material On Earth. They Are Naturally OccurringPotchinoParuntongNo ratings yet
- بلا عنوانDocument1 pageبلا عنوانhajjoabodyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1st Quarter Earth and LifeDocument7 pagesReviewer 1st Quarter Earth and Lifecuaresmaangel1No ratings yet
- Muli Abm 3 Lesson3 RocksDocument2 pagesMuli Abm 3 Lesson3 RocksKristine Joy MuliNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle 2 ModifiedDocument19 pagesRock Cycle 2 ModifiedKernisha AdamsNo ratings yet
- Earth Science New Lesson (Rocks)Document4 pagesEarth Science New Lesson (Rocks)Alisandra UntalanNo ratings yet
- What Are The 3 Basic Types of RocksDocument3 pagesWhat Are The 3 Basic Types of Rocksashok19010No ratings yet
- Rocks & Minerals ExploitationDocument15 pagesRocks & Minerals ExploitationuibikunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Rocks and Soil2Document40 pagesChapter 2 Rocks and Soil2CanhgNo ratings yet
- ELS Geological ProcessDocument139 pagesELS Geological ProcessHannah AlvarezNo ratings yet
- ESCI Test YourselfDocument1 pageESCI Test YourselfSam VilladelgadoNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument2 pagesThe Rock CycleAletta Gregg CataloniaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter NotesDocument6 pages1st Quarter NotesCherry Pink VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Scienceamaeamee ameaimeNo ratings yet
- Geology ReadingDocument2 pagesGeology ReadingYeraldo LCNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- VulcanityDocument11 pagesVulcanityonsongomilkah0No ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument2 pagesClassification of RocksJessa Mae CasipongNo ratings yet
- Earth Science HandoutsDocument6 pagesEarth Science HandoutsPhia ViaNo ratings yet
- GEOSPHEREDocument18 pagesGEOSPHEREPennie KoscaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science. Chapter 2Document13 pagesEarth and Life Science. Chapter 2veronicaNo ratings yet
- Rocka With ExamplesDocument6 pagesRocka With ExamplesAr Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument11 pagesTypes of RocksTriplejayartNo ratings yet
- .Trashed-1719064811-Identificion of Rocks - Hand Specimen - FormatDocument7 pages.Trashed-1719064811-Identificion of Rocks - Hand Specimen - Formatemilypaul929No ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument4 pagesRock Cyclerda405869No ratings yet
- Classification of Rocks 2.aDocument1 pageClassification of Rocks 2.aCelrio Joyce CalumbaNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument27 pagesTypes of RocksPRINCESS TUTORNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 8 Study GuideDocument2 pagesScience Chapter 8 Study Guide3svc33No ratings yet
- Rocks QuizDocument8 pagesRocks QuizAYECKANo ratings yet
- Learnings For Today GeologyDocument2 pagesLearnings For Today GeologyYoo JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Mef#1assignmentbyfaizyab Rock Cycle in Earth CrustDocument5 pagesMef#1assignmentbyfaizyab Rock Cycle in Earth CrustFaizy HereNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 2ndDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography 2ndAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- Topic: Minerals and RocksDocument2 pagesTopic: Minerals and Rocksjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Geography Fact SheetDocument4 pagesGeography Fact Sheetomayma.omarn991No ratings yet
- 5 Rock CycleDocument70 pages5 Rock Cycleapi-251060011No ratings yet
- Marvin Reaction PaperDocument15 pagesMarvin Reaction PaperMarvin SurioNo ratings yet
- 2 - Types of RocksDocument2 pages2 - Types of RocksManna Karim OUEDRAOGONo ratings yet
- The Three Types of RocksDocument10 pagesThe Three Types of RocksEmilio GalangNo ratings yet
- Types of Rock Lesson ObjectivesDocument2 pagesTypes of Rock Lesson ObjectivesKring-kring GumanaNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument24 pagesROCKSGherleen MagayonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document18 pagesLesson 2Ace De Jesus RascoNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument3 pagesThe Rock CycleMeet PatelNo ratings yet
- Local Media5988609580861488696Document9 pagesLocal Media5988609580861488696Dise WrightsNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials: Classification of RocksDocument2 pagesEarth Materials: Classification of RocksHeart ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument28 pagesThe Rock Cycleapi-263638354No ratings yet
- The Types of RockDocument13 pagesThe Types of RockrhodtenauNo ratings yet
- Magma Rock Earth: Igneous Rock, Any of Various Crystalline or Glassy Rocks Formed by The Cooling and SolidificationDocument6 pagesMagma Rock Earth: Igneous Rock, Any of Various Crystalline or Glassy Rocks Formed by The Cooling and SolidificationabcdefghNo ratings yet
- Spiral Review 2Document1 pageSpiral Review 2api-287137309No ratings yet
- There Are A Few Types of Solid Rocks. Explain The Formation of These Solid Rocks Through Rock Cycle. There Are Three Types of Rocks. They AreDocument4 pagesThere Are A Few Types of Solid Rocks. Explain The Formation of These Solid Rocks Through Rock Cycle. There Are Three Types of Rocks. They ArenabilahasrulNo ratings yet
- Rock (Geology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument1 pageRock (Geology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAliaNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of RocksDocument12 pagesThe Three Types of RocksClemencia Eduria MasibaNo ratings yet
- Rocks - Teachers NotesDocument5 pagesRocks - Teachers NotesSaman AkramNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesRocks and MineralsRachelle Monn OcsioNo ratings yet
- Pollution Article ReportDocument3 pagesPollution Article ReportMichael AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Culminating Religion Part BDocument1 pageCulminating Religion Part BMichael AkinolaNo ratings yet
- Balance SheetDocument1 pageBalance SheetMichael AkinolaNo ratings yet
- C 8: Measurement: HapterDocument42 pagesC 8: Measurement: HapterMichael AkinolaNo ratings yet