Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G6 Habitat of The Living
G6 Habitat of The Living
Uploaded by
Kamal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views66 pagesThe document describes the major habitat types found around the world and their defining characteristics. It discusses the five main habitats of forests, deserts, grasslands, mountains, and aquatic. For each habitat, it outlines the location, climate, common flora and fauna. It also describes the adaptations that allow organisms to survive in each particular habitat.
Original Description:
Original Title
G6 Habitat of the Living
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the major habitat types found around the world and their defining characteristics. It discusses the five main habitats of forests, deserts, grasslands, mountains, and aquatic. For each habitat, it outlines the location, climate, common flora and fauna. It also describes the adaptations that allow organisms to survive in each particular habitat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views66 pagesG6 Habitat of The Living
G6 Habitat of The Living
Uploaded by
KamalThe document describes the major habitat types found around the world and their defining characteristics. It discusses the five main habitats of forests, deserts, grasslands, mountains, and aquatic. For each habitat, it outlines the location, climate, common flora and fauna. It also describes the adaptations that allow organisms to survive in each particular habitat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 66
Habitat
•A habitat is a place or an area where an organisms
lives naturally and gets what it needs to survive.
•5 major habitat-
•forest,
•desert,
•aquatic,
•mountain
• polar
Forest
• Large area cover with plant
• One third of plant present in forest
• Different types of plants and animals are
available.
Types of forest
• 3 major type
• Tropical forest(rain forest)
• Found between the equator and 2
tropics(tropic of cancer and tropic of
capricorn)
• Amazon basin in SA and Congo basin in Central
Africa
• 20 degree C to 34 degree C
• Receive heavy rain fall
• Day-12 hours
• Annual rainfall more than 2500mm
• Flora and fauna
• Plants:orchid, vine, ebony rubber
• Animals:bat, gorilla, monkey, jaguar, sloth,
macaw, toucan and variety of insects.
• No winter
Temperate forest
• Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle
• Eastern north america, north eastern asia and
western and central europe
• -30 degree C to 30 degree C
• Annual rainfall 1500mm
Deciduous forest
• Well defined winter and summer seasons
• Plants: maple, oak and elm
• Animals:Fox, bald eagle, mountain lion, bobcat
and black bear
Evergreen forest
• Broad leaves
• Not shed all their leaves
Boreal forest
• Taiga
• North of temperate forest and extend upto
Arctic Circle
• Canada, russia, scandinavia, china, monglia
and northern japan
• Low temp
• -50 degree C to 30 degree C
• Annual snowfall 400mm to 1000mm
• Plants:pine, fir and spruce
• Animals:wolf, lynx,fox, deer, woodpecker and
chipmunk
• Long winter and short summers
Grassland
• Below the Arctic circle to slightly below the
tropic of Capricorn
• North America, Africa, Australia, Argentina,
Russia and India
Grassland
• Not too many trees and shrub
• -20 degree C and 30 degree C
• Rainfall 50cm and 90cm
• Shelter for giraffe, zebra, lion , elephant and
gazelle, red-tailed hawks and prairie dogs
• Flora-buffalo grass, blue grass, blue grama
grass, coneflowers and wild indigo
• Thick grass
Desert
• Parallel to equator between 25 degree to 30
degree N and S latitude
• One fifth of total land
• Central Asia, Arabian peninsula, India, South
West Africa, North and South America
Deserts
• Sahara, kalahari and thar
• Dry and Very little rainfall
• Day time temp 45degree C to 50 C(summer)
• Annual rainfall 25cm
• Gobi desert(china)-hot and very cold
• Cactus, camel, rattlesnake, gilamonster and
kangaroo rat
Mountains
• All continents
• Very cold and wind
• Flora-broad leaf plants, coniferous trees(pine
and alpine)
• Fauna-Polar bear, penguin, seal and walrus
• Mountains are rocky ,form of snow and ice
Polar regions
• Artic region in north and Antarctic region
• Cold climate
• Artic-30 degree C
• Antartic -89 degree C
• Flora- arctic poppy, reindeer moss
• Fauna-polar bears arctic foxes
• Antarctica is covered with 2km thick sheet of
ice and snow.
Aquatic habitat
• Water bodies
• Freshwater, marine and coastal
• Fresh water habitat: river, lakes, ponds and
streams .
• Fish, frog, duck, lotus and water lily
Freshwater
• Flora-lotus and water lily
• Fauna-frogs and fish
• Freshwater wetlands
• Flora-grasses, reeds(tall plant), water hyacinth
• Marine habitat
• Ocean and seas form largest habitat
• Salty water
• Large variety of animals
• Tiny plankton
• Blue whale(largest animal)
• Fish, whale, shark, jellyfish, crab, starfish, sea
turtle, octopus and seaweed
• Coastal habitat: Region- land meet sea
• Estuaries: Salt water mixes with fresh
water(brackish water)
• Shelter-marine birds and animals
• Animals:crab, oyster, waterfowl and worm
• Mangroves, seaweed and marsh grasses
• Sundarban delta(west bengal and bangladesh)
Contains
Mangrove forest
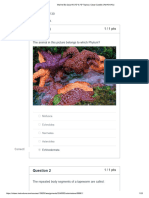
Coral reefs
• Rock like structure made by calcium carbonate
• Rainforest of the sea
• Shelter:marine organisms
• Sea anemones, starfish octopus, sea urchins
• Great barrier reef of Australia and Andaman
and Nicobar Islands in India
Adaptation
• Changes in the structure or behavior of an
organism which allow it to survive in a
particular habitat are called adaptation
• Changes in body:special body
part(modification)
• Changes in behaviour: deep sleep in extremely
cold condition-hibernation
• Changes in location:migration
Adaptation for tropical forest
• Plants
• Drip tips-flow water fast, waxy surface
• Leaves: climbing up and broader leaf
• Animals:
• know to eat particular food(which doest act as
food for other)
• Sloth and insects-camouflage
• Birds-strong beak to crack hard nut
• High competition for food
Adaptation for temperate forest
• Plants: Deciduous-thin and broad leaf carry
photosynthesis
• Leaves will fall down during winter
• Woody vines climb up on trees to access the
sunlight
• Animals: hibernate and migrate(hedgehogs
and bears)
• Chipmunk- gather food during summer
Adaptation for boreal forest
• Plants: conical shape leaf-fall snow
• Evergreen trees
• Needle like leaves(protect leaf)
• Close stomata to restrict water loss
• Animals: migrate and thick layer of fur will
protect them.
• Siberian tiger- furry coat , long legs, large paws
Adaptation of grassland
• Plants: flexible stem, strong root protect from
uprooting
• Narrow and tiny leaf(reduce water lost)
• Baobab tree(store water in trunk)
• Roots goes inside(protect from overgrazing)
• Animals: run very fast-escape from fire and
predators
• Animals nocturnal life
Adaptation for desert
• Plants: long roots
• Cacti-store water in fleshy stem succulents
Cactus:leaves-spines-minimize water loss
Stem-green
Stem-swollen and fleshy to store water
Thick waxy coat prevent water loss
• Animals: Camel:long eyelash,eyehair and
nostrils(prevent form wind blowen)
• Thick eyebrow provide shade from the bright sun
• Wide feet helps to walk in sand
• Hump –reservoir of fatty tissue.
• Camel can go without water a week and can last
for several month without food.
• Thick lips-eat prickly desert plants
• Camel withstand 34o to 41.7o
• Kangaroo rats:In burrows, recycle moisure
from own breathing
• Active in morning
• Evening scorching heat.
• Not drink water
Adaptation for mountain region
• Plant-cone shaped
• Diapensia-grow few cm
Adaptations of polar regions
• Plants
• Avoid uproot,
• Lichen and mosses
• Animals
• White fur
• Water repellent and camouflage
• Blubber-thick fat
• Large paws
• Animals
• Hibernate-squirrel
• Goat-long hair protect from cold
• Yak long hair-more RBC
Adaptations for aquatic habitat
• Long and narrow stems
• Air chamber in stem
• Leaf with waxy cover
Aquatic animals
• Ducks-webbed feet
• Hallow bones
• Oil produced under their tail-feather
waterproof
• Fish
• Gills
• Streamlined body
• Octopus and squid
Dolphin and whale
• Lungs
• Blowholes at upper part of head
• Come to water surface breathe
1. Which parts of India have tropical forests?
• Western Ghats in Kerala and Karnataka hills of
Jaintia and Khasi
2.Why are rainforests full of life?
• They have most suitable climate for flora and
fauna. It is receive enough rainfall and
sunlight.
• Many medicinal plants, foods and resources
are found here.
• They have more potential for sustaining life.
Acclimatization
• Changes for short time with surroundings
• Sheep with wool
• Altitude sickness
You might also like
- Outlander Crossword 3Document3 pagesOutlander Crossword 3littlemrssNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument42 pagesBiomesdkretzmerNo ratings yet
- Major Biomes of The WorldDocument15 pagesMajor Biomes of The Worldraktim.gaziNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources-CompressedDocument34 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources-Compressedcome2sandhyaNo ratings yet
- Taiga BiomeDocument21 pagesTaiga Biomeobsidiangc910No ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument28 pagesNatural Vegetation and WildlifeAvichal TatuNo ratings yet
- Biomes (Bs Physics Env - Sci Notes)Document9 pagesBiomes (Bs Physics Env - Sci Notes)UsmanMustafaNo ratings yet
- LongbiomeDocument23 pagesLongbiomeapi-197811403No ratings yet
- TundraDocument14 pagesTundraduckofc1820No ratings yet
- Indian Climate and Animal AdaptionsDocument28 pagesIndian Climate and Animal AdaptionsTee Bee100% (1)
- Natural Vegetation and Wild LifeDocument76 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wild LifeGagan SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 5 BiomesDocument62 pagesModule 5 Biomesricky bergantinosNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument61 pagesUntitledomg-its-a-treeNo ratings yet
- HABITAT OF THE LIVING - Part IDocument15 pagesHABITAT OF THE LIVING - Part Iashutoshbombatkar2No ratings yet
- Extra - Terrestrial BiomesDocument21 pagesExtra - Terrestrial Biomesapi-375285021No ratings yet
- Types of EcosystemDocument31 pagesTypes of Ecosystemmeet rakholiyaNo ratings yet
- E.V.S Unit 4 Biodiversity and ConservationDocument11 pagesE.V.S Unit 4 Biodiversity and ConservationSHIREEN TEKADENo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Ecosystems and CommunitiesDocument48 pagesLesson 4 Ecosystems and CommunitiesJohn CincoNo ratings yet
- Science Class 7 HabitatDocument17 pagesScience Class 7 HabitatshiraazgrewalNo ratings yet
- HABITAT OF THE LIVING - CompleteDocument35 pagesHABITAT OF THE LIVING - Completeashutoshbombatkar2No ratings yet
- Ecosystem: Hecho Por: Catalin Daniel BudeaDocument15 pagesEcosystem: Hecho Por: Catalin Daniel BudeaCatalinNo ratings yet
- Biomes and EcosystemsDocument31 pagesBiomes and EcosystemsFrance KennethNo ratings yet
- Flora and Fauna in Arctic TundraDocument20 pagesFlora and Fauna in Arctic TundraCalvin Klein Gadilla TanNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument28 pagesBiomesapi-294395989No ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument11 pagesNatural Vegetation and WildlifeHimangshu SenNo ratings yet
- Terrestrial BiomesDocument29 pagesTerrestrial Biomesapi-297045638No ratings yet
- Tundra BiomeDocument17 pagesTundra BiomeFrance KennethNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Ecosystems and CommunitiesDocument48 pagesLesson 4 Ecosystems and CommunitiesJohn CincoNo ratings yet
- Habitats For PlantsDocument8 pagesHabitats For PlantsRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- BiomesDocument74 pagesBiomesHallares, Maxine Kate F.No ratings yet
- Notes of CH 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ClaDocument15 pagesNotes of CH 5 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ClaGurman SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Life in The Temperature ZonesDocument32 pagesChapter 5 - Life in The Temperature Zonesvenkat.raghu2012No ratings yet
- EVS Lecture 10Document9 pagesEVS Lecture 10SHREE KRIPA SHANKARI SNo ratings yet
- Tundra Biome: By: Esther Kim & Mae Lesko AP Biology 7/8 BDocument36 pagesTundra Biome: By: Esther Kim & Mae Lesko AP Biology 7/8 BEsther KimNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation, Different Types of Forests of IndiaDocument3 pagesNatural Vegetation, Different Types of Forests of Indiakatrina167No ratings yet
- Chapter - 5 Natural - Vegetation - and - Wildlife - WatermarkDocument16 pagesChapter - 5 Natural - Vegetation - and - Wildlife - Watermarkbijoj2000No ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument23 pagesEcosystemvihaan.kharbandaNo ratings yet
- 1705385875685.17 - Forests Our Lifeline - Notes (2023-24)Document22 pages1705385875685.17 - Forests Our Lifeline - Notes (2023-24)Kashyap DaveNo ratings yet
- Biomes Interactive Study GuideDocument32 pagesBiomes Interactive Study Guideapi-169639475No ratings yet
- Tropical RainforestDocument20 pagesTropical RainforestDebbie Eclarino100% (1)
- 3) Types of Ecosystem - Sept23Document51 pages3) Types of Ecosystem - Sept23Dhana Priya KesavanNo ratings yet
- EnviScie (Week 4)Document28 pagesEnviScie (Week 4)Shienna MillareNo ratings yet
- Naturalvegetationandwildlife9th 171217053225Document30 pagesNaturalvegetationandwildlife9th 171217053225dnbabu4No ratings yet
- CH 05 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Notes Class 09Document4 pagesCH 05 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Notes Class 09Hridya PrasadNo ratings yet
- Training On Ecosystem Benefit PPT 2008Document77 pagesTraining On Ecosystem Benefit PPT 2008Rafez JoneNo ratings yet
- Forest EcosystemDocument21 pagesForest Ecosystemmaheshboobalan0% (1)
- Life in DesertDocument10 pagesLife in DesertSatyabrataNo ratings yet
- BIOMES+and+ECOSYSTEMS+Lesson+1 7+Pages+42+Adn+43+in+WorkbookDocument42 pagesBIOMES+and+ECOSYSTEMS+Lesson+1 7+Pages+42+Adn+43+in+Workbookjeremyskipworth173No ratings yet
- India-Natural Vegetation, Wildlife and ConservationDocument23 pagesIndia-Natural Vegetation, Wildlife and Conservationtarunvenu2007No ratings yet
- BIOMESDocument75 pagesBIOMESh.tabuena.533718No ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument20 pagesNatural Vegetation and Wildlifekaltamash526No ratings yet
- Natural Vege Eng 73Document4 pagesNatural Vege Eng 73mahimalakhore77No ratings yet
- Coastal EcosystemsDocument27 pagesCoastal EcosystemsDasari100% (1)
- Biomes PRJDocument32 pagesBiomes PRJResty DamasoNo ratings yet
- M VGG 38 HYODhe 9 COC970Document18 pagesM VGG 38 HYODhe 9 COC970kaltamash526No ratings yet
- Northern Coniferous Forests (Taiga) : By: IvosomesDocument19 pagesNorthern Coniferous Forests (Taiga) : By: IvosomesSteph GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Trop Marine Climate and VegDocument34 pagesTrop Marine Climate and VegJosh HenryNo ratings yet
- Savanna & Tundra BiomeDocument21 pagesSavanna & Tundra BiomeLucia WassonNo ratings yet
- Desert EcosystemDocument36 pagesDesert EcosystemmadhumithavaniNo ratings yet
- By Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistDocument27 pagesBy Dr. B. Williams, Media SpecialistAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Narrative TextDocument6 pagesNarrative TextAmandaNo ratings yet
- Guinea FowlDocument33 pagesGuinea FowlIdris Sunusi IdrisNo ratings yet
- OPD FormDocument11 pagesOPD FormJohn Almin LarosaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Chicken Author The South African Poultry AssociationDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Chicken Author The South African Poultry AssociationCharbel AounNo ratings yet
- PFW Mini PosterDocument2 pagesPFW Mini PosterS M Asif Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Marine Bio Quiz #3 ( - D - & - E - Topics)Document23 pagesMarine Bio Quiz #3 ( - D - & - E - Topics)Julio CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Applications For The Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesMathematical Applications For The Management Life and Social Sciences 11th Edition Harshbarger Solutions Manualbessieguerreroaid6q100% (24)
- Integumentary System Short QuizDocument3 pagesIntegumentary System Short Quizkenneth PradoNo ratings yet
- AdorableDocument2 pagesAdorableКарина ШишковскаяNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science TemplateDocument10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science TemplateSharlene Jane Chavez Eleccion0% (1)
- Proses Perkembangan Embrio Pada Tahapan CleavageDocument43 pagesProses Perkembangan Embrio Pada Tahapan CleavageAnton TubagusNo ratings yet
- Social Organisation in Animals.: Saju J Zacharia 17-PZO-017Document29 pagesSocial Organisation in Animals.: Saju J Zacharia 17-PZO-017Saju John ZachariaNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS Big 7 GenapDocument4 pagesSoal PTS Big 7 GenapAnang Mahmudi100% (1)
- TOEpelDocument6 pagesTOEpelIndra Yostra SurbaktiiNo ratings yet
- HIPPOCAMPUSDocument12 pagesHIPPOCAMPUSMadhav GoelNo ratings yet
- Final Project Lesson Plan PeDocument2 pagesFinal Project Lesson Plan Peapi-250794188No ratings yet
- Wildlife Fact File - Mammals Pgs. 311-320Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Mammals Pgs. 311-320ClearMind84100% (1)
- HSN Code & GST Rate For Live Animals and PoultryDocument2 pagesHSN Code & GST Rate For Live Animals and PoultryalokesenguptaNo ratings yet
- Poult Sci 2016 Effects of Floor Eggs On HatchabilityDocument8 pagesPoult Sci 2016 Effects of Floor Eggs On HatchabilityMihajlo PopovicNo ratings yet
- Jakes Nature Guide Birding For BeginnersDocument26 pagesJakes Nature Guide Birding For Beginnersmadhavkrishna gargNo ratings yet
- Ocean Game PackDocument14 pagesOcean Game PackLim LimNo ratings yet
- Uts P2.1Document4 pagesUts P2.1nadia imaniar julia kahfiNo ratings yet
- National Geographic Little Kids 2014 07-08Document36 pagesNational Geographic Little Kids 2014 07-08Nadine ButovaNo ratings yet
- Animals in The City Level B2 Level ExerciseDocument2 pagesAnimals in The City Level B2 Level Exercisert1992No ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesInterview QuestionsSiyi 思伊No ratings yet
- Adaptation in AnimalsDocument4 pagesAdaptation in AnimalsSobithaa SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Types of PestsDocument26 pagesLecture 1 Types of PestsArooj Fatima100% (1)
- Ncert Line by Line ZoologyDocument237 pagesNcert Line by Line ZoologyYash SinghNo ratings yet
- Living Things in Their EnvironmentDocument48 pagesLiving Things in Their EnvironmentEdwardNo ratings yet