Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mean Value Theorem
Mean Value Theorem
Uploaded by
Shivam Sen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesLagrange's Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), then there exists a value c in [a,b] where the derivative of f equals the slope of the line between f(a) and f(b). Rolle's Theorem is a special case where if f is continuous on [a,b], differentiable on (a,b), and f(a)=f(b), then there exists a c in (a,b) where the derivative of f is 0.
Original Description:
For Math teaching Exams
Original Title
Mean Value Theorem Pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLagrange's Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), then there exists a value c in [a,b] where the derivative of f equals the slope of the line between f(a) and f(b). Rolle's Theorem is a special case where if f is continuous on [a,b], differentiable on (a,b), and f(a)=f(b), then there exists a c in (a,b) where the derivative of f is 0.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views5 pagesMean Value Theorem
Mean Value Theorem
Uploaded by
Shivam SenLagrange's Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), then there exists a value c in [a,b] where the derivative of f equals the slope of the line between f(a) and f(b). Rolle's Theorem is a special case where if f is continuous on [a,b], differentiable on (a,b), and f(a)=f(b), then there exists a c in (a,b) where the derivative of f is 0.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
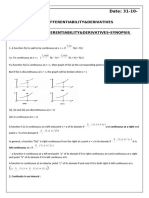
Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorem
If a function f is defined on the closed interval [a,b] satisfying
the following conditions –
i) The function f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]
ii)The function f is differentiable on the open interval (a, b)
Then there exists a value x = c in such a way that
f'(c) = [f(b) – f(a)]/(b-a)
This theorem is also known as the Lagrange’s mean value
theorem.
Rolle’s Theorem
A special case of Lagrange’s mean value theorem is Rolle’s Theorem
which states that:
If a function f is defined in the closed interval [a, b] in such a way that it
satisfies the following conditions.
i) The function f is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]
ii)The function f is differentiable on the open interval (a, b)
iii) Now if f (a) = f (b) , then there exists at least one value of x, let us
assume this value to be c, which lies between a and b i.e. (a < c < b )
in such a way that f‘(c) = 0 .
You might also like
- Abbott Intro To Real Analysis CH 4Document3 pagesAbbott Intro To Real Analysis CH 4Anonymous ds6sqpdVNo ratings yet
- Situations Involving Rolle's Theorem and Mean Value Theorem: A Simple SituationDocument1 pageSituations Involving Rolle's Theorem and Mean Value Theorem: A Simple Situationapi-240156957No ratings yet
- Rolle's Theorem NotesDocument2 pagesRolle's Theorem Noteskokaged464No ratings yet
- Lecture 28Document7 pagesLecture 28The tricksterNo ratings yet
- Btech 1st Sem: Maths: Mean Value TheoremDocument7 pagesBtech 1st Sem: Maths: Mean Value TheoremTechno India Group80% (5)
- The Mean Value TheoremDocument5 pagesThe Mean Value TheoremMoetassem SarayaNo ratings yet
- Akki Rolles TheoremDocument2 pagesAkki Rolles TheoremVenkat ReddyNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Functions I: 5.1 Is There Any - . - of A Continuous Function?Document9 pagesInvestigation of Functions I: 5.1 Is There Any - . - of A Continuous Function?Kelvin LauNo ratings yet
- Calculus I - The Mean Value TheoremDocument4 pagesCalculus I - The Mean Value Theoremmayur6578No ratings yet
- Rolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric NotationDocument5 pagesRolle's, Langrage's and Cauchy's Theorem Numeric Notationchauhangoli2425No ratings yet
- Mathematics-I All Unit NotesDocument121 pagesMathematics-I All Unit NotescoachingteslaNo ratings yet
- Applications of DifferentiationDocument57 pagesApplications of Differentiationdbreddy287No ratings yet
- 1 Applications of Differentiation: 1.1 Maximum and Minimum Values of FunctionsDocument7 pages1 Applications of Differentiation: 1.1 Maximum and Minimum Values of Functionsprica_adrianNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Lecture NotesDocument4 pages4.2 Lecture NotesDevil InsideNo ratings yet
- Calculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23Document9 pagesCalculus2014 Lecturenote 10 23盧思宇No ratings yet
- MeanvalhhhhueDocument4 pagesMeanvalhhhhueKaitPadillaNo ratings yet
- Real Analysis Notes9Document3 pagesReal Analysis Notes9MathsisCoolV1No ratings yet
- Lecture6 PDFDocument2 pagesLecture6 PDFPrateek YuvrajNo ratings yet
- Unit-10 Properties of Continuous FunctionsDocument14 pagesUnit-10 Properties of Continuous FunctionsChandradeep Reddy TeegalaNo ratings yet
- Cauchy's Mean Value Theorem: ProofDocument20 pagesCauchy's Mean Value Theorem: ProofShilpee ShilpeeNo ratings yet
- PieceWise Functions and ExtremasDocument4 pagesPieceWise Functions and Extremassnalo mdludluNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesPart 2 Continuous Functions and Their Properties: 2.1 DefinitionmercyNo ratings yet
- The Mean Value Theorem Math 120 Calculus IDocument4 pagesThe Mean Value Theorem Math 120 Calculus IJérômeNo ratings yet
- Difference Equations To: Section 3.7 Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value TheoremDocument13 pagesDifference Equations To: Section 3.7 Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value TheoremAnonymous Go6ClqNo ratings yet
- MathDocument12 pagesMathamandogra4565No ratings yet
- The Mean Value TheoremDocument6 pagesThe Mean Value TheoremPaul BunhuNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegralDocument3 pagesDefinite IntegralAgrim Kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 RollesDocument13 pagesLecture 1 RollesSydney Chongo ChipambalaNo ratings yet
- Year of Establishment - 1997: Department of Mathematics, CvrceDocument17 pagesYear of Establishment - 1997: Department of Mathematics, CvrceRam Swaroop100% (1)
- Chapter 4.1Document47 pagesChapter 4.1inglenish30No ratings yet
- Calculus I - 3.2 PDFDocument4 pagesCalculus I - 3.2 PDFLuseane Matavesi Fe'aoNo ratings yet
- Semi Finals - Applic. of Diff. 2. Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value TheoremDocument16 pagesSemi Finals - Applic. of Diff. 2. Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value TheoremAndoy Morales IIINo ratings yet
- UW Möbius - Extreme ValuesDocument12 pagesUW Möbius - Extreme ValuesEmma ScottNo ratings yet
- CALCDocument22 pagesCALCjrqagua00332No ratings yet
- Monotonicity 3Document22 pagesMonotonicity 3APS Apoorv prakash singhNo ratings yet
- Implicit Function TheoremDocument52 pagesImplicit Function TheoremabraksaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document22 pagesChapter 19Ariana Ribeiro Lameirinhas100% (1)
- Calculus I Chapter 3 (Printed Version)Document94 pagesCalculus I Chapter 3 (Printed Version)tranvutruynamNo ratings yet
- WeberciseDocument1 pageWeberciseapi-334654894No ratings yet
- Highly Nonlinear Balanced Boolean With A Correlation-ImmunityDocument14 pagesHighly Nonlinear Balanced Boolean With A Correlation-Immunitynico59_2No ratings yet
- A Constructive Proof of Simpson's Rule: Hierry Oquand AS PittersDocument8 pagesA Constructive Proof of Simpson's Rule: Hierry Oquand AS PittersBrian FerNo ratings yet
- 2024 3 (Updated)Document20 pages2024 3 (Updated)a.emera22No ratings yet
- Assignment For B.tech First Sem Mathematics I 2017Document29 pagesAssignment For B.tech First Sem Mathematics I 2017Debdutta ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- MTH341Document107 pagesMTH341johnpaulinusogyeNo ratings yet
- M4.2 Continuity Major TheoremsDocument2 pagesM4.2 Continuity Major TheoremsJason CostanzoNo ratings yet
- ContinuityDocument23 pagesContinuityMarjorie Palconit NoqueraNo ratings yet
- C&D SynopsisDocument7 pagesC&D SynopsisprekshithreddygattlaNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1Document47 pagesCalculus 1Nitya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- MTH165 Unit 3Document154 pagesMTH165 Unit 3RahulNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Application of The Derivative 4.1. Local and Absolute Extrema of A Continuous FunctionDocument10 pagesChapter Four Application of The Derivative 4.1. Local and Absolute Extrema of A Continuous FunctionBelew BelewNo ratings yet
- Continuous FunctionDocument9 pagesContinuous FunctionNur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Mean Value TheoremsDocument20 pagesUnit 12 Mean Value TheoremsChandradeep Reddy TeegalaNo ratings yet
- MA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakDocument19 pagesMA10001 (Advanced Calculus) : C NahakSaurabhNo ratings yet
- 1dmetmath101 Zoom Meeting (15july23) - No AnswersDocument96 pages1dmetmath101 Zoom Meeting (15july23) - No AnswersYvanneNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Ivt Squeeze THM and More ContinuityDocument2 pages1.4 Ivt Squeeze THM and More ContinuityD SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Rolle's Theorem and Lagrange's Mean Value TheoremDocument17 pagesLecture 1-Rolle's Theorem and Lagrange's Mean Value TheoremDuffer BoysNo ratings yet
- Cal1 Chapter 3Document80 pagesCal1 Chapter 3Vân Anh Nguyễn NgọcNo ratings yet
- Functions Continuity CalcDocument24 pagesFunctions Continuity CalcRegis OmondiNo ratings yet