Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Nutrition
Plant Nutrition
Uploaded by
akshai.ar130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
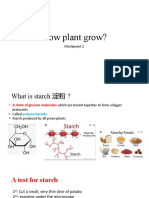
16 views9 pagesGreen plants are capable of photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants produce carbohydrates from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts in plant leaves use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose, which plants use for growth. Glucose is converted into sucrose and then starch for storage in plant organs like potato tubers.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGreen plants are capable of photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants produce carbohydrates from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts in plant leaves use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose, which plants use for growth. Glucose is converted into sucrose and then starch for storage in plant organs like potato tubers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views9 pagesPlant Nutrition
Plant Nutrition
Uploaded by
akshai.ar13Green plants are capable of photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants produce carbohydrates from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. During photosynthesis, chloroplasts in plant leaves use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and glucose, which plants use for growth. Glucose is converted into sucrose and then starch for storage in plant organs like potato tubers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Green plants are described as autotrophs, which they can
produce their own food.
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process by which plants
manufacture food molecules (carbohydrates) from raw
materials CO2 and H2O using energy from light.
• Energy is needed to convert the carbon
dioxide and water molecules into
glucose, which is required for a plant's
growth.
• This energy is provided by sunlight.
Sunlight is trapped in a plant by
chlorophyll.
• Chlorophyll is the green colored pigment
that contains magnesium. It is found
within the chloroplast of cells, where
photosynthesis takes place.
• Carbon dioxide is obtained from air. Carbon dioxide enters by diffusion into
the leaf through the tiny pores mostly situated in the lower surface of the
leaf called stomata
• Water is obtained from soil. The root hair cells absorb it by osmosis. It is
carried up to the leaf in the xylem vessels. Water then travels from the
xylem vessels to the mesophyll cells by osmosis.
• Oxygen is produced as a by-product during photosynthesis.
• Glucose is produced during photosynthesis
which is a simple sugar and it is soluble.
• Glucose is then converted to sucrose and carried
to the storage organs of a plant.
• Sucrose is then converted to starch and stored
for later use.
• The tuber of a potato is an example of a plant’s
storage organ.
Importance of photosynthesis
• Almost all the other forms of life on Earth depend on plants for food
in some or other way.
• Animals depend on plant material directly or indirectly.
• The oxygen produced by photosynthesis is essential for respiration of
most life forms.
• Photosynthesis also use up the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
and contribute to maintaining carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere.
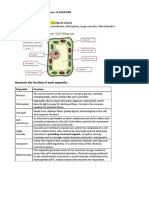
Leaf structure
• Leaves are usually green in color due to the
presence of a substance called chlorophyll.
• A leaf has a stalk also called the petiole,
which attaches the leaf to the plant.
• The broad, flat part of the leaf is called leaf
blade, which absorbs sunlight.
• The veins carry water to the cells in the leaf.
They also help to support the leaf and hold
it out flat. There is a large main vein called
the midrib, which runs across the center of
the leaf. It helps to hold the leaf, facing the
Sun.
• Cuticle: It is a waxy layer that prevents water loss by evaporation.
• Upper epidermis: It is a protective layer of cells that produces
the cuticle.
• Palisade mesophyll: This layer contains rod-shaped cells that
have large numbers of chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
• Spongy mesophyll: Cells in this layer are found in the lower part
of the leaf. They are smaller than those of the palisade
mesophyll. They also contain chloroplasts. These cells have large
air spaces between them that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen
to diffuse between them.
• Lower epidermis: It is a protective layer of cells. It too produce a
waxy cuticle in some plant species. The lower epidermis contains
pores called stomata that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to
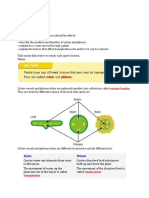
• Stomata: They are tiny pores (small holes) located in lower
epidermis surrounded by a pair of sausage-shaped guard
cells.
• Guard cells can change shape to close the pore. In very hot
conditions, water inside the leaf evaporates and the water
vapor can escape through the stomata.
• Closing them not only reduces water loss but also limits the
diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen in and out of the leaf.
You might also like
- (Franz F. P. Kollmann, Wilfred A. Cote Jr. Vol IDocument604 pages(Franz F. P. Kollmann, Wilfred A. Cote Jr. Vol IGiorgie Amorim100% (5)
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology 1Document60 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiology 1keron100% (1)
- Cano Et Al - 2013 - A Revision of Trithrinax PDFDocument53 pagesCano Et Al - 2013 - A Revision of Trithrinax PDFHenoh100% (3)
- Flower ArrangementDocument8 pagesFlower ArrangementTanay Singh100% (1)
- Desert Magazine 1968 MarchDocument44 pagesDesert Magazine 1968 Marchdm1937100% (2)
- LeavesDocument3 pagesLeavessssfiresssNo ratings yet
- The Leaf OrganDocument12 pagesThe Leaf OrganGEN EL NISSI SUELTONo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - RegDocument35 pagesNUTRITION - Regwairimucarren77No ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- Preig Point 8 Unit1Document30 pagesPreig Point 8 Unit1myatthirisan2010No ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument28 pagesTransport in PlantsGautam Dayal100% (1)
- 28 02 14 The Exchange System in PlantsDocument53 pages28 02 14 The Exchange System in Plantsapi-263322904No ratings yet
- LeavesDocument30 pagesLeavesjada tuckerNo ratings yet
- The Leaf As An OrganDocument11 pagesThe Leaf As An OrganAlana DariesNo ratings yet
- PMA LeavesDocument37 pagesPMA Leavesalaiza.reblandoNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport-Grade 11-EditedDocument37 pagesPlant Transport-Grade 11-EditedAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems ch5 3Document10 pagesEcosystems ch5 3api-259271169No ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument15 pagesPlant Nutritionthabogabriel626No ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Leaf Stem and RootDocument15 pagesCross Sections of Leaf Stem and Rootlwandlemkhonza96No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument24 pagesTransport in PlantsAreebNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport in PlantsForthtNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesCh-8 Transport in Plantsdaveymilan36No ratings yet
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument38 pagesInternal Structure of A Leafnozel77100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationDocument28 pagesIGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationhannahhishamNo ratings yet
- Basic BotanyDocument47 pagesBasic Botanyartadiel28No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - Chapter 8Document2 pagesTransport in Plants - Chapter 8Viviana PlacentinoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Document44 pagesAgricultural Biology Anatomy and Physiology SPU 2024 Notes 1Gift ThobaneNo ratings yet
- How Plant GrowDocument16 pagesHow Plant GrowSelinaNo ratings yet
- Plant NutirionDocument29 pagesPlant NutirionRaidioactiveguyNo ratings yet
- Cluster Biology of PlantsDocument48 pagesCluster Biology of Plantsapi-452104023100% (1)
- PPT - PhotosynthesisDocument56 pagesPPT - PhotosynthesisTarun BisenNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes PDFDocument79 pagesBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Document3 pagesGCSE Biology Physiology Part 2 (Transport in Plants)Fasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 How Green Plants FeedDocument41 pagesChapter 5 How Green Plants FeedAnonymous s5veYTCyWHNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Xii Botany Notes (Karachi Board)Document83 pagesXii Botany Notes (Karachi Board)Own CreationsNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument35 pagesTransport in PlantsChantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Organs: Leaves: Lakehead UniversityDocument40 pagesLecture 7 - Organs: Leaves: Lakehead UniversityClara HrestakNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument31 pagesPlant NutritionAbhay BhingradiaNo ratings yet
- Tissues System of The Plant BodyDocument47 pagesTissues System of The Plant BodyJana Natassia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesLecture 12 - Transport in PlantsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Leaves:: Form and StructureDocument37 pagesLeaves:: Form and StructureJane ManalusNo ratings yet
- Biology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?Document11 pagesBiology Photosynthesis How Do Plants Get Their Energy?rickyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- Section 22.2 Grades 10 (10049)Document47 pagesSection 22.2 Grades 10 (10049)reinaNo ratings yet
- Describe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaDocument16 pagesDescribe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaStudy's AnayNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument20 pagesInternal Structure of A LeafRell Dog100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument57 pagesTransport in PlantsIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Science C1Document44 pagesYear 9 Science C1Ventus TanNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsAbdiwahab IssackNo ratings yet
- PBS100 - PPT 7 - RootsDocument56 pagesPBS100 - PPT 7 - RootsMayMenderoNo ratings yet
- 6.3 LeavesDocument18 pages6.3 LeavesdusikNo ratings yet
- Biology - Leaf ChapterDocument4 pagesBiology - Leaf ChapterWriddhi MononNo ratings yet
- Leaf Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesLeaf Structure and FunctionShameel PervezNo ratings yet
- Plant Transport To WriteDocument17 pagesPlant Transport To WritelaibahundekarNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Plant ScienceDocument8 pagesBiology Notes - Plant Sciencesarah_beck100% (1)
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant - Class NotesDocument32 pagesTransport in Plant - Class Noteszaijah taylor4ANo ratings yet
- Self-Paced Learning Module Gen Bio 1 Week 2Document10 pagesSelf-Paced Learning Module Gen Bio 1 Week 2Ashley Jade DomalantaNo ratings yet
- LeafDocument50 pagesLeafJawher AliNo ratings yet
- Plants 21-24Document30 pagesPlants 21-24Brandi Hughes CaldwellNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 6Document2 pagesBiology Unit 6Emma FernandezNo ratings yet
- 16 Reproduction Notes 3Document2 pages16 Reproduction Notes 3akshai.ar13No ratings yet
- Coral Reefs NotesDocument7 pagesCoral Reefs Notesakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism NotesDocument6 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Notesakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument2 pagesDigestive System Notesakshai.ar13No ratings yet
- Rhizoma RheiDocument7 pagesRhizoma RheiBahar JatrophaNo ratings yet
- LawandeDocument2 pagesLawandeAnonymous Sp6ut2qZNo ratings yet
- Namibia Medicinal Plants-VanDamme3Document30 pagesNamibia Medicinal Plants-VanDamme3Valmik SoniNo ratings yet
- Plants E. Spore Formation F. Does Not Involve Gametes Animals B. Sexual Selection D. Involves Sperm and Egg CellDocument5 pagesPlants E. Spore Formation F. Does Not Involve Gametes Animals B. Sexual Selection D. Involves Sperm and Egg CellKazandra Cassidy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaDocument7 pagesReactive Oxygen Species and Seed Germination: Marcelo Pedrosa Gomes & Queila Souza GarciaBetina PNo ratings yet
- GoldenAcre GardenGuideDocument186 pagesGoldenAcre GardenGuidecristian_iacomi3416No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Modern Principles Microeconomics 2nd Edition CowenDocument34 pagesTest Bank For Modern Principles Microeconomics 2nd Edition Cowenbrokeazarole6rv8pl100% (37)
- Bamboo ConstructionDocument40 pagesBamboo Constructionanbarasan0100% (1)
- AmiDocument12 pagesAmiAnonymous UoRu4sNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Virtual LabsDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Virtual Labsapi-235160519No ratings yet
- Caneva 2020Document16 pagesCaneva 2020Attila Lébényi-PalkovicsNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesSanjay AdakNo ratings yet
- Imp Questions Class Xii PCMDocument13 pagesImp Questions Class Xii PCMAnsh VohraNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesInvestigatory ProjectKailas ArunNo ratings yet
- (Ksat - Ii) : CLASS - L..K.GDocument25 pages(Ksat - Ii) : CLASS - L..K.Gsurya100% (1)
- Xfrogplants - : Oceania 2 LibraryDocument23 pagesXfrogplants - : Oceania 2 LibrarycatrachosNo ratings yet
- Afin Canadian PDFDocument11 pagesAfin Canadian PDFradulet raduNo ratings yet
- Descriptions of The 16 Major Forest Type-Groups According To Champion and Seth (1968)Document4 pagesDescriptions of The 16 Major Forest Type-Groups According To Champion and Seth (1968)RajKumarNo ratings yet
- The Causal Dimension of ' Goethe's Morphology: J. Social Biol. Struct. 1984 7, 325-344Document20 pagesThe Causal Dimension of ' Goethe's Morphology: J. Social Biol. Struct. 1984 7, 325-344Pedro EspindolaNo ratings yet
- How To Make Cricket BatDocument5 pagesHow To Make Cricket BatmindcrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Plant PhysiologyRose Romero80% (5)
- Phytotoxicity and Phytoremediation Potential of Mercury in Indian Mustard and Two Ferns With Mercury Contaminated Water and Oak Ridge Soil - 9241Document12 pagesPhytotoxicity and Phytoremediation Potential of Mercury in Indian Mustard and Two Ferns With Mercury Contaminated Water and Oak Ridge Soil - 9241レテイ サマ ヒルカNo ratings yet
- Bibek's Biology Project ReportDocument16 pagesBibek's Biology Project Reportbibek212221No ratings yet
- Climate and Adaptation in Tropical RainforestDocument9 pagesClimate and Adaptation in Tropical Rainforesthweta173No ratings yet
- Pure Bio CH 9 Textbook Answers PDFDocument3 pagesPure Bio CH 9 Textbook Answers PDFMahamIsmailNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Pembahasan UN SMP Bahasa Inggris 2012-2013Document14 pagesSoal Dan Pembahasan UN SMP Bahasa Inggris 2012-2013Genius Edukasi100% (1)