Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physiology of Exercise
Physiology of Exercise
Uploaded by
K Manosakthi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesThe document discusses the respiratory system and its function during exercise. It outlines the structure of the respiratory system including the conducting zone and respiratory zone. It describes the mechanics of breathing through inspiration and expiration. Key topics covered include gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in blood, ventilation-perfusion relationships, and the control of ventilation at rest and during exercise. The purpose of the respiratory system during exercise is to facilitate gas exchange and regulate acid-base balance as the body works.
Original Description:
Respiratory System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the respiratory system and its function during exercise. It outlines the structure of the respiratory system including the conducting zone and respiratory zone. It describes the mechanics of breathing through inspiration and expiration. Key topics covered include gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in blood, ventilation-perfusion relationships, and the control of ventilation at rest and during exercise. The purpose of the respiratory system during exercise is to facilitate gas exchange and regulate acid-base balance as the body works.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesPhysiology of Exercise
Physiology of Exercise
Uploaded by
K ManosakthiThe document discusses the respiratory system and its function during exercise. It outlines the structure of the respiratory system including the conducting zone and respiratory zone. It describes the mechanics of breathing through inspiration and expiration. Key topics covered include gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in blood, ventilation-perfusion relationships, and the control of ventilation at rest and during exercise. The purpose of the respiratory system during exercise is to facilitate gas exchange and regulate acid-base balance as the body works.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
RESPIRATION
DURING EXERCISE
Alagappa University College of Physical
Education, Karaikudi
OUTLINE FUNCTION OF THE LUNG
VENTILATION- PERFUSION RELATIONSHIPS
Structure of the Respiratory System
Conducting Zone Respiratory Zone
Mechanics of Breathing
Inspiration Expiration Airway Resistance
Diffusion of Gases
Blood Flow to the Lung
Ventilation-Perfusion Relationships
O2 and CO2 Transport in Blood
Hemoglobin and O2 Transport Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve
O2 Transport in Muscle O2 Transport in Blood
Ventilation and Acid-Base Balance
Ventilation and Blood-Gas Responses to Exercise
Rest-to-Work Transition Prolonged Exercise in a Hot Environment
Incremental Exercise
Control of Ventilation
Ventilatory Regulation at Rest Respiratory Control Center
Ventilatory Control During Submaximal Exercise
Ventilatory Control During Heavy Exercise
INTRODUCTION PULMONARY
RESPIRATION VENTILATION
Pulmonary Respiration
Ventilation
Exchange of O2 and Co2 in the lungs
• Cellular respiration
• O2 utilization and CO2 production by the
tissues
• Purposes of the respiratory system during
exercise
• Gas exchange between the environment and
the body
• Regulation of acid-base balance during
exercise
FUNCTION OF THE LUNG
Means of gas exchange between the
external environment and the body
Replacing O2
Removing CO2
Regulation of acid-base balance
Ventilation
Mechanical process of moving air into
and out of lungs
Diffusion
Random movement of molecules from
an area of high concentration to an
area of lower concentration
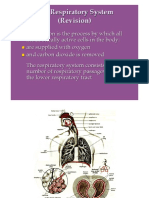
STRUCTURE OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Organs
Nose and nasal cavities
Pharynx and larynx
Trachea and bronchial tree
Lungs
Site of gas exchange
Diaphragm
Major muscle of inspiration
You might also like
- Septy Dwi Indriani: Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesSepty Dwi Indriani: Physiology of The Respiratory SystemSepty Dwi IndrianiNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1720047Document106 pagesNihms 1720047karenmichelletorres3No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument68 pagesRespirationNorhidayah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Blok 2 Transport Oksigen Oleh Sistem PernafasahDocument20 pagesBlok 2 Transport Oksigen Oleh Sistem PernafasahOrflimeEmmyNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Resp System - PADocument27 pagesOverview of The Resp System - PAwajdjnbNo ratings yet
- Aula 5 Sistema RespiratorioDocument40 pagesAula 5 Sistema RespiratorioBrenno RyanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Oxygenation Orpeza Cezar 1 7Document8 pages3.1 Oxygenation Orpeza Cezar 1 7Mika Marielle TrincheraNo ratings yet
- Lung Function in Health and Disease Basic Concepts of Respiratory Physiology and PathophysiologyFrom EverandLung Function in Health and Disease Basic Concepts of Respiratory Physiology and PathophysiologyNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Respirasi: Rafikah HasyimDocument49 pagesFisiologi Respirasi: Rafikah HasyimRaniyah Az-zahraNo ratings yet
- 1 Respiratory DisordersDocument17 pages1 Respiratory DisordersLulu MushiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Response To Exercise EssayDocument2 pagesRespiratory Response To Exercise EssayscholifyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and Its RegulationDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory System and Its Regulationraian claudeNo ratings yet
- 05 RespiratoryDocument38 pages05 Respiratoryglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Regulation During ExerciseDocument20 pagesRespiratory Regulation During ExerciseDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (2)
- Pulmnonary SystemDocument13 pagesPulmnonary Systemnatalie muyengwaNo ratings yet
- First Step To ModDocument41 pagesFirst Step To Modcarlos ali issaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology PostedDocument25 pagesRespiratory Physiology PostedYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 2Document26 pagesRespiratory System 2KelvinNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Gas Exchange: Presented By: Mrdaniel Angelitog Hernandez, LPTDocument17 pagesMechanism of Gas Exchange: Presented By: Mrdaniel Angelitog Hernandez, LPTjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapy and Instrumentation: Mechanical Ventilator &respiratory MechanismDocument23 pagesRespiratory Therapy and Instrumentation: Mechanical Ventilator &respiratory MechanismAhmed YehyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 - Concept in OxygenationDocument173 pagesNCM 102 - Concept in OxygenationNess Korosu100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Respiratory SystemShaila AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Document36 pagesTopic 7 - Respiratory System 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi PernapasanDocument87 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi PernapasanAndre ChundawanNo ratings yet
- Function of The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Respiratory SystemRachelHatcher123No ratings yet
- Respiration+and+PollutionDocument45 pagesRespiration+and+Pollutioncaceresrihany1206No ratings yet
- Wepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Wonders of The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesWepik The Breath of Life Exploring The Wonders of The Respiratory SystemJia TabioloNo ratings yet
- Notes of Human Physiology Class 11Document9 pagesNotes of Human Physiology Class 11ADWAITH LALU100% (1)
- Lab 6 Respiratory PrelabDocument23 pagesLab 6 Respiratory Prelabkkk13whyNo ratings yet
- 24 - Physiology of The Respiratory System PDFDocument38 pages24 - Physiology of The Respiratory System PDFlovelyc95No ratings yet
- Topic 2.3 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesTopic 2.3 - Human Respiratory Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pages4.2 - Respiratory SystemBenJenkinsNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17Document8 pagesNcert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17TheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument28 pagesRespiratory Anatomy & PhysiologyKaye CorNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument4 pages11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Respiratory VolumesDocument20 pagesVentilation and Respiratory VolumesJessa mae CabredoNo ratings yet
- CH 17Document7 pagesCH 17Akanksha AvasthiNo ratings yet
- 1 Gas Exchange in HumansDocument15 pages1 Gas Exchange in HumansMUHAMMAD REHAN IJAZNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 NotesDocument54 pagesExam 4 NotesAnonymous qaAbg65dCNo ratings yet
- BMI - Unit VDocument63 pagesBMI - Unit VHirshitha RajeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10, 12, 13, 15 Convert 2Document14 pagesChapter 10, 12, 13, 15 Convert 2treNo ratings yet
- Pleno B Blok 7 2012Document37 pagesPleno B Blok 7 2012illiyyahsyahabNo ratings yet
- Assigment Anatomi NUR SYUHADADocument11 pagesAssigment Anatomi NUR SYUHADANur SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Review FaalDocument38 pagesReview FaalNjwNo ratings yet
- 06 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument43 pages06 Respiratory System PhysiologyKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Emsp 1355 !!! Co2Document17 pagesEmsp 1355 !!! Co2acctsacctsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemASHLEY JADE NAIGANNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRaluca MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration 2Document31 pagesPhysiology of Respiration 2kuhutansittinurhalizaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument51 pagesRespiratory PhysiologyumaNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiration: Human Respiratory SystemSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology LecturesDocument37 pagesRespiratory Physiology LectureswiasonNo ratings yet
- VENTILATIONDocument27 pagesVENTILATIONezeudunicholas16No ratings yet
- Forum Fisiologi SenamDocument3 pagesForum Fisiologi SenamErwan Sha HabinullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Respiratory System 2Document33 pagesLecture 6 Respiratory System 2hafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Changes To ExerciseDocument31 pagesAcute Respiratory Changes To Exerciseapi-115744109No ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Second HalfDocument35 pagesRespiratory System: The Second HalfnicopiiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Powerpoint GaDocument28 pagesRespiratory Powerpoint Gakevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- Physiology of ExerciseDocument6 pagesPhysiology of ExerciseK ManosakthiNo ratings yet
- BiomechanicsDocument31 pagesBiomechanicsK ManosakthiNo ratings yet
- Nutritional DisordersDocument1 pageNutritional DisordersK ManosakthiNo ratings yet
- Insulated and United Influence of Hydraulic Resistance and Ladder Agility Training On SelectedDocument9 pagesInsulated and United Influence of Hydraulic Resistance and Ladder Agility Training On SelectedK ManosakthiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydraulic Training On Selected Physical Fitness Variables Among College Women StudentsDocument7 pagesEffect of Hydraulic Training On Selected Physical Fitness Variables Among College Women StudentsK ManosakthiNo ratings yet