Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 5 - Earths Layer
Lesson 5 - Earths Layer
Uploaded by
jerelyn erme0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pagesThe Earth consists of four main layers from outermost to innermost: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin solid outer layer that the continents and ocean floors reside on. Below the crust is the mantle, which makes up the largest portion of the Earth's volume and is composed of semi-molten rock. Within the mantle is the asthenosphere, which flows and facilitates the movement of tectonic plates. Below the mantle is the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel. The innermost layer is the solid inner core, also made of iron and nickel, which reaches temperatures over 5,500°C and acts as a heat engine for the planet.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lesson 5- Earths Layer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Earth consists of four main layers from outermost to innermost: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin solid outer layer that the continents and ocean floors reside on. Below the crust is the mantle, which makes up the largest portion of the Earth's volume and is composed of semi-molten rock. Within the mantle is the asthenosphere, which flows and facilitates the movement of tectonic plates. Below the mantle is the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel. The innermost layer is the solid inner core, also made of iron and nickel, which reaches temperatures over 5,500°C and acts as a heat engine for the planet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views18 pagesLesson 5 - Earths Layer
Lesson 5 - Earths Layer
Uploaded by
jerelyn ermeThe Earth consists of four main layers from outermost to innermost: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin solid outer layer that the continents and ocean floors reside on. Below the crust is the mantle, which makes up the largest portion of the Earth's volume and is composed of semi-molten rock. Within the mantle is the asthenosphere, which flows and facilitates the movement of tectonic plates. Below the mantle is the liquid outer core made of iron and nickel. The innermost layer is the solid inner core, also made of iron and nickel, which reaches temperatures over 5,500°C and acts as a heat engine for the planet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
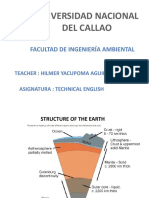
The Earth consists of four concentric
layers: inner core, outer core, mantle
and crust. The crust is made up of
tectonic plates, which are in constant
motion. Earthquakes and volcanoes are
most likely to occur at plate
boundaries.
The crust is the outer layer of the earth. It is a
thin layer between 0-60 km thick. The crust is
the solid rock layer upon which we live. There
are two different types of crust: continental
crust, which carries land, and oceanic crust,
which carries water.The boundary that
separates the crust and mantle is called
MOHOROVICIC DISCONTINUITY. Named after
by Andrija Mohorovicic.
Elements present are: Fe, Ca, H, Al, Si, O, Na, K
and Ti.
The mantle is the widest section of the Earth. It has a
thickness of approximately 2,900 km. The mantle is
made up of semi-molten rock called magma. In the
upper parts of the mantle the rock is hard, but lower
down the rock is soft and beginning to melt. The upper
mantle has with it a soft weak layer called
ASTHENOSPHERE, which is capable flowing. This
property facilitates the movement of the lithospheric
plates. The boundary between the mantle and outer
core is called GUTENBERG DISCONTINUITY. Named after
by Beno Gutenberg.
The outer core is the layer surrounding
the inner core. It is a liquid layer, also
made up of iron and nickel. It is still
extremely hot, with temperatures
similar to the inner core. The transition
period between outer core and inner
core is called Lehmann Discontinuity.
Named after by Inge Lehmann.
The inner core is in the centre
and is the hottest part of the
Earth.
-It is solid and made up of iron
and nickel with temperatures of
up to 5,500°C. With its immense
heat energy, the inner core is like
the engine room of the Earth.
You might also like
- I. Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesI. Plate TectonicsChristian GanganNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 SeismologyDocument96 pagesLecture1 SeismologyShah Nawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Layers of EarthDocument31 pagesLayers of EarthPrincess Raychel Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- Project1 Earths StructureDocument18 pagesProject1 Earths StructureZIAALYNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The EarthDocument1 pageThe Structure of The EarthBernard BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Lesson Activity SDocument3 pagesLesson Activity SPsyche NarutoNo ratings yet
- Eart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreDocument23 pagesEart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreRhiza Mae Lax100% (1)
- The Structure of The EarthDocument1 pageThe Structure of The EarthRita El ifrikiNo ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument3 pagesLayers of The Earthapi-308660483100% (1)
- Layers of The Earth (Science)Document19 pagesLayers of The Earth (Science)Mar Sela100% (1)
- Physical Layers of The EarthDocument2 pagesPhysical Layers of The Earthokoroebube218No ratings yet
- Structure of The EarthDocument14 pagesStructure of The Earthalejandro sanchezNo ratings yet
- Earths Layers Project Leticha Lea NelDocument4 pagesEarths Layers Project Leticha Lea NelMichelle NelNo ratings yet
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument66 pagesLayers of The EarthIreneo Villanueva BatagaNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth PowerPointDocument31 pagesLayers of Earth PowerPointkartik.goel3010No ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument2 pagesLayers of The EarthtorebsuicoNo ratings yet
- Whatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFDocument23 pagesWhatkindofevidencedoscientistsuseto 160207164642 PDFragini singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Jashan MatadeenNo ratings yet
- 8 - GeosphereDocument45 pages8 - Geospherejohnflor456No ratings yet
- Science PPTDocument28 pagesScience PPTquencia beth radinNo ratings yet
- Earth Science AssignmentDocument7 pagesEarth Science AssignmentOFFICE OF THE CLERK OF COURT ILOILO CITYNo ratings yet
- Corelower MantleDocument2 pagesCorelower MantleJeremiah ConalesNo ratings yet
- LAYERS OF EARTh JhiaDocument3 pagesLAYERS OF EARTh JhiaJocelyn GomezNo ratings yet
- The Internal Structure of EarthDocument12 pagesThe Internal Structure of EarthAlona EstilleroNo ratings yet
- Earth's InteriorDocument22 pagesEarth's InteriorAngel PerrerasNo ratings yet
- Session 9Document9 pagesSession 9Abdelrahman HishamNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument7 pagesLayers of The EarthBiancaAsyifa PritadewiNo ratings yet
- Geo notesDocument9 pagesGeo notesRod Andal vargasNo ratings yet
- 03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMDocument84 pages03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMCarlo Bryan Ramento100% (1)
- Grade10 Lesson 3Document20 pagesGrade10 Lesson 3Ka Klasmeyt0% (1)
- About The MantleDocument3 pagesAbout The MantleCj QueñanoNo ratings yet
- Science10 - Earth's InteriorDocument18 pagesScience10 - Earth's InteriorArt TemisNo ratings yet
- Composition of The Earth SummaryDocument3 pagesComposition of The Earth Summaryclarence antalanNo ratings yet
- Sci10 UNIT II Lesson 1Document26 pagesSci10 UNIT II Lesson 1Hezil Mae MancaoNo ratings yet
- DISCUSSION 3 - Layers of The EarthDocument27 pagesDISCUSSION 3 - Layers of The EarthJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Earth - MNADocument46 pagesStructure of The Earth - MNAHatim AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2 Interior of The EarthDocument5 pages2 Interior of The EarthCHRISTIAN NATHANIEL PALMANo ratings yet
- Celine Jamaica Q SciDocument5 pagesCeline Jamaica Q SciCygresy GomezNo ratings yet
- Earth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDocument2 pagesEarth'S Layers Layers Based On Chemical Composition Mantle: Seismic TomographyDudrey Anne SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument19 pagesLayers of The EarthMonica JanelleNo ratings yet
- Earths InteriorDocument1 pageEarths InteriorJosh QuinanolaNo ratings yet
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University South La Union College of Arts and Science Agoo, La UnionDocument54 pagesDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University South La Union College of Arts and Science Agoo, La UnionCamille AndreaNo ratings yet
- CHP 02 - Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesCHP 02 - Structure of The EarthKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument37 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleJade QuitoNo ratings yet
- Mantle 1Document3 pagesMantle 1SUNRICK GilberoNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Lesson 1 The Composition and Structure of The EarthDocument10 pagesScience 6 Lesson 1 The Composition and Structure of The EarthMary Jane WatsonNo ratings yet
- Earth's Internal StructureDocument1 pageEarth's Internal StructureLoneSoulNo ratings yet
- Yna's EarthDocument11 pagesYna's EarthYnara VillaunuevaNo ratings yet
- Earths Interior2Document34 pagesEarths Interior2Aices Jasmin Melgar BongaoNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument42 pagesLayers of The EarthDrei BangateNo ratings yet
- Earth's Layer: Its Way To The Top. Meanwhile It Is Forcing The Lithosphere To Go Down and Take Its PlaceDocument1 pageEarth's Layer: Its Way To The Top. Meanwhile It Is Forcing The Lithosphere To Go Down and Take Its Placejayven esplanaNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology CH 2Document16 pagesGeomorphology CH 2Tezera Mark TmhNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument17 pagesLayers of The EarthSandeep Kumar K RNo ratings yet
- LayerDocument36 pagesLayerKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- Layer Chage OptionDocument36 pagesLayer Chage OptionKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- G10 Geosphere - Sync DiscussionDocument206 pagesG10 Geosphere - Sync Discussionhatdog dakoNo ratings yet
- Earth's StructureDocument12 pagesEarth's StructureMelissa MoralesNo ratings yet