Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
169 viewsCompressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Uploaded by
KVRCHCompressed biogas (CBG) is a purified form of biogas produced from organic waste sources through anaerobic digestion. It is a renewable energy source that is chemically similar to compressed natural gas (CNG) but produced from biomass rather than petroleum. The document outlines various raw material sources that can be used to produce CBG, including agricultural waste, cow dung, food waste, and waste from sewage treatment plants and industries. It also lists potential locations in India to establish CBG plants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- StepUp 4Document106 pagesStepUp 4ailyn antillon0% (1)
- Biogas Calculation From CodDocument41 pagesBiogas Calculation From CodReuben Malambugi100% (2)
- Market Profile On Sulphuric AcidDocument4 pagesMarket Profile On Sulphuric AcidGovindanayagi PattabiramanNo ratings yet
- Biogas An All-Rounder New Opportunities For Farming, Industry and The EnvironmentDocument102 pagesBiogas An All-Rounder New Opportunities For Farming, Industry and The EnvironmentNikolas Ferreira100% (1)
- Ethanol Production From Sugarcane Molasses PDFDocument2 pagesEthanol Production From Sugarcane Molasses PDFDaryl100% (1)
- Electrical Operation of Electrostatic PrecipitatorsDocument285 pagesElectrical Operation of Electrostatic PrecipitatorsPG100% (1)
- SHE Handbook (Onshore)Document44 pagesSHE Handbook (Onshore)samsam100% (1)
- Synthesis of Aromatic Trifluoromethyl Compounds:: The Potential For Large Scale ApplicationDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Aromatic Trifluoromethyl Compounds:: The Potential For Large Scale ApplicationisosicaNo ratings yet
- G. Kachaniwsky and C. Newman Eds. Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Co-Sponsored by the Non-Ferrous Pyrometallurgy and Hydrometallurgy Sections OfDocument279 pagesG. Kachaniwsky and C. Newman Eds. Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Co-Sponsored by the Non-Ferrous Pyrometallurgy and Hydrometallurgy Sections Ofsgaluf5No ratings yet
- On Biogas Enrichment and Bottling Technology - IITD - IndiaDocument38 pagesOn Biogas Enrichment and Bottling Technology - IITD - Indiaअश्विनी सोनी100% (3)
- BIo Gas Project Report Group 1Document20 pagesBIo Gas Project Report Group 1tryingNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bio Gas Production & Bottling PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On Bio Gas Production & Bottling PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Techno Commercial Aspects of bio-CNG From 100 TPD Press Mud PlantDocument12 pagesTechno Commercial Aspects of bio-CNG From 100 TPD Press Mud Plantpriyank sharmaNo ratings yet
- Potential of Biogas Generation From Hybrid Napier GrassDocument5 pagesPotential of Biogas Generation From Hybrid Napier GrassEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Compressed Biogas Plant: Geon EngineersDocument8 pagesCompressed Biogas Plant: Geon Engineersanuj tomarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Bio-CNGDocument24 pagesPresentation On Bio-CNGKondeti Muralidhar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- PESO Project Report For BioCNG Projects in IndiaDocument3 pagesPESO Project Report For BioCNG Projects in Indiaabhi2010visionNo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument20 pagesBio GasMajor Singh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Bio CNG PDFDocument39 pagesBio CNG PDFpriyank sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Gas Seminar ReportDocument49 pagesBio Gas Seminar ReportLalitBisht100% (2)
- Landscape Report of BioCNG in India GGGI 1Document51 pagesLandscape Report of BioCNG in India GGGI 1Karthik Keyan100% (2)
- Bio Energy High Purity Solutions Engineering Businesses BioproductsDocument13 pagesBio Energy High Purity Solutions Engineering Businesses BioproductsGaurav Maniyar100% (1)
- Bio CNG From City WasteDocument12 pagesBio CNG From City WastenehareshailNo ratings yet
- CBG 30 - Tender Document - CBG04.01.21Document49 pagesCBG 30 - Tender Document - CBG04.01.21Rahul Jain100% (1)
- Vasantdada Sugar Institute PDFDocument26 pagesVasantdada Sugar Institute PDFNanasaheb PatilNo ratings yet
- Brief Industrial Profile of VISAKHAPATNAM District - DC MsmeDocument26 pagesBrief Industrial Profile of VISAKHAPATNAM District - DC MsmeParas AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biofuel Roadmap For IndiaDocument57 pagesBiofuel Roadmap For IndiaSuryadev Sinh Sisodiya100% (1)
- Rimika IITD BiogasDocument47 pagesRimika IITD BiogasRimika KNo ratings yet
- Tender Specifications-Raw Water Tanks For Bhimtal Mandal FinalDocument5 pagesTender Specifications-Raw Water Tanks For Bhimtal Mandal FinalRostfrei Steels Pvt LTD.No ratings yet
- CBG Project - Goal Bio Oil - 6 TPD - 13 PagesDocument13 pagesCBG Project - Goal Bio Oil - 6 TPD - 13 PagesAWANEENDRA DUBEY100% (2)
- CBG 50 TPD Production Project NewDocument14 pagesCBG 50 TPD Production Project NewPARTEEK SINGLANo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument4 pagesBio GasSaroj Kumar0% (1)
- Greening Indias New Energy Mix Low ResDocument96 pagesGreening Indias New Energy Mix Low ResNanasaheb PatilNo ratings yet
- Biogas Plant Development Handbook by Biogas WorldDocument39 pagesBiogas Plant Development Handbook by Biogas WorldRocky KhareNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper On: Establishment of Biogas Energy PlantsDocument5 pagesConcept Paper On: Establishment of Biogas Energy PlantsHamza ZahoorNo ratings yet
- CBG 50 TPD Production ProjectDocument13 pagesCBG 50 TPD Production ProjectAkash SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBG and Pellets ProfileDocument50 pagesCBG and Pellets ProfileAbhishek PantNo ratings yet
- " "A Study On Workers Engagement Activities ": Indu Management Institute VadodaraDocument30 pages" "A Study On Workers Engagement Activities ": Indu Management Institute Vadodarajay patelNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument41 pagesSWOT AnalysisMohamed Tarek Kamar100% (1)
- CPCB - Grain Based DistilleriesDocument37 pagesCPCB - Grain Based Distilleriesmyself_riteshNo ratings yet
- Request Letter: Sub:Requesting Experience Certificate For Applying BOE ExamDocument3 pagesRequest Letter: Sub:Requesting Experience Certificate For Applying BOE ExammaheshNo ratings yet
- CNG Vs LPG - Difference and Comparison - Diffen PDFDocument4 pagesCNG Vs LPG - Difference and Comparison - Diffen PDFUdit Davinci PandeyNo ratings yet
- 100 TPD Press Mud To BioCNG PlantDocument12 pages100 TPD Press Mud To BioCNG PlantRocky Khare100% (2)
- Energy Recovery From WasteDocument31 pagesEnergy Recovery From WasteSyed UmerNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control in Refineries and Fertilizer IndustriesDocument18 pagesPollution Control in Refineries and Fertilizer IndustriesTinu Paul Jepin100% (1)
- Process Design and Economics For The Conversion of The Lignocellulosic To HydrocarbonsDocument133 pagesProcess Design and Economics For The Conversion of The Lignocellulosic To HydrocarbonsCristhian Camilo Vargas QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Coal To Urea at TalcherDocument37 pagesCoal To Urea at TalcherAlfin A. N.No ratings yet
- FGD Presentation (ILFS)Document40 pagesFGD Presentation (ILFS)proloy12100% (2)
- Thermo PacDocument4 pagesThermo Pacsushant_jhawerNo ratings yet
- Firing of BiomassDocument8 pagesFiring of BiomassBrianNo ratings yet
- Glass 4 - 5 11 - 2015Document70 pagesGlass 4 - 5 11 - 2015Laxman KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3c - Cellulose DerivativesDocument37 pagesChapter 3c - Cellulose DerivativesVanessa LimNo ratings yet
- DR Seema ParohaDocument21 pagesDR Seema ParohaTEERATH RAJNo ratings yet
- 1 - Vasudeo Joshi PDFDocument52 pages1 - Vasudeo Joshi PDFKoushik DeyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Grain and Biomass Based Ethanol PlantDocument9 pagesProject Report On Grain and Biomass Based Ethanol PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers33% (3)
- Boiler Efficiency Calculation - A Complete GuideDocument9 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculation - A Complete GuideShujjat HussainNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black Production Analyzing and CharacterizationDocument86 pagesCarbon Black Production Analyzing and CharacterizationabdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Biogas Generation From Press Mud in Batch ReactorDocument6 pagesOptimization of Biogas Generation From Press Mud in Batch Reactorscm996No ratings yet
- Ethanol Production: Faculty of Mathematics and Science Education International Program On Science EducationDocument2 pagesEthanol Production: Faculty of Mathematics and Science Education International Program On Science EducationPutra Habib Dhitareka50% (2)
- Niir Manufacture Value Added Products From Rice Husk Hull Rice Husk Ash Rha 2nd Revised EditionDocument7 pagesNiir Manufacture Value Added Products From Rice Husk Hull Rice Husk Ash Rha 2nd Revised EditionShivam DangNo ratings yet
- Lactic PDFDocument13 pagesLactic PDFNadaNo ratings yet
- Sci 401pptDocument107 pagesSci 401pptNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Report Cement Sector PDFDocument76 pagesBenchmarking Report Cement Sector PDFGuilherme Pierre PaivaNo ratings yet
- Pre Feasibility Study For MIBK Plant - IndiaDocument35 pagesPre Feasibility Study For MIBK Plant - IndiaShiv KothariNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument46 pagesBiomass EnergyRohit RathoreNo ratings yet
- SG - Zero Waste Masterplan SummaryDocument1 pageSG - Zero Waste Masterplan SummaryAlvin SohNo ratings yet
- PG StraMaDocument79 pagesPG StraMaMykhaellah Ting100% (1)
- Chapter 18 FiltrationDocument18 pagesChapter 18 FiltrationGMDGMD11No ratings yet
- Sour Water StrippingDocument10 pagesSour Water StrippingAhmet Samet ÖzdilekNo ratings yet
- Alcatel OneTouch 8020 8020d User Manual English 2Document83 pagesAlcatel OneTouch 8020 8020d User Manual English 2Raza RizviNo ratings yet
- Deed of Restrictions PDFDocument7 pagesDeed of Restrictions PDFBryan Dave RosalesNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Class 567Document14 pagesComprehension Class 567SANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- 8400 M117 O1 - 201Document158 pages8400 M117 O1 - 201pedro castilloNo ratings yet
- 12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResDocument2 pages12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Organelle Nicknames!Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Organelle Nicknames!Justine OledanNo ratings yet
- How Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonDocument6 pagesHow Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonMaricar RaciramNo ratings yet
- Brochure Orc Organic Rankine Cycle Technology - EN PDFDocument7 pagesBrochure Orc Organic Rankine Cycle Technology - EN PDFdolphinNo ratings yet
- Samsung DVD Camcorder VP-dx100 Eng Ib 0725-bDocument125 pagesSamsung DVD Camcorder VP-dx100 Eng Ib 0725-bkonguarasuNo ratings yet
- Nightwalker Winter 2015Document24 pagesNightwalker Winter 2015Gi GlerNo ratings yet
- PCP Evaluation ExamDocument10 pagesPCP Evaluation ExamMark Dimagiba VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- KKD Suo Motu - 0Document29 pagesKKD Suo Motu - 0jeevan820No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Philipines2010 - 431 - 05 PDFDocument33 pagesSolid Waste Philipines2010 - 431 - 05 PDFJune Alapa100% (1)
- Acknowledgement: Ikjot Singh 3070Document23 pagesAcknowledgement: Ikjot Singh 3070Ghost ModeNo ratings yet
- St. Scholastica's College Tacloban: I. Community ProfileDocument24 pagesSt. Scholastica's College Tacloban: I. Community ProfileJosh LozadaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater MGMT HandbookDocument187 pagesWastewater MGMT HandbookangbenaNo ratings yet
- HDB SOR CE Jul 2011Document86 pagesHDB SOR CE Jul 2011kokueiNo ratings yet
- Ma. Stella F. ArnaldoDocument152 pagesMa. Stella F. ArnaldoLeah LabelleNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Useful and Harmful Materials - EditedDocument25 pagesWeek 1 Useful and Harmful Materials - EditedLady Gweneth YangyangNo ratings yet
- Students Loan Trust Fund: Student Loan Application GuidelinesDocument8 pagesStudents Loan Trust Fund: Student Loan Application GuidelinesNicholas SaahNo ratings yet
- GATRONOVA Internship ReportDocument34 pagesGATRONOVA Internship ReportAbdulmunaf SheikhNo ratings yet
Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Uploaded by
KVRCH100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
169 views15 pagesCompressed biogas (CBG) is a purified form of biogas produced from organic waste sources through anaerobic digestion. It is a renewable energy source that is chemically similar to compressed natural gas (CNG) but produced from biomass rather than petroleum. The document outlines various raw material sources that can be used to produce CBG, including agricultural waste, cow dung, food waste, and waste from sewage treatment plants and industries. It also lists potential locations in India to establish CBG plants.
Original Description:
Original Title
Compressed Bio Gas [CBG]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCompressed biogas (CBG) is a purified form of biogas produced from organic waste sources through anaerobic digestion. It is a renewable energy source that is chemically similar to compressed natural gas (CNG) but produced from biomass rather than petroleum. The document outlines various raw material sources that can be used to produce CBG, including agricultural waste, cow dung, food waste, and waste from sewage treatment plants and industries. It also lists potential locations in India to establish CBG plants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
169 views15 pagesCompressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Compressed Bio Gas (CBG)
Uploaded by
KVRCHCompressed biogas (CBG) is a purified form of biogas produced from organic waste sources through anaerobic digestion. It is a renewable energy source that is chemically similar to compressed natural gas (CNG) but produced from biomass rather than petroleum. The document outlines various raw material sources that can be used to produce CBG, including agricultural waste, cow dung, food waste, and waste from sewage treatment plants and industries. It also lists potential locations in India to establish CBG plants.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
Compressed Bio Gas
[CBG]
The Fuel of the Future
What is Bio Gas?
Bio-gas is produced through a bio-chemical process
in which certain types of bacteria convert the
biological wastes into useful bio-gas.
It mainly comprises of hydro-carbon which is
combustible and can produce heat and energy when
burnt.
Since the useful gas originates from biological
process, it has been termed as bio-gas.
Methane gas is the main constituent of biogas.
It is a renewable energy source.
What is CBG?
It is a purified form of biogas.
It is a mixture of various
hydrocarbon gases, produced by
decomposition of animal and plant
waste, consisting mainly of Methane.
How is CBG different from Compressed
Natural Gas(CNG)?
Chemically, CBG is the same as CNG — both are compressed
methane — and have the same calorific value.
But, CNG is a by-product of petroleum, and CBG can be
produced from any biomass.
CBG makes a commercially viable option as it can be directly
used to replace CNG in transportation fuel. Just like CNG, CBG
too can be transported through cylinders or pipelines to retail
outlets.
Raw materials used to produce CBG:
Napier grass
Agricultural Waste
Cow Dung
Press Mud
MSW (Municipal Solid Waste)
Food Waste
Municipal Sewage Treatment Plants
Industrial Wastewater etc.
Napier grass
The feature of Napier grass is high
yield 40-80 tonnes per cut and 3-4
cuts per year.
This grass is also a forage crop.
The best biogas yield is demonstrated
by the grass 120-130 days cut and
33% dry matter.
This yields a biogas output of 220 m³
per ton. To provide 10 tonnes of clean
bio methane per day 122 tons of
Napier grass per day are needed.
Contract farming will be done with the
farmers to get the required grass
quantity.
Agricultural Waste
This is one of the most easily accessible options, due to
its ample availability in the Indian Subcontinent.
Rice straw is a significant agricultural waste that
contributes greatly to air pollution in northern India, but
it can be effectively converted to compressed biogas.
Apart from rice straw, some other agricultural materials
can be used for biogas production, such as sugar cane,
cassava, corn etc.
Also, other agricultural residues like cassava rhizome,
corn cobs etc., wood and wood residues can be utilised.
Cow Dung & Poultry litter
It is also known as cattle manure is another readily available feedstock
that can be converted to biogas.
Viable compressed Biogas plants can be installed at the locations where
bulk manure is generated such as large cow shelters (goshalas), dairy
farms, and other clusters, among others.
For instance, 100 cows produce 6.25 tons of waste every day.
However, the biogas from cow dung has high water content.
The microbes in the digester convert 20-30% of volatile compounds
into biogas. Cow dung can be used as the only feedstock for the digester.
In India, 69.9 % population resides in rural areas where cow is major
cattle and generates 9–15 kg dung/day.
The farmers are paid Rs.1 per kg of cow dung. The payment of cow
dung is paid to farmer with the milk payment on every 15 days.
Chicken manure is a suitable feedstock for digesters because 100kg of
litter will produce approximately 20m3 of biogas.
In this session it is assumed that all gas produced is fully consumed.
And it is based upon the following assumption. - 50 Kg of poultry waste
produced 3.0m3 biogas per day per plant.
It takes about 30 days for complete digestion of chicken litter. A digester
tank of 2000 m3 can handle approx. 17 ton of chicken litter/day. This
would give you 3400 m3 biogas.
Press Mud
Another source of feedstock is press mud, which is a
waste product from sugar mills in India.
It is a rich source of organic material that can be
easily turned into compressed biogas.
It is the residue from the treatment of sugar cane
juice by filtration, accounting for 2% of the weight
of sugarcane crushed.
It is to say 10 tons of sugar output can produce 1
ton of dry filter mud.
Roughly 1.3 MMT of press mud is generated
annually and it can have an huge contribution in
producing compressed biogas.
18 mm Press Mud Pellet costs ₹ 4,500 / Tonne.
90mm Press Mud Briquettes costs ₹ 5,000 / Tonne.
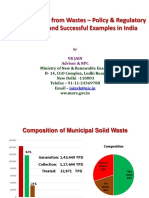
MSW (Municipal Solid Waste)
India generates more than 60 MMT (Million Metric
Tons) of Municipal Solid Waste.
MSW can be transformed into biogas, however, the
barrier to this transformation is the segregation
process.
Only after proper segregation of organic and inorganic
waste can the potential of generating biogas at
the compressed biogas plant be unlocked.
The biomass resource in MSW comprises the
putrescible, paper and plastic and averages 80% of the
total MSW collected.
Municipal solid waste can be converted into energy by
direct combustion, or by natural anaerobic digestion in
the engineered landfill.
Food Waste
India is renowned for its diverse cuisine across
the county.
However, we waste a lot of food in an
organised value chain, including hotels and
restaurants.
There are number of small and luxurious
hotels and restaurants and all having their own
individual mess, From where daily a large
amount of kitchen waste/food waste is
obtained.
Municipal Sewage Treatment Plants
There are a grand total of 1093 sewage treatment plants in India.
According to the Central Pollution Control Board, there are 15,730
sewage treatment plants in India, out of which 530 are non-
complying.
The majority of STPs in India use aerobic treatment methods.
These methods produce large amounts of sludge, which can be
anaerobically processed to create biogas.
Moving forward, government policy should make it mandatory to
implement anaerobic treatment methods to create biogas from
STPs.
In India, the existing treatment capacity is just 18.6 % of present
sewage generation and another 5.2 % capacity is being added.
However, the actual capacity utilization of STPs is only 72.2% and as
such only 13.5% of the sewage is treated.
Wastewater sludge will be able to produced up to 44.82 ml
biogas/kg of sludge.
Industrial Wastewater
Whenever possible, all industrial effluent with a high
organic content and biogas generation potential
should be considered for CBG generation rather than
heat and power.
Working of Compressed Biogas plant :
Locations of CBG Plant to be established:
Canacona in South Goa
Udupi in Karnataka
Mudabidri in Karnataka
Nelamangala/ Dabaspet
in Bangalore
Magadi in Ramanagar
You might also like
- StepUp 4Document106 pagesStepUp 4ailyn antillon0% (1)
- Biogas Calculation From CodDocument41 pagesBiogas Calculation From CodReuben Malambugi100% (2)
- Market Profile On Sulphuric AcidDocument4 pagesMarket Profile On Sulphuric AcidGovindanayagi PattabiramanNo ratings yet
- Biogas An All-Rounder New Opportunities For Farming, Industry and The EnvironmentDocument102 pagesBiogas An All-Rounder New Opportunities For Farming, Industry and The EnvironmentNikolas Ferreira100% (1)
- Ethanol Production From Sugarcane Molasses PDFDocument2 pagesEthanol Production From Sugarcane Molasses PDFDaryl100% (1)
- Electrical Operation of Electrostatic PrecipitatorsDocument285 pagesElectrical Operation of Electrostatic PrecipitatorsPG100% (1)
- SHE Handbook (Onshore)Document44 pagesSHE Handbook (Onshore)samsam100% (1)
- Synthesis of Aromatic Trifluoromethyl Compounds:: The Potential For Large Scale ApplicationDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Aromatic Trifluoromethyl Compounds:: The Potential For Large Scale ApplicationisosicaNo ratings yet
- G. Kachaniwsky and C. Newman Eds. Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Co-Sponsored by the Non-Ferrous Pyrometallurgy and Hydrometallurgy Sections OfDocument279 pagesG. Kachaniwsky and C. Newman Eds. Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Co-Sponsored by the Non-Ferrous Pyrometallurgy and Hydrometallurgy Sections Ofsgaluf5No ratings yet
- On Biogas Enrichment and Bottling Technology - IITD - IndiaDocument38 pagesOn Biogas Enrichment and Bottling Technology - IITD - Indiaअश्विनी सोनी100% (3)
- BIo Gas Project Report Group 1Document20 pagesBIo Gas Project Report Group 1tryingNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bio Gas Production & Bottling PlantDocument7 pagesProject Report On Bio Gas Production & Bottling PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Techno Commercial Aspects of bio-CNG From 100 TPD Press Mud PlantDocument12 pagesTechno Commercial Aspects of bio-CNG From 100 TPD Press Mud Plantpriyank sharmaNo ratings yet
- Potential of Biogas Generation From Hybrid Napier GrassDocument5 pagesPotential of Biogas Generation From Hybrid Napier GrassEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Compressed Biogas Plant: Geon EngineersDocument8 pagesCompressed Biogas Plant: Geon Engineersanuj tomarNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Bio-CNGDocument24 pagesPresentation On Bio-CNGKondeti Muralidhar ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- PESO Project Report For BioCNG Projects in IndiaDocument3 pagesPESO Project Report For BioCNG Projects in Indiaabhi2010visionNo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument20 pagesBio GasMajor Singh SidhuNo ratings yet
- Bio CNG PDFDocument39 pagesBio CNG PDFpriyank sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Gas Seminar ReportDocument49 pagesBio Gas Seminar ReportLalitBisht100% (2)
- Landscape Report of BioCNG in India GGGI 1Document51 pagesLandscape Report of BioCNG in India GGGI 1Karthik Keyan100% (2)
- Bio Energy High Purity Solutions Engineering Businesses BioproductsDocument13 pagesBio Energy High Purity Solutions Engineering Businesses BioproductsGaurav Maniyar100% (1)
- Bio CNG From City WasteDocument12 pagesBio CNG From City WastenehareshailNo ratings yet
- CBG 30 - Tender Document - CBG04.01.21Document49 pagesCBG 30 - Tender Document - CBG04.01.21Rahul Jain100% (1)
- Vasantdada Sugar Institute PDFDocument26 pagesVasantdada Sugar Institute PDFNanasaheb PatilNo ratings yet
- Brief Industrial Profile of VISAKHAPATNAM District - DC MsmeDocument26 pagesBrief Industrial Profile of VISAKHAPATNAM District - DC MsmeParas AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biofuel Roadmap For IndiaDocument57 pagesBiofuel Roadmap For IndiaSuryadev Sinh Sisodiya100% (1)
- Rimika IITD BiogasDocument47 pagesRimika IITD BiogasRimika KNo ratings yet
- Tender Specifications-Raw Water Tanks For Bhimtal Mandal FinalDocument5 pagesTender Specifications-Raw Water Tanks For Bhimtal Mandal FinalRostfrei Steels Pvt LTD.No ratings yet
- CBG Project - Goal Bio Oil - 6 TPD - 13 PagesDocument13 pagesCBG Project - Goal Bio Oil - 6 TPD - 13 PagesAWANEENDRA DUBEY100% (2)
- CBG 50 TPD Production Project NewDocument14 pagesCBG 50 TPD Production Project NewPARTEEK SINGLANo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument4 pagesBio GasSaroj Kumar0% (1)
- Greening Indias New Energy Mix Low ResDocument96 pagesGreening Indias New Energy Mix Low ResNanasaheb PatilNo ratings yet
- Biogas Plant Development Handbook by Biogas WorldDocument39 pagesBiogas Plant Development Handbook by Biogas WorldRocky KhareNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper On: Establishment of Biogas Energy PlantsDocument5 pagesConcept Paper On: Establishment of Biogas Energy PlantsHamza ZahoorNo ratings yet
- CBG 50 TPD Production ProjectDocument13 pagesCBG 50 TPD Production ProjectAkash SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBG and Pellets ProfileDocument50 pagesCBG and Pellets ProfileAbhishek PantNo ratings yet
- " "A Study On Workers Engagement Activities ": Indu Management Institute VadodaraDocument30 pages" "A Study On Workers Engagement Activities ": Indu Management Institute Vadodarajay patelNo ratings yet
- SWOT AnalysisDocument41 pagesSWOT AnalysisMohamed Tarek Kamar100% (1)
- CPCB - Grain Based DistilleriesDocument37 pagesCPCB - Grain Based Distilleriesmyself_riteshNo ratings yet
- Request Letter: Sub:Requesting Experience Certificate For Applying BOE ExamDocument3 pagesRequest Letter: Sub:Requesting Experience Certificate For Applying BOE ExammaheshNo ratings yet
- CNG Vs LPG - Difference and Comparison - Diffen PDFDocument4 pagesCNG Vs LPG - Difference and Comparison - Diffen PDFUdit Davinci PandeyNo ratings yet
- 100 TPD Press Mud To BioCNG PlantDocument12 pages100 TPD Press Mud To BioCNG PlantRocky Khare100% (2)
- Energy Recovery From WasteDocument31 pagesEnergy Recovery From WasteSyed UmerNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control in Refineries and Fertilizer IndustriesDocument18 pagesPollution Control in Refineries and Fertilizer IndustriesTinu Paul Jepin100% (1)
- Process Design and Economics For The Conversion of The Lignocellulosic To HydrocarbonsDocument133 pagesProcess Design and Economics For The Conversion of The Lignocellulosic To HydrocarbonsCristhian Camilo Vargas QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Coal To Urea at TalcherDocument37 pagesCoal To Urea at TalcherAlfin A. N.No ratings yet
- FGD Presentation (ILFS)Document40 pagesFGD Presentation (ILFS)proloy12100% (2)
- Thermo PacDocument4 pagesThermo Pacsushant_jhawerNo ratings yet
- Firing of BiomassDocument8 pagesFiring of BiomassBrianNo ratings yet
- Glass 4 - 5 11 - 2015Document70 pagesGlass 4 - 5 11 - 2015Laxman KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3c - Cellulose DerivativesDocument37 pagesChapter 3c - Cellulose DerivativesVanessa LimNo ratings yet
- DR Seema ParohaDocument21 pagesDR Seema ParohaTEERATH RAJNo ratings yet
- 1 - Vasudeo Joshi PDFDocument52 pages1 - Vasudeo Joshi PDFKoushik DeyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Grain and Biomass Based Ethanol PlantDocument9 pagesProject Report On Grain and Biomass Based Ethanol PlantEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers33% (3)
- Boiler Efficiency Calculation - A Complete GuideDocument9 pagesBoiler Efficiency Calculation - A Complete GuideShujjat HussainNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black Production Analyzing and CharacterizationDocument86 pagesCarbon Black Production Analyzing and CharacterizationabdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Biogas Generation From Press Mud in Batch ReactorDocument6 pagesOptimization of Biogas Generation From Press Mud in Batch Reactorscm996No ratings yet
- Ethanol Production: Faculty of Mathematics and Science Education International Program On Science EducationDocument2 pagesEthanol Production: Faculty of Mathematics and Science Education International Program On Science EducationPutra Habib Dhitareka50% (2)
- Niir Manufacture Value Added Products From Rice Husk Hull Rice Husk Ash Rha 2nd Revised EditionDocument7 pagesNiir Manufacture Value Added Products From Rice Husk Hull Rice Husk Ash Rha 2nd Revised EditionShivam DangNo ratings yet
- Lactic PDFDocument13 pagesLactic PDFNadaNo ratings yet
- Sci 401pptDocument107 pagesSci 401pptNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Report Cement Sector PDFDocument76 pagesBenchmarking Report Cement Sector PDFGuilherme Pierre PaivaNo ratings yet
- Pre Feasibility Study For MIBK Plant - IndiaDocument35 pagesPre Feasibility Study For MIBK Plant - IndiaShiv KothariNo ratings yet
- Biomass EnergyDocument46 pagesBiomass EnergyRohit RathoreNo ratings yet
- SG - Zero Waste Masterplan SummaryDocument1 pageSG - Zero Waste Masterplan SummaryAlvin SohNo ratings yet
- PG StraMaDocument79 pagesPG StraMaMykhaellah Ting100% (1)
- Chapter 18 FiltrationDocument18 pagesChapter 18 FiltrationGMDGMD11No ratings yet
- Sour Water StrippingDocument10 pagesSour Water StrippingAhmet Samet ÖzdilekNo ratings yet
- Alcatel OneTouch 8020 8020d User Manual English 2Document83 pagesAlcatel OneTouch 8020 8020d User Manual English 2Raza RizviNo ratings yet
- Deed of Restrictions PDFDocument7 pagesDeed of Restrictions PDFBryan Dave RosalesNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Class 567Document14 pagesComprehension Class 567SANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- 8400 M117 O1 - 201Document158 pages8400 M117 O1 - 201pedro castilloNo ratings yet
- 12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResDocument2 pages12 - Safe Handling of Sharps - March 3 - Low ResRasheda PickettNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Organelle Nicknames!Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Organelle Nicknames!Justine OledanNo ratings yet
- How Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonDocument6 pagesHow Many Days Does A Butterfly Stay in Its CocoonMaricar RaciramNo ratings yet
- Brochure Orc Organic Rankine Cycle Technology - EN PDFDocument7 pagesBrochure Orc Organic Rankine Cycle Technology - EN PDFdolphinNo ratings yet
- Samsung DVD Camcorder VP-dx100 Eng Ib 0725-bDocument125 pagesSamsung DVD Camcorder VP-dx100 Eng Ib 0725-bkonguarasuNo ratings yet
- Nightwalker Winter 2015Document24 pagesNightwalker Winter 2015Gi GlerNo ratings yet
- PCP Evaluation ExamDocument10 pagesPCP Evaluation ExamMark Dimagiba VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- KKD Suo Motu - 0Document29 pagesKKD Suo Motu - 0jeevan820No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Philipines2010 - 431 - 05 PDFDocument33 pagesSolid Waste Philipines2010 - 431 - 05 PDFJune Alapa100% (1)
- Acknowledgement: Ikjot Singh 3070Document23 pagesAcknowledgement: Ikjot Singh 3070Ghost ModeNo ratings yet
- St. Scholastica's College Tacloban: I. Community ProfileDocument24 pagesSt. Scholastica's College Tacloban: I. Community ProfileJosh LozadaNo ratings yet
- Wastewater MGMT HandbookDocument187 pagesWastewater MGMT HandbookangbenaNo ratings yet
- HDB SOR CE Jul 2011Document86 pagesHDB SOR CE Jul 2011kokueiNo ratings yet
- Ma. Stella F. ArnaldoDocument152 pagesMa. Stella F. ArnaldoLeah LabelleNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Useful and Harmful Materials - EditedDocument25 pagesWeek 1 Useful and Harmful Materials - EditedLady Gweneth YangyangNo ratings yet
- Students Loan Trust Fund: Student Loan Application GuidelinesDocument8 pagesStudents Loan Trust Fund: Student Loan Application GuidelinesNicholas SaahNo ratings yet
- GATRONOVA Internship ReportDocument34 pagesGATRONOVA Internship ReportAbdulmunaf SheikhNo ratings yet