Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Uploaded by
Adnan Iqbal Pharmacology Department0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesConnective tissue is one of the four main types of tissue and provides structure and support throughout the body similar to timber framing in a house. It has three main components - ground substance, fibers, and cells. The composition of these components varies between organs and provides diversity in connective tissue types, which include connective proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Original Description:
Original Title
connective tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConnective tissue is one of the four main types of tissue and provides structure and support throughout the body similar to timber framing in a house. It has three main components - ground substance, fibers, and cells. The composition of these components varies between organs and provides diversity in connective tissue types, which include connective proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesConnective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Uploaded by
Adnan Iqbal Pharmacology DepartmentConnective tissue is one of the four main types of tissue and provides structure and support throughout the body similar to timber framing in a house. It has three main components - ground substance, fibers, and cells. The composition of these components varies between organs and provides diversity in connective tissue types, which include connective proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Histology Connective tissue
Dr. Adnan Iqbal
407 Physiology Lab
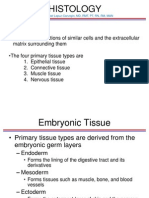
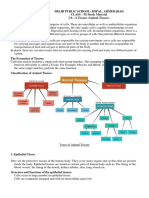
Connective tissue (CT)
• Connective tissue (CT) is a one of
the four main classes of tissues.
• It is the most abundant and
widely distributed.
• Like to the timber framing of a
house, the connective tissue
provides structure and support
throughout the body.
Structure of Connective Tissue
• Connective tissue has three main components:
1. Ground substance
2. Fibers
3. Cells
• Together the ground substance and fibers make up
the extracellular matrix.
• The composition of these three elements vary
tremendously from one organ to the other. This
offers great diversity in the types of connective
tissue.
Ground substance and Fibers
• Ground substance is a clear, colorless, viscous fluid that fills the space between the cells and
fibers.
• It is composed of glycosaminoglycan, proteoglycans and glycoproteins that allow the connective
tissue to act as glue for the cells to attach to the matrix.
• Three types of fibers are found in connective tissue:
• Collagen
• Elastic fibers
• Reticular fibers
Types of Connective Tissue
• Connective tissue is divided into four main categories:
• Connective proper – Fibroblast
• Cartilage – Chondroblast
• Bone - Osteoblast
• Blood - Atypical Connective tissue
You might also like
- 04 Lecture PPTDocument46 pages04 Lecture PPTSam Tagarda100% (1)
- 45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument26 pages45.1 The Human Body Plan: Unit 2: Circulatory and Respiratory Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 pagesUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue of AnimalsDocument27 pagesCell and Tissue of AnimalsUtami100% (1)
- AnaPhy 3 TissuesDocument42 pagesAnaPhy 3 TissuesFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument94 pagesAnimal TissuesMercel MacasinagNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue RecentDocument11 pagesConnective Tissue RecentEzeoke ChristabelNo ratings yet
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowDocument35 pagesBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainNo ratings yet
- BSC Connective Tissues PDFDocument54 pagesBSC Connective Tissues PDFPuneeT Raj 470No ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument7 pagesBody Tissuesapi-277938821No ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NiketDocument22 pagesAnimal Tissues NiketNiketNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument22 pagesAnimal TissuesNiketNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument55 pagesAnimal TissuesFarah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues (Anatomy) PDFDocument17 pagesBody Tissues (Anatomy) PDFNixonr RamsaranNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument19 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- DR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesDocument49 pagesDR Kiran: Tissues and Its TypesAnnie Khan100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument2 pagesConnective Tissueiananicole.b30No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Nur-aine Hajijul100% (1)
- Tissue Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiologysnp88100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue NotesDocument58 pagesEpithelial Tissue Noteslinetmuthoniw4No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- Animal Tissue GKDocument6 pagesAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study NotesDocument26 pagesGrade 10 Term 2: Life Science Study Noteschedza FordNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesDocument40 pagesCell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec-2Document25 pagesAnatomy Lec-2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-277771710No ratings yet
- TissueDocument17 pagesTissueanurag.dNo ratings yet
- THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANISATION Connective TissueDocument16 pagesTHE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANISATION Connective Tissuetahartpro786No ratings yet
- Tissue SystemDocument41 pagesTissue Systemrahul royNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Week 4 - TissuesDocument41 pagesWeek 4 - TissuesJuvy CambeNo ratings yet
- What Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?Document47 pagesWhat Are The Four Basic Types of Tissues That Make Up The Human Body?SireRyūjinSkylerNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- TISSUESDocument12 pagesTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: Tissue Matrix MuscleDocument8 pagesBody Tissues: Tissue Matrix Muscle9. Hoàng Mai ChiNo ratings yet
- 6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarDocument25 pages6 Histologi 1 - Jaringan DasarAstri Ggamjong Xiao LuNo ratings yet
- AP Module4 Trans DiazDocument18 pagesAP Module4 Trans DiazJohn Rafael DiazNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument55 pagesModule 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTDocument48 pagesWeek 4 Lecture Notes On Tissues, Membranes, Inflammation and Tissue Repair STUDENTwarrenjames0217No ratings yet
- Tissues and HomeostasisDocument42 pagesTissues and Homeostasissubeyr963No ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument57 pagesConnective TissueSunil DhatwaliaNo ratings yet
- A Connective - Tissue1 16 12 14 PDFDocument41 pagesA Connective - Tissue1 16 12 14 PDFShobhit GargNo ratings yet
- Presentación 117Document28 pagesPresentación 117Ángel David Flores SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Cds Day1Document15 pagesCds Day1Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cell SpecializationadpataionDocument67 pagesCell SpecializationadpataionMarc AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Cells-and-Tissues 1Document33 pagesCells-and-Tissues 1Susan Batan BandongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Unit-1 PDFDocument27 pagesAnatomy Unit-1 PDFdharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- 00 Life Sciences Grade 10 PPT Connective TissuesDocument28 pages00 Life Sciences Grade 10 PPT Connective TissuesCleopatra NomathamsanqaNo ratings yet
- Awdal College Department of Health: General HistologyDocument24 pagesAwdal College Department of Health: General HistologyAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Ferdinand V. Escalante, LPT Vvinzons Pilot High School Ppt3 7/01/19Document59 pagesCell Biology: Ferdinand V. Escalante, LPT Vvinzons Pilot High School Ppt3 7/01/19MaKenJi EscalanteNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Tortora Aus1e ch04Document34 pagesTortora Aus1e ch04jonas hingcoNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Zedrick John Dosado, Shane Loraine CalezeDocument47 pagesTissues: Zedrick John Dosado, Shane Loraine Calezealthea vergaraNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument14 pagesAnimal TissueReshmi SanjayNo ratings yet
- Tissues 4Document65 pagesTissues 4marianisie448100% (3)
- Tructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and CellmodificationDocument53 pagesTructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cellmodificationako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- TISSUES Class IXDocument6 pagesTISSUES Class IXdjjagu908No ratings yet