Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CB1 Revision Worksheet
CB1 Revision Worksheet
Uploaded by
Phoebe RothwellOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CB1 Revision Worksheet
CB1 Revision Worksheet
Uploaded by
Phoebe RothwellCopyright:
Available Formats
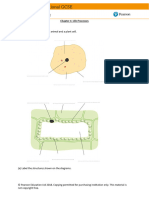
CB1 Revision Worksheet Match up the following organelles to their Label the bacteria cell:
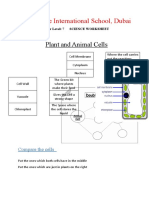
Define the following words: functions:
Controls what happens in the
cell and carries genetic
Magnification Nucleus information.
Controls what gets in and out
Resolution Cytoplasm
of the cell.
Cell Membrane Jelly like substance where State the function of the following components:
Using the formula triangle- the size of an chemical reactions happen.
organism is 0.003mm and the size of the Chromosomal DNA- …………………………………………………………
image is 4.2mm. What magnification was Where respiration occurs to ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Ribosome
used? make energy. Plasmid DNA- ……………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
Mitochondria Where new proteins are Flagella- ………………………………………………………………………………
made. ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Vacuole Where the cell makes food
through photosynthesis. Tick or cross which features are found in which
types of cell:
Complete the following: Chloroplast Where cell sap is stored
Total magnification= …………………… x ………………… Feature Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial
Gives the cell structure and Cell
Cell Wall support.
Eyepiece Objective Overall Cell
Magnification Magnification Magnification Membrane
Draw a specialised cell found in the
X10 X4 Nucleus
reproductive or digestive system.
x15 x400 Plasmids
Chloroplasts
Describe three differences between a light Cell Wall
microscope and an electron microscope:
Cytoplasm
…………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… Define the following words:
………………………………………………………………………………… Function:
………………………………………………………………………………… Adaptations: Eukaryotic
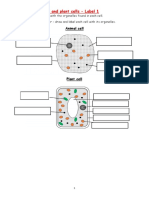
Label all the organelles in the animal and plant cells below: Prokaryotic
Explain what an enzyme is and what they do:
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
CB1 Revision Worksheet Explain the differences between osmosis, diffusion and active transport:
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Give some examples of enzymes in the body and what they
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
do:
Where it is What reaction is …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
ENZYME
found? catalysed?
Rate each of the learning outcomes for how you feel about them:
CB1.4 Calculate total magnification using a formula.
CB1.5 Interpret the SI prefixes milli-, micro-, nano and pico-.
CB1.3 Recall what an electron microscope is.
CB1.4 Calculate sizes using magnifications.
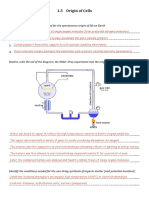
Draw a diagram and explain how proteins are broken down in CB1.3 Recall what is meant by an instrument’s resolution.
CB1.3 Explain why some cell structures can be seen with an electron microscope but not with a light microscope.
the body- including what breaks them down and what CB1.1 Identify the parts of plant and animal cells.
they’re broken in to: CB1.1 Recall the parts of plant and animal cells.
CB1.1/CB1.6 Make drawings of plant and animal cells using a light microscope and identify their parts.
CB1.1 Describe the functions of the sub-cellular structures commonly found in eukaryotic cells (nucleus, cell
membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, mitochondria and ribosomes).
CB1.5 Estimate sizes using microscope fields of view.
CB1.5 Estimate sizes using scale bars.
CB1.2 Describe how sperm cells are adapted to their function.
CB1.2 Describe how egg cells are adapted to their function.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… CB1.2 Describe how ciliated epithelial cells are adapted to their function.
CB1.2 Draw conclusions about a cell's function from its adaptations.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… CB1.1 Identify the common parts of bacteria.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… CB1.1 Describe the functions of common parts of bacteria.
CB1.1 Describe why bacteria are classified as being prokaryotic.
CB1.5 Change numbers to and from standard form.
What does denatured What does optimum CB1.1 Compare eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
CB1.12 State that enzymes are proteins.
mean? What might cause temperature / pH mean? CB1.12 Give examples of enzymes and where they are found in the human body and in other species.
an enzyme to denature? What happens beyond/below CB1.12 Recall the subunits from which carbohydrates, proteins and lipids are formed sugars, amino acids, fatty acids
…………………………………………… this? and glycerol).
CB1.12 Describe what enzymes do (catalyse the synthesis and breakdown of substances, such as carbohydrates,
…………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… proteins and lipids, by speeding up the rate of reaction).
…………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… CB1.12 Define an enzyme as a biological catalyst
CB1.12 Explain why catalysis by enzymes is important for life processes (because reactions happen much faster).
…………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… CB1.7 State what enzyme specificity means.
…………………………………………… ……………………………………………………… CB1.7 State that an enzyme's action is due to its active site.
……………………………………………………… CB1.7 Describe the role of the active site in enzyme function (including specificity).
CB1.7 Use the lock-and-key model to develop explanations for enzyme activity.
Match up the following: CB1.7 Explain why enzymes have a particular shape, as a result of the sequence of amino acids in the chain.
CB1.8 Explain how enzymes become denatured.
Substrate temperature pH CB1.9 Describe the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
CB1.9 Describe the effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity.
concentration CB1.9 Describe the effect of pH on enzyme activity.
CB1.9 Explain what is meant by the optimum pH/temperature of an enzyme.
CB1.11 Calculate the rate of enzyme activity from experimental data.
CB1.9 Explain why temperature, substrate concentration and pH affect enzyme activity.
CB1.15 State that substances are transported by diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
CB1.15 Describe how substances are transported by active transport (including the need for energy).
CB1.15 Explain how substances are transported by diffusion.
CB1.15 Explain how substances are transported by osmosis.
CB1.15 Explain the effects of osmosis on cells and tissues.
CB1.16 Investigate osmosis in potatoes.
CB1.17 Calculate percentage gain and loss of mass in osmosis.
You might also like
- IGCSE - Bio - Worksheet 1 - Life ProcessesDocument16 pagesIGCSE - Bio - Worksheet 1 - Life ProcessesAngkelova ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Revision WorksheetCally Chew100% (5)
- 2.1.1 CELL STRUCTUREDocument13 pages2.1.1 CELL STRUCTURERathnanghi GajendranNo ratings yet
- 7a QPDocument7 pages7a QPsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Cells, Diffusion & Osmosis QuestionsDocument11 pagesCells, Diffusion & Osmosis QuestionsGozde Ozan BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Y7 2023 TextbookDocument42 pagesY7 2023 TextbookAdina GuttentagNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document2 pagesUnit 2Camila Paula Mendoza ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 CellsDocument4 pagesQuiz 3 Cells02quantum.beagleNo ratings yet
- SF 10 Minutes On CellsDocument2 pagesSF 10 Minutes On CellssciencedocsmanNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus Exam QuestionsDocument21 pagesNew Syllabus Exam QuestionsKhaled DabourNo ratings yet
- End of Unit 1 TestDocument6 pagesEnd of Unit 1 TestSherey ElmasryNo ratings yet
- Mock Cells TestDocument5 pagesMock Cells TestDavid LeechNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell StructureDocument21 pages3.1 Cell Structure袁愉棋No ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision BookletDocument72 pagesYear 10 Revision BookletwolfpackoftrioNo ratings yet
- Y9 Biology BookletDocument61 pagesY9 Biology BookletJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Day-2 Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetDocument2 pagesDay-2 Plant and Animal Cells - WorksheetmanojNo ratings yet
- EI 9G BIO Cell-Revision-WorksheetDocument3 pagesEI 9G BIO Cell-Revision-WorksheetNaghul MxNo ratings yet
- Cell - Revision Worksheet 2Document9 pagesCell - Revision Worksheet 2ariaNo ratings yet
- U1 Aos1 1-1Document4 pagesU1 Aos1 1-1ayaanaghariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 QuestionsDocument191 pagesUnit 1 QuestionsSulthan RamizNo ratings yet
- Biology f211 Mixed Question PaperDocument191 pagesBiology f211 Mixed Question Paperapi-275024237No ratings yet
- Year 10 Revision Booklet AnswersDocument71 pagesYear 10 Revision Booklet AnswersArooj AbidNo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit Test Grade 6 Micro-Organisms and CellsDocument3 pages2nd Unit Test Grade 6 Micro-Organisms and CellsIda Bagus Alit ManuabaNo ratings yet
- 1.2.3 The Nervous System WorksheetDocument4 pages1.2.3 The Nervous System WorksheetTavon FloydNo ratings yet
- 2001 Jan Module 1Document9 pages2001 Jan Module 1paolo maldiniNo ratings yet
- B2.2 Vesicle-Compartments-QnsDocument2 pagesB2.2 Vesicle-Compartments-QnsParidhi BhandariNo ratings yet
- Definitions: Which Structures Are Found in All Types of Living Cells?Document5 pagesDefinitions: Which Structures Are Found in All Types of Living Cells?qiratNo ratings yet
- Bio Topic 1.5 Worksheet (Answers)Document2 pagesBio Topic 1.5 Worksheet (Answers)Mahina WongNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) Describe and Explain How Cell Fractionation and Ultracentrifugation Can Be Used To IsolateDocument18 pagesQ1. (A) Describe and Explain How Cell Fractionation and Ultracentrifugation Can Be Used To IsolateiNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) Describe and Explain How Cell Fractionation and Ultracentrifugation Can Be Used To IsolateDocument18 pagesQ1. (A) Describe and Explain How Cell Fractionation and Ultracentrifugation Can Be Used To IsolateiNo ratings yet
- British International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment BiologyDocument7 pagesBritish International College: Year 9-10 Half Term Assessment BiologyHarry SonNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument34 pagesCell OrganellesadamshakyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFDocument22 pagesCell Organelles - Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFIsa KhanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesEnzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . DateCarl Dominique De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cell Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Revision WorksheetXu Tianlong DanielNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina QuestionsDocument70 pagesUnit 5-Nervous System Brain Retina Questionsareyouthere92No ratings yet
- Cells Microscopes Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions 24 36Document13 pagesCells Microscopes Cell Cycle and Immunity Questions 24 36Tiffany RosneyNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 F5 BiologyDocument37 pagesChap 2 F5 Biologyg-16355677No ratings yet
- Biology Term 1 Revision WS Yr 9Document5 pagesBiology Term 1 Revision WS Yr 9Alina Vinay SivaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 WorksheetDocument2 pagesTopic 3.2 WorksheetYixuan PENGNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October ExamHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October ExamHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October Exam (Key Answers)Document2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October Exam (Key Answers)HisokagenNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and FunctionKhairul NizamNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 5 QPDocument13 pagesEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 5 QPVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Modul Chapter 2Document20 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Modul Chapter 2Fendy11100% (2)
- Abbey College Cambridge 1Document6 pagesAbbey College Cambridge 1BeaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Ordinary Level Sample: Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations CommissionDocument15 pagesBiology - Ordinary Level Sample: Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations CommissionHaidery SalumuNo ratings yet
- Biology Summative AssesmentDocument10 pagesBiology Summative AssesmentSharara YMNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Prep Questions NewDocument18 pagesTopic 3 Prep Questions NewDIYA SURESHNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology QPDocument14 pagesCell Biology QPPraveen KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- BTEC First Applied Science: Unit 3: Biology and Our EnvironmentDocument2 pagesBTEC First Applied Science: Unit 3: Biology and Our Environmentabu imaanNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument10 pagesMy TestBukhara PS PILEDUNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - Ib Style Questions: © David Faure, InthinkingDocument1 pageMitosis - Ib Style Questions: © David Faure, InthinkingDavid Castro0% (1)
- 2.2 The Cell Cycle Including Mitosis QPDocument8 pages2.2 The Cell Cycle Including Mitosis QPmiatomlin93No ratings yet
- IGCSE-Revision-Booklet-Part-1-2018-2019 - (New-Spec)Document69 pagesIGCSE-Revision-Booklet-Part-1-2018-2019 - (New-Spec)MaryamNo ratings yet
- AJC H2 BIO P3 QuestionDocument16 pagesAJC H2 BIO P3 Questionazs8t1No ratings yet
- Nervous System Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesNervous System Worksheet PDFRosalie Tilos OritoNo ratings yet
- 7 Motility Determination by Hanging Drop TechniqueDocument5 pages7 Motility Determination by Hanging Drop TechniqueGaurav MudaduNo ratings yet
- Biofirm BacteriaDocument87 pagesBiofirm BacteriaThuý SmilerNo ratings yet
- VPH 311 PDFDocument335 pagesVPH 311 PDFkuldeep sainiNo ratings yet
- Leather ZnoDocument7 pagesLeather ZnoNaveed SheikhNo ratings yet
- Stalosan Hygiene Powder ProductsDocument12 pagesStalosan Hygiene Powder ProductsWILLIAM RENATO QUEVEDO GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- 2013-CLSIFDA-table-update Range Disk Kultur PDFDocument5 pages2013-CLSIFDA-table-update Range Disk Kultur PDFYULI222No ratings yet
- Kingdom MoneraDocument19 pagesKingdom MoneraRay Noel Medina DeldaNo ratings yet
- Bacterianew AnswersDocument6 pagesBacterianew AnswersJoshua WatsonNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diversity For BiotechnologyDocument305 pagesMicrobial Diversity For BiotechnologySai Bharath100% (1)
- MCQ MicrobiologyDocument24 pagesMCQ MicrobiologyKhadija100% (3)
- Biological Activities of Crude Extracts and Chemical Constituents of Aegle MarmelosDocument13 pagesBiological Activities of Crude Extracts and Chemical Constituents of Aegle MarmeloskavalapparaNo ratings yet
- Bty111 - Biotechnology PerspectivesDocument3 pagesBty111 - Biotechnology PerspectivesadityamduttaNo ratings yet
- Animal Science TerminologiesDocument14 pagesAnimal Science TerminologiesMariaNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological and Pathological Investigation of Nasal Passage Infections of Chickens (Gallus Gallus)Document9 pagesBacteriological and Pathological Investigation of Nasal Passage Infections of Chickens (Gallus Gallus)Noman FarookNo ratings yet
- A Versatile Stain For Pollen Fungi, Yeast and Bacteria'Document6 pagesA Versatile Stain For Pollen Fungi, Yeast and Bacteria'Weslaine AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Ptu MLT SyllabusDocument11 pagesPtu MLT SyllabusparveenkeskarNo ratings yet
- Garcinia XanthochymusDocument11 pagesGarcinia Xanthochymusfonny elfirasNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imunologic in Bolile Animalelor de Companie-CanideDocument87 pagesDiagnostic Imunologic in Bolile Animalelor de Companie-CanidePetre RazvanNo ratings yet
- Hocut 795 Article by Hank LimperDocument4 pagesHocut 795 Article by Hank LimperLORENZO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1: Media, Culture & StainingDocument26 pagesLaboratory 1: Media, Culture & StainingSirine AjourNo ratings yet
- Microbial SpoilageDocument9 pagesMicrobial SpoilageCay DuboisNo ratings yet
- Archeabacteria and ExtremophilesDocument52 pagesArcheabacteria and ExtremophilesMonisha SamuelNo ratings yet
- Human Biology & Frequency Healing - POOR MAN'S ZAPPER - Low-Tech Rife Generator AlternativeDocument2 pagesHuman Biology & Frequency Healing - POOR MAN'S ZAPPER - Low-Tech Rife Generator AlternativeJulio LoraNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument58 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRUSHIKESH SINDKHEDKARNo ratings yet
- GCBR Tech Report MinDocument71 pagesGCBR Tech Report MinDetoxed InfoNo ratings yet
- My SeminarDocument52 pagesMy SeminarvinnycoolbuddyNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Binary Fission in BacteriaDocument11 pagesAlternatives To Binary Fission in BacteriaCLAUDIA SICHELNo ratings yet
- The Natural History of Infection: M. R. BarerDocument6 pagesThe Natural History of Infection: M. R. Barernour achkarNo ratings yet
- 5-Bacterial Morphology Lab Instruction SummaryDocument6 pages5-Bacterial Morphology Lab Instruction SummaryAnastasia VeldboomNo ratings yet
- Are Microorganism Boon or Bane? Why?Document2 pagesAre Microorganism Boon or Bane? Why?Ellah GutierrezNo ratings yet