Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.8 - Cell Respiration
2.8 - Cell Respiration
Uploaded by
pjhave0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pagesCell respiration supplies energy for life through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that break bonds in organic molecules like glucose. This releases energy that is trapped in ATP molecules, which directly fuel most biological reactions. Aerobic respiration using oxygen as a final electron acceptor is the most efficient pathway for generating ATP through the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
Original Description:
Original Title
2.8- Cell Respiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCell respiration supplies energy for life through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that break bonds in organic molecules like glucose. This releases energy that is trapped in ATP molecules, which directly fuel most biological reactions. Aerobic respiration using oxygen as a final electron acceptor is the most efficient pathway for generating ATP through the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pages2.8 - Cell Respiration
2.8 - Cell Respiration
Uploaded by
pjhaveCell respiration supplies energy for life through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that break bonds in organic molecules like glucose. This releases energy that is trapped in ATP molecules, which directly fuel most biological reactions. Aerobic respiration using oxygen as a final electron acceptor is the most efficient pathway for generating ATP through the citric acid cycle and electron transport chain in the mitochondria.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
2.
8- Cell Respiration
Essential Idea- Cell respiration supplies Pp 122- 128
energy for the functions of life
Nature of Science:
Understandings:
Applications and skills:
Define Cell Respiration
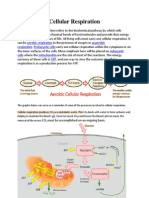
• Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy
from organic compounds in cells to form ATP
• Glucose is the major substrate for respiration
• If a cell does not have glucose available, other
organic molecules such as fatty acids or amino
acids may be substituted as substrate
• Cell respiration is catalysed by enzymes which
ensures a sequential series of reactions in which
the covalent bonds are broken one at a time
• The energy released when covalent bonds are
broken is trapped in the form of ATP molecules
• Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the molecule
which directly fuels the majority of biological
reactions
Why cell respiration
• Cells require a constant source of energy to perform various tasks
Eg-
• Movement
• Transport
• division
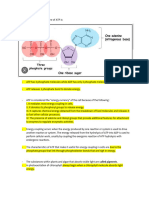
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
• ATP is the chemical molecule which
directly fuels the majority of biological
reactions
• About 10 25 ATP molecules are
hydrolysed to ADP and inorganic
phosphate (Pi) daily
• ADP is reduced back to ATP using the
free energy from the oxidation of
organic molecules
ATP Cycle
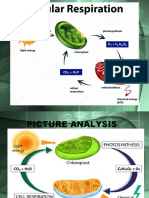
Types of Respiration
Anaerobic versus Aerobic Cell Respiration
Glycolysis and Cell Respiration
Glycolysis
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3dOaQQQrHqA
You might also like
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- lesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyDocument10 pageslesson-4-Role-of-ATP-in-Energy-Coupling-and-Transfer (1) EnergyKivo ZoshikoroNo ratings yet
- ATP PPTDocument14 pagesATP PPTagotsolania5No ratings yet
- What Is ATPDocument15 pagesWhat Is ATPEira LeyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document19 pagesLesson 11Cath DetoperezNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy Part 1Document18 pagesFlow of Energy Part 1nancie8No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetic: Atp CycleDocument28 pagesBioenergetic: Atp CycleRahmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Atp Adp CycleDocument18 pagesAtp Adp CycleLyn Dela Cruz Fontila100% (1)
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Cellular RespirationDocument57 pagesLesson 12 Cellular RespirationNhelle IronVoltoxNo ratings yet
- ATP - ADP CycleDocument13 pagesATP - ADP CycleDanessa Mina BalboaNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument19 pagesEnergy TransformationRicardo ErioNo ratings yet
- Energy and ATPDocument5 pagesEnergy and ATPMilka Rahman100% (1)
- GenbioDocument5 pagesGenbioYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration-1Document25 pagesEnergy and Respiration-1Rohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Energy TransformationsDocument49 pagesUnit 5 Energy TransformationsFiguracion, Zhass Naye D.No ratings yet
- Life Processes: RespirationDocument17 pagesLife Processes: RespirationYashaswini.V.No ratings yet
- HyacinthDocument52 pagesHyacinthHyacinth Rae Ramirez Aranas - LipatNo ratings yet
- Cellular1 2Document16 pagesCellular1 2Kaeshamaureen DresNo ratings yet
- 02 - Energy Production - Atp WebDocument15 pages02 - Energy Production - Atp Webapi-240330821No ratings yet
- 2-Energy and RespirationDocument34 pages2-Energy and RespirationLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Document47 pagesCellular - Respiration LECTURE 111Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument51 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint Guidelaloo01No ratings yet
- ATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointDocument18 pagesATP-ADP Cycle PowerpointJohn Iderf LagardeNo ratings yet
- Professor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, IbadanDocument25 pagesProfessor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, Ibadanolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument34 pagesCellular RespirationJonathan Blaza100% (2)
- Cell Structure & MetabolismDocument9 pagesCell Structure & MetabolismChami VillaNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationMohammad ZayanNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResDocument21 pagesAerobic Anaerobic Cellular ResRex IanNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism 052124Document89 pagesMicrobial Metabolism 052124Marina Abd CebrianNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- The Cell (Energy)Document15 pagesThe Cell (Energy)Luka IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument214 pagesBiology NotesbloomNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular RespirationVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformation (N)Document56 pagesEnergy Transformation (N)Princess Lorreine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahiraDocument43 pagesCellular Respiration: Amelia Putri Nariya Astri Yohana Putri Gabriellia Oktaviani P. Muhammad Fauzan Safina ZahirasafinazahiraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: TOPIC 2.8 (Core)Document18 pagesCellular Respiration: TOPIC 2.8 (Core)NikolozNo ratings yet
- AtpDocument10 pagesAtpSheba HernandezNo ratings yet
- Metabolism and AtpDocument20 pagesMetabolism and AtpAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Lee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeDocument25 pagesLee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeShivaveerakumar S. Chandrikimath100% (1)
- Gen Bio1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio1 ReviewerRhea SuarezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Second GradingDocument7 pagesGen Bio - Second GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Energy Coupling/ Coupled ReactionDocument20 pagesEnergy Coupling/ Coupled ReactionAshley Nicole VillegasNo ratings yet
- Bio103 Fall 2022 T08Document28 pagesBio103 Fall 2022 T08Noshin TabassumNo ratings yet
- Atp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasDocument12 pagesAtp Production & Consumption: Ian A. Tolomia Jonel V ParagasIan AusejoNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationsDocument21 pagesEnergy TransformationsLove CayaNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 3 Module 5 Aerobic Vs Anaerobic RespirationDocument8 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q2 Week 3 Module 5 Aerobic Vs Anaerobic RespirationReygie Ann SuenoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Key PointsDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Key PointsKathleen RamiloNo ratings yet
- What Is Energy and What Is Atp?Document18 pagesWhat Is Energy and What Is Atp?azwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Lesson 4Document10 pagesMetabolism: Lesson 4DASHNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Biologic Oxidation (New)Document71 pagesBiologic Oxidation (New)Muhammad Nur DelaphanEnamNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration - 1 THDocument12 pagesCellular - Respiration - 1 THarin.mekan1985No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument2 pagesRespirationmubasherkatbar562No ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Digital Footprint Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDigital Footprint Lesson PlanpjhaveNo ratings yet
- 2.9 PhotosynthesisDocument18 pages2.9 PhotosynthesispjhaveNo ratings yet
- Marketing An Art GalleryDocument17 pagesMarketing An Art GallerypjhaveNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Species, Communities and EcosystemsDocument16 pages4.1 Species, Communities and EcosystemspjhaveNo ratings yet