Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsLes 08
Les 08
Uploaded by
cr.pretecoOracle SQL - Regular Expression Support
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Extending The Standard IDOC For Outbound DeliveryDocument16 pagesExtending The Standard IDOC For Outbound DeliverySalih SahinNo ratings yet
- HW5Document7 pagesHW5Rahul Patil100% (1)
- Regular Expression SupportDocument14 pagesRegular Expression SupportClaudian Paduraru100% (1)
- 1Z0 052 Exam Dumps 2018Document26 pages1Z0 052 Exam Dumps 2018Kazi Mobaidul Islam ShovonNo ratings yet
- Regexp - Like: Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1)Document16 pagesRegexp - Like: Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1)Sandeep DesaiNo ratings yet
- Python Course: Session 6b - Regular ExpressionsDocument11 pagesPython Course: Session 6b - Regular ExpressionsDimitris LyberisNo ratings yet
- Oracle Searching MatchingDocument27 pagesOracle Searching MatchingDrRohini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sys LW-08EN Regex-FiltersDocument31 pagesSys LW-08EN Regex-Filtersredhoua.ghezlene.gasmiNo ratings yet
- Andrei's Regex Clinic - PHP Quebec 2009Document209 pagesAndrei's Regex Clinic - PHP Quebec 2009kaplumb_aga100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6elias ferhanNo ratings yet
- 03.0 PHP Regular ExpressionDocument20 pages03.0 PHP Regular Expressionhey youNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument26 pagesIntroductionRAMSURYA PERUMALLANo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL Language Quick Reference: 40020GC10 Production 1.0 April 1999 M08684Document56 pagesOracle SQL Language Quick Reference: 40020GC10 Production 1.0 April 1999 M08684EvaNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions: Regular Expression Syntax in PythonDocument11 pagesRegular Expressions: Regular Expression Syntax in PythonHa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Hw5 PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info Hw5 PRJamal Al-jaziNo ratings yet
- SQLDocument861 pagesSQLAnonymous E8FG7X19RNo ratings yet
- Oracle PLSQL Interview AdvDocument25 pagesOracle PLSQL Interview AdvZainul AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Re ExpressionDocument23 pagesRe ExpressionDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- Regular Expression PythonDocument23 pagesRegular Expression PythonYASH DOSHINo ratings yet
- Database Programming: Case and Character ManipulationDocument30 pagesDatabase Programming: Case and Character ManipulationKevin Van MalderenNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Data-Manipulation-LanguageDMLDocument16 pagesLab 2 Data-Manipulation-LanguageDMLKaram SalahNo ratings yet
- Loadrunner Questions:: Example 1Document27 pagesLoadrunner Questions:: Example 1Lavanya GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Java Regex Tutorial: Lars VogelDocument20 pagesJava Regex Tutorial: Lars Vogelhasan_maxNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six DBDocument11 pagesChapter Six DBbirtukan aregaNo ratings yet
- Reg - Replace: SyntaxDocument1 pageReg - Replace: SyntaxshareefNo ratings yet
- Ora-10g Reg. ExpressionsDocument3 pagesOra-10g Reg. ExpressionsPrasanna GhareNo ratings yet
- Understanding New Features of JSP2.0Document13 pagesUnderstanding New Features of JSP2.0api-3791744100% (2)
- Lecture 4-6 (R.A)Document22 pagesLecture 4-6 (R.A)Huzaifa MemonNo ratings yet
- REGEX ExtendedDocument39 pagesREGEX ExtendedLaurenţiu GavrilescuNo ratings yet
- Horstkeller Cd200 Sent inDocument118 pagesHorstkeller Cd200 Sent inSandeep SivanNo ratings yet
- Perlre Perl Regular ExpressionsDocument16 pagesPerlre Perl Regular Expressionsfippifuppi78No ratings yet
- DP 4 1 PracticeDocument4 pagesDP 4 1 PracticeJessica IreneNo ratings yet
- Apex BasicsDocument7 pagesApex BasicsshahbojjaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-IiDocument82 pagesDBMS Unit-IiNeha SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Matching Sets of CharactersDocument8 pagesLesson 3: Matching Sets of CharactersMe ItsNo ratings yet
- Jim Sears's Summary: Regular Expressions in QTPDocument6 pagesJim Sears's Summary: Regular Expressions in QTPRohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Python Quide Part 4Document3 pagesPython Quide Part 4AgnieszkaStyśNo ratings yet
- 'Ab' 'A' 'B' 'A' 'A' 'B': Class Public VoidDocument5 pages'Ab' 'A' 'B' 'A' 'A' 'B': Class Public VoidCLINICAL LAB SOFTNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure: UMBC CMSC 461 Spring '99Document2 pagesBasic Structure: UMBC CMSC 461 Spring '99aviNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document127 pagesCH 02mehari kirosNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Beefs Up VBScript With Regular ExpressionsDocument10 pagesMicrosoft Beefs Up VBScript With Regular ExpressionsSrikanth PentyalaNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions: Item 15: Know The Precedence of Regular Expression OperatorsDocument36 pagesRegular Expressions: Item 15: Know The Precedence of Regular Expression OperatorsPinky NaharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SQLDocument63 pagesIntroduction To SQLzaibunnisaahmed7890No ratings yet
- Regular Expression 01Document48 pagesRegular Expression 01Aamna RazaNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts: Introduction To SQLDocument57 pagesDatabase System Concepts: Introduction To SQLUmma HabibaNo ratings yet
- SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) : Eng. Ibraheem LubbadDocument16 pagesSQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) : Eng. Ibraheem LubbadaNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Introduction To SQLDocument63 pages1.3. Introduction To SQLragulNo ratings yet
- POSIX Regular Expressions: BracketsDocument5 pagesPOSIX Regular Expressions: BracketsMalathi SankarNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 6 - SubqueriesDocument17 pages12 - Chapter 6 - SubqueriesNguyen Hoang Kien (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Unit-3: 1. TurbodbadminDocument24 pagesUnit-3: 1. TurbodbadminmanjuNo ratings yet
- Transact-SQL Syntax Conventions (Transact-SQL)Document2 pagesTransact-SQL Syntax Conventions (Transact-SQL)FrancesHsiehNo ratings yet
- PL SQL FunctionsDocument219 pagesPL SQL Functionsboddu_raghunarayanaNo ratings yet
- Regular ExpressionDocument28 pagesRegular Expressionapi-3875928No ratings yet
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDocument26 pagesWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNo ratings yet
- Metacharacters in PythonDocument7 pagesMetacharacters in PythonAnonymous DFpzhrRNo ratings yet
- Using Arrays: The Basics: George Matthews The University of GeorgiaDocument3 pagesUsing Arrays: The Basics: George Matthews The University of GeorgiaGanti1977No ratings yet
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandAdvanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Les 06 Conf Alerts RptsDocument7 pagesLes 06 Conf Alerts Rptscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 10 ManageDocument7 pagesLes 10 Managecr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 05 Audit SettingsDocument29 pagesLes 05 Audit Settingscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 01 IntroDocument21 pagesLes 01 Introcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 03 Install AgentDocument23 pagesLes 03 Install Agentcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 02 Install ServerDocument34 pagesLes 02 Install Servercr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 04 Conf AVDocument15 pagesLes 04 Conf AVcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 08 AlertsDocument11 pagesLes 08 Alertscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 07 ReportsDocument14 pagesLes 07 Reportscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 09 SecurityDocument8 pagesLes 09 Securitycr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- ProduseDocument21 pagesProduseAnyelaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Nipper Studio - TitaniaDocument6 pagesIntroducing Nipper Studio - TitaniaRandyRaharjaNo ratings yet
- SM2258AA FW Release Note - Q1107B - 20171206Document2 pagesSM2258AA FW Release Note - Q1107B - 20171206AlexNo ratings yet
- HCIA RS - MOOC and Pre-Test ExamDocument7 pagesHCIA RS - MOOC and Pre-Test ExamRajdeep Dash SojibNo ratings yet
- Linked List - Solution To Assignment 02 - (PW Skills (Decode)Document8 pagesLinked List - Solution To Assignment 02 - (PW Skills (Decode)soumya dasNo ratings yet
- Reference Manual (0.6) (2020.09.06) : OpencoreDocument37 pagesReference Manual (0.6) (2020.09.06) : OpencorecistacimliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Program Example: 3.1 How To Make Project and Open ProgramDocument21 pagesChapter 3. Program Example: 3.1 How To Make Project and Open Programjhon hernanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Service OverviewDocument48 pagesAmazon Web Service OverviewPriyank OzaNo ratings yet
- PP QuizDocument10 pagesPP QuizAlapati RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument32 pagesChangelogEduardo LemosNo ratings yet
- asm1-1618- Mai Trần Nguyên KhôiDocument26 pagesasm1-1618- Mai Trần Nguyên KhôiLe Thanh Huy (FGW HCM)No ratings yet
- PRPC5-4SP2 J2EE Install Guide TomcatDocument69 pagesPRPC5-4SP2 J2EE Install Guide TomcatingenixNo ratings yet
- LMT Basic Principles: LMT Licence Management ToolDocument4 pagesLMT Basic Principles: LMT Licence Management ToolAntnhe BayuNo ratings yet
- Lista ActualizadaDocument13 pagesLista ActualizadaNoganet EmpNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller Laboratory Manualanand_gudnavarNo ratings yet
- Real Time UT Simulator: Sunday, June 24, 2007Document4 pagesReal Time UT Simulator: Sunday, June 24, 2007blos789No ratings yet
- Fault Tolerant Ethernet (FTE)Document20 pagesFault Tolerant Ethernet (FTE)baohuy_plaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii: LinuxDocument32 pagesUnit - Ii: LinuxKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Hearts of Iron IVDocument8 pagesTutorial - Hearts of Iron IVasdkmflaNo ratings yet
- 03 Evolution of The Hearing Aid Programming DeviceDocument7 pages03 Evolution of The Hearing Aid Programming DeviceDEANo ratings yet
- HANA Based BW Transformation - SAP BlogsDocument33 pagesHANA Based BW Transformation - SAP BlogsSmith KumarNo ratings yet
- 9704Document51 pages9704jivasumanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 5Document6 pagesAssessment 5Aahan JainNo ratings yet
- Arm Cortex M55 Product BriefDocument4 pagesArm Cortex M55 Product BriefEdda Andrade RosalesNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument6 pagesLinked Listdarshancool25No ratings yet
- Exp No 3Document4 pagesExp No 3dharanikaNo ratings yet
- 11 NoSQL-slidesDocument26 pages11 NoSQL-slidesAkshayNo ratings yet
- Cp341 eDocument238 pagesCp341 ePaulo HardyNo ratings yet
- 5 1005874576149708806Document6 pages5 1005874576149708806firzenilyas0% (1)
Les 08
Les 08
Uploaded by
cr.preteco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesOracle SQL - Regular Expression Support
Original Title
Les08
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOracle SQL - Regular Expression Support
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesLes 08
Les 08
Uploaded by
cr.pretecoOracle SQL - Regular Expression Support
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
8
Regular Expression Support
Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to
use regular expression support in SQL to search,
match, and replace strings in terms of regular
expressions.
8-2 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
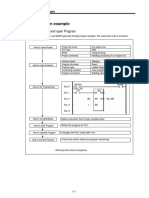
Regular Expression: Overview
A multilingual
regular expression
support for SQL
and PL/SQL string
types
ABC
A method of
describing both Several new
simple and complex functions to
patterns for support regular
searching and expressions
manipulating
8-3 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Meta Characters
Symbol Description
* Matches zero or more occurrences
| Alteration operator for specifying alternative matches
^/$ Matches the start-of-line/end-of-line
[] Bracket expression for a matching list matching any one of the
expressions represented in the list
{m} Matches exactly m times
{m,n} Matches at least m times but no more than n times
[: :] Specifies a character class and matches any character in that class
\ Can have 4 different meanings: 1. Stand for itself. 2. Quote the next
character. 3. Introduce an operator. 4. Do nothing.
+ Matches one or more occurrences
? Matches zero or one occurrence
. Matches any character in the supported character set, except NULL
() Grouping expression, treated as a single subexpression
[==] Specifies equivalence classes
\n Back-reference expression
[..] Specifies one collation element, such as a multicharacter element
8-4 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Using Meta Characters
Problem: Find 'abc' within a string:
Solution: 'abc' 1
Matches: abc
Does not match: 'def'
Problem: To find 'a' followed by any character, followed
by 'c'
Meta Character: any character is defined by '.'
Solution: 'a.c'
Matches: abc
2
Matches: adc
Matches: alc
Matches: a&c
Does not match: abb
Problem: To find one or more occurrences of 'a'
Meta Character: Use'+' sign to match one or more of the
previous characters
Solution: 'a+' 3
Matches: a
Matches: aa
Does not match: bbb
8-5 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Regular Expression Functions
Function Name Description
REGEXP_LIKE Similar to the LIKE operator, but performs
regular expression matching instead of
simple pattern matching
REGEXP_REPLACE Searches for a regular expression pattern
and replaces it with a replacement string
REGEXP_INSTR Searches for a given string for a regular
expression pattern and returns the
position where the match is found
REGEXP_SUBSTR Searches for a regular expression pattern
within a given string and returns the
matched substring
8-7 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
REGEXP Function Syntax
REGEXP_LIKE (srcstr, pattern [,match_option])
REGEXP_INSTR (srcstr, pattern [, position [, occurrence
[, return_option [, match_option]]]])
REGEXP_SUBSTR (srcstr, pattern [, position
[, occurrence [, match_option]]])
REGEXP_REPLACE(srcstr, pattern [,replacestr [, position
[, occurrence [, match_option]]]])
8-8 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Performing Basic Searches
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE REGEXP_LIKE (first_name, '^Ste(v|ph)en$');
8-9 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Checking the Presence of a Pattern
SELECT street_address,
REGEXP_INSTR(street_address,'[^[:alpha:]]')
FROM locations
WHERE
REGEXP_INSTR(street_address,'[^[:alpha:]]')> 1;
8-10 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Example of Extracting Substrings
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR(street_address , ' [^ ]+ ')
"Road" FROM locations;
8-11 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Replacing Patterns
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE( country_name, '(.)',
'\1 ') "REGEXP_REPLACE"
FROM countries;
8-12 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Regular Expressions and
Check Constraints
ALTER TABLE emp8
ADD CONSTRAINT email_addr 1
CHECK(REGEXP_LIKE(email,'@'))NOVALIDATE ;
INSERT INTO emp8 VALUES
(500,'Christian','Patel', 2
'ChrisP2creme.com', 1234567890,
'12-Jan-2004', 'HR_REP', 2000, null, 102, 40) ;
8-13 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Summary
In this lesson, you should have learned how to use
regular expression support in SQL and PL/SQL to
search, match, and replace strings in terms of regular
expressions.
8-14 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Practice 8: Overview
This practice covers using regular expressions.
8-15 Copyright © 2006, Oracle. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Extending The Standard IDOC For Outbound DeliveryDocument16 pagesExtending The Standard IDOC For Outbound DeliverySalih SahinNo ratings yet
- HW5Document7 pagesHW5Rahul Patil100% (1)
- Regular Expression SupportDocument14 pagesRegular Expression SupportClaudian Paduraru100% (1)
- 1Z0 052 Exam Dumps 2018Document26 pages1Z0 052 Exam Dumps 2018Kazi Mobaidul Islam ShovonNo ratings yet
- Regexp - Like: Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1)Document16 pagesRegexp - Like: Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 1 (10.1)Sandeep DesaiNo ratings yet
- Python Course: Session 6b - Regular ExpressionsDocument11 pagesPython Course: Session 6b - Regular ExpressionsDimitris LyberisNo ratings yet
- Oracle Searching MatchingDocument27 pagesOracle Searching MatchingDrRohini SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sys LW-08EN Regex-FiltersDocument31 pagesSys LW-08EN Regex-Filtersredhoua.ghezlene.gasmiNo ratings yet
- Andrei's Regex Clinic - PHP Quebec 2009Document209 pagesAndrei's Regex Clinic - PHP Quebec 2009kaplumb_aga100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6elias ferhanNo ratings yet
- 03.0 PHP Regular ExpressionDocument20 pages03.0 PHP Regular Expressionhey youNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument26 pagesIntroductionRAMSURYA PERUMALLANo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL Language Quick Reference: 40020GC10 Production 1.0 April 1999 M08684Document56 pagesOracle SQL Language Quick Reference: 40020GC10 Production 1.0 April 1999 M08684EvaNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions: Regular Expression Syntax in PythonDocument11 pagesRegular Expressions: Regular Expression Syntax in PythonHa NguyenNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Hw5 PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info Hw5 PRJamal Al-jaziNo ratings yet
- SQLDocument861 pagesSQLAnonymous E8FG7X19RNo ratings yet
- Oracle PLSQL Interview AdvDocument25 pagesOracle PLSQL Interview AdvZainul AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Re ExpressionDocument23 pagesRe ExpressionDiveshDuttNo ratings yet
- Regular Expression PythonDocument23 pagesRegular Expression PythonYASH DOSHINo ratings yet
- Database Programming: Case and Character ManipulationDocument30 pagesDatabase Programming: Case and Character ManipulationKevin Van MalderenNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Data-Manipulation-LanguageDMLDocument16 pagesLab 2 Data-Manipulation-LanguageDMLKaram SalahNo ratings yet
- Loadrunner Questions:: Example 1Document27 pagesLoadrunner Questions:: Example 1Lavanya GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Java Regex Tutorial: Lars VogelDocument20 pagesJava Regex Tutorial: Lars Vogelhasan_maxNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six DBDocument11 pagesChapter Six DBbirtukan aregaNo ratings yet
- Reg - Replace: SyntaxDocument1 pageReg - Replace: SyntaxshareefNo ratings yet
- Ora-10g Reg. ExpressionsDocument3 pagesOra-10g Reg. ExpressionsPrasanna GhareNo ratings yet
- Understanding New Features of JSP2.0Document13 pagesUnderstanding New Features of JSP2.0api-3791744100% (2)
- Lecture 4-6 (R.A)Document22 pagesLecture 4-6 (R.A)Huzaifa MemonNo ratings yet
- REGEX ExtendedDocument39 pagesREGEX ExtendedLaurenţiu GavrilescuNo ratings yet
- Horstkeller Cd200 Sent inDocument118 pagesHorstkeller Cd200 Sent inSandeep SivanNo ratings yet
- Perlre Perl Regular ExpressionsDocument16 pagesPerlre Perl Regular Expressionsfippifuppi78No ratings yet
- DP 4 1 PracticeDocument4 pagesDP 4 1 PracticeJessica IreneNo ratings yet
- Apex BasicsDocument7 pagesApex BasicsshahbojjaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-IiDocument82 pagesDBMS Unit-IiNeha SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Matching Sets of CharactersDocument8 pagesLesson 3: Matching Sets of CharactersMe ItsNo ratings yet
- Jim Sears's Summary: Regular Expressions in QTPDocument6 pagesJim Sears's Summary: Regular Expressions in QTPRohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Python Quide Part 4Document3 pagesPython Quide Part 4AgnieszkaStyśNo ratings yet
- 'Ab' 'A' 'B' 'A' 'A' 'B': Class Public VoidDocument5 pages'Ab' 'A' 'B' 'A' 'A' 'B': Class Public VoidCLINICAL LAB SOFTNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure: UMBC CMSC 461 Spring '99Document2 pagesBasic Structure: UMBC CMSC 461 Spring '99aviNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document127 pagesCH 02mehari kirosNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Beefs Up VBScript With Regular ExpressionsDocument10 pagesMicrosoft Beefs Up VBScript With Regular ExpressionsSrikanth PentyalaNo ratings yet
- Regular Expressions: Item 15: Know The Precedence of Regular Expression OperatorsDocument36 pagesRegular Expressions: Item 15: Know The Precedence of Regular Expression OperatorsPinky NaharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SQLDocument63 pagesIntroduction To SQLzaibunnisaahmed7890No ratings yet
- Regular Expression 01Document48 pagesRegular Expression 01Aamna RazaNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts: Introduction To SQLDocument57 pagesDatabase System Concepts: Introduction To SQLUmma HabibaNo ratings yet
- SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) : Eng. Ibraheem LubbadDocument16 pagesSQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) : Eng. Ibraheem LubbadaNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Introduction To SQLDocument63 pages1.3. Introduction To SQLragulNo ratings yet
- POSIX Regular Expressions: BracketsDocument5 pagesPOSIX Regular Expressions: BracketsMalathi SankarNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chapter 6 - SubqueriesDocument17 pages12 - Chapter 6 - SubqueriesNguyen Hoang Kien (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Unit-3: 1. TurbodbadminDocument24 pagesUnit-3: 1. TurbodbadminmanjuNo ratings yet
- Transact-SQL Syntax Conventions (Transact-SQL)Document2 pagesTransact-SQL Syntax Conventions (Transact-SQL)FrancesHsiehNo ratings yet
- PL SQL FunctionsDocument219 pagesPL SQL Functionsboddu_raghunarayanaNo ratings yet
- Regular ExpressionDocument28 pagesRegular Expressionapi-3875928No ratings yet
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDocument26 pagesWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNo ratings yet
- Metacharacters in PythonDocument7 pagesMetacharacters in PythonAnonymous DFpzhrRNo ratings yet
- Using Arrays: The Basics: George Matthews The University of GeorgiaDocument3 pagesUsing Arrays: The Basics: George Matthews The University of GeorgiaGanti1977No ratings yet
- Advanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandAdvanced SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Les 06 Conf Alerts RptsDocument7 pagesLes 06 Conf Alerts Rptscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 10 ManageDocument7 pagesLes 10 Managecr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 05 Audit SettingsDocument29 pagesLes 05 Audit Settingscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 01 IntroDocument21 pagesLes 01 Introcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 03 Install AgentDocument23 pagesLes 03 Install Agentcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 02 Install ServerDocument34 pagesLes 02 Install Servercr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 04 Conf AVDocument15 pagesLes 04 Conf AVcr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 08 AlertsDocument11 pagesLes 08 Alertscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 07 ReportsDocument14 pagesLes 07 Reportscr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- Les 09 SecurityDocument8 pagesLes 09 Securitycr.pretecoNo ratings yet
- ProduseDocument21 pagesProduseAnyelaNo ratings yet
- Introducing Nipper Studio - TitaniaDocument6 pagesIntroducing Nipper Studio - TitaniaRandyRaharjaNo ratings yet
- SM2258AA FW Release Note - Q1107B - 20171206Document2 pagesSM2258AA FW Release Note - Q1107B - 20171206AlexNo ratings yet
- HCIA RS - MOOC and Pre-Test ExamDocument7 pagesHCIA RS - MOOC and Pre-Test ExamRajdeep Dash SojibNo ratings yet
- Linked List - Solution To Assignment 02 - (PW Skills (Decode)Document8 pagesLinked List - Solution To Assignment 02 - (PW Skills (Decode)soumya dasNo ratings yet
- Reference Manual (0.6) (2020.09.06) : OpencoreDocument37 pagesReference Manual (0.6) (2020.09.06) : OpencorecistacimliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Program Example: 3.1 How To Make Project and Open ProgramDocument21 pagesChapter 3. Program Example: 3.1 How To Make Project and Open Programjhon hernanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web Service OverviewDocument48 pagesAmazon Web Service OverviewPriyank OzaNo ratings yet
- PP QuizDocument10 pagesPP QuizAlapati RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- ChangelogDocument32 pagesChangelogEduardo LemosNo ratings yet
- asm1-1618- Mai Trần Nguyên KhôiDocument26 pagesasm1-1618- Mai Trần Nguyên KhôiLe Thanh Huy (FGW HCM)No ratings yet
- PRPC5-4SP2 J2EE Install Guide TomcatDocument69 pagesPRPC5-4SP2 J2EE Install Guide TomcatingenixNo ratings yet
- LMT Basic Principles: LMT Licence Management ToolDocument4 pagesLMT Basic Principles: LMT Licence Management ToolAntnhe BayuNo ratings yet
- Lista ActualizadaDocument13 pagesLista ActualizadaNoganet EmpNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller Laboratory Manualanand_gudnavarNo ratings yet
- Real Time UT Simulator: Sunday, June 24, 2007Document4 pagesReal Time UT Simulator: Sunday, June 24, 2007blos789No ratings yet
- Fault Tolerant Ethernet (FTE)Document20 pagesFault Tolerant Ethernet (FTE)baohuy_plaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii: LinuxDocument32 pagesUnit - Ii: LinuxKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Hearts of Iron IVDocument8 pagesTutorial - Hearts of Iron IVasdkmflaNo ratings yet
- 03 Evolution of The Hearing Aid Programming DeviceDocument7 pages03 Evolution of The Hearing Aid Programming DeviceDEANo ratings yet
- HANA Based BW Transformation - SAP BlogsDocument33 pagesHANA Based BW Transformation - SAP BlogsSmith KumarNo ratings yet
- 9704Document51 pages9704jivasumanaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 5Document6 pagesAssessment 5Aahan JainNo ratings yet
- Arm Cortex M55 Product BriefDocument4 pagesArm Cortex M55 Product BriefEdda Andrade RosalesNo ratings yet
- Linked ListDocument6 pagesLinked Listdarshancool25No ratings yet
- Exp No 3Document4 pagesExp No 3dharanikaNo ratings yet
- 11 NoSQL-slidesDocument26 pages11 NoSQL-slidesAkshayNo ratings yet
- Cp341 eDocument238 pagesCp341 ePaulo HardyNo ratings yet
- 5 1005874576149708806Document6 pages5 1005874576149708806firzenilyas0% (1)