Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Types
Cell Types
Uploaded by
Rhea Gulay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views19 pagesThere are different types of cells in the human body based on their structure and function. Key cell types include bone cells which provide strength and structure, cartilage cells which help bones bend, nerve cells which transmit electrical signals, epithelial cells which form protective layers, and muscle cells which allow for movement. Additional cell types are secretory cells which produce important substances, adipose cells which store fat, and blood cells which include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Cells can also be classified based on their functions, such as conductive cells which transmit signals, connective cells which join tissues, and glandular cells which form glands and secrete substances.
Original Description:
Cell Types
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are different types of cells in the human body based on their structure and function. Key cell types include bone cells which provide strength and structure, cartilage cells which help bones bend, nerve cells which transmit electrical signals, epithelial cells which form protective layers, and muscle cells which allow for movement. Additional cell types are secretory cells which produce important substances, adipose cells which store fat, and blood cells which include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Cells can also be classified based on their functions, such as conductive cells which transmit signals, connective cells which join tissues, and glandular cells which form glands and secrete substances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views19 pagesCell Types
Cell Types
Uploaded by
Rhea GulayThere are different types of cells in the human body based on their structure and function. Key cell types include bone cells which provide strength and structure, cartilage cells which help bones bend, nerve cells which transmit electrical signals, epithelial cells which form protective layers, and muscle cells which allow for movement. Additional cell types are secretory cells which produce important substances, adipose cells which store fat, and blood cells which include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Cells can also be classified based on their functions, such as conductive cells which transmit signals, connective cells which join tissues, and glandular cells which form glands and secrete substances.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
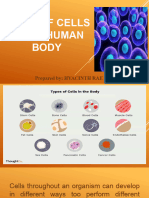
CELL TYPES
Different Types of cells in the human
body based on tissue formation
Bone Cells (Osteocytes)
The toughest body cell
Give strength, support and
framework to the body
3 types:
Osteoblast- they build the bone.
Osteocyte- bone cover
Osteoclasts- make white blood cells
and repair bone.
Cartilage Cells (chondrocytes)
Bendable
Ear bone
In between large bones to help
them bend and move freely like
in between two ribs, spinal
bones, joints.
Nerve Cells
Very long and have many branching at either
ends.
They never multiply in one’s life time.
Present all over the body and are sometimes as
long as few meters long.
Human brain cells and are found in plenty in brain
and the spinal cord and from the nervous tissue.
Dendrites receive and send
chemical messages
Brain and central and peripheral
nervous system
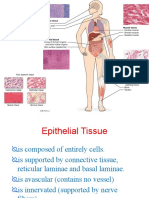
Epithelial cells
Simple cells
Covering layers of all the organs
Serves as the barriers for pathogens, fluid
loss and mechanical injuries.
Muscle Cells
Cells are most of muscle tissue mostly long, large and have ability
to contract and relax providing movements.
3 types:
Skeletal muscle cells-attached to long bones and assist in their
movement
Cardiac muscle cells- present only in heart muscle and are
responsible for heart beats
Smooth muscle cells- flexible yet, can contract and relax present in
stomach, intestine, blood vessel walls (vascular tissue) helping in
movement of food through the gut.
Secretory cells
Secretory in nature.
Form glands and secretes something important- pancreatic
cells which secretes insulin, glucagon, salivary gland which
secrete salivary amylase, sebaceous gland which secretes oil
on the skin.
Found in secretory gland.
Adipose cells
Fat cells
Storage by nature to store fat.
Seen in the soles palms, and bums.
Reduce fiction to the body.
Blood cells
Includes RBC’s, WBC and Thrombocytes
Always motile and never stay in one place.
Limited life span and they never multiply to form new
cells.
Instead new cells are formed from other cells.
Red Blood Cells-
carry oxygen
around the body
White blood cell-
part of the
immune system
Platelet- help blood
clot to prevent
blood loss after
injury.
Types of cells In human based on their
function
Conductive Cells- nerve cells and muscle cells.
- have internal ability to conduct an
electric impulse from one regions to other distant
region in the body.
Connective Cells- bone cells, blood cells
- they help connect other cells and tissues.
Glandular Cells- secretory cells
- form glands like pancreas,
salivary glands and help in production of
enzymes, hormones.
Storage Cells- act as support to adjacent cells.
Glial cells in the brain and spinal
cord help provide nourishment to the nerve
cells and also protect them from shock and
trauma.
Special Type of Cells
a. Sperms-haploid (one set of chromosome)
- represent males after puberty.
-have tails, which enable them to swim and
move in the female uterus.
- hayaluronidase (enzyme) helps them
penetrate through uterine tissue and reach oocytes.
b. oocytes- haploid
- present in adult female genital system
- they accept sperm cell to form zygote
C stem cells- basic cell or parent cells.
- treatment of disorder in the future.
d. Rods and cones- in the eyes.
- have capacity to capture image color
and light.
e. Ciliated cells- lining of respiratory tract and
esophagus, have pointed tread-like cilia which move
in one particular direction to pass material.
f. Blood cells- never attached to one another.
You might also like
- Grade 10 Biology NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Biology Noteskatwal0986% (21)
- AP Biology-Tissue Types ChartDocument1 pageAP Biology-Tissue Types ChartJeannie WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Biological Science NotesDocument35 pagesBiological Science NotesPianomanSuperman100% (2)
- GEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDocument4 pagesGEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDonnalyn Mae EscrupoloNo ratings yet
- Types: Gwynette de Guzman Chrismaine Bell Rivas Alreah Razel PahayacDocument29 pagesTypes: Gwynette de Guzman Chrismaine Bell Rivas Alreah Razel PahayacchrismaineNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument33 pagesCell TypesJanreve Xhylem Martirez OdangoNo ratings yet
- Performance Task For Science 7Document5 pagesPerformance Task For Science 7Abdullah MundasNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue: Epidermis (Outermost Covering) Simple Tissues: Epidermis TissueBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- 05 - 1.3 - Specialized Plant and Animal CellsDocument18 pages05 - 1.3 - Specialized Plant and Animal CellsfabishchikutsaNo ratings yet
- Types of Cells in The BodyDocument27 pagesTypes of Cells in The BodyGulali KhanNo ratings yet
- Types of CellsDocument9 pagesTypes of CellsJacqueline MarilaoNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument3 pagesAnimal TissueC1B-33-AdityaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1Document60 pagesLesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1abdullahfahdelm.adiongNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Cell TypesDocument27 pagesGen Bio Cell TypesJonaya AmpasoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument74 pagesTissuesMonica Sree100% (1)
- Types of Cells in The Human BodyDocument24 pagesTypes of Cells in The Human BodyHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Types Human and AnimalsDocument2 pagesCell Types Human and AnimalsBianca GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue ReviewerDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissue ReviewerAli NamialusNo ratings yet
- Study of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifDocument60 pagesStudy of Animal Tissues: Dr. AarifEntirety 4uNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Cell TypesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Cell TypesClauriz Keith Ashley SanicoNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument6 pagesHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 6 - Tissues Revision NotesAbhishek100% (1)
- Samarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceDocument16 pagesSamarjeet FA-1 Activity ScienceSamarjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Types of CellsDocument6 pagesCell Theory and Types of CellsLance Afraim MortelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - 2013 Animal TissuesSiti Juwairiah ZainurinNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument24 pagesCell TypesKim TaehyungNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument13 pagesTissuesAvika Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Project in General BiologyDocument4 pagesProject in General Biologyfed shiranNo ratings yet
- Cell Types 1Document28 pagesCell Types 1IngridNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument16 pagesCYTOLOGYRheimon Jay Abuan BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types TissuesDocument26 pagesCell Types Tissueskurtandreinace04No ratings yet
- Types of CellsDocument7 pagesTypes of CellsRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- CCCC C CDocument16 pagesCCCC C CLennon Mars LamsinNo ratings yet
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocument60 pagesHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 2 Study NotesDocument41 pagesBiology Module 2 Study NotesKatie BellNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Anatomy Unit 4 - Tissue TypesDocument31 pagesAnatomy Unit 4 - Tissue TypesDevaki SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument6 pagesTissuesvaidika.soni12009No ratings yet
- General Biology IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument12 pagesImmune SystemCasper Irra Marcos100% (1)
- Animal TissueDocument45 pagesAnimal TissueAyesha YusopNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Cell?Jeah Mae CastroNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticDocument11 pagesCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornNo ratings yet
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionDocument27 pages10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىNo ratings yet
- Cell TissuesDocument28 pagesCell TissuesStifany Dianne VillasNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument70 pagesTissuesayssNo ratings yet
- Electron Microscopic Cell StructureDocument26 pagesElectron Microscopic Cell StructureMaria ArshadNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyalmahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 - Tissues - Class Ix - ScienceDocument20 pagesChapter - 6 - Tissues - Class Ix - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue Hand-Out Bio 101Amor Panopio MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissue 6 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument11 pagesPlant and Animal Tissue 6 MARCH 2013: Lesson Descriptiondeepa100% (1)
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 1Document45 pagesAnimal Tissues 1sirajNo ratings yet
- Biology: VitaminsDocument6 pagesBiology: VitaminskeshavNo ratings yet
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Document33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Ch. 4 Chapter Review - Anatomy and Physiology 2Document4 pagesCh. 4 Chapter Review - Anatomy and Physiology 2amorris0906No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Celll: Theory, Structure and FunctionsDocument30 pagesCelll: Theory, Structure and FunctionsRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument15 pagesCell CycleRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument28 pagesThe CellsRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- 001 Drugs Affecting Calcium RegulationDocument2 pages001 Drugs Affecting Calcium RegulationReddy Mohan100% (1)
- PRODUCTION OF MILKFISH Chanos Chanos BONES IN MAKING NUTRITIOUS LUMPIA WRAPPERDocument32 pagesPRODUCTION OF MILKFISH Chanos Chanos BONES IN MAKING NUTRITIOUS LUMPIA WRAPPERPaul Adam XianNo ratings yet
- Aaid Joi D 12 00028Document9 pagesAaid Joi D 12 00028NancyLiaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AdhyapakDocument50 pagesAnatomy AdhyapakChief Nike - Clash RoyaleNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Microscopic Anatomy (Histology) Lab: Lecture 01: The MicroscopeDocument21 pagesVeterinary Microscopic Anatomy (Histology) Lab: Lecture 01: The MicroscopeFor AstroNo ratings yet
- Revision Hallux Valgus SurgeryDocument20 pagesRevision Hallux Valgus SurgeryosteonectinNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHDocument51 pagesConnective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- Nejmcp 2113128Document9 pagesNejmcp 2113128Jordi Piñeros AriasNo ratings yet
- Histology NotesDocument38 pagesHistology Notesyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Exercise For Better Bones - The Complete Guide To Safe and Effective Exercises For OsteoporosisDocument292 pagesExercise For Better Bones - The Complete Guide To Safe and Effective Exercises For Osteoporosisseema1sharma-675% (4)
- Calcitonin and OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesCalcitonin and OsteoporosisadilNo ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument29 pagesBone TumorsmatameaNo ratings yet
- Tortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesTortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologybebeNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)Document26 pagesMusculoskeletal System - Ii: MBBS Year-3 (Academic Year 2020-2021)Danyal AzamNo ratings yet
- Condition Assessment of Osteological Collections: V C N ODocument19 pagesCondition Assessment of Osteological Collections: V C N OChascón PérezNo ratings yet
- 173 Anatomy SkeletalDocument23 pages173 Anatomy SkeletalChristian Phaul AsendidoNo ratings yet
- Chicken Wing Dissection InstructionsDocument4 pagesChicken Wing Dissection InstructionsSandra Fowler100% (1)
- ListeningsDocument8 pagesListeningssilviaNo ratings yet
- Cranial BaseDocument25 pagesCranial BasesealovesriverNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresDocument22 pagesGeriatric Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of SignaturesDocument7 pagesDoctrine of SignaturesNathan PapuniNo ratings yet
- Implant Dentistry - The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry PDFDocument488 pagesImplant Dentistry - The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry PDFnaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cementoma of The Calcaneus: A Case Report: Casereport Open AccessDocument4 pagesCementoma of The Calcaneus: A Case Report: Casereport Open AccessadintaNo ratings yet
- Greenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology - 272-279Document8 pagesGreenspan's Basic & Clinical Endocrinology - 272-279Jurnal MedikaNo ratings yet
- BSE Viva v1.0 PDFDocument173 pagesBSE Viva v1.0 PDFKavivarma Raj RajendranNo ratings yet
- Medical EnglishDocument133 pagesMedical EnglishKristina TomakNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Bone Markings - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument1 page7.2 Bone Markings - Anatomy & PhysiologydonaldooiNo ratings yet
- ContentServer Asp-3Document16 pagesContentServer Asp-3Santiago Durango HurtadoNo ratings yet
- NCSF Chapter 8 Nutrition-Non Energy NutientsDocument22 pagesNCSF Chapter 8 Nutrition-Non Energy NutientsJessie Tang0% (1)