Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Photosynthesis
3 Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
harshit khare0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views21 pagesPhotosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It involves the transformation of light energy to chemical energy to produce organic molecules from inorganic materials. Photosynthesis provides food and energy for all life on Earth and releases oxygen into the atmosphere. It occurs in chloroplasts through two stages - the light dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH, and the light independent Calvin cycle where carbon is incorporated into organic compounds like glucose using ATP and NADPH.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhotosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It involves the transformation of light energy to chemical energy to produce organic molecules from inorganic materials. Photosynthesis provides food and energy for all life on Earth and releases oxygen into the atmosphere. It occurs in chloroplasts through two stages - the light dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH, and the light independent Calvin cycle where carbon is incorporated into organic compounds like glucose using ATP and NADPH.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views21 pages3 Photosynthesis
3 Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
harshit kharePhotosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It involves the transformation of light energy to chemical energy to produce organic molecules from inorganic materials. Photosynthesis provides food and energy for all life on Earth and releases oxygen into the atmosphere. It occurs in chloroplasts through two stages - the light dependent reactions where sunlight is absorbed to make ATP and NADPH, and the light independent Calvin cycle where carbon is incorporated into organic compounds like glucose using ATP and NADPH.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
• Greek words: photo = "light" and
synthesis = "putting together".
• The process by which green plants, algae,
some bacteria use the energy of the sun
to synthesize organic compounds (sugars)
from inorganic compounds (CO2 and
water) is known as photosynthesis.
• Involves transformation of light energy to
chemical energy
• Anabolic (small molecules combined)
• Endergonic (stores energy)
• Makes organic molecules (glucose) out of inorganic materials
(carbon dioxide and water).
• Primary source of food and energy (ATP) for all forms of life,
either directly or indirectly. Thus all life is supported by this
process.
• Photosynthesis releases O2 and hence helps to purify air, and
also maintains balance of O2 and CO2 in nature.
• The energy stored in all the fossil fuels (e.g. natural gas, coal,
petroleum(oil),etc.) is basically the solar energy which was
trapped and stored during photosynthesis in the geological past.
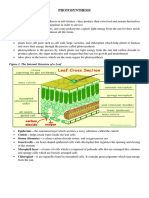
STRUCTURE OF CHLOROPLAST
• Outer membrane:-It is permeable to small organic molecules
• Inner membrane:-It is less permeable & is studded with
transport protein.
• Thylakoid:- It is a sheet-like membrane bound struture which is
site of all the light dependent reaction in chloroplast .
• Granum:-Stack of thylakoids. Grana are interconnected to each
other through lamella.
• Stroma:-It is the fluid surrounding the thylakoid in the
chloroplast. It is the site where light independent reaction of
photosynthesis occurs.
Chloroplast contain chlorophylls as the
key energy trapping molecule
Chlorophyll: A Light Absorbing Pigment
The Solar Panel Chemical!
Red and Blue
CALVIN CYCLE OF DARK REACTION
LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION
• In light-dependent reactions, which take place at the
thylakoid membrane, the light energy captured by pigment
molecules, called chlorophylls is used to generate high-energy
electrons with great reducing potential.
• These electrons are used to produce NADPH and ATP
(chemical energy) with the use of water. The production of ATP
in this way is called photophosphorylation.
• The light-dependent reactions release oxygen as a byproduct
as water is broken apart (photolysis).
ATP SYNTHESIS IN CHLOROPLAST
• At various stages during light reaction, protons
are released into the thylakoid lumen making it
markedly acidic (pH 4) than stroma (pH 8)
thereby generating a proton gradient.
• This trans-membrane proton gradient is used
to drive ATP synthesis in stroma with the help
of ATP synthase (also called the CF1- CF0
complex).
• CF0 conducts protons down their concentration
gradient into the matrix across the thylakoid
membrane, whereas CF1 catalyzes the formation
of ATP from ADP and Pi.
FUTURE OF GLUCOSE SYNTHESISED BY THE GREEN
LEAVES
• Plants store excess glucose as starch (since starch is insoluble,
water cannot enter the cells by osmosis). In some plants, starch is
stored in cell organelles called amyloplasts. Some plant roots and
embryos, in the form of seeds and fruit, also serve as storage
units for starch.
• When required, starch is broken down, in the presence of certain
enzymes and water, into its constituent monomer glucose units.
• The glucose then gets translocated to other parts of the plant by
phloem for storage or to get energy.
QUESTIONS
1) What is photosynthesis? State the importance of
photosynthesis.
2) Draw a neat well-labeled diagram of a chloroplast. State
the differences between light and dark reaction.
3) Discuss how light and dark reactions work together to
produce sugar during photosynthesis.
4) What are the major steps involved in Calvin Cycle?
5) Describe how ATP is synthesized in chloroplast.
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chirality and Aldehyde HomeworkDocument3 pagesChirality and Aldehyde HomeworkQuang Huy PhạmNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Flow of Energy and Matter in EcosystemDocument23 pagesFlow of Energy and Matter in EcosystemJazille LardizabalNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisJESSERYL MARGALLONo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PDFDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis PDFShegNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes - BiologyDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes - Biologythe lillyNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Class 10Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis Class 10shreya morajkarNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Unit 4 TOPIC 5: PhotosynthesisSamara HusainNo ratings yet
- 11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFDocument14 pages11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFToni HeaterNo ratings yet
- BIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermDocument40 pagesBIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Life of PlantsDocument8 pagesLife of PlantsKhlane R. LunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document77 pagesChapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Notes Chloroplast: Characteristics of ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesNotes Chloroplast: Characteristics of ChloroplastsSamantha JerezNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesiscanihavehaloloNo ratings yet
- Q2 L3 Science 9Document31 pagesQ2 L3 Science 9Raph tsuNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsBonny Ya SakeusNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesispwssewwandiNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument34 pagesEnergy Transformationandrew.agana1No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesisrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- Chemical ProcessesDocument4 pagesChemical ProcessesKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- Biology Task Lo 10Document12 pagesBiology Task Lo 10Abdellatif KhashabaNo ratings yet
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocument54 pagesBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 123Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis 123Alyssa L.J. Dela Cruz (Aly)No ratings yet
- Write Ups Chapter 7Document12 pagesWrite Ups Chapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Week - 3 - Lectures 1-1Document74 pagesWeek - 3 - Lectures 1-1Benjamin SamaniNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes FelixDocument29 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes FelixSean SolemNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants 1 PDFDocument6 pagesNutrition in Plants 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument40 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISBry RafNo ratings yet
- Unveiling The Light Reaction Event in PhotosynthesisDocument18 pagesUnveiling The Light Reaction Event in Photosynthesiszbplayer8No ratings yet
- The Erudite'sDocument4 pagesThe Erudite'sfestusatere192No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsDocument67 pagesBiology Unit 4 Part 1 Last Minute Revision ReallyacademicsWill AndyNo ratings yet
- Bio CellDocument102 pagesBio Cellcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Autotrophic NutritionDocument48 pagesUnit 7. Autotrophic Nutritionmunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Reporter: Levin Christellle S. Dela CruzDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis: Reporter: Levin Christellle S. Dela CruzLevin D CeeNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)monica_elysabethNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)reziegeoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis LECTUREDocument36 pagesPhotosynthesis LECTUREAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Biology Reporting FinaleDocument29 pagesBiology Reporting FinaleJohn Carlo RelosaNo ratings yet
- Report Group 11Document5 pagesReport Group 11Boyd benson kayomboNo ratings yet
- 8 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pages8 PhotosynthesisRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument48 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- Atp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument6 pagesAtp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesJhondel GuirrenNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationjhenjhentot24No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PresentationDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis PresentationveberlyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyMARCO ANTONIO CONDOR CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Q2 ReviewerDocument9 pagesGen Bio Q2 Reviewer2JoshDaveTernedaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2Document4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Organelles Involved in PhotosynthesisDocument39 pagesPlant Parts and Organelles Involved in PhotosynthesisClaire EstimadaNo ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 26 - Light Reactions of Photosynthesis OnDocument49 pagesLesson 26 - Light Reactions of Photosynthesis OnKamto EzenwamaduNo ratings yet
- c4 l1 Energy Flow in EcosystemDocument19 pagesc4 l1 Energy Flow in EcosystemShinesky GupongNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Mind MapDocument79 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants: Mind MapMiryaNo ratings yet
- Biology, LS-1001-2019-end SemDocument3 pagesBiology, LS-1001-2019-end Semharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Biology, LS-1001-2019-1Document2 pagesBiology, LS-1001-2019-1harshit khareNo ratings yet
- 5 Immune SystemDocument22 pages5 Immune Systemharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Stem CellsDocument12 pagesStem Cellsharshit khareNo ratings yet
- 4 BioremediationDocument10 pages4 Bioremediationharshit khareNo ratings yet
- 2-Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidDocument2 pages2-Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acidharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Taber D.F. - Organic Synthesis - State of The Art 2007-2009 (2011)Document253 pagesTaber D.F. - Organic Synthesis - State of The Art 2007-2009 (2011)Hi HiNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution: Causes and Prevention: October 2020Document9 pagesWater Pollution: Causes and Prevention: October 2020ASHISH SINGH BHADOURIYANo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Webinar - 3mcpd and Ge Mitigation - PresentationDocument42 pagesAlfa Laval Webinar - 3mcpd and Ge Mitigation - PresentationImam DarmantoNo ratings yet
- Recent Progress in Three-Component Reactions. An Update: M. SyamalaDocument68 pagesRecent Progress in Three-Component Reactions. An Update: M. SyamalaSalman RIAZNo ratings yet
- MSC Project Work, Anis Ahmed, SA-28.5.19Document24 pagesMSC Project Work, Anis Ahmed, SA-28.5.19mahfooz zin noorineNo ratings yet
- Proximate PrincipalDocument13 pagesProximate PrincipalDR. BHARGAV SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Advanced Tea Package Psp39Document2 pagesAdvanced Tea Package Psp39Furqon HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Zepoxy RER 128Document2 pagesZepoxy RER 128Aahsan Iqbal احسن اقبالNo ratings yet
- Compatibility of PaintsDocument1 pageCompatibility of Paintslonglong3003100% (1)
- Microbiology Principles and Explorations 10th Edition Black Test BankDocument38 pagesMicrobiology Principles and Explorations 10th Edition Black Test Bankcharles90br100% (19)
- Test Bank For Alcamos Fundamentals of Microbiology 9th Edition by PommervilleDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Alcamos Fundamentals of Microbiology 9th Edition by Pommervillethomasbrownmjtbonysgk100% (37)
- RASFF Portal: Week 05 - 2024Document8 pagesRASFF Portal: Week 05 - 2024Léa Sanchez-JammesNo ratings yet
- Mbaa TQ 55 4 1218 01 Hidden Secrets of The New England Ipa 1601582666648Document5 pagesMbaa TQ 55 4 1218 01 Hidden Secrets of The New England Ipa 1601582666648louzadasamaNo ratings yet
- LB79064-CPC TDAE Rubber Processing OilDocument1 pageLB79064-CPC TDAE Rubber Processing OilLeonie SaputriNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastic Polymers PDFDocument17 pagesThermoplastic Polymers PDFSontosidad, Febie Jynn A.No ratings yet
- Emollient For Cosmetic TestingDocument9 pagesEmollient For Cosmetic TestingAGNEL ANTONY RAJNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Essential Biochemistry Charlotte W Pratt Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Essential Biochemistry Charlotte W Pratt Online PDF All Chaptersatoshmakino0100% (12)
- Differentiate Between Sludge & Scale Sludge ScaleDocument4 pagesDifferentiate Between Sludge & Scale Sludge ScaleSankalp ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Cetiol CC (OPP)Document1 pageCetiol CC (OPP)paromanikNo ratings yet
- Cellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimuliDocument12 pagesCellular Responses To Stress and Noxious StimulialaboudimuhammadNo ratings yet
- TANNINSDocument22 pagesTANNINSHira NasirNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Interpretation of Infrared SpectraDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Interpretation of Infrared SpectraBenni WewokNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Benzene and Its DerivativeDocument46 pagesReactions of Benzene and Its Derivativequyenda08hhaNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides CHM457Document59 pagesAlkyl Halides CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Total Synthesis of ( ) - Calyciphylline N: Artem Shvartsbart and Amos B. Smith, IIIDocument4 pagesTotal Synthesis of ( ) - Calyciphylline N: Artem Shvartsbart and Amos B. Smith, IIIHưng PhúNo ratings yet
- ადამიანის ფიზიოლოგია 1Document377 pagesადამიანის ფიზიოლოგია 1giorgi borcvaZeNo ratings yet
- Patent 5Document8 pagesPatent 5ALEXANDER FRANCO CASTRILLONNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesHarish DharavathNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet