Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 viewsChapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Chapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Uploaded by
Malik Umar KhakhThe document discusses Poisson's ratio, which is a measure of the deformation of a material under axial loading. It defines Poisson's ratio as the ratio of the contraction strain perpendicular to the applied load to the elongation strain in the direction of the applied load. The document also discusses Hooke's law, shear modulus, and the relationships between modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio for isotropic materials. It provides examples calculating these values for different materials and loading conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211Document20 pages36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211muralihare100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document30 pagesLecture 2hania dogar0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesDocument28 pagesChapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesIrfan KabirNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials I: Introduction - Concept of StressDocument23 pagesMechanics of Materials I: Introduction - Concept of StressAnonymous vvZDiaNo ratings yet
- MECH3020 Solid Mechanics II (Spring 2015)Document17 pagesMECH3020 Solid Mechanics II (Spring 2015)BillyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document17 pagesLecture 3aqsa zahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning Objectives楊子慶No ratings yet
- Me2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Document164 pagesMe2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Vidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis of Structure: SyllabusDocument28 pagesPlastic Analysis of Structure: SyllabusRaffal NejimNo ratings yet
- Plastic Characterization of Metals by Combining Nanoindentation Test and Finite Element SimulationDocument6 pagesPlastic Characterization of Metals by Combining Nanoindentation Test and Finite Element SimulationdfNo ratings yet
- Thanoon 2004-Inelastic Analysis of Composite SectionsDocument8 pagesThanoon 2004-Inelastic Analysis of Composite SectionsDiego Bengoechea IrazoquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsMohd AjmainNo ratings yet
- Determination of True Stress-Strain Curve of Type 304 and 316 Stainless Steels Using A Typical Tensile Test and Finite Element AnalysisDocument10 pagesDetermination of True Stress-Strain Curve of Type 304 and 316 Stainless Steels Using A Typical Tensile Test and Finite Element AnalysisDavid GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleDocument65 pagesMech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleGibson DiangoNo ratings yet
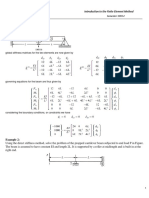
- Example 1:: K. N. Toosi Univ. of Technology Introduction To The Finite Element Method Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesExample 1:: K. N. Toosi Univ. of Technology Introduction To The Finite Element Method Faculty of Mechanical Engineeringmadhuri reddyNo ratings yet
- Rate Dependent Theory of Failure I Ductile MaterialDocument14 pagesRate Dependent Theory of Failure I Ductile Materialmohanad tariqNo ratings yet
- Instructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Document15 pagesInstructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument103 pagesStrength of MaterialsHundera DiribaNo ratings yet
- Ceg 201 Lab ReportdddDocument21 pagesCeg 201 Lab ReportdddEmenike-Ukah Michael ChiedozieNo ratings yet
- MSM Unit No.2 NotesDocument39 pagesMSM Unit No.2 NotesPratik SaindanePatilNo ratings yet
- CV1011 - 7 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument17 pagesCV1011 - 7 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsMarcus HuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2, Analysis of Strain, Concepts and Deformations - DR - Kassab-20 SlidesDocument21 pagesLecture 2, Analysis of Strain, Concepts and Deformations - DR - Kassab-20 SlidesNathan Romany FaresNo ratings yet
- Analytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadsDocument19 pagesAnalytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadscemadaroNo ratings yet
- Composite Beam BoxDocument11 pagesComposite Beam BoxAscanio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- CM03Document6 pagesCM03문주성No ratings yet
- Chapter6 Mechanical PropertiesDocument30 pagesChapter6 Mechanical Propertieszerimar333100% (1)
- ME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Document8 pagesME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Firas RocktNo ratings yet
- Loadings and Concept of Normal StressDocument12 pagesLoadings and Concept of Normal StressG. Dancer Gh100% (1)
- Koo 2014Document7 pagesKoo 2014ching2001.21No ratings yet
- ME255-mod 2Document30 pagesME255-mod 2Owusu Gyamera Justice DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Continuous BeamsDocument11 pagesChapter 7-Continuous BeamsMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- SM Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument21 pagesSM Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - inVittal PiseNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Chapter 3Document22 pagesStrength of Material Chapter 3naserunnNo ratings yet
- Text Book: "Advanced Mechanics of Materials"Document22 pagesText Book: "Advanced Mechanics of Materials"developmental biologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3Ahmed OsmanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Simple StrainDocument7 pagesMODULE 2 Simple StrainGeri LazaroNo ratings yet
- Determination of True Stress-Strain Curve of TypeDocument32 pagesDetermination of True Stress-Strain Curve of TypeGeethu R BabuNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration Hysteresis Paper 5-1-11Document34 pagesFree Vibration Hysteresis Paper 5-1-11Dan MendelsohnNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: ReferencesDocument15 pagesMechanics of Materials: Referencesعبدالله خيريNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Static Response of An Eccentrically Loaded ColumnDocument12 pagesNonlinear Static Response of An Eccentrically Loaded ColumnSelman DjeffalNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Lec01Document25 pagesStrength of Materials - Lec01Dheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- On The Mechanisms of Ductile Failure in High-Strength Steels Subjected To Multi-Axial Stress-StatesDocument28 pagesOn The Mechanisms of Ductile Failure in High-Strength Steels Subjected To Multi-Axial Stress-Statessgssgs1No ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics: 1), The Max. Stress Equation Can Be Approximated byDocument20 pagesFracture Mechanics: 1), The Max. Stress Equation Can Be Approximated bykarrar333 ALIYAHIANo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument32 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyHassaan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 4 (Mechanical Properties of Material)Document29 pagesME 2201-Lecture 4 (Mechanical Properties of Material)fontawesome111No ratings yet
- Engineering Materials2Document18 pagesEngineering Materials2Alex AlexeyNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration Hysteresis Paper 4-10-11Document28 pagesFree Vibration Hysteresis Paper 4-10-11Dan MendelsohnNo ratings yet
- Tensile PropertiesDocument4 pagesTensile Propertiesjontylee87No ratings yet
- Materials 14 02273Document20 pagesMaterials 14 02273Silas Sverre ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument28 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyAnwaar SafdarNo ratings yet
- MEMSDocument71 pagesMEMSSantosh VishnuNo ratings yet
- 4 Poissons Ratio 2Document17 pages4 Poissons Ratio 2ba3oda90No ratings yet
- Scia 3Document10 pagesScia 3Bora CobanogluNo ratings yet
- "Small-Span Bending TestDocument7 pages"Small-Span Bending TestMinhazul Abedin RiadNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument60 pagesStress and StrainMuhammad Shafie100% (1)
- Strength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and StrainsDocument34 pagesStrength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and Strainscoolguyraj.bkNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 7 - Shear and Bending Moment in BeamsDocument23 pagesME 2201-Lecture 7 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beamsfontawesome111No ratings yet
- 6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionDocument40 pages6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionWilliams AkandiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave DispersionFrom EverandMechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave DispersionYvon ChevalierNo ratings yet
- KV IIT Notebook List 2021Document12 pagesKV IIT Notebook List 2021laxmaxNo ratings yet
- BLINDAJES CANADA Version 2Document42 pagesBLINDAJES CANADA Version 2Carlos CadavidNo ratings yet
- June 2019 LEA STRUCLDocument30 pagesJune 2019 LEA STRUCLnoadspls2029No ratings yet
- Caie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Document27 pagesCaie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Arun GhatanNo ratings yet
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaDocument2 pagesKarl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaAnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Water CycleDocument4 pagesLesson 4 - Water Cycleapi-552754990No ratings yet
- Underwater Control of MobileDocument46 pagesUnderwater Control of Mobileshaik roshanNo ratings yet
- Whisperflo Vent Diffuser: Bulletin 80.3:6014Document4 pagesWhisperflo Vent Diffuser: Bulletin 80.3:6014Datt NguyenNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Day 1 (MD)Document4 pagesEnhancement Day 1 (MD)Albert Julian M. BarjoseNo ratings yet
- 5 Metfloor Installation GuideDocument9 pages5 Metfloor Installation GuideTùng Hì100% (1)
- CDS VAM TOP ® 2.875in. 7.8lb-ft L80 Type 1 API Drift 2.229in.Document1 pageCDS VAM TOP ® 2.875in. 7.8lb-ft L80 Type 1 API Drift 2.229in.BaurzhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Amir SaadNo ratings yet
- FST-4C (ICSE - G-2) Phy+Chem (C-09) 04-08-2023 - SOLDocument5 pagesFST-4C (ICSE - G-2) Phy+Chem (C-09) 04-08-2023 - SOLManas YadavNo ratings yet
- Kolhan University, Chaibasa: Proposed Syllabus For B.Sc. (Honours) PHYSICSDocument63 pagesKolhan University, Chaibasa: Proposed Syllabus For B.Sc. (Honours) PHYSICSBikashNo ratings yet
- Rabia7 Base 28.02 EmbedDocument7 pagesRabia7 Base 28.02 EmbedvengadNo ratings yet
- 120-10788 Isir RepDocument3 pages120-10788 Isir RepMechtek LabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTSDocument7 pagesLecture 9 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTSTasin Safwath ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTDocument4 pagesAdvanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTKermit GooeyNo ratings yet
- USA Test HKRiflesDocument45 pagesUSA Test HKRiflesJaume StrumbolNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelAMINA ATTANo ratings yet
- Activity 7 5 1Document4 pagesActivity 7 5 1Nicole MendozaNo ratings yet
- Clay Behaviour and The Selection of Design ParametersDocument11 pagesClay Behaviour and The Selection of Design Parametersbadrul79No ratings yet
- Kloeckner Westok A5 Pocket GuideDocument36 pagesKloeckner Westok A5 Pocket GuidekyleNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (QB)Document28 pagesParticle Dynamics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- WCD P3Document43 pagesWCD P3RupaliNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ExpectationDocument38 pagesMathematical ExpectationraachelongNo ratings yet
- Harish Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesHarish Physics Projectjnv bhindNo ratings yet
- Empirical Solutions: Ozgur KisiDocument73 pagesEmpirical Solutions: Ozgur Kisieko dateshidzeNo ratings yet
- 02 - IND360 Installation ManualDocument44 pages02 - IND360 Installation Manualwads.ele21No ratings yet
- SP 52.13330.2016 (Updated SNiP 23-05-95) - Natural and Artificial LightingDocument67 pagesSP 52.13330.2016 (Updated SNiP 23-05-95) - Natural and Artificial LightingValentínNo ratings yet
Chapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Chapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Uploaded by
Malik Umar Khakh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesThe document discusses Poisson's ratio, which is a measure of the deformation of a material under axial loading. It defines Poisson's ratio as the ratio of the contraction strain perpendicular to the applied load to the elongation strain in the direction of the applied load. The document also discusses Hooke's law, shear modulus, and the relationships between modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio for isotropic materials. It provides examples calculating these values for different materials and loading conditions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Poisson's ratio, which is a measure of the deformation of a material under axial loading. It defines Poisson's ratio as the ratio of the contraction strain perpendicular to the applied load to the elongation strain in the direction of the applied load. The document also discusses Hooke's law, shear modulus, and the relationships between modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio for isotropic materials. It provides examples calculating these values for different materials and loading conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesChapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Chapter 2 Poisson's Ratio
Uploaded by
Malik Umar KhakhThe document discusses Poisson's ratio, which is a measure of the deformation of a material under axial loading. It defines Poisson's ratio as the ratio of the contraction strain perpendicular to the applied load to the elongation strain in the direction of the applied load. The document also discusses Hooke's law, shear modulus, and the relationships between modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, and Poisson's ratio for isotropic materials. It provides examples calculating these values for different materials and loading conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
Mechanics Of Materials I
Poisson’s Ratio
Main Reference
Mechanics of Materials 3rd Edition by Ferdinand P. Beer,
E. Russell Johnston , Jr. , John T. Dewolf
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Poisson’s Ratio
For a slender bar subjected to axial loading:
The elongation in the x-direction is
accompanied by a contraction in the other
directions. Assuming that the material is
isotropic (no directional dependence),
Poisson’s ratio is defined as
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Poisson’s Ratio
Example 2.07:
A 500-mm-long, 16-mm-
diameter rod made of a
homogenous, isotropic material
is observed to increase in length
by 300 mm, and to decrease in
diameter by 2.4 mm when
subjected to an axial 12-kN load.
Determine the modulus of
elasticity and Poisson’s ratio of
the material.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Generalized Hooke’s Law
For an element subjected to multi-axial
loading, the normal strain components
resulting from the stress components may be
determined from the principle of
superposition. This requires:
1) strain is linearly related to stress
2) deformations are small
With these restrictions:
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Poisson’s Ratio
Example 2.08:
The steel block as shown in
figure is subjected to a uniform
pressure on all its faces.
Knowing that the change in
length of edge AB is -1.2 * 10-3
in., determine
(a) the change in length of the
other two edges,
(b) the pressure p applied to the
faces of the block. Assume E =
29 * 106 psi and υ = 0.29.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Shearing Strain
A cubic element subjected to a shear stress will
deform into a rhomboid. The corresponding shear
strain is quantified in terms of the change in angle
between the sides,
A plot of shear stress vs. shear strain is similar to the
previous plots of normal stress vs. normal strain
except that the strength values are approximately
half. For small strains,
where G is the modulus of rigidity or shear modulus.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Poisson’s Ratio
Example 2.08:
A rectangular block of a material with a
modulus of rigidity G = 90 ksi is bonded
to two rigid horizontal plates. The lower
plate is fixed, while the upper plate is
subjected to a horizontal force P.
Knowing that the upper plate moves
through 0.04 in. under the action of the
force, determine
A. the average shearing strain in the
material,
B. the force P exerted on the upper plate.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
Relation between G, E and υ
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UCE&T, Bahauddin Zakariya University
You might also like
- 36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211Document20 pages36b73ed7-6794-4c83-9d92-6b3676675211muralihare100% (1)
- Lecture 2Document30 pagesLecture 2hania dogar0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesDocument28 pagesChapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesIrfan KabirNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials I: Introduction - Concept of StressDocument23 pagesMechanics of Materials I: Introduction - Concept of StressAnonymous vvZDiaNo ratings yet
- MECH3020 Solid Mechanics II (Spring 2015)Document17 pagesMECH3020 Solid Mechanics II (Spring 2015)BillyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document17 pagesLecture 3aqsa zahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Normal Stress: Learning Objectives楊子慶No ratings yet
- Me2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Document164 pagesMe2003d Solid Mechanics - 16-11Vidhya NairNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis of Structure: SyllabusDocument28 pagesPlastic Analysis of Structure: SyllabusRaffal NejimNo ratings yet
- Plastic Characterization of Metals by Combining Nanoindentation Test and Finite Element SimulationDocument6 pagesPlastic Characterization of Metals by Combining Nanoindentation Test and Finite Element SimulationdfNo ratings yet
- Thanoon 2004-Inelastic Analysis of Composite SectionsDocument8 pagesThanoon 2004-Inelastic Analysis of Composite SectionsDiego Bengoechea IrazoquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsDocument30 pagesChapter 3 - Mechanic of MaterialsMohd AjmainNo ratings yet
- Determination of True Stress-Strain Curve of Type 304 and 316 Stainless Steels Using A Typical Tensile Test and Finite Element AnalysisDocument10 pagesDetermination of True Stress-Strain Curve of Type 304 and 316 Stainless Steels Using A Typical Tensile Test and Finite Element AnalysisDavid GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleDocument65 pagesMech 30a March 21 2022 Eteeap ModuleGibson DiangoNo ratings yet
- Example 1:: K. N. Toosi Univ. of Technology Introduction To The Finite Element Method Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesExample 1:: K. N. Toosi Univ. of Technology Introduction To The Finite Element Method Faculty of Mechanical Engineeringmadhuri reddyNo ratings yet
- Rate Dependent Theory of Failure I Ductile MaterialDocument14 pagesRate Dependent Theory of Failure I Ductile Materialmohanad tariqNo ratings yet
- Instructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Document15 pagesInstructional Material in Mechanics of Deformable Bodies (CE BSC 232b)Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument103 pagesStrength of MaterialsHundera DiribaNo ratings yet
- Ceg 201 Lab ReportdddDocument21 pagesCeg 201 Lab ReportdddEmenike-Ukah Michael ChiedozieNo ratings yet
- MSM Unit No.2 NotesDocument39 pagesMSM Unit No.2 NotesPratik SaindanePatilNo ratings yet
- CV1011 - 7 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument17 pagesCV1011 - 7 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsMarcus HuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2, Analysis of Strain, Concepts and Deformations - DR - Kassab-20 SlidesDocument21 pagesLecture 2, Analysis of Strain, Concepts and Deformations - DR - Kassab-20 SlidesNathan Romany FaresNo ratings yet
- Analytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadsDocument19 pagesAnalytical Approach To Predict Nonlinear Parameters For Dynamic Analysis of Structures Applied To Blast LoadscemadaroNo ratings yet
- Composite Beam BoxDocument11 pagesComposite Beam BoxAscanio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- CM03Document6 pagesCM03문주성No ratings yet
- Chapter6 Mechanical PropertiesDocument30 pagesChapter6 Mechanical Propertieszerimar333100% (1)
- ME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Document8 pagesME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Firas RocktNo ratings yet
- Loadings and Concept of Normal StressDocument12 pagesLoadings and Concept of Normal StressG. Dancer Gh100% (1)
- Koo 2014Document7 pagesKoo 2014ching2001.21No ratings yet
- ME255-mod 2Document30 pagesME255-mod 2Owusu Gyamera Justice DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Continuous BeamsDocument11 pagesChapter 7-Continuous BeamsMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- SM Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument21 pagesSM Mod1@AzDOCUMENTS - inVittal PiseNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Chapter 3Document22 pagesStrength of Material Chapter 3naserunnNo ratings yet
- Text Book: "Advanced Mechanics of Materials"Document22 pagesText Book: "Advanced Mechanics of Materials"developmental biologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document34 pagesChapter 3Ahmed OsmanNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Simple StrainDocument7 pagesMODULE 2 Simple StrainGeri LazaroNo ratings yet
- Determination of True Stress-Strain Curve of TypeDocument32 pagesDetermination of True Stress-Strain Curve of TypeGeethu R BabuNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration Hysteresis Paper 5-1-11Document34 pagesFree Vibration Hysteresis Paper 5-1-11Dan MendelsohnNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: ReferencesDocument15 pagesMechanics of Materials: Referencesعبدالله خيريNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Static Response of An Eccentrically Loaded ColumnDocument12 pagesNonlinear Static Response of An Eccentrically Loaded ColumnSelman DjeffalNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Lec01Document25 pagesStrength of Materials - Lec01Dheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- On The Mechanisms of Ductile Failure in High-Strength Steels Subjected To Multi-Axial Stress-StatesDocument28 pagesOn The Mechanisms of Ductile Failure in High-Strength Steels Subjected To Multi-Axial Stress-Statessgssgs1No ratings yet
- Fracture Mechanics: 1), The Max. Stress Equation Can Be Approximated byDocument20 pagesFracture Mechanics: 1), The Max. Stress Equation Can Be Approximated bykarrar333 ALIYAHIANo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument32 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyHassaan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 4 (Mechanical Properties of Material)Document29 pagesME 2201-Lecture 4 (Mechanical Properties of Material)fontawesome111No ratings yet
- Engineering Materials2Document18 pagesEngineering Materials2Alex AlexeyNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration Hysteresis Paper 4-10-11Document28 pagesFree Vibration Hysteresis Paper 4-10-11Dan MendelsohnNo ratings yet
- Tensile PropertiesDocument4 pagesTensile Propertiesjontylee87No ratings yet
- Materials 14 02273Document20 pagesMaterials 14 02273Silas Sverre ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument28 pagesStructural Mechanics (CE-312) : University of Engineering and TechnologyAnwaar SafdarNo ratings yet
- MEMSDocument71 pagesMEMSSantosh VishnuNo ratings yet
- 4 Poissons Ratio 2Document17 pages4 Poissons Ratio 2ba3oda90No ratings yet
- Scia 3Document10 pagesScia 3Bora CobanogluNo ratings yet
- "Small-Span Bending TestDocument7 pages"Small-Span Bending TestMinhazul Abedin RiadNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument60 pagesStress and StrainMuhammad Shafie100% (1)
- Strength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and StrainsDocument34 pagesStrength of Materials (15CV 32) : Module 1: Simple Stresses and Strainscoolguyraj.bkNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 7 - Shear and Bending Moment in BeamsDocument23 pagesME 2201-Lecture 7 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beamsfontawesome111No ratings yet
- 6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionDocument40 pages6.0 Mechanical Properties of Materials: Tension Compression Shear TorsionWilliams AkandiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave DispersionFrom EverandMechanical Characterization of Materials and Wave DispersionYvon ChevalierNo ratings yet
- KV IIT Notebook List 2021Document12 pagesKV IIT Notebook List 2021laxmaxNo ratings yet
- BLINDAJES CANADA Version 2Document42 pagesBLINDAJES CANADA Version 2Carlos CadavidNo ratings yet
- June 2019 LEA STRUCLDocument30 pagesJune 2019 LEA STRUCLnoadspls2029No ratings yet
- Caie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Document27 pagesCaie A2 Maths 9709 Pure 3Arun GhatanNo ratings yet
- Karl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaDocument2 pagesKarl Pearson's Coefficient of Correlation: FormulaAnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Water CycleDocument4 pagesLesson 4 - Water Cycleapi-552754990No ratings yet
- Underwater Control of MobileDocument46 pagesUnderwater Control of Mobileshaik roshanNo ratings yet
- Whisperflo Vent Diffuser: Bulletin 80.3:6014Document4 pagesWhisperflo Vent Diffuser: Bulletin 80.3:6014Datt NguyenNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Day 1 (MD)Document4 pagesEnhancement Day 1 (MD)Albert Julian M. BarjoseNo ratings yet
- 5 Metfloor Installation GuideDocument9 pages5 Metfloor Installation GuideTùng Hì100% (1)
- CDS VAM TOP ® 2.875in. 7.8lb-ft L80 Type 1 API Drift 2.229in.Document1 pageCDS VAM TOP ® 2.875in. 7.8lb-ft L80 Type 1 API Drift 2.229in.BaurzhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3Amir SaadNo ratings yet
- FST-4C (ICSE - G-2) Phy+Chem (C-09) 04-08-2023 - SOLDocument5 pagesFST-4C (ICSE - G-2) Phy+Chem (C-09) 04-08-2023 - SOLManas YadavNo ratings yet
- Kolhan University, Chaibasa: Proposed Syllabus For B.Sc. (Honours) PHYSICSDocument63 pagesKolhan University, Chaibasa: Proposed Syllabus For B.Sc. (Honours) PHYSICSBikashNo ratings yet
- Rabia7 Base 28.02 EmbedDocument7 pagesRabia7 Base 28.02 EmbedvengadNo ratings yet
- 120-10788 Isir RepDocument3 pages120-10788 Isir RepMechtek LabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTSDocument7 pagesLecture 9 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTSTasin Safwath ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Advanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTDocument4 pagesAdvanced-Physics-Reviewer 4th-Quarter Perio LTKermit GooeyNo ratings yet
- USA Test HKRiflesDocument45 pagesUSA Test HKRiflesJaume StrumbolNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelAMINA ATTANo ratings yet
- Activity 7 5 1Document4 pagesActivity 7 5 1Nicole MendozaNo ratings yet
- Clay Behaviour and The Selection of Design ParametersDocument11 pagesClay Behaviour and The Selection of Design Parametersbadrul79No ratings yet
- Kloeckner Westok A5 Pocket GuideDocument36 pagesKloeckner Westok A5 Pocket GuidekyleNo ratings yet
- Particle Dynamics (QB)Document28 pagesParticle Dynamics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- WCD P3Document43 pagesWCD P3RupaliNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ExpectationDocument38 pagesMathematical ExpectationraachelongNo ratings yet
- Harish Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesHarish Physics Projectjnv bhindNo ratings yet
- Empirical Solutions: Ozgur KisiDocument73 pagesEmpirical Solutions: Ozgur Kisieko dateshidzeNo ratings yet
- 02 - IND360 Installation ManualDocument44 pages02 - IND360 Installation Manualwads.ele21No ratings yet
- SP 52.13330.2016 (Updated SNiP 23-05-95) - Natural and Artificial LightingDocument67 pagesSP 52.13330.2016 (Updated SNiP 23-05-95) - Natural and Artificial LightingValentínNo ratings yet