Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 viewsG7 - Bones and Skeleton
G7 - Bones and Skeleton
Uploaded by
Listya RahmawatiThe document discusses the human skeleton and related structures. It describes the skeleton's roles in supporting the body, protecting organs, and enabling movement. It discusses different types of joints like fixed joints in the skull and movable ball-and-socket joints in the shoulders. Muscles like the biceps and triceps are also described, including how they attach via tendons and work in opposing pairs to contract and relax, bending and straightening the elbow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Grade 7 Practical Sheet Observing Onion CellDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Practical Sheet Observing Onion CellListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Haw Catalogue EbookDocument290 pagesHaw Catalogue Ebookneeraj pandeyNo ratings yet
- Sunbeam: Instructor ManualDocument88 pagesSunbeam: Instructor ManualWill AsinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Haier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaDocument14 pagesHaier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaArun Kumar80% (5)
- Sciences 6 - Sample PagesDocument12 pagesSciences 6 - Sample PagesLili Muñoz Mendoza100% (1)
- P.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcDocument105 pagesP.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcMonydit SantinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Document15 pagesChapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Marinette Valencia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy PDFDocument22 pagesHuman Anatomy PDFWally WallyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Science - MusclesDocument19 pagesGrade 7 - Science - MusclesPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PE FinalDocument14 pagesModule 3 PE FinalStephanie De Guzman LimNo ratings yet
- Learningtarget:: Activity 1 ADocument4 pagesLearningtarget:: Activity 1 ApoonamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Ib SehsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Ib SehsMaggie-Louise BellamyNo ratings yet
- Muscles - Workbook PDFDocument71 pagesMuscles - Workbook PDFakash100% (1)
- Muscles WorkbookDocument35 pagesMuscles WorkbookProdosh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ch-8 Our SkeletalDocument8 pagesch-8 Our Skeletalxhtk3em03zNo ratings yet
- Pal Upper Limb WorksheetDocument4 pagesPal Upper Limb Worksheetkrutipatel934No ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Skeletal System - Study MaterialDocument4 pagesSkeletal System - Study MaterialNabeel UndreNo ratings yet
- 06 Skeletal System Notes PDFDocument12 pages06 Skeletal System Notes PDFshjsjNo ratings yet
- Unit 7.4 - Moving The BodyDocument42 pagesUnit 7.4 - Moving The BodyJessNo ratings yet
- Make A Model of The Human Body: Science ProjectDocument5 pagesMake A Model of The Human Body: Science ProjectEris Putra SulaemanNo ratings yet
- 10bja Medsci - Mckenzie CheyneDocument60 pages10bja Medsci - Mckenzie Cheyneapi-284323075No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument74 pagesStructure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemBernhard BrinkerNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Notes For P - 7 - 2018Document64 pagesScience Lesson Notes For P - 7 - 2018simbi yusuf100% (1)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- 1.4 JointsDocument23 pages1.4 JointsParia SrinelisNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionDocument4 pagesICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 2nd QuarterDocument20 pagesScience Week 1 2nd QuarterAnya BasilioNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 3Document7 pagesDLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 3Roselle Joy EgeraNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 pagesApplied Anatomy and PhysiologyLinet HuchuNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument32 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemArmine Angela SolimanNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Checkpoint Grade 7Document25 pagesCanbridge Checkpoint Grade 7seema sarathNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Muscles and MovementtDocument13 pagesLesson 2 Muscles and MovementtDwight DsilvaNo ratings yet
- The SkeletonDocument29 pagesThe SkeletonAustin AcademyNo ratings yet
- 3major Organs of The Human BodyDocument13 pages3major Organs of The Human BodyRosemarie Mascual IndocNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Document24 pagesAnatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Venus Tumampil AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of The Skeletal System PowerPointDocument31 pagesThe Structure and Function of The Skeletal System PowerPointKokomma EtokudoNo ratings yet
- Ch-8. Body Movements (Notes)Document4 pagesCh-8. Body Movements (Notes)JAINAM SHAHNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25Document5 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25S JNo ratings yet
- 1.5. MusclesDocument22 pages1.5. MusclesParia SrinelisNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Science Workbook Term 3: Name: - ClassDocument21 pages4th Grade Science Workbook Term 3: Name: - ClassJezabel MolinaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Body MovementsDocument11 pages2 - Body MovementsShikha BhumaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Rogielyn Dominguez Labrador78% (9)
- Joints FullDocument12 pagesJoints FullMekala WithanaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit Reviewer Taylors-VersionDocument10 pagesPathfit Reviewer Taylors-VersionvncbckNo ratings yet
- Skeleton and JointsDocument22 pagesSkeleton and JointsAlmas Talib50% (2)
- SLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Document23 pagesSLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Racel AbulaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year ScienceDocument15 pagesSkeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Musculoeskeletal Anatomy: Sports, Exercise and ScienceDocument36 pagesMusculoeskeletal Anatomy: Sports, Exercise and SciencePaulaNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton1Document28 pagesThe Skeleton1Best FriendsNo ratings yet
- Grade V ScienceDocument3 pagesGrade V Scienceswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- L 8 - Body MovementsDocument29 pagesL 8 - Body MovementsChaitra KamuriNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System OfficialDocument14 pagesHuman Skeletal System Officialconirv1No ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Document7 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Uwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bodymovement HumanDocument13 pagesBodymovement HumanKavitha KNo ratings yet
- What Is This Module About?Document38 pagesWhat Is This Module About?camilleNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEMDocument9 pagesStudent's Booklet - THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEMRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- Skeleton and Locomotion Powe Point LessonDocument33 pagesSkeleton and Locomotion Powe Point LessonGamela MoonoNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument28 pagesStructure of AtomListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Element - Metal ReactionDocument29 pagesG8 - Element - Metal ReactionListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 EcosystemDocument13 pagesG8 EcosystemListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Bones and SkeletonDocument19 pagesG8 - Bones and SkeletonListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Making Reactivity SeriesDocument18 pagesG8 - Making Reactivity SeriesListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G7 - Classification of VertebrateDocument16 pagesG7 - Classification of VertebrateListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Manufacture of Yogurt Practice QuestionDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Manufacture of Yogurt Practice QuestionListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Rman Standby Copy-2Document8 pagesRman Standby Copy-2SHAHID FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Change RelationshipDocument10 pagesEstablishing A Change Relationshipravelyn bresNo ratings yet
- BBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020Document12 pagesBBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020SARIPAH NOOR FARAH AIN BINTI P.AFDZAL SHAH STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Skill Development Sector - Achievement ReportDocument10 pagesSkill Development Sector - Achievement ReportShivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- PF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeDocument1 pagePF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeAngel CazaresNo ratings yet
- REPORT Phulkari PDFDocument19 pagesREPORT Phulkari PDFVritti Malhotra100% (2)
- 4.-Revised-Tle-As-Css10-Q3-Disk ManagementDocument5 pages4.-Revised-Tle-As-Css10-Q3-Disk ManagementJonald SalinasNo ratings yet
- Name: Waguma Leticia: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology Nakuru CampusDocument9 pagesName: Waguma Leticia: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology Nakuru CampusWaguma LeticiaNo ratings yet
- 16.1.3 Lab - Implement IPsec Site-to-Site - ITExamAnswersDocument37 pages16.1.3 Lab - Implement IPsec Site-to-Site - ITExamAnswershayltonmonteiroNo ratings yet
- 0650-EDW-00009-02 - Seaking DST Parts List - Customer Parts ListDocument11 pages0650-EDW-00009-02 - Seaking DST Parts List - Customer Parts ListJosianeMacielNo ratings yet
- GA Weather Decision-Making Dec05 PDFDocument36 pagesGA Weather Decision-Making Dec05 PDFPete AndreNo ratings yet
- No. Student Name: Nadil Use A Tick To Confirm Your Subject ÜDocument2 pagesNo. Student Name: Nadil Use A Tick To Confirm Your Subject ÜNadil AdhikariwattageNo ratings yet
- AOS-S and AOS-CX Transceiver GuideDocument138 pagesAOS-S and AOS-CX Transceiver GuideBoweeNo ratings yet
- Econ 157 - Problem Set #2: Question 11 - Chapter 5Document10 pagesEcon 157 - Problem Set #2: Question 11 - Chapter 5lkplmlhNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 RoadmapDocument42 pagesJEE 2024 Roadmaplilop27557No ratings yet
- Invoice: (Your Company Name)Document1 pageInvoice: (Your Company Name)Kemal ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Low Vision Weekly Exam Question Set-1Document9 pagesLow Vision Weekly Exam Question Set-1akhilaslam3No ratings yet
- Raghavendran V Piping Supervisor: ResumeDocument5 pagesRaghavendran V Piping Supervisor: Resumeandi dipayadnyaNo ratings yet
- Math10 SLHT, Q3, WK8, M10SP-IIIg-h-1Document7 pagesMath10 SLHT, Q3, WK8, M10SP-IIIg-h-1Justiniano SalicioNo ratings yet
- Eecs166 267 Syllabus15Document3 pagesEecs166 267 Syllabus15Bhanu Pratap ReddyNo ratings yet
- Power Homes vs. SECDocument22 pagesPower Homes vs. SEChaileyraincloudNo ratings yet
- Letter VirajDocument1 pageLetter VirajPratyushAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Democratic Life Skill 1Document1 pageDemocratic Life Skill 1andinurzamzamNo ratings yet
- 1 Measurement 2020 ModuleDocument16 pages1 Measurement 2020 ModuleNajibah AtiqahNo ratings yet
- Avnet TP Sap Arp PL May14Document77 pagesAvnet TP Sap Arp PL May14Kathak DancerNo ratings yet
- Patient NameDocument3 pagesPatient NameSmith91No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3Document9 pagesRisk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3kanchana rameshNo ratings yet
G7 - Bones and Skeleton
G7 - Bones and Skeleton
Uploaded by
Listya Rahmawati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views27 pagesThe document discusses the human skeleton and related structures. It describes the skeleton's roles in supporting the body, protecting organs, and enabling movement. It discusses different types of joints like fixed joints in the skull and movable ball-and-socket joints in the shoulders. Muscles like the biceps and triceps are also described, including how they attach via tendons and work in opposing pairs to contract and relax, bending and straightening the elbow.
Original Description:
bones and skeleton for grade 7
Original Title
G7_Bones and Skeleton
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the human skeleton and related structures. It describes the skeleton's roles in supporting the body, protecting organs, and enabling movement. It discusses different types of joints like fixed joints in the skull and movable ball-and-socket joints in the shoulders. Muscles like the biceps and triceps are also described, including how they attach via tendons and work in opposing pairs to contract and relax, bending and straightening the elbow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views27 pagesG7 - Bones and Skeleton
G7 - Bones and Skeleton
Uploaded by
Listya RahmawatiThe document discusses the human skeleton and related structures. It describes the skeleton's roles in supporting the body, protecting organs, and enabling movement. It discusses different types of joints like fixed joints in the skull and movable ball-and-socket joints in the shoulders. Muscles like the biceps and triceps are also described, including how they attach via tendons and work in opposing pairs to contract and relax, bending and straightening the elbow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 27
Bone and Skeleton
This Material can be found on your Science Book
pg. 34 - 37
Slide show this slide!
Lesson Objective
In the end of the lesson you will be able to:
• Describe the role of the skeleton
• Describe the role of joint
• Describe the principle of antagonistic muscles
The words that you have to be familiar with
• Skeleton : Rangka
• Joint : Sendi
• Muscle: Otot
• Antagonistic Muscle: Otot antagonis
• Lubricate: Oli/ Pelumas/Pelicin
• Skull: Tengkorak
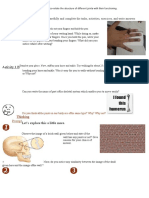
The Human Skeleton
• Your skeleton supports
your body and helps it to
move
• It also protects some of
the soft organs inside you
1. List three functions of the
Questions A
Answer the following questions in your skeleton.
notebook or Ms. Word. Upload your
work on Google Classroom 2. Look at the diagram of the
skeleton. How are the bones in
the arm (lengan) and legs
(kaki)similar?
3. As well as supporting the body,
some bones protect other
organs. Name the bones
protect: brain, heart, and Lungs.
• List three functions of the
skeleton.
1. Look at the diagram of the
skeleton. How are the
bones in the arm (lengan)
and legs (kaki)similar?
1. Name the bones protect:
brain, heart, and Lungs.
Joints (Sendi)
• A joint is a place where
two bones meet.
• There are two main types
of joints in our bodies:
– Fixed joints (sendi yang
tidak dapat bergerak)
– Moveable joints (sendi
yang dapat bergerak)
Fixed and Moveable joints
• The skull has fixed joints in
the cranium.
• Cranium is made up of several
bones.
• This helps the cranium to
protect the brain
• The jawbone is joined to the
rest of the skull by a
moveable joint
(Rahang)
ball-and-socket joints
• Try to move your
Shoulder!
• Your shoulder joint can
move in almost all
direction
• This is because of the
shoulder joint is a ball –
and – socket joints
Hinge joints
• Your elbow joint is a hinge
(read: Hinj) joint. elbow (siku-
• It can move in only one Siku)
direction
• It moves like a door on a
hinge
hinge Knee
(engsel) (lutut)
• State one place in the body
QUESTIONS B
Answer the following questions in your
where you have a fixed
notebook or Ms. Word. Upload your
work on Google Classroom joint. Why is it useful to
have a fixed joint in this
place?
• Name the bones that form
the hinge joint at your
elbow.
• State one place in the body
where you have a fixed
joint. Why is it useful to
have a fixed joint in this
place?
• Name the bones that form
the ball – and – socket joint
in your shoulder.
• Name the bones that form
the hinge joint at your
elbow.
Activity 1.4
(Which kind of joint?)
• Try moving each of these joints in your body, and decide
whether each one is :
A fixed joint A hinge joint A ball – and – socket joint
Joints in your body:
a. A finger joint
b. The knee joint
c. A toe (jempol kaki) joint
d. The hip (panggul) joint
Write the answers on your note or MS. Word (it can be in the same file
from the previous work)
Muscle
• Muscles are organs that help
us to move.
• The diagram shows the two
main muscles in the upper
arm.
• The muscles are attached to
the bones by tendons.
• Tendons are very strong, and
they do not stretch
• Name the bones that the biceps
QUESTIONS C muscles is attached (menempel)
Answer the following questions in your
notebook or Ms. Word. Upload your to.
work on Google Classroom
• Name the bones that the triceps
is attached to.
• ‘bi’ means ‘two’. ‘tri’ means
three. Look carefully at the
diagram and suggest why the
biceps and triceps are given their
names.
• Name the bones that the
biceps muscles is
attached (menempel) to.
• Name the bones that the
triceps is attached to.
• ‘bi’ means ‘two’. ‘tri’ means three. Look
carefully at the diagram and suggest why
the biceps and triceps are given their
names.
How muscles work
• Muscle can get shorter. This
called contraction.
• When muscles contract, they
produce a pulling force (gaya
tarik).
• Look at the diagram of the
muscles in the arm.
• When the biceps muscle
contracts, it pulls on the radius
and scapula.
Antagonistic Muscles
• When a muscle is not
contracting, we say that it is
relaxed.
• The diagram shows what
happens when the biceps
muscle contracts and the
triceps relaxes.
• The contracting biceps makes
the arm bend at the elbow joint.
Antagonistic Muscles
• The diagram shows how
the arm can be made
straight again.
• The triceps contract
and the biceps relaxes,
it makes the arm
straighten.
Antagonistic Muscles
• Antagonistic muscles occur in
pairs. These pairs of muscles
work against each other to create
movement.
• Triceps and biceps are an
example of a pair of antagonistic
muscles.
• As one muscle contracts
(shortens (memendek) the other
muscle relaxes
(lengthens(memanjang)).
summary
Copy the paragraph and choose words from the list to complete
it. Each word may be used once, more than once or not at all.
tendons Contract
opposite pulling
Muscles produce a __________ force when they contract . They
can only pull. They cannot push. Muscles are joined to bones by
the________. Antagonistic muscles are a pair of muscles
working together, pulling in __________ direction.
You might also like
- Grade 7 Practical Sheet Observing Onion CellDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Practical Sheet Observing Onion CellListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Haw Catalogue EbookDocument290 pagesHaw Catalogue Ebookneeraj pandeyNo ratings yet
- Sunbeam: Instructor ManualDocument88 pagesSunbeam: Instructor ManualWill AsinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Haier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaDocument14 pagesHaier in India Building Presence in A Mass Market Beyond ChinaArun Kumar80% (5)
- Sciences 6 - Sample PagesDocument12 pagesSciences 6 - Sample PagesLili Muñoz Mendoza100% (1)
- P.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcDocument105 pagesP.7 Best Science Notes Term One - Teacher - AcMonydit SantinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Document15 pagesChapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Marinette Valencia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy PDFDocument22 pagesHuman Anatomy PDFWally WallyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Science - MusclesDocument19 pagesGrade 7 - Science - MusclesPathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PE FinalDocument14 pagesModule 3 PE FinalStephanie De Guzman LimNo ratings yet
- Learningtarget:: Activity 1 ADocument4 pagesLearningtarget:: Activity 1 ApoonamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Ib SehsDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Musculoskeletal Anatomy: Ib SehsMaggie-Louise BellamyNo ratings yet
- Muscles - Workbook PDFDocument71 pagesMuscles - Workbook PDFakash100% (1)
- Muscles WorkbookDocument35 pagesMuscles WorkbookProdosh ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ch-8 Our SkeletalDocument8 pagesch-8 Our Skeletalxhtk3em03zNo ratings yet
- Pal Upper Limb WorksheetDocument4 pagesPal Upper Limb Worksheetkrutipatel934No ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument37 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Skeletal System - Study MaterialDocument4 pagesSkeletal System - Study MaterialNabeel UndreNo ratings yet
- 06 Skeletal System Notes PDFDocument12 pages06 Skeletal System Notes PDFshjsjNo ratings yet
- Unit 7.4 - Moving The BodyDocument42 pagesUnit 7.4 - Moving The BodyJessNo ratings yet
- Make A Model of The Human Body: Science ProjectDocument5 pagesMake A Model of The Human Body: Science ProjectEris Putra SulaemanNo ratings yet
- 10bja Medsci - Mckenzie CheyneDocument60 pages10bja Medsci - Mckenzie Cheyneapi-284323075No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument74 pagesStructure and Function of The Musculoskeletal SystemBernhard BrinkerNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Notes For P - 7 - 2018Document64 pagesScience Lesson Notes For P - 7 - 2018simbi yusuf100% (1)
- The Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- 1.4 JointsDocument23 pages1.4 JointsParia SrinelisNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionDocument4 pagesICSE Class 9 Chapter 12 Skelatal and LocomotionArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 2nd QuarterDocument20 pagesScience Week 1 2nd QuarterAnya BasilioNo ratings yet
- DLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 3Document7 pagesDLP SCIENCE 6 Q2 WK 1 Day 3Roselle Joy EgeraNo ratings yet
- Applied Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 pagesApplied Anatomy and PhysiologyLinet HuchuNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument32 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemArmine Angela SolimanNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Checkpoint Grade 7Document25 pagesCanbridge Checkpoint Grade 7seema sarathNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Muscles and MovementtDocument13 pagesLesson 2 Muscles and MovementtDwight DsilvaNo ratings yet
- The SkeletonDocument29 pagesThe SkeletonAustin AcademyNo ratings yet
- 3major Organs of The Human BodyDocument13 pages3major Organs of The Human BodyRosemarie Mascual IndocNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Document24 pagesAnatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Venus Tumampil AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingDocument79 pagesAnatomi - Olah Raga 1st MeetingR DarmawanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of The Skeletal System PowerPointDocument31 pagesThe Structure and Function of The Skeletal System PowerPointKokomma EtokudoNo ratings yet
- Ch-8. Body Movements (Notes)Document4 pagesCh-8. Body Movements (Notes)JAINAM SHAHNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25Document5 pagesCBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 8 - Body Movements Important Questions 2024-25S JNo ratings yet
- 1.5. MusclesDocument22 pages1.5. MusclesParia SrinelisNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Science Workbook Term 3: Name: - ClassDocument21 pages4th Grade Science Workbook Term 3: Name: - ClassJezabel MolinaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Body MovementsDocument11 pages2 - Body MovementsShikha BhumaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Rogielyn Dominguez Labrador78% (9)
- Joints FullDocument12 pagesJoints FullMekala WithanaNo ratings yet
- Pathfit Reviewer Taylors-VersionDocument10 pagesPathfit Reviewer Taylors-VersionvncbckNo ratings yet
- Skeleton and JointsDocument22 pagesSkeleton and JointsAlmas Talib50% (2)
- SLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Document23 pagesSLM QUARTER 2 Module 2 WEEK 1Racel AbulaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year ScienceDocument15 pagesSkeletal & Muscular Systems: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- Musculoeskeletal Anatomy: Sports, Exercise and ScienceDocument36 pagesMusculoeskeletal Anatomy: Sports, Exercise and SciencePaulaNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton1Document28 pagesThe Skeleton1Best FriendsNo ratings yet
- Grade V ScienceDocument3 pagesGrade V Scienceswetha swithinNo ratings yet
- L 8 - Body MovementsDocument29 pagesL 8 - Body MovementsChaitra KamuriNo ratings yet
- Human Skeletal System OfficialDocument14 pagesHuman Skeletal System Officialconirv1No ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Document7 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Uwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bodymovement HumanDocument13 pagesBodymovement HumanKavitha KNo ratings yet
- What Is This Module About?Document38 pagesWhat Is This Module About?camilleNo ratings yet
- Student's Booklet - THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEMDocument9 pagesStudent's Booklet - THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEMRafa Rguez PerezNo ratings yet
- Skeleton and Locomotion Powe Point LessonDocument33 pagesSkeleton and Locomotion Powe Point LessonGamela MoonoNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument28 pagesStructure of AtomListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Element - Metal ReactionDocument29 pagesG8 - Element - Metal ReactionListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 EcosystemDocument13 pagesG8 EcosystemListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Bones and SkeletonDocument19 pagesG8 - Bones and SkeletonListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G8 - Making Reactivity SeriesDocument18 pagesG8 - Making Reactivity SeriesListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- G7 - Classification of VertebrateDocument16 pagesG7 - Classification of VertebrateListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Manufacture of Yogurt Practice QuestionDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Manufacture of Yogurt Practice QuestionListya RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Rman Standby Copy-2Document8 pagesRman Standby Copy-2SHAHID FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Change RelationshipDocument10 pagesEstablishing A Change Relationshipravelyn bresNo ratings yet
- BBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020Document12 pagesBBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020SARIPAH NOOR FARAH AIN BINTI P.AFDZAL SHAH STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Skill Development Sector - Achievement ReportDocument10 pagesSkill Development Sector - Achievement ReportShivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- PF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeDocument1 pagePF100/PF150 Manual Postformers: Process For Postforming A Waterfall (90°) EdgeAngel CazaresNo ratings yet
- REPORT Phulkari PDFDocument19 pagesREPORT Phulkari PDFVritti Malhotra100% (2)
- 4.-Revised-Tle-As-Css10-Q3-Disk ManagementDocument5 pages4.-Revised-Tle-As-Css10-Q3-Disk ManagementJonald SalinasNo ratings yet
- Name: Waguma Leticia: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology Nakuru CampusDocument9 pagesName: Waguma Leticia: Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology Nakuru CampusWaguma LeticiaNo ratings yet
- 16.1.3 Lab - Implement IPsec Site-to-Site - ITExamAnswersDocument37 pages16.1.3 Lab - Implement IPsec Site-to-Site - ITExamAnswershayltonmonteiroNo ratings yet
- 0650-EDW-00009-02 - Seaking DST Parts List - Customer Parts ListDocument11 pages0650-EDW-00009-02 - Seaking DST Parts List - Customer Parts ListJosianeMacielNo ratings yet
- GA Weather Decision-Making Dec05 PDFDocument36 pagesGA Weather Decision-Making Dec05 PDFPete AndreNo ratings yet
- No. Student Name: Nadil Use A Tick To Confirm Your Subject ÜDocument2 pagesNo. Student Name: Nadil Use A Tick To Confirm Your Subject ÜNadil AdhikariwattageNo ratings yet
- AOS-S and AOS-CX Transceiver GuideDocument138 pagesAOS-S and AOS-CX Transceiver GuideBoweeNo ratings yet
- Econ 157 - Problem Set #2: Question 11 - Chapter 5Document10 pagesEcon 157 - Problem Set #2: Question 11 - Chapter 5lkplmlhNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 RoadmapDocument42 pagesJEE 2024 Roadmaplilop27557No ratings yet
- Invoice: (Your Company Name)Document1 pageInvoice: (Your Company Name)Kemal ZiyadNo ratings yet
- Low Vision Weekly Exam Question Set-1Document9 pagesLow Vision Weekly Exam Question Set-1akhilaslam3No ratings yet
- Raghavendran V Piping Supervisor: ResumeDocument5 pagesRaghavendran V Piping Supervisor: Resumeandi dipayadnyaNo ratings yet
- Math10 SLHT, Q3, WK8, M10SP-IIIg-h-1Document7 pagesMath10 SLHT, Q3, WK8, M10SP-IIIg-h-1Justiniano SalicioNo ratings yet
- Eecs166 267 Syllabus15Document3 pagesEecs166 267 Syllabus15Bhanu Pratap ReddyNo ratings yet
- Power Homes vs. SECDocument22 pagesPower Homes vs. SEChaileyraincloudNo ratings yet
- Letter VirajDocument1 pageLetter VirajPratyushAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Democratic Life Skill 1Document1 pageDemocratic Life Skill 1andinurzamzamNo ratings yet
- 1 Measurement 2020 ModuleDocument16 pages1 Measurement 2020 ModuleNajibah AtiqahNo ratings yet
- Avnet TP Sap Arp PL May14Document77 pagesAvnet TP Sap Arp PL May14Kathak DancerNo ratings yet
- Patient NameDocument3 pagesPatient NameSmith91No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3Document9 pagesRisk Assessment Techniques (IEC 31010:2019) : Session - 3kanchana rameshNo ratings yet