Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Virus Powerpoint
Virus Powerpoint
Uploaded by
chandrika kumari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesViruses are small particles that contain genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. They can only reproduce by entering living cells and using the cell's machinery. Examples include influenza, colds, chickenpox, and measles. Viruses come in different shapes and sizes and only infect certain types of organisms. Some viruses like HIV contain RNA that is converted to DNA when infecting cells. Viruses may cause lytic infections, where the cell bursts releasing new viruses, or lysogenic infections where the viral DNA remains inactive inside the cell for periods of time. Common defenses against viruses include vaccines to prompt an immune response, interferons that prevent viral attachment, and antibodies that attack viruses.
Original Description:
Original Title
virus powerpoint
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentViruses are small particles that contain genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. They can only reproduce by entering living cells and using the cell's machinery. Examples include influenza, colds, chickenpox, and measles. Viruses come in different shapes and sizes and only infect certain types of organisms. Some viruses like HIV contain RNA that is converted to DNA when infecting cells. Viruses may cause lytic infections, where the cell bursts releasing new viruses, or lysogenic infections where the viral DNA remains inactive inside the cell for periods of time. Common defenses against viruses include vaccines to prompt an immune response, interferons that prevent viral attachment, and antibodies that attack viruses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views10 pagesVirus Powerpoint
Virus Powerpoint
Uploaded by
chandrika kumariViruses are small particles that contain genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. They can only reproduce by entering living cells and using the cell's machinery. Examples include influenza, colds, chickenpox, and measles. Viruses come in different shapes and sizes and only infect certain types of organisms. Some viruses like HIV contain RNA that is converted to DNA when infecting cells. Viruses may cause lytic infections, where the cell bursts releasing new viruses, or lysogenic infections where the viral DNA remains inactive inside the cell for periods of time. Common defenses against viruses include vaccines to prompt an immune response, interferons that prevent viral attachment, and antibodies that attack viruses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
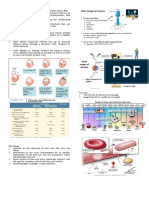
Viruses are particles of
nucleic acid, protein, and
lipids that invade living
cells and reproduce. They
are composed of a core of
DNA or RNA surrounded
by a protein coat called a
capsid.
Examples of Viruses:
Influenza, colds, chicken
pox, measles, polio, and
AIDS.
1. Shape – they come in a variety of shapes.
(see next slide)
2. Size 20-400 nanometers.
1 nanometer = 1 billionth of a meter.
3. Specificity = certain viruses only infect
certain organisms…your dog can’t get
chickenpox!
Retroviruses: Contain
RNA as their genetic
information. It is then
copied to DNA. This is
“backwards” or “retro”.
Viruses are considered
parasites because they
must infect a living cell in
order to grow and
reproduce.
1. Lytic Infection – a
virus enters a cell, makes
copies of itself and causes
the cell to burst
Attaches, entry,
replication, assembly and
release
http://
www.npr.org/templates/st
ory/story.php?storyId
=114075029
Lysogenic Infection – a
virus integrates its
DNA into the DNA of
the host cell. It many
remain inactive for a
period of time.
The viral DNA is
called a prophage.
1. Vaccine – a weakened
dose of the virus. When
injected it usually prompts
the body to produce an
immune reaction to
prevent illness.
2. Interferon – proteins
that prevent virus from
attaching to your cells
and reproducing.
3. Antibodies – immune system proteins that
attack and kill bacteria and viruses.
You might also like
- Viruses:: The Non-Living EntityDocument48 pagesViruses:: The Non-Living EntityhannNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Virus Morphology and InfectionDocument100 pagesLecture 6 Virus Morphology and InfectionArcee Feb Dela PazNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument13 pagesVirusMaharani Putri ChaniaNo ratings yet
- VIRUSDocument26 pagesVIRUSCrystal Ann TadiamonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 111Document31 pagesGeneral Biology 111Chioma AlexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document14 pagesChapter 11Alec SavieNo ratings yet
- Chap4 UpdatedDocument35 pagesChap4 UpdatedROZZANE LOVELY RODNEY MoeNo ratings yet
- Viruses, Viroids, and PrionsDocument59 pagesViruses, Viroids, and Prionsjimoji7012No ratings yet
- VIRUSES, Viroids and PrionsDocument66 pagesVIRUSES, Viroids and PrionsGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument6 pagesVirusAmeena Beebi B Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument19 pagesDocumentfaiqan93No ratings yet
- Virology: Characteristics of Viruses Are Viruses Living or Non-Living?Document6 pagesVirology: Characteristics of Viruses Are Viruses Living or Non-Living?Castiel NguyenNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument17 pagesVirusesSara SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Virusesmbft451 210328135532Document50 pagesVirusesmbft451 210328135532DELLA BLATAMANo ratings yet
- Biology Virus NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Virus NotesTiffany Gallina100% (3)
- Introduction To VirusesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To VirusesWhite RoseNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument3 pagesVirusesjohnosborne100% (1)
- Immunology 1Document8 pagesImmunology 1zaina.malikNo ratings yet
- Day 5 Virology - January 2021Document183 pagesDay 5 Virology - January 2021ShriefElghazalyNo ratings yet
- Viruses Their ReplicationDocument39 pagesViruses Their ReplicationYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- I20 II20 Lecture 20 of 20Document34 pagesI20 II20 Lecture 20 of 20Alros ManteltNo ratings yet
- Virus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCDocument33 pagesVirus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCJulia NepoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Virus?: MaterialsDocument22 pagesWhat Is A Virus?: Materialswahyu kurniawanNo ratings yet
- English Short SemesterDocument9 pagesEnglish Short SemesterSelestin NisfuNo ratings yet
- Virus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCDocument33 pagesVirus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCAyu Roossea MustikaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Virology I Introduction To Virology IDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Virology I Introduction To Virology IVincent RacanielloNo ratings yet
- Ciri-Ciri Virus: Glikoprotein: Protein Pada AmplopDocument4 pagesCiri-Ciri Virus: Glikoprotein: Protein Pada AmplopRabila NsNo ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- 2018 Virologi 1 Introduction To Medical Virology PDFDocument48 pages2018 Virologi 1 Introduction To Medical Virology PDFDave JhonsonNo ratings yet
- Bio111 2017 Lec28 VirusesDocument12 pagesBio111 2017 Lec28 VirusesBoitumeloNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument33 pagesVirusesShermaine GenistonNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidDocument47 pagesAntiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidhadeelNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 4 Biosci VirusDocument3 pagesLecture No. 4 Biosci VirusJenny MendozaNo ratings yet
- 4 VirusDocument21 pages4 VirusegaNo ratings yet
- Bot 101 NotesDocument2 pagesBot 101 NotesAbid Hussain100% (1)
- VirologyDocument183 pagesVirologyVeronica KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Viruses: Bioed OnlineDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Viruses: Bioed OnlineCaro Torres GaleanoNo ratings yet
- 7.1 - Medical Virology Part 1Document29 pages7.1 - Medical Virology Part 1Kaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- Virus Is An Inert Material Outside: General Characteristics of VirusesDocument45 pagesVirus Is An Inert Material Outside: General Characteristics of VirusesNERA AYONNo ratings yet
- This Is ItDocument19 pagesThis Is Itmagadanarianne276No ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-2Document31 pagesChapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-2Hillani TadesseNo ratings yet
- Exercise12 PDFDocument17 pagesExercise12 PDFHayna RoseNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Viruses PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Viruses PDFabdulNo ratings yet
- ViroDocument139 pagesViroXyprus Darina VeloriaNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument6 pagesBiodiversityDevil HackerNo ratings yet
- 20.1 Viruses BIODocument42 pages20.1 Viruses BIOZac ToglawNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument46 pagesVirusesJohn TharakanNo ratings yet
- Mls 424 Introduction To Virology (Autosaved) - 1-1Document30 pagesMls 424 Introduction To Virology (Autosaved) - 1-1Mayowa OgunmolaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Viruses of Livestocks and PoultryDocument11 pagesDNA and RNA Viruses of Livestocks and PoultryDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.chapter 2 - 2022Document7 pagesMicro F2.chapter 2 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - VirusDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Virusshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document11 pagesChapter 05Wajeeh Ahmed ZakaiNo ratings yet
- LBHS Yr 12 Biology Assessment Task The Search For Better Health by Tyrone WestwoodDocument7 pagesLBHS Yr 12 Biology Assessment Task The Search For Better Health by Tyrone WestwoodtyronewestwoodNo ratings yet
- Viruses: By: Dennie Grace Seal Tel JessicaDocument14 pagesViruses: By: Dennie Grace Seal Tel JessicasealtelNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument31 pagesVirology007ginniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology AssignmentDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Assignment2022337020No ratings yet
- VirusesDocument7 pagesVirusesRegine FeynmanNo ratings yet
- Altamash General VirologyDocument81 pagesAltamash General VirologysuidckNo ratings yet
- RetrovirusDocument23 pagesRetrovirusali haidarNo ratings yet
- Viruses and Bacteria Notes 2023Document57 pagesViruses and Bacteria Notes 2023FARHAN KHANNo ratings yet