Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 viewsLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Uploaded by
catizfavsThis document discusses security measures for computer networks. It describes different types of network security devices including active devices like firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and antivirus software that monitor network traffic in real-time. It also discusses passive devices like intrusion detection systems that inspect network traffic logs to identify threats. Preventative devices like vulnerability scanners are also mentioned which identify potential security issues. The document provides details on these various tools and how they help secure networks and systems from unauthorized access and other risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021From EverandCEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021No ratings yet
- Juniper Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesJuniper Cheat SheetRavindra Singh100% (1)
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsZak RyderNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053Document7 pagesAssignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053KashifNo ratings yet
- PR1 Introduction To CNS FinalDocument6 pagesPR1 Introduction To CNS FinalprafullaNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assignment 04Document4 pagesInformation Security Assignment 04Rai AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument48 pagesUnit IVYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Document7 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Sonia Sultana100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Introduction To Cryptography and Network Security - OKDocument7 pagesPR1 - Introduction To Cryptography and Network Security - OKPrafulla Durgadhar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Computer Security ResearchDocument24 pagesComputer Security ResearchJayanth kumarNo ratings yet
- CYBERSECURITY ApplicationDocument5 pagesCYBERSECURITY ApplicationRakesh SawaiNo ratings yet
- Need For Network SecurityDocument8 pagesNeed For Network SecurityRyan CooperNo ratings yet
- الأسئلة المتوقعة لمقابلات الأمن السيبرانيDocument8 pagesالأسئلة المتوقعة لمقابلات الأمن السيبرانيAbood AlotibiNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- A Literature Survey On Network Attacks and Prevention: AbstractDocument7 pagesA Literature Survey On Network Attacks and Prevention: Abstractmani DILLSNo ratings yet
- NETWORKSECURITYDocument4 pagesNETWORKSECURITYytbarekukNo ratings yet
- NSE 1 Key Cybersecurity TermsDocument6 pagesNSE 1 Key Cybersecurity TermsJuan Pablo CordobaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - SecurityDocument25 pagesTask 1 - SecurityMuheet zahidNo ratings yet
- Basics of IT SecurityDocument18 pagesBasics of IT SecurityMayuriMahajan141No ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument16 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document7 pagesUnit 4lo leeeNo ratings yet
- TryHackMe Redes InformaticasDocument38 pagesTryHackMe Redes InformaticaseugeniapalaciosdatoNo ratings yet
- Security Technology - Firewall and VPN, Intrusion Detection System, Access ControlDocument3 pagesSecurity Technology - Firewall and VPN, Intrusion Detection System, Access ControlDev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security1Document6 pagesCyber Security1mnkanyi24No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber Security: Important Part of Any OrganizationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Security: Important Part of Any OrganizationHimanshu GoelNo ratings yet
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocument22 pages18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01No ratings yet
- Network Security DesignDocument5 pagesNetwork Security DesignMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Security: Challenges/Threats To Is SecurityDocument16 pagesSecurity: Challenges/Threats To Is SecuritysarvemNo ratings yet
- Privacy Unit1Document6 pagesPrivacy Unit1SwetankNo ratings yet
- Theory TimeTable SYBSC CSDocument4 pagesTheory TimeTable SYBSC CSpinkuchopra17No ratings yet
- Ethical HackingDocument109 pagesEthical HackingRameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unauthorized Access and RisksDocument2 pagesUnauthorized Access and RisksudayahariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Attacks, Concepts and TechniquesDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - Attacks, Concepts and TechniquesS. M. AkashNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Document9 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Kutty Pupps688No ratings yet
- Please Do Not Share These Notes On Apps Like Whatsapp or TelegramDocument12 pagesPlease Do Not Share These Notes On Apps Like Whatsapp or TelegramPayal PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument15 pagesUnit IVmenakarameshNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Briefly Describe Network SecurityDocument4 pagesBriefly Describe Network SecurityAlem GirmaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide For CybersecurityDocument11 pagesReference Guide For CybersecurityHomiyar SukhiaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Unit 5Document12 pagesCyber Security Unit 5Amit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Cyber SecurityDocument40 pagesUnit - II Cyber SecurityRitesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- NSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENDocument6 pagesNSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENitachi uchihaNo ratings yet
- Virus, Types and FirewallsDocument3 pagesVirus, Types and Firewalls23-cs-124No ratings yet
- Cisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2Document9 pagesCisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2MukeshNo ratings yet
- System For IntrusionDocument8 pagesSystem For IntrusionVictoria OdemakinNo ratings yet
- Siberseguridad Todo Copiado Aqui 2020Document29 pagesSiberseguridad Todo Copiado Aqui 2020vladi reyNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Info SecuDocument8 pagesUnit-4 Info Secuworkwithasr04No ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Nitisha ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Monitor Threats To The NetworkDocument12 pagesMonitor Threats To The NetworkAlage TekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Need For SecurityDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - The Need For SecurityAshura OsipNo ratings yet
- Incident Response ProcessDocument14 pagesIncident Response ProcessvanessaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Ijcatr 03091009Document6 pagesIjcatr 03091009ATSNo ratings yet
- Dhamm Nis ProjectDocument6 pagesDhamm Nis ProjectHrx XNo ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- TIN (Triangular Irregular Network - Run Length Encoded Data Structures - Chain Encoding - Quad Tree Data StructureDocument2 pagesTIN (Triangular Irregular Network - Run Length Encoded Data Structures - Chain Encoding - Quad Tree Data StructurecatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Cyber CriminologyDocument4 pagesCyber CriminologycatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Forensic PsychologyDocument2 pagesForensic PsychologycatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report 2.0Document32 pagesFinal Project Report 2.0catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Curtis Kibanya 21/08155: Stationary AccountDocument2 pagesCurtis Kibanya 21/08155: Stationary AccountcatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Signals and DataDocument54 pagesSignals and DatacatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Bisf Group A TimetableDocument2 pagesBisf Group A TimetablecatizfavsNo ratings yet
- As An IT StudentDocument2 pagesAs An IT StudentcatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Kariobangi South Church: 13 March 2022Document1 pageKariobangi South Church: 13 March 2022catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Assignment 1Document5 pagesFinancial Management Assignment 1catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Information Management According To BS EN ISO 19650 Facilitating The Common Data Environment (Workflow and Technical Solutions)Document34 pagesInformation Management According To BS EN ISO 19650 Facilitating The Common Data Environment (Workflow and Technical Solutions)NeedleandMortar100% (1)
- Attendance Management SystemDocument29 pagesAttendance Management SystemMahak Mittal64% (14)
- Sample Table - Worker: Perform Following SQL QueriesDocument2 pagesSample Table - Worker: Perform Following SQL QueriesNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module6 HA PDFDocument7 pagesModule6 HA PDFsrinubasaniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Command Used To Create Key-Pairs (Public/private Keys) in Unix/Linux/Mac?Document7 pagesWhat Is The Command Used To Create Key-Pairs (Public/private Keys) in Unix/Linux/Mac?jagdish modiNo ratings yet
- NXC5500 2 PDFDocument283 pagesNXC5500 2 PDFLilik Lholak LholokNo ratings yet
- Aws 13Document28 pagesAws 13sprasadn66No ratings yet
- GCP 101Document16 pagesGCP 101Cloud LearnNo ratings yet
- En Cuisine Libro de FrancesDocument113 pagesEn Cuisine Libro de FrancesMarisa PeiroNo ratings yet
- 5 - Data Conversion Specification - BOM TemplateDocument5 pages5 - Data Conversion Specification - BOM Templatevenkay1123No ratings yet
- Mcs 041 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument66 pagesMcs 041 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruPRAVIN KUMAR JALODIYANo ratings yet
- Linux Post TestDocument5 pagesLinux Post TestK Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- KGSSAPALink 45Document99 pagesKGSSAPALink 45Sankar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- ARANDA MALVAR PERALTA EBrgyRecord A Web Application Barangay Monitoring and Management SystemDocument68 pagesARANDA MALVAR PERALTA EBrgyRecord A Web Application Barangay Monitoring and Management SystemFrans Anacis GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Exam Rate CardDocument1 page2014 Exam Rate CardTees101No ratings yet
- Managing Big Datafor Scientific VisualizationDocument18 pagesManaging Big Datafor Scientific VisualizationTaniaRosasNo ratings yet
- Week 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeDocument7 pagesWeek 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeTokla XenNo ratings yet
- Configuring OPMN To Manage ODI Standalone AgentsDocument8 pagesConfiguring OPMN To Manage ODI Standalone AgentsnareshreddyguntakaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Online Exam System: TitleDocument4 pagesSynopsis On Online Exam System: TitleNishant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Configuring Integration Broker Messaging Between PeopleSoft Instances at Different PeopleTools LevelsDocument4 pagesConfiguring Integration Broker Messaging Between PeopleSoft Instances at Different PeopleTools LevelsSRINIVAS KOTTENo ratings yet
- H4 Chapter1Document12 pagesH4 Chapter1Rhea BadanaNo ratings yet
- Apm Book PDFDocument314 pagesApm Book PDFZahid MasoodNo ratings yet
- SivaSatyaNarayanaRajuKammella (9 0)Document8 pagesSivaSatyaNarayanaRajuKammella (9 0)vineeth rockstar1999No ratings yet
- Sample Test PlanDocument39 pagesSample Test Planapi-370433480% (5)
- VB .NET Unit-1Document72 pagesVB .NET Unit-1Yashas JainNo ratings yet
- Enabling SSL in Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12Document35 pagesEnabling SSL in Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12Thiên Trần100% (1)
- Shreyansh Singh: Education Technical Competence and Behavioral SkillsDocument1 pageShreyansh Singh: Education Technical Competence and Behavioral SkillsS1626No ratings yet
- Rosoka General 2015Document20 pagesRosoka General 2015swTechieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Requirement EngineeringDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Requirement EngineeringSUREDDY TANUJA MSCS2018No ratings yet
Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Uploaded by
catizfavs0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views28 pagesThis document discusses security measures for computer networks. It describes different types of network security devices including active devices like firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and antivirus software that monitor network traffic in real-time. It also discusses passive devices like intrusion detection systems that inspect network traffic logs to identify threats. Preventative devices like vulnerability scanners are also mentioned which identify potential security issues. The document provides details on these various tools and how they help secure networks and systems from unauthorized access and other risks.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses security measures for computer networks. It describes different types of network security devices including active devices like firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and antivirus software that monitor network traffic in real-time. It also discusses passive devices like intrusion detection systems that inspect network traffic logs to identify threats. Preventative devices like vulnerability scanners are also mentioned which identify potential security issues. The document provides details on these various tools and how they help secure networks and systems from unauthorized access and other risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, Applications
Uploaded by
catizfavsThis document discusses security measures for computer networks. It describes different types of network security devices including active devices like firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and antivirus software that monitor network traffic in real-time. It also discusses passive devices like intrusion detection systems that inspect network traffic logs to identify threats. Preventative devices like vulnerability scanners are also mentioned which identify potential security issues. The document provides details on these various tools and how they help secure networks and systems from unauthorized access and other risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 28
Security of Network,
systems, Application &
Data
Lecture 6
Security of Network
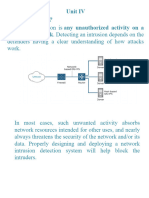
Network security is the security provided to a network from
unauthorized access and risks.
It is the duty of network administrators to adopt preventive measures
to protect their networks from potential security threats.
Computer networks that are involved in regular transactions and
communication within the government, individuals, or business
require security.
The most common and simple way of protecting a network resource
is by assigning it a unique name and a corresponding password.
1) Types of Network Security Devices
1. Active Network Security Devices
These can be firewalls, Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), web
proxies, web application firewalls (WAF) and anti-malware as the
devices are In-Line with the network.
Meaning, they receive the data packets and forward them to the
intended destination.
NB: Active Security Devices are excellent at identifying and stopping
threats in real-time because the traffic has to go through the device.
The downside is that the devices often slow or stop traffic and thus
degrade network performance.
a) Firewalls
A firewall is a network security system that manages and regulates the network traffic
based on some protocols. A firewall establishes a barrier between a trusted internal
network and the internet.
Firewalls exist both as software that run on a hardware and as hardware appliances.
Firewalls that are hardware-based also provide other functions like acting as a DHCP server
for that network.
Most personal computers use software-based firewalls to secure data from threats from
the internet.
Many routers that pass data between networks contain firewall components and
conversely, many firewalls can perform basic routing functions.
Firewalls are commonly used in private networks or intranets to prevent unauthorized
access from the internet. Every message entering or leaving the intranet goes through the
firewall to be examined for security measures.
An ideal firewall configuration consists of both hardware and software based devices. A
firewall also helps in providing remote access to a private network through secure
authentication certificates and logins.
4 Types of firewalls
Read and make short notes on the following types of firewalls
Packet-filtering firewalls
Stateful packet-filtering firewalls
Proxy firewalls
Web application firewalls.
b) Antivirus
An antivirus is a tool that is used to detect and remove malicious
software. It was originally designed to detect and remove viruses
from computers.
Modern antivirus software provide protection not only from virus,
but also from worms, Trojan-horses, adware's, spywares, keyloggers,
etc. Some products also provide protection from malicious URLs,
spam, phishing attacks, botnets, DDoS attacks, etc.
c) Content Filtering
Content filtering devices screen unpleasant and offensive emails or webpages.
These are used as a part of firewalls in corporations as well as in personal computers.
These devices generate the message "Access Denied" when someone tries to access
any unauthorized web page or email.
Content is usually screened for pornographic content and also for violence- or hate-
oriented content. Organizations also exclude shopping and job related contents.
Content filtering can be divided into the following categories −
Web filtering
Screening of Web sites or pages
E-mail filtering
Screening of e-mail for spam
Other objectionable content
d) Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Is a network security/threat prevention technology that examines network
traffic flows to detect and prevent vulnerability exploits.
Prevention: The IPS often sits directly behind the firewall and provides a
complementary layer of analysis that negatively selects for dangerous
content.
The IPS is placed inline (in the direct communication path between source
and destination), actively analyzing and taking automated actions on all
traffic flows that enter the network. Specifically, these actions include:
Sending an alarm to the administrator (as would be seen in an IDS)
Dropping the malicious packets
Blocking traffic from the source address
Resetting the connection
Detection: The IPS has a number of detection methods for finding exploits,
but signature-based detection and statistical anomaly-based detection are
the two dominant mechanisms.
Signature-based detection is based on a dictionary of uniquely identifiable
patterns (or signatures) in the code of each exploit. As an exploit is
discovered, its signature is recorded and stored in a continuously growing
dictionary of signatures. Signature detection for IPS breaks down into two
types:
1. Exploit-facing signatures identify individual exploits by triggering on the
unique patterns of a particular exploit attempt. The IPS can identify specific
exploits by finding a match with an exploit-facing signature in the traffic stream
2.Vulnerability-facing signatures are broader signatures that target the
underlying vulnerability in the system that is being targeted. These signatures
allow networks to be protected from variants of an exploit that may not have
Statistical anomaly detection takes samples of network traffic at
random and compares them to a pre-calculated baseline performance
level.
When the sample of network traffic activity is outside the parameters
of baseline performance, the IPS takes action to handle the situation.
2. Passive Network Security Devices
These include Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), User Behavior Analytics
(UBA), most Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions and
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
They operate outside the network by inspecting forensic artifacts such as
copies of network traffic or log data generated by various IT tools to
identify irregular traffic or malicious behavior.
NB: Passive Security Devices are designed to provide insight for security
analysts to review after the traffic has passed through the network.
Thus, passive devices do not typically degrade network performance,
however, they are not able to “block” unwanted traffic as Active Devices
can.
a) Intrusion Detection Systems
An IDS enhances cybersecurity by spotting a hacker or malicious
software on a network so you can remove it promptly to prevent a
breach or other problems, and use the data logged about the event to
better defend against similar intrusion incidents in the future.
Investing in an IDS that enables you respond to attacks quickly can be
far less costly than rectifying the damage from an attack and dealing
with the subsequent legal issues.
From time to time, attackers will manage to compromise other
security measures, such as cryptography, firewalls and so on.
It is crucial that information about these compromises immediately
flow to administrators — which can be easily accomplished using an
intrusion detection system.
Read and make short notes on the following 4 types of IDS:
Network Intrusion Detection System
Host Based Intrusion Detection System
Perimeter Intrusion Detection System
VM-Based Intrusion Detection System
3. Preventive Devices
These devices scan the networks and identify potential security
problems. For example, penetration testing devices and vulnerability
assessment appliances.
Penetration Testing devices
Penetration Testing: (or pen testing) is a simulated cyber attack
where professional ethical hackers break into corporate networks to
find weaknesses, before attackers do.
Software and tools used include Nmap, Metaspoilt, Wireshark,
Burpsuite, John The Ripper Password Cracker
Vulnerability assessment appliances
Vulnerability scanning or vulnerability assessment is a systematic process of
finding security loopholes in any system addressing the potential vulnerabilities.
Tools are: Netsparker, Nmap, GoLismero
The purpose of vulnerability assessments is to prevent the possibility of
unauthorized access to systems.
Types of Vulnerability Scanners:
Cloud-Based Vulnerability Scanners
Host-Based Vulnerability Scanners
Network-Based Vulnerability Scanners
Database-Based Vulnerability Scanners
4. Unified Threat Management (UTM)
These devices serve as all-in-one security devices. Examples include
firewalls, content filtering, web caching, etc.
Protection and Security in Operating
System
Security refers to providing a protection system to computer system
resources such as CPU, memory, disk, software programs and most
importantly data/information stored in the computer system.
If a computer program is run by an unauthorized user, then he/she
may cause severe damage to computer or data stored in it.
So a computer system must be protected against unauthorized
access, malicious access to system memory, viruses, worms.
Program Threats
If a user program is altered and further made to perform some malicious unwanted tasks,
then it is known as Program Threats. One of the common example of program threat is a
program installed in a computer which can store and send user credentials via network to
some hacker. Following is the list of some well-known program threats.
Trojan Horse − Such program traps user login credentials and stores them to send to
malicious user who can later on login to computer and can access system resources.
Trap Door − If a program which is designed to work as required, have a security hole in
its code and perform illegal action without knowledge of user then it is called to have a
trap door.
Logic Bomb − Logic bomb is a situation when a program misbehaves only when certain
conditions met otherwise it works as a genuine program. It is harder to detect.
Virus − They are highly dangerous and can modify/delete user files, crash systems. A
virus is generally a small code embedded in a program. As user accesses the program,
the virus starts getting embedded in other files/ programs and can make system
unusable for user. It replicates itself.
System Threats
These threats involve the abuse of system services. They strive to create a situation in
which operating-system resources and user files are misused. They are also used as a
medium to launch program threats. Following is the list of some well-known system
threats.
Worm − Worm is a process which can choked down a system performance by using
system resources to extreme levels. A Worm process generates its multiple copies
where each copy uses system resources, prevents all other processes to get required
resources. Worms processes can even shut down an entire network.
Port Scanning − Port scanning is a mechanism or means by which a hacker can
detects system vulnerabilities to make an attack on the system.
Denial of Service − Denial of service attacks normally prevents user to make
legitimate use of the system. For example, a user may not be able to use internet if
denial of service attacks browser's content settings.
Protection and Security Methods
Authentication
This deals with identifying each user in the system and making sure they are who
they claim to be. The operating system makes sure that all the users are
authenticated before they access the system. The different ways to make sure that
the users are authentic are:
Username/ Password: Each user has a distinct username and password
combination and they need to enter it correctly before they can access the
system.
User Key/ User Card: The users need to punch a card into the card slot or use
they individual key on a keypad to access the system.
User Attribute Identification: Different user attribute identifications that can be
used are fingerprint, eye retina etc. These are unique for each user and are
compared with the existing samples in the database. The user can only access
the system if there is a match.
One Time Password
These passwords provide a lot of security for authentication purposes.
A one time password can be generated exclusively for a login every
time a user wants to enter the system. It cannot be used more than
once. The various ways a one time password can be implemented are −
Random Numbers: The system can ask for numbers that
correspond to alphabets that are pre arranged. This combination
can be changed each time a login is required.
Secret Key: A hardware device can create a secret key related to
the user id for login. This key can change each time.
Computer Security - Securing OS
In this section we will treat how to secure or harden (harden is
another word used for securing OS) a workstation from the practical
point of view and what are the steps to follow. We will treat the
Windows OS
Guidelines for Windows OS Security
Following are the list of guidelines for Windows Operating System
Security.
I. Use the licensed versions of Windows OS: not the cracked or
pirated ones and activate them in order to take genuine updates.
II. Disable unused shares − By default, Windows OS creates shares,
please see the following screenshot
III. Take updates regularly for Windows OS: It is recommended to do
them automatically and periodically.
IV. Put your Windows System Firewall up: this will block all the
unauthorized services that make traffic.
v. Install a licensed antivirus
vi. You should always Configure a password protected Screen Saver.
vii. Disable Auto-play for Removable Media. This blocks the viruses to
run automatically from removable devices.
viii. Install only trusted internet explorer browsers like Internet
explorer, Chrome or Mozilla Firefox and then update them regularly.
Missing the updates can lead to possible hacking.
• Thank you
You might also like
- CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021From EverandCEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021No ratings yet
- Juniper Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesJuniper Cheat SheetRavindra Singh100% (1)
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsZak RyderNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053Document7 pagesAssignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053KashifNo ratings yet
- PR1 Introduction To CNS FinalDocument6 pagesPR1 Introduction To CNS FinalprafullaNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assignment 04Document4 pagesInformation Security Assignment 04Rai AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument48 pagesUnit IVYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Document7 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: Name: Md. Matiur Rahman Student ID: 000646848Sonia Sultana100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- PR1 - Introduction To Cryptography and Network Security - OKDocument7 pagesPR1 - Introduction To Cryptography and Network Security - OKPrafulla Durgadhar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Computer Security ResearchDocument24 pagesComputer Security ResearchJayanth kumarNo ratings yet
- CYBERSECURITY ApplicationDocument5 pagesCYBERSECURITY ApplicationRakesh SawaiNo ratings yet
- Need For Network SecurityDocument8 pagesNeed For Network SecurityRyan CooperNo ratings yet
- الأسئلة المتوقعة لمقابلات الأمن السيبرانيDocument8 pagesالأسئلة المتوقعة لمقابلات الأمن السيبرانيAbood AlotibiNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- A Literature Survey On Network Attacks and Prevention: AbstractDocument7 pagesA Literature Survey On Network Attacks and Prevention: Abstractmani DILLSNo ratings yet
- NETWORKSECURITYDocument4 pagesNETWORKSECURITYytbarekukNo ratings yet
- NSE 1 Key Cybersecurity TermsDocument6 pagesNSE 1 Key Cybersecurity TermsJuan Pablo CordobaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - SecurityDocument25 pagesTask 1 - SecurityMuheet zahidNo ratings yet
- Basics of IT SecurityDocument18 pagesBasics of IT SecurityMayuriMahajan141No ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument16 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technology School of Computing and Informatics Department of Information TechnologyAbdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document7 pagesUnit 4lo leeeNo ratings yet
- TryHackMe Redes InformaticasDocument38 pagesTryHackMe Redes InformaticaseugeniapalaciosdatoNo ratings yet
- Security Technology - Firewall and VPN, Intrusion Detection System, Access ControlDocument3 pagesSecurity Technology - Firewall and VPN, Intrusion Detection System, Access ControlDev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security1Document6 pagesCyber Security1mnkanyi24No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber Security: Important Part of Any OrganizationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Security: Important Part of Any OrganizationHimanshu GoelNo ratings yet
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocument22 pages18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01No ratings yet
- Network Security DesignDocument5 pagesNetwork Security DesignMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Security: Challenges/Threats To Is SecurityDocument16 pagesSecurity: Challenges/Threats To Is SecuritysarvemNo ratings yet
- Privacy Unit1Document6 pagesPrivacy Unit1SwetankNo ratings yet
- Theory TimeTable SYBSC CSDocument4 pagesTheory TimeTable SYBSC CSpinkuchopra17No ratings yet
- Ethical HackingDocument109 pagesEthical HackingRameswar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unauthorized Access and RisksDocument2 pagesUnauthorized Access and RisksudayahariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Attacks, Concepts and TechniquesDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - Attacks, Concepts and TechniquesS. M. AkashNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Document9 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument Wordprocessingml Document&rendition 1Kutty Pupps688No ratings yet
- Please Do Not Share These Notes On Apps Like Whatsapp or TelegramDocument12 pagesPlease Do Not Share These Notes On Apps Like Whatsapp or TelegramPayal PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument15 pagesUnit IVmenakarameshNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Briefly Describe Network SecurityDocument4 pagesBriefly Describe Network SecurityAlem GirmaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide For CybersecurityDocument11 pagesReference Guide For CybersecurityHomiyar SukhiaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Unit 5Document12 pagesCyber Security Unit 5Amit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit - II Cyber SecurityDocument40 pagesUnit - II Cyber SecurityRitesh KelkarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- NSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENDocument6 pagesNSE1 Key Cybersecurity Terms-ENitachi uchihaNo ratings yet
- Virus, Types and FirewallsDocument3 pagesVirus, Types and Firewalls23-cs-124No ratings yet
- Cisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2Document9 pagesCisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2MukeshNo ratings yet
- System For IntrusionDocument8 pagesSystem For IntrusionVictoria OdemakinNo ratings yet
- Siberseguridad Todo Copiado Aqui 2020Document29 pagesSiberseguridad Todo Copiado Aqui 2020vladi reyNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Info SecuDocument8 pagesUnit-4 Info Secuworkwithasr04No ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Nitisha ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Monitor Threats To The NetworkDocument12 pagesMonitor Threats To The NetworkAlage TekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Need For SecurityDocument17 pagesChapter 2 - The Need For SecurityAshura OsipNo ratings yet
- Incident Response ProcessDocument14 pagesIncident Response ProcessvanessaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Ijcatr 03091009Document6 pagesIjcatr 03091009ATSNo ratings yet
- Dhamm Nis ProjectDocument6 pagesDhamm Nis ProjectHrx XNo ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- TIN (Triangular Irregular Network - Run Length Encoded Data Structures - Chain Encoding - Quad Tree Data StructureDocument2 pagesTIN (Triangular Irregular Network - Run Length Encoded Data Structures - Chain Encoding - Quad Tree Data StructurecatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Cyber CriminologyDocument4 pagesCyber CriminologycatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Forensic PsychologyDocument2 pagesForensic PsychologycatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report 2.0Document32 pagesFinal Project Report 2.0catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Curtis Kibanya 21/08155: Stationary AccountDocument2 pagesCurtis Kibanya 21/08155: Stationary AccountcatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Signals and DataDocument54 pagesSignals and DatacatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Bisf Group A TimetableDocument2 pagesBisf Group A TimetablecatizfavsNo ratings yet
- As An IT StudentDocument2 pagesAs An IT StudentcatizfavsNo ratings yet
- Kariobangi South Church: 13 March 2022Document1 pageKariobangi South Church: 13 March 2022catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Assignment 1Document5 pagesFinancial Management Assignment 1catizfavsNo ratings yet
- Information Management According To BS EN ISO 19650 Facilitating The Common Data Environment (Workflow and Technical Solutions)Document34 pagesInformation Management According To BS EN ISO 19650 Facilitating The Common Data Environment (Workflow and Technical Solutions)NeedleandMortar100% (1)
- Attendance Management SystemDocument29 pagesAttendance Management SystemMahak Mittal64% (14)
- Sample Table - Worker: Perform Following SQL QueriesDocument2 pagesSample Table - Worker: Perform Following SQL QueriesNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module6 HA PDFDocument7 pagesModule6 HA PDFsrinubasaniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Command Used To Create Key-Pairs (Public/private Keys) in Unix/Linux/Mac?Document7 pagesWhat Is The Command Used To Create Key-Pairs (Public/private Keys) in Unix/Linux/Mac?jagdish modiNo ratings yet
- NXC5500 2 PDFDocument283 pagesNXC5500 2 PDFLilik Lholak LholokNo ratings yet
- Aws 13Document28 pagesAws 13sprasadn66No ratings yet
- GCP 101Document16 pagesGCP 101Cloud LearnNo ratings yet
- En Cuisine Libro de FrancesDocument113 pagesEn Cuisine Libro de FrancesMarisa PeiroNo ratings yet
- 5 - Data Conversion Specification - BOM TemplateDocument5 pages5 - Data Conversion Specification - BOM Templatevenkay1123No ratings yet
- Mcs 041 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument66 pagesMcs 041 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruPRAVIN KUMAR JALODIYANo ratings yet
- Linux Post TestDocument5 pagesLinux Post TestK Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- KGSSAPALink 45Document99 pagesKGSSAPALink 45Sankar SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- ARANDA MALVAR PERALTA EBrgyRecord A Web Application Barangay Monitoring and Management SystemDocument68 pagesARANDA MALVAR PERALTA EBrgyRecord A Web Application Barangay Monitoring and Management SystemFrans Anacis GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Exam Rate CardDocument1 page2014 Exam Rate CardTees101No ratings yet
- Managing Big Datafor Scientific VisualizationDocument18 pagesManaging Big Datafor Scientific VisualizationTaniaRosasNo ratings yet
- Week 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeDocument7 pagesWeek 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeTokla XenNo ratings yet
- Configuring OPMN To Manage ODI Standalone AgentsDocument8 pagesConfiguring OPMN To Manage ODI Standalone AgentsnareshreddyguntakaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Online Exam System: TitleDocument4 pagesSynopsis On Online Exam System: TitleNishant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Configuring Integration Broker Messaging Between PeopleSoft Instances at Different PeopleTools LevelsDocument4 pagesConfiguring Integration Broker Messaging Between PeopleSoft Instances at Different PeopleTools LevelsSRINIVAS KOTTENo ratings yet
- H4 Chapter1Document12 pagesH4 Chapter1Rhea BadanaNo ratings yet
- Apm Book PDFDocument314 pagesApm Book PDFZahid MasoodNo ratings yet
- SivaSatyaNarayanaRajuKammella (9 0)Document8 pagesSivaSatyaNarayanaRajuKammella (9 0)vineeth rockstar1999No ratings yet
- Sample Test PlanDocument39 pagesSample Test Planapi-370433480% (5)
- VB .NET Unit-1Document72 pagesVB .NET Unit-1Yashas JainNo ratings yet
- Enabling SSL in Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12Document35 pagesEnabling SSL in Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12Thiên Trần100% (1)
- Shreyansh Singh: Education Technical Competence and Behavioral SkillsDocument1 pageShreyansh Singh: Education Technical Competence and Behavioral SkillsS1626No ratings yet
- Rosoka General 2015Document20 pagesRosoka General 2015swTechieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Requirement EngineeringDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Requirement EngineeringSUREDDY TANUJA MSCS2018No ratings yet