Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsRefrigeration C3
Refrigeration C3
Uploaded by
Hương LêThe document discusses concepts related to air conditioning and cooling. It introduces moisture in air, parameters to describe moisture content, psychrometric charts, and air conditioning processes. It also describes a single-level air conditioning system with its components and calculations. Finally, it discusses heat loads in buildings and air transport systems for air conditioning, including ductwork and diffusers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Easy Drive GT20manualV1.1Document102 pagesEasy Drive GT20manualV1.1Musa inverter HouseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2Saman Brookhim100% (4)
- Final Report Air ConditioningDocument42 pagesFinal Report Air ConditioningAzmi Matali73% (11)
- Scrib 2Document4 pagesScrib 2Aldwin Abidin50% (2)
- Design Solutions and Innovations in Temporary Structures Robert BealeDocument518 pagesDesign Solutions and Innovations in Temporary Structures Robert Bealerenzo divendra100% (1)
- Dougs Thermo 2a Complete Course Work Report FinalDocument23 pagesDougs Thermo 2a Complete Course Work Report Finaldoug2710No ratings yet
- Planning Design Marine TerminalsDocument9 pagesPlanning Design Marine TerminalsJoemarbert YapNo ratings yet
- Air CndtoningDocument34 pagesAir Cndtoningsusanooabc100% (9)
- Air On Coil TemperatureDocument8 pagesAir On Coil TemperatureMohamed RiyaazNo ratings yet
- Me2121-2 Performance Evaluation of Air-Conditioners (E1-03-01)Document11 pagesMe2121-2 Performance Evaluation of Air-Conditioners (E1-03-01)hybri8No ratings yet
- SBS5225 1718 Lab AC ProcessesDocument8 pagesSBS5225 1718 Lab AC ProcessesSam C M HuiNo ratings yet
- Sgre20120100004 89211808Document5 pagesSgre20120100004 89211808pramod_20253No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning ProcessDocument22 pagesAir Conditioning ProcessAsyraf MJNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry Exp2Document8 pagesPsychrometry Exp2Mohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Me2121 2Document12 pagesMe2121 2Wei QuanNo ratings yet
- Determine Specific Air Capacity Using Air Conditioning UnitDocument13 pagesDetermine Specific Air Capacity Using Air Conditioning UnitTan Xing YanNo ratings yet
- AC Exp2Document8 pagesAC Exp2sososivar55No ratings yet
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 pagesExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2Document0 pages02 Chapter 2Imtinan MohsinNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet Air CondDocument8 pagesLab Sheet Air CondAhmad AbaNo ratings yet
- U2 Psychrometrics-HPFWDocument22 pagesU2 Psychrometrics-HPFW04122No ratings yet
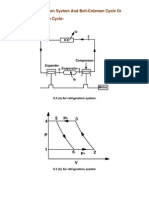
- 6.3 Air Refrigeration System and Bell-Coleman Cycle or Reversed Brayton CycleDocument5 pages6.3 Air Refrigeration System and Bell-Coleman Cycle or Reversed Brayton Cyclesumit42007No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Lab Report: Bach Khoa University Office For International Study Programs (OISP)Document23 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Lab Report: Bach Khoa University Office For International Study Programs (OISP)Minh Hồ BìnhNo ratings yet
- Air Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)Document15 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)emawz21No ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument163 pagesRefrigerationali105No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Refrigeration System 2021 22Document13 pagesLab 2 Refrigeration System 2021 22Thaneswaran BaluNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Air Conditioning 1Document8 pagesLab 9 Air Conditioning 1khairi_mohammadNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Hvac: Thermofluid LabDocument13 pagesRefrigeration & Hvac: Thermofluid LabMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Lab (Mey-303) Experiment No. 3 Aim: To Evaluate The Performance of Domestic Air ConditionerDocument9 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning Lab (Mey-303) Experiment No. 3 Aim: To Evaluate The Performance of Domestic Air ConditionerIshwarjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Air CondDocument34 pagesAir CondAnonymous k90SvONo ratings yet
- RAC 5 EdrisDocument18 pagesRAC 5 EdrisMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFDocument6 pagesLS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFdildin01No ratings yet
- T2. Air Conditioning StudyDocument8 pagesT2. Air Conditioning StudyHaha WoNgNo ratings yet
- Lab Session # 03: Newton's Law of CoolingDocument6 pagesLab Session # 03: Newton's Law of CoolingMuhammad TanveerNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EBMV3103Document13 pagesLab Manual EBMV3103VOON KIN ONNNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric RefrigerationDocument6 pagesThermoelectric RefrigerationSARABJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- ME 4122 - Thermo Fluids LabDocument9 pagesME 4122 - Thermo Fluids LabwhaleeNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Engineering PDFDocument85 pagesRefrigeration Engineering PDFanilkumarNo ratings yet
- Jobsheet 5Document12 pagesJobsheet 5g-13551554No ratings yet
- Prediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningDocument8 pagesPrediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningHammad PervezNo ratings yet
- NT3036 - Air Conditioning Lab Report Assessment Brief (HK) 30oct2021Document14 pagesNT3036 - Air Conditioning Lab Report Assessment Brief (HK) 30oct2021ho Po wongNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 SHEET - MECHANICAL HEAT PUMP 2020 - Group 1Document15 pagesLAB 3 SHEET - MECHANICAL HEAT PUMP 2020 - Group 1Thaneswaran BaluNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Comp. LinkedDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Comp. LinkedDin TescoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AIR REFRIGERATION CYCLE (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AIR REFRIGERATION CYCLE (Compatibility Mode) PDFVarun SinghNo ratings yet
- CAUNK9EB Performance Improvement of The Combined Cycle Power Plant by Intake Air Cooling Using ADocument11 pagesCAUNK9EB Performance Improvement of The Combined Cycle Power Plant by Intake Air Cooling Using APeerasak ArunNo ratings yet
- Labsheet SKKC 2721 20162017 - 02Document32 pagesLabsheet SKKC 2721 20162017 - 02HoongNo ratings yet
- Lab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerDocument21 pagesLab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerShahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document17 pagesLab 2Callum BiggsNo ratings yet
- CPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterDocument21 pagesCPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterJeeEianYannNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument85 pagesRefrigeration CycleNeha MiracleNo ratings yet
- TWP-CK-Eng VerDocument6 pagesTWP-CK-Eng VerVũ Hoàng BáchNo ratings yet
- JCIT3528PPLDocument8 pagesJCIT3528PPLgajendra2010No ratings yet
- Modelling An Air-Conditionning Plant Within The Trnsys EnvironmentDocument12 pagesModelling An Air-Conditionning Plant Within The Trnsys Environment10 000 de cartiNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor TempeDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor Tempeحسن عرقسوسيNo ratings yet
- CHP5 RefrigerationDocument22 pagesCHP5 RefrigerationKaushal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Characteristics of Fan Coil Unit FCUDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer Characteristics of Fan Coil Unit FCUShehan WijesingheNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentFrom EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Lillian Cicerchia - Why Does Class MatterDocument26 pagesLillian Cicerchia - Why Does Class Matterdoraszujo1994No ratings yet
- ECSS E ST 10 03 Rev.1 (31may2022) - Annex - A - (AIT Plan)Document3 pagesECSS E ST 10 03 Rev.1 (31may2022) - Annex - A - (AIT Plan)LNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Marketing Research Problem and Developing ApproachDocument32 pagesChapter - 2 Marketing Research Problem and Developing ApproachAyushman UpretiNo ratings yet
- UK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesDocument17 pagesUK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesПриходько РомаNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFElishaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Green Supply Chain Management Practices On Firms ' Performance: An Empirical Study From The Perspective of PakistanDocument16 pagesImpact of Green Supply Chain Management Practices On Firms ' Performance: An Empirical Study From The Perspective of PakistansyedNo ratings yet
- 46 To 54 Available DigestDocument9 pages46 To 54 Available DigestLAW10101No ratings yet
- Example An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureDocument23 pagesExample An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureAthiyo Martin100% (1)
- Chapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemDocument4 pagesChapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemZara KhanNo ratings yet
- Bringing Big Ideas To Life: NSW Innovation StrategyDocument14 pagesBringing Big Ideas To Life: NSW Innovation StrategyNG-FM KPMGNo ratings yet
- The 5 R'S: An Emerging Bold Standard For Conducting Relevant Research in A Changing WorldDocument9 pagesThe 5 R'S: An Emerging Bold Standard For Conducting Relevant Research in A Changing WorldFotachi IrinaNo ratings yet
- CPM Lab Assignment-02Document14 pagesCPM Lab Assignment-02Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety RFQDocument71 pagesFire Safety RFQAbdulgaffar HawaldarNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Practice Makes Perfect English Conversation Premium Second Edition Jean Yates All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Practice Makes Perfect English Conversation Premium Second Edition Jean Yates All Chapter PDFlinda.leary529100% (6)
- Seismic Study of Building With Roof Top Telecommunication TowersDocument4 pagesSeismic Study of Building With Roof Top Telecommunication TowersSyed Ehtesham aliNo ratings yet
- "8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)Document20 pages"8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- (Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideDocument3 pages(Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideKevin MalloryNo ratings yet
- Market Driven StrategyDocument43 pagesMarket Driven StrategyAhsan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument26 pagesNumerical DifferentiationchibenNo ratings yet
- Advances Against SecuritiesDocument26 pagesAdvances Against SecuritiesSAMBIT SAHOONo ratings yet
- Communication PlanDocument5 pagesCommunication PlanErnani Moveda FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Disinterested PersonDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Disinterested PersonDexter John SuyatNo ratings yet
- Save Money. Live BetterDocument1 pageSave Money. Live BetterdopoviNo ratings yet
- Substantive ProceduressDocument8 pagesSubstantive ProceduressayyazmNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Minimum Wages For The Year 2021Document1 pageKarnataka Minimum Wages For The Year 2021Anusree RoyNo ratings yet
- Woosung LOVD 36Document52 pagesWoosung LOVD 36sayeem bikashNo ratings yet
Refrigeration C3
Refrigeration C3
Uploaded by
Hương Lê0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesThe document discusses concepts related to air conditioning and cooling. It introduces moisture in air, parameters to describe moisture content, psychrometric charts, and air conditioning processes. It also describes a single-level air conditioning system with its components and calculations. Finally, it discusses heat loads in buildings and air transport systems for air conditioning, including ductwork and diffusers.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses concepts related to air conditioning and cooling. It introduces moisture in air, parameters to describe moisture content, psychrometric charts, and air conditioning processes. It also describes a single-level air conditioning system with its components and calculations. Finally, it discusses heat loads in buildings and air transport systems for air conditioning, including ductwork and diffusers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesRefrigeration C3
Refrigeration C3
Uploaded by
Hương LêThe document discusses concepts related to air conditioning and cooling. It introduces moisture in air, parameters to describe moisture content, psychrometric charts, and air conditioning processes. It also describes a single-level air conditioning system with its components and calculations. Finally, it discusses heat loads in buildings and air transport systems for air conditioning, including ductwork and diffusers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 26
TON DUC THANG UNIVERSITY
Faculty of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
VIETNAM GENERAL CONFEDERATION
OF LABOUR
TON DUC THANG UNIVERSITY
401081
MODERN REFRIGERATION
AND AIR CONDITIONING ENGINEERING
CHAPTER 3: AIR CONDITIONING (COOLING)
PhD. Nguyen Dao
OBJECTIVES
THIS COURSE INTRODUCES
3.1 Moisture-Air.
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.3 Air conditioning in Building
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 2
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.1 Heat transfer to and from the Body of human
1.The body gives off and absorbs heat:
-The body- temperature 98,60F= 370C,
-The body gives heat to air-atmosphere.
-The three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection,
and radiation.
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 3
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.1 Heat transfer to and from the Body of human
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 4
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.2 The Parameters of moisture air
1) Introduces
- Dry air consists of approximately 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen,
and 1% other gases.
-In air is water-vapor,
-Water in the form of low-pressure vapor, is called humidity .
-Two types:
absolute humidity and relative humidity.
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 5
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.2 The Parameters of moist air
2) The absolute humidity
The moisture content in moist air: ρva = Mva/V (Mva- capacity of
vapor in air-g; V- volume of moist-air –m3)
SI system: g/m3
British unit: lb/ft3
3) The relative humidity φ(%) = ρva/ρsa
ρva -The absolute humidity of air actual (at t0F, tC)
ρsa- The absolute humidity of air 100% saturated (vapor) (at t0F,
tC).
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 6
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.2 The Parameters of moisture air
4) The moisture content :
d = Mva /Mair ;
Mva(g)- moist ; mass of moist air:
Mva + Mair- 1kg dry air)
SI system: g/kg
British unit:lb/lb
or grain /lb = 1 gr/lb = 0,1428 g/kg
5) Dry-bulb (tD or- t ) and wet-bulb (tW - tư) temperatures:
-Using tD and tW to Calculating the relative humidity φ-% (in tables
or diagrams)
-Example: room: tD= 760F, tW= 640F-> Δt =tD-tW=120F and φ= 52%.
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 7
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.2 The Parameters of moist air
5) Dry-bulb and wet-bulb temperatures
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 8
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.2 The Parameters of moist air
6) Dew point temperatures tdw: is the
temperature at witch moisture begins
to condense
7. Enthalpy of moisture air-h
-Enthalpy of air is the measure of heat
content in air – kJ/kg; Btu/lb.
8)The Parameters of Psychrometric chart (ẩm đồ): tD; tW; ; h,
d
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 9
3.1 The Moisture Air
Psychrometric chart
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 10
3.1 The The Moisture Air
Psychrometric chart
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 11
3.1 The Moisture Air
3.1.4 The plotting of Air-conditioning processes
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 12
V.Bài tập: quá trình ĐHKK trên đồ thị t-d
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 13
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.1.The
. mixing process of recovery air R-T
and fresh air F-N produces M-H mixture
401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling)
02/11/2015 14
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.2. The Components of air conditioning system
1/ The Equipments
1-Compressor;
2- Condenser;
3-Expansion devices;
4- Evaporator;
5-Fan;
6- Conditioned air
7-Diffuser;
8-room;
9- Return air;
10- Fresh air;
11- Fan for exhaust air;
12- Exhaust air
(T=R, N=F), The scheme of air conditioning system
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 15
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.3. The Air handler(AHU)
.
2/ The Prosess
- H-O- Process cooling of air in
evaporator (φo= 90 - 95%)
- VO) -T- Process changed
parameters of air in room
- T-H-N- Process Mixture of air
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 16
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.1.The mixing
. process of
recovery air R-T and fresh air F
produces M-H mixture
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 17
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.4.The calculating of Heat capacity in the air cooling process
.
1. Grand (at point H):
-Grand Sensible Heat capacity: QHG = 1.2 LG (tH - tO); W
- Grand Latent Heat capacity: QAG = 3 LG (dH - dO); W
2. Fresh air (at point N): :
-Fresh air Sensible Heat capacity: QHN = 1.2 LN (tN - tT); W
- Fresh air Latent Heat capacity: QAN = 3 LN (dN - dT); W
3. Room (at point T): :
- Room Sensible Heat capacity: QHT = 1.2 LT (tT - tO); W
- Room Latent Heat capacity: QAT = 3 LT (dT - dO); W
- Units of quantities in the formulas: L (l / s), t (0C), d (g / kg)
LN- fresh air flow; liter/s, LT- room air flow; l/s; LH- air flow at the mixing
point; l/s L H = LT + LN = LG
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 18
3.2 Air conditioner scheme with air circulation 1 level
3.2.4.The calculating of Heat capacity in the
.
air cooling process
4. Effective Sensible Heat
- Effective Sensible Grand Heat (Hs nhiệt hiên
tổng)
SHG = QHG/ (QHG + QAG)
- Effective Sensible Room Heat (Hs nhiệt hiên
phòng R=T)
SHR = QHR/ (QHR + QAR)
5. Calculated:
- Capacity of indoor unit:
Q0 = 1,2.LH (hH - hO); W; (LH- m3 / s)
- Condensate water flow at indoor unit:
W = 1.2 LH (dH- dO); g/s 19
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling)
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.1. The same floor plan of Building with cool load
2.cool load of room
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 20
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.2 Types of Heat load Q in Building
-Air conditioning (cooling) is to keeping the space temperature of
building cool.
-The air-conditioning system (refrigeration) for removes the heat
from the outside through to structure, and heat born in the house
-When air are warm and the
humidity is high, it is no good
to rest well (removes).
-Human induction domain is
within φ = 30-70%;
tD = 73-800F (23-270C)
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 21
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.2 Heat load Q in Building
Qth = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 + Q5 + Q6; W
Qth- total excess heat in the room
Q1- heat passes through the structure
Q2 - heat emitted by humans
Q3- heat is generated by electrical equipment
Q4 - heat generated by lighting
Q5- Heat due to solar radiation
Q6- Other heat sources ( wind fresh leakage)
Sensible H.: ΣQHi = Q1 + Q2h +Q3 + Q4 +Q5 +Q6h
Latent Heat: ΣQAi =Q2a +Q6a
Cool load: Q0 >= Qth = ΣQHi 401081-chapter
02/11/2015
+ ΣQAi 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 22
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.4 The air transport system
1.Air transport system:
- the fan and moter,
- the return air system
- The duct and diffuser system
- The exhaust air system
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 23
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.4. The air transport system
2.The duct system
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 24
3.3 Air Conditioning in Building
3.3.4. The air transport system
2.The duct system
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 25
SUMMARY AND ASSIGNMENT
In this chapter, we have learnt:
• Moisture-Air.
• Single-level air conditioner diagram
• Air conditioning in building.
Reading assignment:
[1]: 897-985, [2]:5-7;44-62;215-222.;285-289;
224-231, [3]: 727-759
02/11/2015 401081-chapter 3: Air conditioning (Cooling) 26
You might also like
- Easy Drive GT20manualV1.1Document102 pagesEasy Drive GT20manualV1.1Musa inverter HouseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2Saman Brookhim100% (4)
- Final Report Air ConditioningDocument42 pagesFinal Report Air ConditioningAzmi Matali73% (11)
- Scrib 2Document4 pagesScrib 2Aldwin Abidin50% (2)
- Design Solutions and Innovations in Temporary Structures Robert BealeDocument518 pagesDesign Solutions and Innovations in Temporary Structures Robert Bealerenzo divendra100% (1)
- Dougs Thermo 2a Complete Course Work Report FinalDocument23 pagesDougs Thermo 2a Complete Course Work Report Finaldoug2710No ratings yet
- Planning Design Marine TerminalsDocument9 pagesPlanning Design Marine TerminalsJoemarbert YapNo ratings yet
- Air CndtoningDocument34 pagesAir Cndtoningsusanooabc100% (9)
- Air On Coil TemperatureDocument8 pagesAir On Coil TemperatureMohamed RiyaazNo ratings yet
- Me2121-2 Performance Evaluation of Air-Conditioners (E1-03-01)Document11 pagesMe2121-2 Performance Evaluation of Air-Conditioners (E1-03-01)hybri8No ratings yet
- SBS5225 1718 Lab AC ProcessesDocument8 pagesSBS5225 1718 Lab AC ProcessesSam C M HuiNo ratings yet
- Sgre20120100004 89211808Document5 pagesSgre20120100004 89211808pramod_20253No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning ProcessDocument22 pagesAir Conditioning ProcessAsyraf MJNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry Exp2Document8 pagesPsychrometry Exp2Mohamed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Me2121 2Document12 pagesMe2121 2Wei QuanNo ratings yet
- Determine Specific Air Capacity Using Air Conditioning UnitDocument13 pagesDetermine Specific Air Capacity Using Air Conditioning UnitTan Xing YanNo ratings yet
- AC Exp2Document8 pagesAC Exp2sososivar55No ratings yet
- Experimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %Document31 pagesExperimentno.1:The Psychrometric Processes: Relative Humidity RH %JayZx WayNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2Document0 pages02 Chapter 2Imtinan MohsinNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet Air CondDocument8 pagesLab Sheet Air CondAhmad AbaNo ratings yet
- U2 Psychrometrics-HPFWDocument22 pagesU2 Psychrometrics-HPFW04122No ratings yet
- 6.3 Air Refrigeration System and Bell-Coleman Cycle or Reversed Brayton CycleDocument5 pages6.3 Air Refrigeration System and Bell-Coleman Cycle or Reversed Brayton Cyclesumit42007No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Lab Report: Bach Khoa University Office For International Study Programs (OISP)Document23 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer Lab Report: Bach Khoa University Office For International Study Programs (OISP)Minh Hồ BìnhNo ratings yet
- Air Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)Document15 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)emawz21No ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument163 pagesRefrigerationali105No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Refrigeration System 2021 22Document13 pagesLab 2 Refrigeration System 2021 22Thaneswaran BaluNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Air Conditioning 1Document8 pagesLab 9 Air Conditioning 1khairi_mohammadNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Hvac: Thermofluid LabDocument13 pagesRefrigeration & Hvac: Thermofluid LabMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Lab (Mey-303) Experiment No. 3 Aim: To Evaluate The Performance of Domestic Air ConditionerDocument9 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning Lab (Mey-303) Experiment No. 3 Aim: To Evaluate The Performance of Domestic Air ConditionerIshwarjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Air CondDocument34 pagesAir CondAnonymous k90SvONo ratings yet
- RAC 5 EdrisDocument18 pagesRAC 5 EdrisMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- LS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFDocument6 pagesLS2 - Refrigeration Comp. Linked New PDFdildin01No ratings yet
- T2. Air Conditioning StudyDocument8 pagesT2. Air Conditioning StudyHaha WoNgNo ratings yet
- Lab Session # 03: Newton's Law of CoolingDocument6 pagesLab Session # 03: Newton's Law of CoolingMuhammad TanveerNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EBMV3103Document13 pagesLab Manual EBMV3103VOON KIN ONNNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric RefrigerationDocument6 pagesThermoelectric RefrigerationSARABJEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- ME 4122 - Thermo Fluids LabDocument9 pagesME 4122 - Thermo Fluids LabwhaleeNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Engineering PDFDocument85 pagesRefrigeration Engineering PDFanilkumarNo ratings yet
- Jobsheet 5Document12 pagesJobsheet 5g-13551554No ratings yet
- Prediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningDocument8 pagesPrediction of Thermal Performance of Cooling Tower of A Chiller Plant Using Machine LearningHammad PervezNo ratings yet
- NT3036 - Air Conditioning Lab Report Assessment Brief (HK) 30oct2021Document14 pagesNT3036 - Air Conditioning Lab Report Assessment Brief (HK) 30oct2021ho Po wongNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 SHEET - MECHANICAL HEAT PUMP 2020 - Group 1Document15 pagesLAB 3 SHEET - MECHANICAL HEAT PUMP 2020 - Group 1Thaneswaran BaluNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Comp. LinkedDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Comp. LinkedDin TescoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - AIR REFRIGERATION CYCLE (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 2 - AIR REFRIGERATION CYCLE (Compatibility Mode) PDFVarun SinghNo ratings yet
- CAUNK9EB Performance Improvement of The Combined Cycle Power Plant by Intake Air Cooling Using ADocument11 pagesCAUNK9EB Performance Improvement of The Combined Cycle Power Plant by Intake Air Cooling Using APeerasak ArunNo ratings yet
- Labsheet SKKC 2721 20162017 - 02Document32 pagesLabsheet SKKC 2721 20162017 - 02HoongNo ratings yet
- Lab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerDocument21 pagesLab Refrigeration N Cooling TowerShahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document17 pagesLab 2Callum BiggsNo ratings yet
- CPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterDocument21 pagesCPT-325 - 13 - Model of A 3-Zone FW HeaterJeeEianYannNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument85 pagesRefrigeration CycleNeha MiracleNo ratings yet
- TWP-CK-Eng VerDocument6 pagesTWP-CK-Eng VerVũ Hoàng BáchNo ratings yet
- JCIT3528PPLDocument8 pagesJCIT3528PPLgajendra2010No ratings yet
- Modelling An Air-Conditionning Plant Within The Trnsys EnvironmentDocument12 pagesModelling An Air-Conditionning Plant Within The Trnsys Environment10 000 de cartiNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor TempeDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Refrigerant Charge and Outdoor Tempeحسن عرقسوسيNo ratings yet
- CHP5 RefrigerationDocument22 pagesCHP5 RefrigerationKaushal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Characteristics of Fan Coil Unit FCUDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer Characteristics of Fan Coil Unit FCUShehan WijesingheNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentFrom EverandSustainable Energy Conversion for Electricity and Coproducts: Principles, Technologies, and EquipmentNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Lillian Cicerchia - Why Does Class MatterDocument26 pagesLillian Cicerchia - Why Does Class Matterdoraszujo1994No ratings yet
- ECSS E ST 10 03 Rev.1 (31may2022) - Annex - A - (AIT Plan)Document3 pagesECSS E ST 10 03 Rev.1 (31may2022) - Annex - A - (AIT Plan)LNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Marketing Research Problem and Developing ApproachDocument32 pagesChapter - 2 Marketing Research Problem and Developing ApproachAyushman UpretiNo ratings yet
- UK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesDocument17 pagesUK Armed Forces Equipment and Formations 2022 TablesПриходько РомаNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesMedia and Information Literacy Prelims Reviewer PDFElishaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Green Supply Chain Management Practices On Firms ' Performance: An Empirical Study From The Perspective of PakistanDocument16 pagesImpact of Green Supply Chain Management Practices On Firms ' Performance: An Empirical Study From The Perspective of PakistansyedNo ratings yet
- 46 To 54 Available DigestDocument9 pages46 To 54 Available DigestLAW10101No ratings yet
- Example An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureDocument23 pagesExample An Op Amp Circuit Analysis LectureAthiyo Martin100% (1)
- Chapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemDocument4 pagesChapter No 7: Data Collection Multiple Choice Questions SUBJECT:Business Research Methods PREPARED BY:Maryum SaleemZara KhanNo ratings yet
- Bringing Big Ideas To Life: NSW Innovation StrategyDocument14 pagesBringing Big Ideas To Life: NSW Innovation StrategyNG-FM KPMGNo ratings yet
- The 5 R'S: An Emerging Bold Standard For Conducting Relevant Research in A Changing WorldDocument9 pagesThe 5 R'S: An Emerging Bold Standard For Conducting Relevant Research in A Changing WorldFotachi IrinaNo ratings yet
- CPM Lab Assignment-02Document14 pagesCPM Lab Assignment-02Muhammad NomanNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety RFQDocument71 pagesFire Safety RFQAbdulgaffar HawaldarNo ratings yet
- Textbook Ebook Practice Makes Perfect English Conversation Premium Second Edition Jean Yates All Chapter PDFDocument43 pagesTextbook Ebook Practice Makes Perfect English Conversation Premium Second Edition Jean Yates All Chapter PDFlinda.leary529100% (6)
- Seismic Study of Building With Roof Top Telecommunication TowersDocument4 pagesSeismic Study of Building With Roof Top Telecommunication TowersSyed Ehtesham aliNo ratings yet
- "8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)Document20 pages"8086 Interrupts" in (Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing)MUHAMMAD ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- (Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideDocument3 pages(Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideKevin MalloryNo ratings yet
- Market Driven StrategyDocument43 pagesMarket Driven StrategyAhsan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument26 pagesNumerical DifferentiationchibenNo ratings yet
- Advances Against SecuritiesDocument26 pagesAdvances Against SecuritiesSAMBIT SAHOONo ratings yet
- Communication PlanDocument5 pagesCommunication PlanErnani Moveda FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Disinterested PersonDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Disinterested PersonDexter John SuyatNo ratings yet
- Save Money. Live BetterDocument1 pageSave Money. Live BetterdopoviNo ratings yet
- Substantive ProceduressDocument8 pagesSubstantive ProceduressayyazmNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Minimum Wages For The Year 2021Document1 pageKarnataka Minimum Wages For The Year 2021Anusree RoyNo ratings yet
- Woosung LOVD 36Document52 pagesWoosung LOVD 36sayeem bikashNo ratings yet