Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
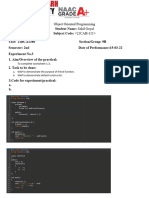
12 viewsLecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Lecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Uploaded by
Sahil GoyalThe document discusses object-oriented design (OOD) and defines key OOD terms. It explains that in OOD, a system is viewed as a collection of objects that represent entities. Objects have attributes and methods, and similar objects form classes that can inherit features from superclasses. The document defines objects, classes, messages, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism as fundamental OOD concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Sequencing Events-Grade 1Document31 pagesSequencing Events-Grade 1Dorothy JeanNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Design: Shruti JatharDocument62 pagesObject Oriented Design: Shruti Jatharravi4185No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1.3.3Document2 pagesLecture Notes 1.3.3Ashutosh mishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-IDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-Ipreetham rNo ratings yet
- L1-Introduction To OOPs ConceptsDocument16 pagesL1-Introduction To OOPs ConceptsKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- CH1 Introduction To OOPDocument24 pagesCH1 Introduction To OOPabenezergebrekirstosNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument3 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and DesignArpita SahaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument41 pagesObject Oriented ProgramminganandNo ratings yet
- Lect1 OdpDocument34 pagesLect1 OdpTim Boy ManNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Design (OOD) : Presenting By: M R Khan Dipu ID: 191-35-393 Department of Software EngineeringDocument14 pagesObject Oriented Design (OOD) : Presenting By: M R Khan Dipu ID: 191-35-393 Department of Software EngineeringM. R. KHAN DIPUNo ratings yet
- Programming Outline Features of OOPDocument21 pagesProgramming Outline Features of OOPpraisechidomayaNo ratings yet
- OOP ImplementationDocument43 pagesOOP Implementationeli indahNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 Units OoadDocument21 pages1 2 3 Units Ooadsamiksha5singhalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5mersimoybekele88No ratings yet
- Object ModelingDocument40 pagesObject Modelingjurihu143No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming SlidesDocument20 pagesObject Oriented Programming Slideslokidddd0No ratings yet
- Opps Notes PythonDocument83 pagesOpps Notes PythonomkarNo ratings yet
- Python Chapter3Document56 pagesPython Chapter3Jatin SharmaNo ratings yet
- OOSE Unit - 1Document41 pagesOOSE Unit - 1Vaibhav BirlaNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Notes OosdDocument20 pagesUnit-3 Notes Oosdyou • were • trolledNo ratings yet
- Ooad - Quick Guide Object Oriented ParadigmDocument50 pagesOoad - Quick Guide Object Oriented ParadigmShamiMalikNo ratings yet
- Oose CH 1Document38 pagesOose CH 1Daniel TunkaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 & 2 - OOAD - Object Oriented ParadigmDocument11 pagesWeek 1 & 2 - OOAD - Object Oriented ParadigmShariff Oluoch OdiwuorNo ratings yet
- DCIT 201 Programming I: Session 1 - Fundamental Concepts of OOD and OOPDocument35 pagesDCIT 201 Programming I: Session 1 - Fundamental Concepts of OOD and OOPPrincess Naomi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- 8.Object-Oriented Modelling DesignDocument49 pages8.Object-Oriented Modelling DesignﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 OoadDocument13 pagesUnit-1 OoadTanya OhriNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ConceptsDocument7 pagesObject Oriented ConceptsdiaeshantonyNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument60 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and DesignMatthew Tedunjaiye100% (1)
- UMLDocument61 pagesUMLmodernjewellaryNo ratings yet
- Java Basics2 (OOPS in Java)Document15 pagesJava Basics2 (OOPS in Java)sahilsecondacc1No ratings yet
- OOMD Unit 1Document13 pagesOOMD Unit 1Saraswati BhusanurNo ratings yet
- Software CrisisDocument120 pagesSoftware CrisisPrince MpofuNo ratings yet
- OOADDocument51 pagesOOADAbi KNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Intro To OOPDocument30 pagesTopic 1 - Intro To OOPAmir EhsanNo ratings yet
- Adbchapter1 240227092312 A1eac3d7Document22 pagesAdbchapter1 240227092312 A1eac3d7tasheebedaneNo ratings yet
- Procedural ProgrammingDocument14 pagesProcedural ProgrammingAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Basic Object Oriented DesignDocument18 pagesUnit 5 - Basic Object Oriented DesignBergue ChrisNo ratings yet
- Lect-18-OO-Design SW EngineeringDocument8 pagesLect-18-OO-Design SW EngineeringAl YarNo ratings yet
- Dit 0202 Week TwoDocument18 pagesDit 0202 Week TwoAli DoyoNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: and AlgorithmsDocument218 pagesData Structures: and AlgorithmsbharathkumarNo ratings yet
- Dbms Student Prepared NotesDocument37 pagesDbms Student Prepared Notesprakash sharmaNo ratings yet
- SE ch2Document39 pagesSE ch2mubarek muhammedNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Modeling, Concepts and PrinciplesDocument42 pagesObject Oriented Modeling, Concepts and Principlesrahul_mhatre_26No ratings yet
- (B) What Is Object Oriented Programming ?Document4 pages(B) What Is Object Oriented Programming ?Danish KhanNo ratings yet
- OopsDocument2 pagesOopsAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oosd Unit 2Document43 pagesOosd Unit 2FrggNo ratings yet
- Unit-4: - Design Axioms - Designing Classes - Access Layer - Object Storage - Object InteroperabilityDocument56 pagesUnit-4: - Design Axioms - Designing Classes - Access Layer - Object Storage - Object Interoperabilitynetrapp100% (2)
- Lecture 4 - OO SEDocument91 pagesLecture 4 - OO SEanteNo ratings yet
- 8.basic Concepts of OOPSDocument17 pages8.basic Concepts of OOPSdoneyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of OopDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts of OopganiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingDijana30No ratings yet
- Soft Engg 4Document12 pagesSoft Engg 4tapstaps902No ratings yet
- Lecture2 04august CAP202Document14 pagesLecture2 04august CAP202vinay jodNo ratings yet
- cs304 ShortDocument23 pagescs304 ShortAli HamxaNo ratings yet
- Assinment cs301Document30 pagesAssinment cs301Namal No OorNo ratings yet
- OOAD All Chapter NOTES - 20211218132503Document79 pagesOOAD All Chapter NOTES - 20211218132503Sushan KawanNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ApproachDocument28 pagesObject Oriented ApproachGlobal AccessNo ratings yet
- Oosd Unit 1Document30 pagesOosd Unit 1Khushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- MiddlewareText 123Document230 pagesMiddlewareText 123Anaida LewisNo ratings yet
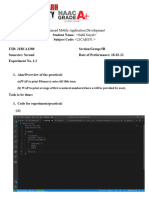
- Exp 4Document4 pagesExp 4Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- MST - Practical Worksheet - OOPsDocument4 pagesMST - Practical Worksheet - OOPsSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Sample WorksheetDocument2 pagesSample WorksheetSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document3 pagesExp 3Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document4 pagesExp 4Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
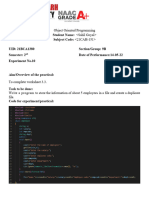
- Exp 7Document3 pagesExp 7Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp1 2Document4 pagesExp1 2Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document5 pagesExp 10Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document4 pagesExp 6Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document5 pagesExp 10Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
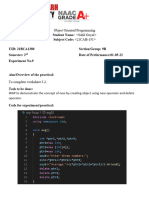
- Exp 9Document3 pagesExp 9Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document3 pagesExp 7Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp1 1Document3 pagesExp1 1Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.5 Test StrategiesDocument23 pagesLecture 3.3.5 Test StrategiesSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document3 pagesExp 8Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.4 Objective of Software TestingDocument9 pagesLecture 3.2.4 Objective of Software TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.4 Black Box TestingDocument14 pagesLecture 3.3.4 Black Box TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document3 pagesExp 8Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.3 Concepts of Software DesignDocument9 pagesLecture 3.1.3 Concepts of Software DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.1 Objective and Levels of SoftwareDocument16 pagesLecture 3.1.1 Objective and Levels of SoftwareSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document3 pagesExp 9Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 PDFDocument4 pagesExp 6 PDFSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.3 White Box TestingDocument13 pagesLecture 3.3.3 White Box TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.1 Procedural DesignDocument8 pagesLecture 3.2.1 Procedural DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.5 Software Testing PrinciplesDocument12 pagesLecture 3.2.5 Software Testing PrinciplesSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.2 Test CaseDocument17 pagesLecture 3.3.2 Test CaseSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.3 Testing FundamentalsDocument8 pagesLecture 3.2.3 Testing FundamentalsSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.1 Software TestabilityDocument17 pagesLecture 3.3.1 Software TestabilitySahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.4 Introduction of Design Methodologies and Data DesignDocument9 pagesLecture 3.1.4 Introduction of Design Methodologies and Data DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.5 Architectural DesignDocument12 pagesLecture 3.1.5 Architectural DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- WaveEv Fault Waveform Analysis Software - Instruction Manual - EN - General - X - R1.01 - (EN - GJRJ0901.0086.0002) PDFDocument73 pagesWaveEv Fault Waveform Analysis Software - Instruction Manual - EN - General - X - R1.01 - (EN - GJRJ0901.0086.0002) PDFNicholasChen100% (1)
- DWH TerminologyDocument4 pagesDWH TerminologysamsurisamNo ratings yet
- KWIC Software ArchitectureDocument17 pagesKWIC Software ArchitectureKaze NikahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. LexicologyDocument2 pagesLecture 5. LexicologyKazbekov SamatNo ratings yet
- Stack, Queue&DequeueDocument4 pagesStack, Queue&DequeueDanishNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Mathematics 4Document6 pagesLesson Plan Mathematics 4Lovely CamposanoNo ratings yet
- 101 Window SKeyboard Shortcut KeysDocument10 pages101 Window SKeyboard Shortcut KeyssathvikNo ratings yet
- Virus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmDocument17 pagesVirus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmMegamozgNo ratings yet
- Growth Mindset Intermediate Lesson Plans The Ned ShowDocument16 pagesGrowth Mindset Intermediate Lesson Plans The Ned ShowGôis Madson100% (2)
- Mikro CDocument6 pagesMikro CLeng SovannarithNo ratings yet
- Servers CentOS 6 - FinalDocument96 pagesServers CentOS 6 - FinalJohnnyNo ratings yet
- Ovftool-410 UserguideDocument50 pagesOvftool-410 UserguiderobertoNo ratings yet
- Hypothetical SyllogismDocument4 pagesHypothetical SyllogismYan Lean DollisonNo ratings yet
- List of Past Simple and Past Participle PDFDocument5 pagesList of Past Simple and Past Participle PDFYnan Esteron HernandezNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Technical Questions Compiled With ExplainationsDocument134 pagesTopic Wise Technical Questions Compiled With ExplainationskavneetrekhiNo ratings yet
- Modul 2: English For Personal CommunicationDocument7 pagesModul 2: English For Personal Communicationayu dindaNo ratings yet
- Kushana Empire Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSCDocument3 pagesKushana Empire Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSCGaurav SindhiyaNo ratings yet
- The Past Perfect Tense Fun Activities Games Information Gap Activities On - 82843Document3 pagesThe Past Perfect Tense Fun Activities Games Information Gap Activities On - 82843EstherPoboSerradillaNo ratings yet
- Selected Essays of Javed Ahmad Ghamidi - Itmam Al-Hujjah of The MessengersDocument6 pagesSelected Essays of Javed Ahmad Ghamidi - Itmam Al-Hujjah of The MessengersMuhammad-YounusNo ratings yet
- Amadeus Labs - Job Profiles 2021Document3 pagesAmadeus Labs - Job Profiles 2021ASHISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Project ListDocument3 pagesProject ListShivamNo ratings yet
- Mediating Effect of Pedagogical Content Knowledge On The Relationship Between Language Learning Beliefs and English Self-Efficacy of StudentsDocument17 pagesMediating Effect of Pedagogical Content Knowledge On The Relationship Between Language Learning Beliefs and English Self-Efficacy of StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- YesDocument2 pagesYesMuhammad Ajie WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Oracle 11 GDocument5 pagesOracle 11 GsnekkalaNo ratings yet
- WT and Fds Practical SlipsDocument32 pagesWT and Fds Practical SlipsRohidas SapkalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7a Deflection of Beams (Determinate)Document14 pagesLecture 7a Deflection of Beams (Determinate)Nile DizonNo ratings yet
- Fra Lippo Lippi - Study Guide YR12 LitDocument9 pagesFra Lippo Lippi - Study Guide YR12 LitMrSmithLCNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesIndirect Speechichda581No ratings yet
- Chapter8 Rise, Set, TwilightDocument5 pagesChapter8 Rise, Set, TwilightYasser MetaweaNo ratings yet
Lecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Lecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Uploaded by
Sahil Goyal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesThe document discusses object-oriented design (OOD) and defines key OOD terms. It explains that in OOD, a system is viewed as a collection of objects that represent entities. Objects have attributes and methods, and similar objects form classes that can inherit features from superclasses. The document defines objects, classes, messages, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism as fundamental OOD concepts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses object-oriented design (OOD) and defines key OOD terms. It explains that in OOD, a system is viewed as a collection of objects that represent entities. Objects have attributes and methods, and similar objects form classes that can inherit features from superclasses. The document defines objects, classes, messages, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism as fundamental OOD concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesLecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Lecture 3.2.2 Object Oriented Design
Uploaded by
Sahil GoyalThe document discusses object-oriented design (OOD) and defines key OOD terms. It explains that in OOD, a system is viewed as a collection of objects that represent entities. Objects have attributes and methods, and similar objects form classes that can inherit features from superclasses. The document defines objects, classes, messages, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism as fundamental OOD concepts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF COMPUTING
UNIT-3
Bachelor of Computer Applications
Software Engineering
(21CAT-312/21SCT-312/22CAT-213/22SCT-213)
DISCOVER . LEARN . EMPOWER
Topics to be Covered
• Object Oriented Design
Object Oriented Design
• Introduction: In the object-oriented design method, the system is viewed as a
collection of objects (i.e., entities). The state is distributed among the objects, and
each object handles its state data.
• For example, in a Library Automation Software, each library representative may
be a separate object with its data and functions to operate on these data. The tasks
defined for one purpose cannot refer or change data of other objects.
• Objects have their internal data which represent their state. Similar objects create
a class. In other words, each object is a member of some class. Classes may
inherit features from the super class.
Object Oriented Design
Object Oriented Design Terms
• Objects: All entities involved in the solution design are known as objects. For
example, person, banks, company, and users are considered as objects. Every
entity has some attributes associated with it and has some methods to perform on
the attributes.
• Classes: A class is a generalized description of an object. An object is an instance
of a class. A class defines all the attributes, which an object can have and methods,
which represents the functionality of the object.
• Messages: Objects communicate by message passing. Messages consist of the
integrity of the target object, the name of the requested operation, and any other
action needed to perform the function. Messages are often implemented as
procedure or function calls.
Object Oriented Design Terms
• Abstraction In object-oriented design, complexity is handled using abstraction.
Abstraction is the removal of the irrelevant and the amplification of the essentials.
• Encapsulation: Encapsulation is also called an information hiding concept. The
data and operations are linked to a single unit. Encapsulation not only bundles
essential information of an object together but also restricts access to the data and
methods from the outside world.
• Inheritance: OOD allows similar classes to stack up in a hierarchical manner
where the lower or sub-classes can import, implement, and re-use allowed
variables and functions from their immediate superclasses.This property of OOD
is called an inheritance. This makes it easier to define a specific class and to create
generalized classes from specific ones.
Object Oriented Design Terms
• Polymorphism: OOD languages provide a mechanism where methods
performing similar tasks but vary in arguments, can be assigned the same name.
This is known as polymorphism, which allows a single interface is performing
functions for different types. Depending upon how the service is invoked, the
respective portion of the code gets executed.
You might also like
- Sequencing Events-Grade 1Document31 pagesSequencing Events-Grade 1Dorothy JeanNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Design: Shruti JatharDocument62 pagesObject Oriented Design: Shruti Jatharravi4185No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1.3.3Document2 pagesLecture Notes 1.3.3Ashutosh mishraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-IDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented Database: Unit-Ipreetham rNo ratings yet
- L1-Introduction To OOPs ConceptsDocument16 pagesL1-Introduction To OOPs ConceptsKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- CH1 Introduction To OOPDocument24 pagesCH1 Introduction To OOPabenezergebrekirstosNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument3 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and DesignArpita SahaNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument41 pagesObject Oriented ProgramminganandNo ratings yet
- Lect1 OdpDocument34 pagesLect1 OdpTim Boy ManNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Design (OOD) : Presenting By: M R Khan Dipu ID: 191-35-393 Department of Software EngineeringDocument14 pagesObject Oriented Design (OOD) : Presenting By: M R Khan Dipu ID: 191-35-393 Department of Software EngineeringM. R. KHAN DIPUNo ratings yet
- Programming Outline Features of OOPDocument21 pagesProgramming Outline Features of OOPpraisechidomayaNo ratings yet
- OOP ImplementationDocument43 pagesOOP Implementationeli indahNo ratings yet
- 1 2 3 Units OoadDocument21 pages1 2 3 Units Ooadsamiksha5singhalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5mersimoybekele88No ratings yet
- Object ModelingDocument40 pagesObject Modelingjurihu143No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming SlidesDocument20 pagesObject Oriented Programming Slideslokidddd0No ratings yet
- Opps Notes PythonDocument83 pagesOpps Notes PythonomkarNo ratings yet
- Python Chapter3Document56 pagesPython Chapter3Jatin SharmaNo ratings yet
- OOSE Unit - 1Document41 pagesOOSE Unit - 1Vaibhav BirlaNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Notes OosdDocument20 pagesUnit-3 Notes Oosdyou • were • trolledNo ratings yet
- Ooad - Quick Guide Object Oriented ParadigmDocument50 pagesOoad - Quick Guide Object Oriented ParadigmShamiMalikNo ratings yet
- Oose CH 1Document38 pagesOose CH 1Daniel TunkaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 & 2 - OOAD - Object Oriented ParadigmDocument11 pagesWeek 1 & 2 - OOAD - Object Oriented ParadigmShariff Oluoch OdiwuorNo ratings yet
- DCIT 201 Programming I: Session 1 - Fundamental Concepts of OOD and OOPDocument35 pagesDCIT 201 Programming I: Session 1 - Fundamental Concepts of OOD and OOPPrincess Naomi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- 8.Object-Oriented Modelling DesignDocument49 pages8.Object-Oriented Modelling DesignﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 OoadDocument13 pagesUnit-1 OoadTanya OhriNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ConceptsDocument7 pagesObject Oriented ConceptsdiaeshantonyNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Analysis and DesignDocument60 pagesObject Oriented Analysis and DesignMatthew Tedunjaiye100% (1)
- UMLDocument61 pagesUMLmodernjewellaryNo ratings yet
- Java Basics2 (OOPS in Java)Document15 pagesJava Basics2 (OOPS in Java)sahilsecondacc1No ratings yet
- OOMD Unit 1Document13 pagesOOMD Unit 1Saraswati BhusanurNo ratings yet
- Software CrisisDocument120 pagesSoftware CrisisPrince MpofuNo ratings yet
- OOADDocument51 pagesOOADAbi KNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Intro To OOPDocument30 pagesTopic 1 - Intro To OOPAmir EhsanNo ratings yet
- Adbchapter1 240227092312 A1eac3d7Document22 pagesAdbchapter1 240227092312 A1eac3d7tasheebedaneNo ratings yet
- Procedural ProgrammingDocument14 pagesProcedural ProgrammingAmandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Basic Object Oriented DesignDocument18 pagesUnit 5 - Basic Object Oriented DesignBergue ChrisNo ratings yet
- Lect-18-OO-Design SW EngineeringDocument8 pagesLect-18-OO-Design SW EngineeringAl YarNo ratings yet
- Dit 0202 Week TwoDocument18 pagesDit 0202 Week TwoAli DoyoNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: and AlgorithmsDocument218 pagesData Structures: and AlgorithmsbharathkumarNo ratings yet
- Dbms Student Prepared NotesDocument37 pagesDbms Student Prepared Notesprakash sharmaNo ratings yet
- SE ch2Document39 pagesSE ch2mubarek muhammedNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Modeling, Concepts and PrinciplesDocument42 pagesObject Oriented Modeling, Concepts and Principlesrahul_mhatre_26No ratings yet
- (B) What Is Object Oriented Programming ?Document4 pages(B) What Is Object Oriented Programming ?Danish KhanNo ratings yet
- OopsDocument2 pagesOopsAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oosd Unit 2Document43 pagesOosd Unit 2FrggNo ratings yet
- Unit-4: - Design Axioms - Designing Classes - Access Layer - Object Storage - Object InteroperabilityDocument56 pagesUnit-4: - Design Axioms - Designing Classes - Access Layer - Object Storage - Object Interoperabilitynetrapp100% (2)
- Lecture 4 - OO SEDocument91 pagesLecture 4 - OO SEanteNo ratings yet
- 8.basic Concepts of OOPSDocument17 pages8.basic Concepts of OOPSdoneyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of OopDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts of OopganiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Object Oriented ProgrammingDijana30No ratings yet
- Soft Engg 4Document12 pagesSoft Engg 4tapstaps902No ratings yet
- Lecture2 04august CAP202Document14 pagesLecture2 04august CAP202vinay jodNo ratings yet
- cs304 ShortDocument23 pagescs304 ShortAli HamxaNo ratings yet
- Assinment cs301Document30 pagesAssinment cs301Namal No OorNo ratings yet
- OOAD All Chapter NOTES - 20211218132503Document79 pagesOOAD All Chapter NOTES - 20211218132503Sushan KawanNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented ApproachDocument28 pagesObject Oriented ApproachGlobal AccessNo ratings yet
- Oosd Unit 1Document30 pagesOosd Unit 1Khushi SharmaNo ratings yet
- MiddlewareText 123Document230 pagesMiddlewareText 123Anaida LewisNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document4 pagesExp 4Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- MST - Practical Worksheet - OOPsDocument4 pagesMST - Practical Worksheet - OOPsSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Sample WorksheetDocument2 pagesSample WorksheetSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document3 pagesExp 3Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document4 pagesExp 4Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document3 pagesExp 7Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp1 2Document4 pagesExp1 2Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document5 pagesExp 10Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 6Document4 pagesExp 6Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document5 pagesExp 10Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document3 pagesExp 9Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 7Document3 pagesExp 7Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp1 1Document3 pagesExp1 1Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.5 Test StrategiesDocument23 pagesLecture 3.3.5 Test StrategiesSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document3 pagesExp 8Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.4 Objective of Software TestingDocument9 pagesLecture 3.2.4 Objective of Software TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.4 Black Box TestingDocument14 pagesLecture 3.3.4 Black Box TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document3 pagesExp 8Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.3 Concepts of Software DesignDocument9 pagesLecture 3.1.3 Concepts of Software DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.1 Objective and Levels of SoftwareDocument16 pagesLecture 3.1.1 Objective and Levels of SoftwareSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 9Document3 pagesExp 9Sahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 PDFDocument4 pagesExp 6 PDFSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.3 White Box TestingDocument13 pagesLecture 3.3.3 White Box TestingSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.1 Procedural DesignDocument8 pagesLecture 3.2.1 Procedural DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.5 Software Testing PrinciplesDocument12 pagesLecture 3.2.5 Software Testing PrinciplesSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.2 Test CaseDocument17 pagesLecture 3.3.2 Test CaseSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2.3 Testing FundamentalsDocument8 pagesLecture 3.2.3 Testing FundamentalsSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.3.1 Software TestabilityDocument17 pagesLecture 3.3.1 Software TestabilitySahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.4 Introduction of Design Methodologies and Data DesignDocument9 pagesLecture 3.1.4 Introduction of Design Methodologies and Data DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.1.5 Architectural DesignDocument12 pagesLecture 3.1.5 Architectural DesignSahil GoyalNo ratings yet
- WaveEv Fault Waveform Analysis Software - Instruction Manual - EN - General - X - R1.01 - (EN - GJRJ0901.0086.0002) PDFDocument73 pagesWaveEv Fault Waveform Analysis Software - Instruction Manual - EN - General - X - R1.01 - (EN - GJRJ0901.0086.0002) PDFNicholasChen100% (1)
- DWH TerminologyDocument4 pagesDWH TerminologysamsurisamNo ratings yet
- KWIC Software ArchitectureDocument17 pagesKWIC Software ArchitectureKaze NikahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5. LexicologyDocument2 pagesLecture 5. LexicologyKazbekov SamatNo ratings yet
- Stack, Queue&DequeueDocument4 pagesStack, Queue&DequeueDanishNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Mathematics 4Document6 pagesLesson Plan Mathematics 4Lovely CamposanoNo ratings yet
- 101 Window SKeyboard Shortcut KeysDocument10 pages101 Window SKeyboard Shortcut KeyssathvikNo ratings yet
- Virus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmDocument17 pagesVirus Programming Basics 1 Hacking Virus Programming AsmMegamozgNo ratings yet
- Growth Mindset Intermediate Lesson Plans The Ned ShowDocument16 pagesGrowth Mindset Intermediate Lesson Plans The Ned ShowGôis Madson100% (2)
- Mikro CDocument6 pagesMikro CLeng SovannarithNo ratings yet
- Servers CentOS 6 - FinalDocument96 pagesServers CentOS 6 - FinalJohnnyNo ratings yet
- Ovftool-410 UserguideDocument50 pagesOvftool-410 UserguiderobertoNo ratings yet
- Hypothetical SyllogismDocument4 pagesHypothetical SyllogismYan Lean DollisonNo ratings yet
- List of Past Simple and Past Participle PDFDocument5 pagesList of Past Simple and Past Participle PDFYnan Esteron HernandezNo ratings yet
- Topic Wise Technical Questions Compiled With ExplainationsDocument134 pagesTopic Wise Technical Questions Compiled With ExplainationskavneetrekhiNo ratings yet
- Modul 2: English For Personal CommunicationDocument7 pagesModul 2: English For Personal Communicationayu dindaNo ratings yet
- Kushana Empire Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSCDocument3 pagesKushana Empire Ancient Indian History Notes For UPSCGaurav SindhiyaNo ratings yet
- The Past Perfect Tense Fun Activities Games Information Gap Activities On - 82843Document3 pagesThe Past Perfect Tense Fun Activities Games Information Gap Activities On - 82843EstherPoboSerradillaNo ratings yet
- Selected Essays of Javed Ahmad Ghamidi - Itmam Al-Hujjah of The MessengersDocument6 pagesSelected Essays of Javed Ahmad Ghamidi - Itmam Al-Hujjah of The MessengersMuhammad-YounusNo ratings yet
- Amadeus Labs - Job Profiles 2021Document3 pagesAmadeus Labs - Job Profiles 2021ASHISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Project ListDocument3 pagesProject ListShivamNo ratings yet
- Mediating Effect of Pedagogical Content Knowledge On The Relationship Between Language Learning Beliefs and English Self-Efficacy of StudentsDocument17 pagesMediating Effect of Pedagogical Content Knowledge On The Relationship Between Language Learning Beliefs and English Self-Efficacy of StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- YesDocument2 pagesYesMuhammad Ajie WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Oracle 11 GDocument5 pagesOracle 11 GsnekkalaNo ratings yet
- WT and Fds Practical SlipsDocument32 pagesWT and Fds Practical SlipsRohidas SapkalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7a Deflection of Beams (Determinate)Document14 pagesLecture 7a Deflection of Beams (Determinate)Nile DizonNo ratings yet
- Fra Lippo Lippi - Study Guide YR12 LitDocument9 pagesFra Lippo Lippi - Study Guide YR12 LitMrSmithLCNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesIndirect Speechichda581No ratings yet
- Chapter8 Rise, Set, TwilightDocument5 pagesChapter8 Rise, Set, TwilightYasser MetaweaNo ratings yet